A Comprehensive Exploration of World Map Topography
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of World Map Topography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of World Map Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of World Map Topography
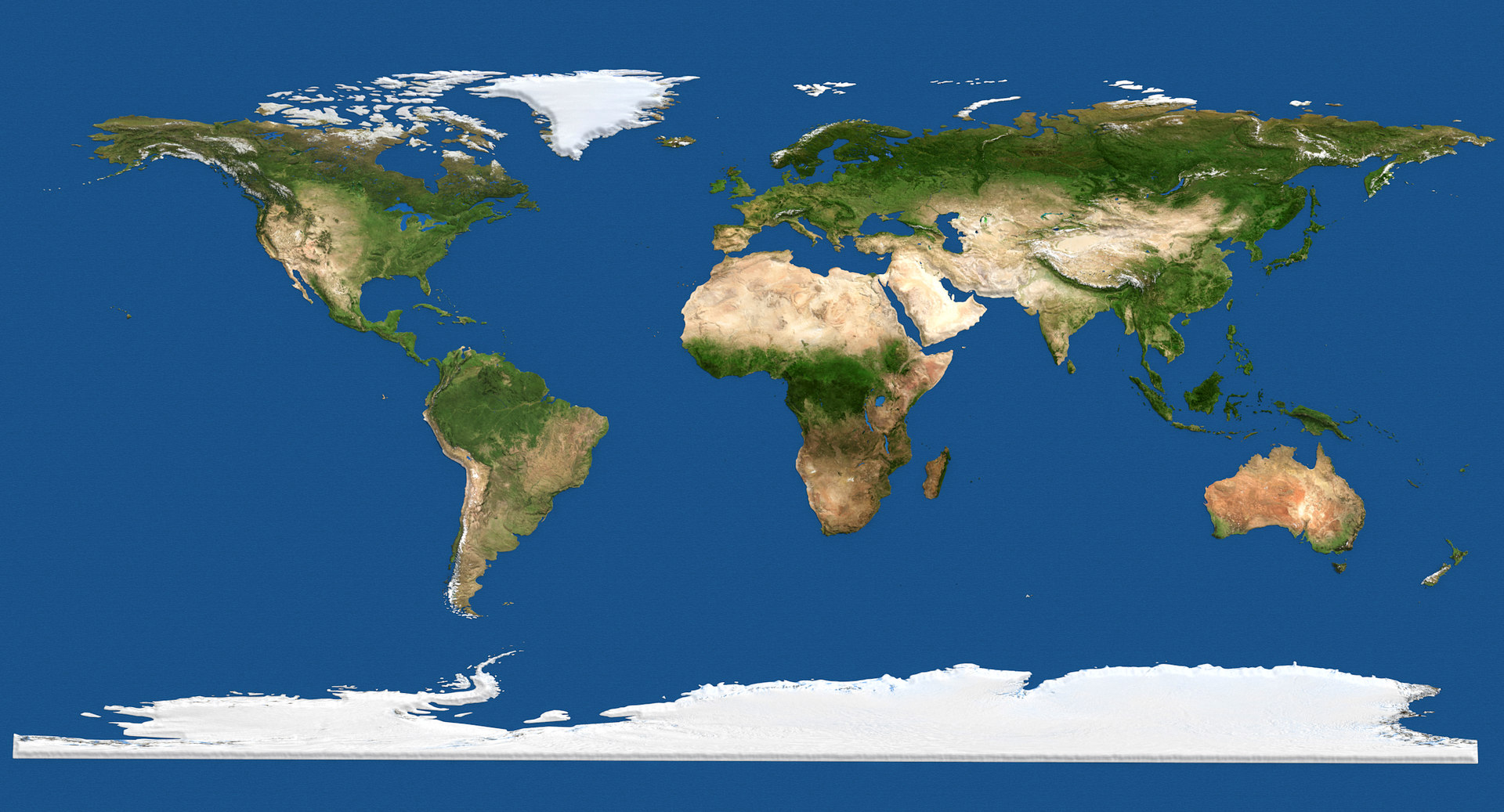
The Earth’s surface is a tapestry of diverse landforms, each with its unique character and influence on human life. This intricate network of mountains, valleys, plains, and plateaus, collectively known as topography, forms the foundation of our planet’s geography. Understanding the topography of the world is crucial for comprehending the distribution of resources, the patterns of climate, the flow of water, and the development of human civilizations.
Unveiling the Earth’s Sculptural Landscape
Topography is essentially the study of the Earth’s surface features and their arrangement. It encompasses the elevation, shape, and configuration of landforms, encompassing everything from towering mountain ranges to vast, flat plains. The most prominent topographic features include:
-
Mountains: These majestic landforms rise significantly above the surrounding terrain, often forming chains or ranges. Mountains are born from tectonic plate collisions, where the Earth’s crust buckles and folds. They play a crucial role in shaping climate, influencing rainfall patterns, and acting as natural barriers. The Himalayas, the Andes, and the Rockies are some of the most notable mountain ranges on Earth.
-
Valleys: Depressions in the Earth’s surface, valleys are typically formed by erosion from rivers or glaciers. They can be broad and flat, like the Nile Valley, or narrow and steep-sided, like the Grand Canyon. Valleys often serve as important routes for transportation and agriculture.
-
Plains: Extensive stretches of relatively flat land, plains are characterized by their gentle slopes and minimal elevation changes. They are typically found in areas where erosion has worn down the land or where sediment has been deposited by rivers or glaciers. Plains are ideal for agriculture and human settlement due to their fertile soils and ease of transportation. The Great Plains of North America and the Eurasian Steppe are examples of vast plains.
