A Comparative Analysis: The Geopolitical Landscape of Russia and Turkey
Related Articles: A Comparative Analysis: The Geopolitical Landscape of Russia and Turkey
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Analysis: The Geopolitical Landscape of Russia and Turkey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Analysis: The Geopolitical Landscape of Russia and Turkey
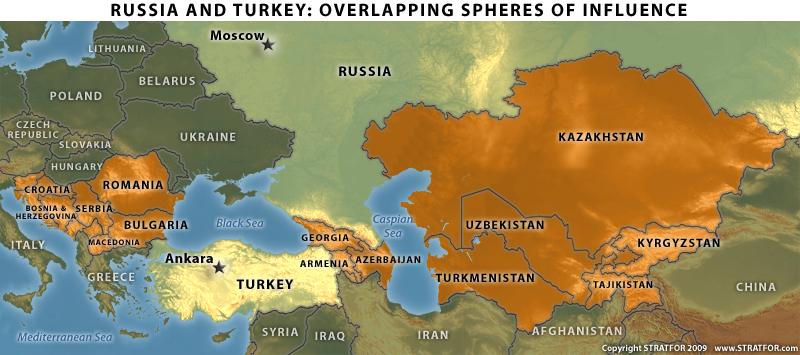
The maps of Russia and Turkey, two geographically and historically significant nations, offer a compelling insight into their respective strengths, vulnerabilities, and the intricate web of relationships they hold with their neighbors. Examining their geographical features, historical legacies, and contemporary political realities provides a comprehensive understanding of their roles in shaping the global landscape.
Russia: A Eurasian Colossus
Russia, a sprawling nation spanning eleven time zones, occupies a vast swathe of land across Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. Its vast territory, encompassing over 17 million square kilometers, makes it the world’s largest country by land area. This immense geographical expanse, coupled with a rich history, has shaped Russia’s unique geopolitical position.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Eurasian Steppe: A vast, fertile plain stretching from the Black Sea to the Pacific Ocean, this region has historically served as a conduit for migration and trade, playing a crucial role in shaping Russian identity and culture.
- The Ural Mountains: These ancient mountains mark the traditional boundary between Europe and Asia, offering a natural barrier while facilitating resource extraction.
- The Siberian Plain: Covering much of Northern Asia, this vast, flat region is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, and timber, but also harbors harsh climatic conditions.
- The Caucasus Mountains: This formidable mountain range, bordering the Black Sea, acts as a natural barrier and has been a site of historical conflict and cultural exchange.
- The Black Sea: This strategically important body of water provides Russia with access to the Mediterranean Sea and offers a crucial outlet for trade and naval power projection.
Historical Influences:
- The Mongol Empire: The Mongol conquest in the 13th century had a profound impact on Russia, shaping its cultural identity and political structure.
- The Tsarist Empire: The expansion of the Russian Empire in the 17th and 18th centuries led to the annexation of vast territories, including Siberia and the Caucasus, solidifying Russia’s position as a Eurasian power.
- The Soviet Union: The establishment of the Soviet Union in 1917 transformed Russia into a communist superpower, shaping its political system and economic policies for decades.
Contemporary Geopolitical Realities:
- A Resurgent Russia: After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia has re-emerged as a significant global actor, asserting its interests on the international stage.
- The Ukraine Crisis: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has highlighted Russia’s concerns over NATO expansion and its determination to maintain its influence in the region.
