A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Landscape of Utah
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Landscape of Utah
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Landscape of Utah. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Landscape of Utah
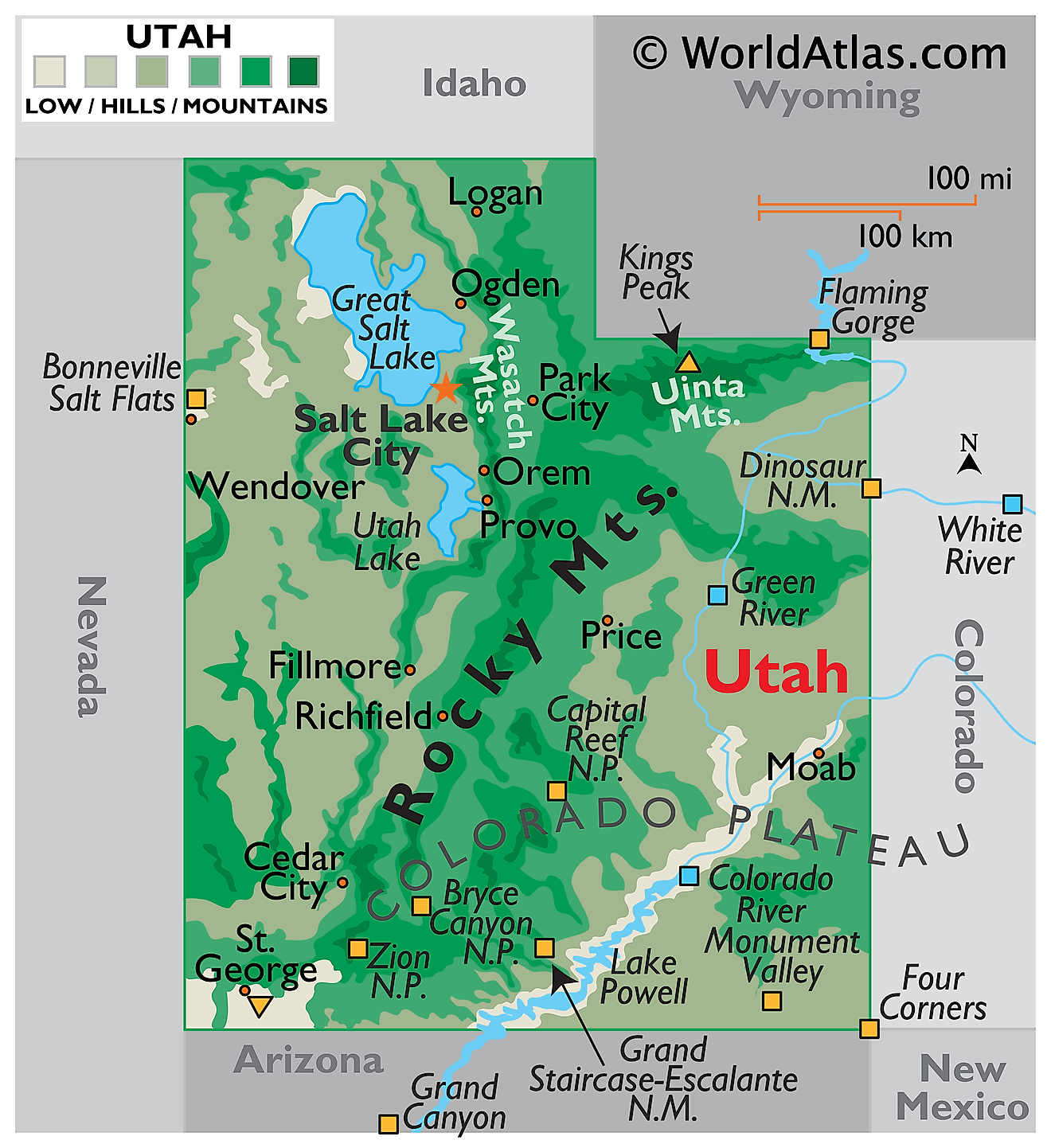
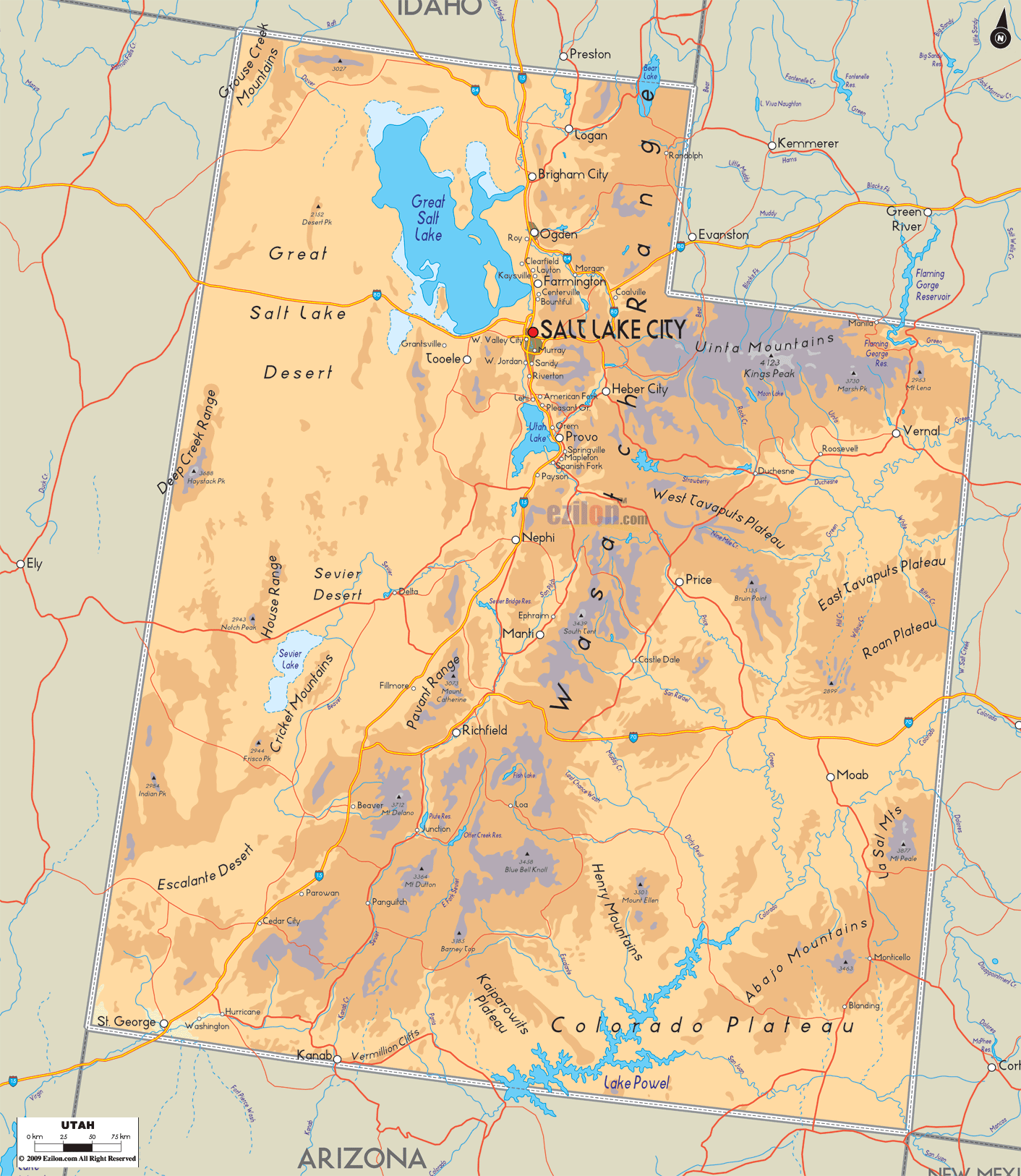
Utah, nestled in the heart of the American West, is a state renowned for its breathtaking landscapes, diverse ecosystems, and rich history. This article delves into the geographical tapestry of Utah, exploring its unique features, geological formations, and the interplay of natural forces that have shaped its distinctive character.
A Land of Contrasts: The Geographical Features of Utah
Utah’s landscape is a testament to the power of geological forces over millennia. From towering mountains to vast deserts, from deep canyons to shimmering lakes, the state presents a diverse and captivating visual spectacle.