-
Plateaus: Elevated areas of relatively flat land, plateaus are often formed by volcanic activity or tectonic uplift. They can be found in diverse climates, from the arid plateaus of the Tibetan Plateau to the humid plateaus of the Brazilian Highlands. Plateaus are often rich in mineral resources and provide unique ecological niches.
The Forces Shaping the Earth’s Topography
The Earth’s topography is not static; it is constantly being shaped by a dynamic interplay of geological forces. These forces, both internal and external, create and modify the landforms we observe.
-
Tectonic Plates: The Earth’s outer layer is composed of massive plates that constantly move and interact with each other. These interactions, known as plate tectonics, are responsible for the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes. The collision of tectonic plates can uplift landmasses, forming mountain ranges like the Himalayas.
-
Erosion: The gradual wearing away of rock and soil by wind, water, and ice is known as erosion. It is a powerful force that sculpts valleys, canyons, and other landforms. Rivers carve out channels, glaciers erode valleys, and wind shapes dunes.
-
Weathering: The breakdown of rocks and minerals due to exposure to the elements is called weathering. Physical weathering occurs when rocks are broken down by mechanical forces, such as freezing and thawing. Chemical weathering involves the alteration of rock composition through chemical reactions. Weathering plays a crucial role in the formation of soil and the release of nutrients into the environment.
-
Volcanic Activity: The eruption of molten rock, ash, and gases from beneath the Earth’s surface is known as volcanic activity. Volcanoes can create new landforms, such as mountains and islands, and release gases that affect the atmosphere. Volcanic activity is particularly prevalent along plate boundaries, where the Earth’s crust is thinner and more prone to eruptions.
The Importance of World Map Topography
Understanding world map topography is essential for a multitude of reasons, impacting various aspects of human life and the environment:
-
Resource Distribution: Topography plays a crucial role in the distribution of natural resources, including water, minerals, and fertile land. Mountain ranges often hold valuable mineral deposits, while valleys and plains provide fertile soil for agriculture. Knowledge of topography helps us locate and manage these resources effectively.
-
Climate Regulation: Topography significantly influences climate patterns by affecting air circulation, rainfall, and temperature. Mountains act as barriers to wind and moisture, creating rain shadows on their leeward sides. Valleys can be prone to flooding, while plateaus experience unique microclimates.
-
Water Management: Topography guides the flow of water, influencing the formation of rivers, lakes, and groundwater systems. Understanding the topography of a region is crucial for managing water resources, preventing flooding, and ensuring sustainable water use.
-
Transportation and Infrastructure: Topography influences the development of transportation networks and infrastructure. Mountainous terrain can make road construction challenging, while valleys and plains provide natural routes for roads, railways, and pipelines.
-
Human Settlement and Development: Topography has a profound impact on human settlement patterns and development. People tend to settle in areas with fertile land, access to water, and favorable climate conditions. Topography also influences the design and construction of buildings and infrastructure, adapting to the unique challenges posed by different landforms.
FAQs on World Map Topography
-
What is the difference between topography and relief?
- Topography refers to the study of the Earth’s surface features and their arrangement, while relief refers to the difference in elevation between different points on the Earth’s surface. In essence, topography describes the overall landscape, while relief focuses on the vertical variations within it.
-
How is topography represented on maps?
- Topography is represented on maps using various techniques, including contour lines, shading, and three-dimensional models. Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the land’s shape. Shading can be used to highlight areas of high or low elevation, while three-dimensional models offer a more realistic portrayal of the terrain.
-
How does topography affect biodiversity?
- Topography creates diverse habitats, supporting a wide range of plant and animal species. Mountains, with their varied elevations and microclimates, often harbor unique ecosystems. Valleys and plains provide habitat for different species, depending on their specific characteristics. Topography also influences the distribution of plant and animal communities, creating distinct biogeographic regions.
-
What are the challenges posed by topography?
- Topography can pose challenges to human activities, such as agriculture, transportation, and construction. Mountainous terrain can make farming difficult, while valleys and plains can be prone to flooding. Steep slopes can make road construction challenging and increase the risk of landslides.
-
How is topography changing over time?
- Topography is constantly evolving due to the ongoing processes of plate tectonics, erosion, weathering, and volcanic activity. These forces can create new landforms, modify existing ones, and reshape the Earth’s surface over time. Human activities, such as deforestation and mining, can also impact topography, leading to erosion and land degradation.
Tips for Understanding World Map Topography
-
Explore topographic maps: Familiarize yourself with topographic maps, which use contour lines to represent elevation changes. Studying these maps can help you visualize the shape and arrangement of landforms.
-
Use online tools: Many online tools and websites provide interactive topographic maps and data, allowing you to explore the Earth’s topography in detail.
-
Visit different landscapes: Experiencing different landscapes firsthand can provide a deeper understanding of topography. Visiting mountains, valleys, plains, and plateaus can help you appreciate the unique characteristics and challenges of each landform.
-
Read books and articles: Numerous books and articles are available that delve into the intricacies of topography, covering topics such as plate tectonics, erosion, and the impact of topography on human life.
-
Engage in discussions: Discuss topography with others, sharing your observations and learning from their perspectives. Engaging in discussions can help you develop a more comprehensive understanding of this complex topic.
Conclusion
World map topography is a fascinating and crucial aspect of our planet’s geography. It shapes the distribution of resources, influences climate patterns, guides the flow of water, and impacts human settlement and development. By understanding the forces that shape the Earth’s surface and the diverse landforms that result, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of our planet and the complex relationships between humans and the environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of World Map Topography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!