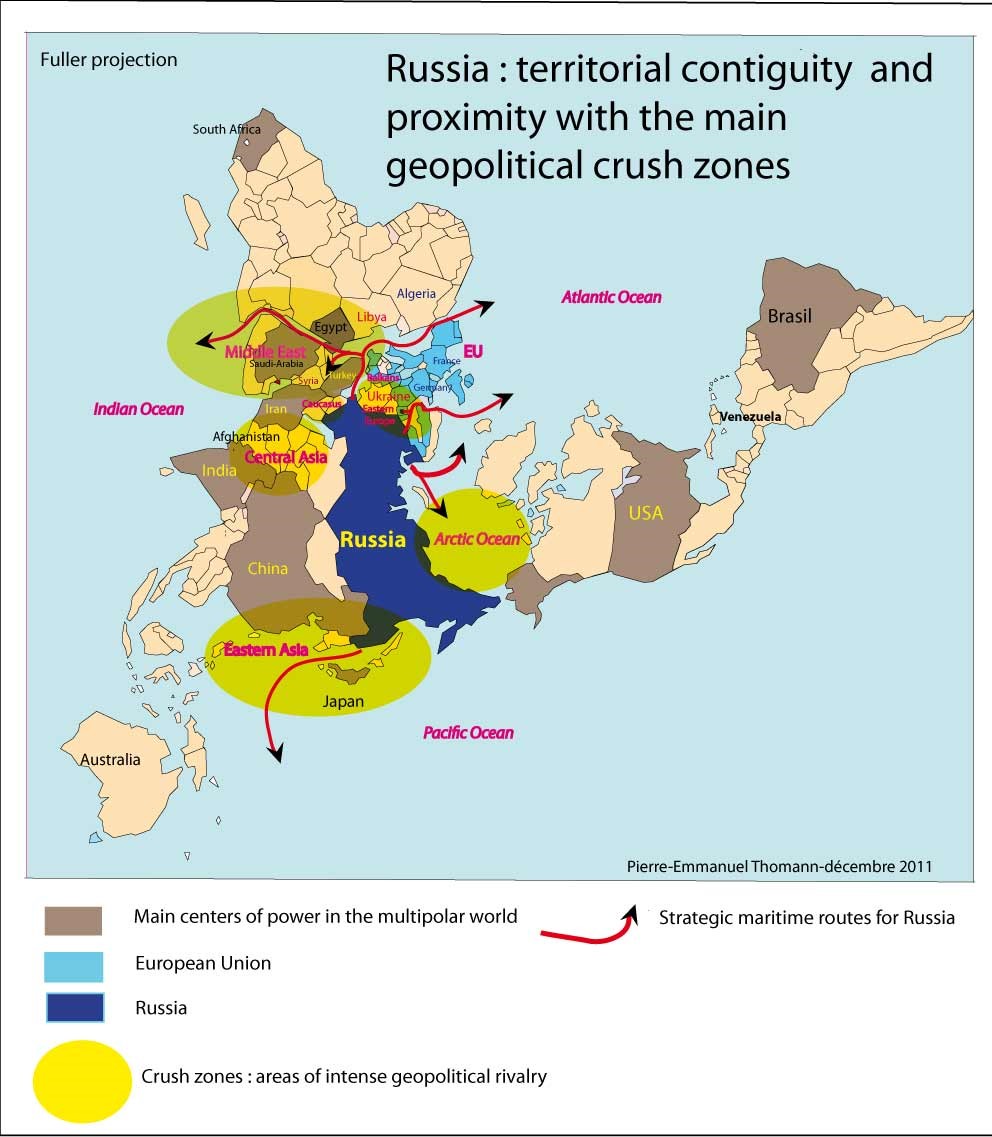
- The Arctic Frontier: With climate change opening up new shipping routes and resource opportunities in the Arctic, Russia is actively asserting its claims in this strategically vital region.
Turkey: A Bridge Between Continents
Turkey, located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, occupies a unique geopolitical position. Its strategic location has made it a hub for trade, cultural exchange, and military power projection throughout history.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Anatolian Peninsula: This vast plateau, bounded by the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea, and Aegean Sea, has served as the heartland of Turkish civilization for centuries.
- The Black Sea: Turkey shares its northern border with the Black Sea, providing it with access to the Eurasian landmass and a strategic advantage in the region.
- The Mediterranean Sea: Turkey’s southern coastline stretches along the Mediterranean Sea, giving it access to important shipping routes and a vital role in regional affairs.
- The Aegean Sea: Turkey’s western coastline borders the Aegean Sea, providing it with access to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Balkan Peninsula.
Historical Influences:
- The Ottoman Empire: The Ottoman Empire, spanning centuries, controlled vast territories across the Middle East, North Africa, and the Balkans, leaving a lasting legacy on Turkish culture and identity.
- The Turkish Republic: The establishment of the Turkish Republic in 1923 marked a significant shift in Turkish history, leading to modernization, secularization, and a focus on national development.
Contemporary Geopolitical Realities:
- A Rising Power: Turkey has emerged as a regional power, playing an active role in Middle Eastern affairs and pursuing a more assertive foreign policy.
- The Syrian Civil War: Turkey’s involvement in the Syrian conflict has significantly impacted its relations with neighboring countries and its role in the region.
- The Kurdish Question: The unresolved issue of Kurdish autonomy within Turkey continues to pose a significant challenge, impacting domestic politics and regional stability.
The Interplay of Interests: Russia and Turkey
The maps of Russia and Turkey reveal a complex interplay of interests, both cooperative and competitive. Their shared history, geographic proximity, and strategic ambitions have resulted in a multifaceted relationship marked by periods of cooperation and tension.
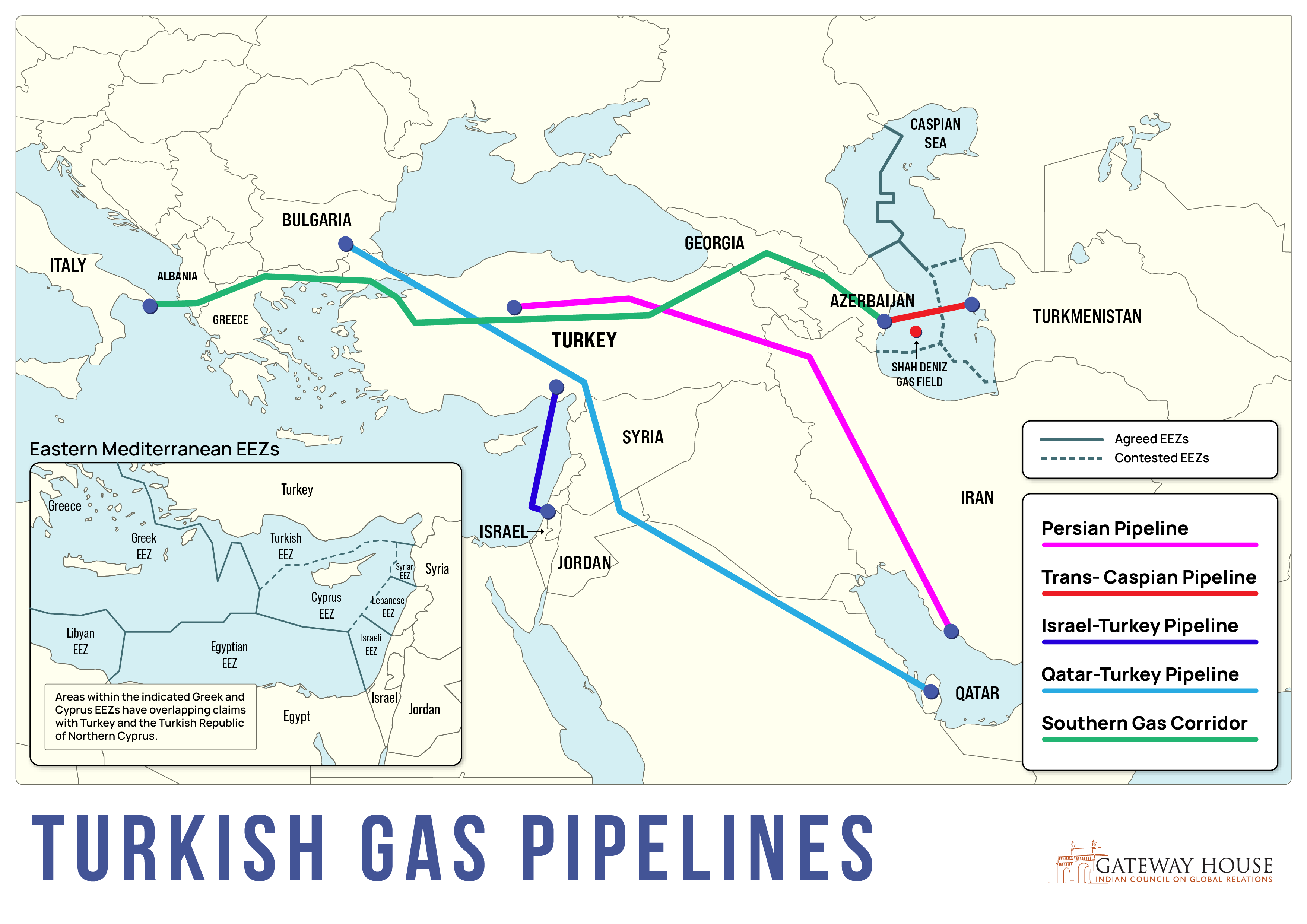
- Energy Cooperation: Russia is a major supplier of natural gas to Turkey, which relies heavily on imported energy. This economic dependence has fostered a degree of cooperation, but also creates vulnerabilities for Turkey.
- Military Cooperation: Russia and Turkey have engaged in joint military exercises and arms deals, particularly in the defense sector. This cooperation reflects their shared concerns about regional security and the potential for collaboration against common threats.
- Competition in the Black Sea: Both Russia and Turkey have a strong presence in the Black Sea, leading to potential competition for resources and influence. This rivalry has been exacerbated by the Ukraine crisis and the increasing tensions in the region.
- The Syrian Conflict: Russia and Turkey have adopted different approaches to the Syrian conflict, with Russia supporting the Assad regime and Turkey backing opposition groups. This divergence has created tensions and strained their relationship.
The Future of the Relationship:
The future of the relationship between Russia and Turkey will be shaped by a combination of factors, including:
- The Ukraine Crisis: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine will continue to impact the regional security environment and influence the dynamics between Russia and Turkey.
- The Syrian Conflict: The resolution of the Syrian civil war will have a significant impact on the stability of the region and the role of both countries.
- Economic Relations: The strength of economic ties between Russia and Turkey will play a crucial role in shaping their relationship, particularly in areas like energy and trade.
- NATO Expansion: Turkey’s membership in NATO and Russia’s concerns about NATO expansion will continue to be a source of tension, potentially impacting their future cooperation.
FAQs
Q: How do the maps of Russia and Turkey reflect their respective historical legacies?
A: The vast size and geographic diversity of Russia’s map reflect its history of expansion and conquest, while the strategic location of Turkey’s map highlights its historical role as a crossroads of civilizations and a bridge between continents.
Q: What are the key geographical features that contribute to Russia’s and Turkey’s geopolitical importance?
A: Russia’s vast territory, access to the Arctic, and control of strategic waterways like the Black Sea make it a major Eurasian power. Turkey’s location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, its control of key shipping routes, and its access to both the Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea give it significant geopolitical influence.
Q: What are the major points of contention between Russia and Turkey?
A: The Ukraine crisis, the Syrian conflict, and the Kurdish question are major sources of tension between Russia and Turkey. Their differing approaches to these issues have led to disagreements and strained relations.
Q: What are the potential benefits of cooperation between Russia and Turkey?
A: Cooperation in areas like energy, military affairs, and regional security could benefit both countries. It could help stabilize the region, promote economic growth, and address shared challenges.
Tips
- Focus on the geographic features: When analyzing the maps of Russia and Turkey, pay attention to the key geographical features that contribute to their geopolitical significance.
- Consider historical influences: Understanding the historical legacies of these nations is crucial for interpreting their present-day relationships.
- Analyze contemporary geopolitical realities: Examine the current political and economic landscape to understand the challenges and opportunities facing both Russia and Turkey.
- Explore the interplay of interests: Identify the areas of cooperation and competition between Russia and Turkey, and analyze the potential implications of these dynamics.
Conclusion
The maps of Russia and Turkey offer a compelling glimpse into the geopolitical complexities of the Eurasian region. Their vast territories, strategic locations, and intertwined histories have shaped their relationships with neighboring countries and their roles in global affairs. Understanding the interplay of their interests, the challenges they face, and the opportunities for cooperation is essential for navigating the complexities of the 21st-century world. As these two nations continue to navigate a rapidly evolving geopolitical landscape, their maps will remain crucial tools for understanding their past, present, and future.

/GettyImages-184932762-5c81a28046e0fb0001431949.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Analysis: The Geopolitical Landscape of Russia and Turkey. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!