-
The Wasatch Range: This imposing mountain chain, running north-south along the eastern edge of the state, is a defining feature of Utah’s geography. Its peaks, reaching elevations exceeding 11,000 feet, provide stunning backdrops for cities like Salt Lake City and Provo, while also offering recreational opportunities for skiing, hiking, and mountaineering.
-
The Colorado Plateau: Covering the majority of Utah’s landmass, the Colorado Plateau is a vast, elevated region characterized by its high altitude, dramatic canyons, and red rock formations. This region is home to iconic landmarks like Zion National Park, Bryce Canyon National Park, and Canyonlands National Park, each showcasing the unique beauty of the plateau’s geological history.
-
The Great Basin: Utah’s western border is defined by the Great Basin, a vast, arid region encompassing much of Nevada and parts of California, Oregon, and Idaho. This area is characterized by its internal drainage, meaning that its rivers and streams do not flow to the ocean but instead evaporate or sink into the ground. The Great Basin is home to unique desert ecosystems and the striking landscape of the Bonneville Salt Flats.
-
The Basin and Range Province: This geological province, extending across much of the western United States, is characterized by alternating mountain ranges and valleys. In Utah, this region is most prominent in the southwestern portion of the state, where the Mojave Desert meets the Colorado Plateau. This area features rugged mountains, dry washes, and a stark, almost lunar-like landscape.
The Shaping Forces: Geology and Climate
Utah’s unique landscape is a product of the interplay between geological processes and climatic conditions.
-
Tectonic Activity: The state is situated in a region of active tectonic activity, where the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate collide. This collision has resulted in the uplift of mountains, the formation of faults, and the creation of valleys. The Wasatch Fault, running along the eastern edge of the Wasatch Range, is a prime example of this ongoing tectonic activity.
-
Erosion: The forces of wind, water, and ice have sculpted Utah’s landscape over millions of years. The Colorado River, carving its way through the Colorado Plateau, has created the awe-inspiring Grand Canyon, a testament to the power of erosion. Similarly, wind erosion has shaped the unique hoodoos of Bryce Canyon National Park.
-
Climate: Utah experiences a diverse range of climates, from the semi-arid conditions of the Great Basin to the alpine climate of the Wasatch Range. These climatic variations influence vegetation patterns, water availability, and the overall character of different regions.
Water: A Vital Resource
Water is a precious resource in Utah, a state with a semi-arid climate. The state’s major rivers, including the Colorado River, the Green River, and the Provo River, are essential for agriculture, municipal water supplies, and recreation.
-
The Colorado River: This mighty river, originating in the Rocky Mountains, flows through Utah, carving out the Grand Canyon and providing water to millions of people in the southwestern United States.
-
The Great Salt Lake: This inland lake, located in the northwestern part of the state, is the largest saltwater lake in the Western Hemisphere. The Great Salt Lake is a vital habitat for migratory birds and a source of brine shrimp, used in aquaculture and other industries.
-
Groundwater: Utah relies heavily on groundwater, particularly in areas where surface water is scarce. However, over-extraction of groundwater can lead to depletion and subsidence, posing challenges for water management in the state.
A Tapestry of Ecosystems
Utah’s diverse landscapes support a wide range of ecosystems, each with its unique flora and fauna.
-
Deserts: The Great Basin and the Mojave Desert in southwestern Utah are home to a variety of desert plants and animals adapted to harsh conditions, including cacti, Joshua trees, desert tortoises, and rattlesnakes.
-
Forests: The Wasatch Range and other mountain ranges in Utah support forests of ponderosa pine, Douglas fir, and aspen, providing habitat for elk, deer, and other wildlife.
-
Wetlands: The Great Salt Lake and other wetlands in Utah provide essential habitats for migratory birds, including ducks, geese, and shorebirds.
-
Riparian Zones: The areas along rivers and streams in Utah support a diverse array of plants and animals, including willows, cottonwoods, beavers, and trout.
Human Impact and Conservation
Utah’s landscape has been shaped by human activity, from agriculture and mining to urbanization and recreation.
-
Agriculture: Utah’s agriculture industry, particularly in the central and northern parts of the state, relies heavily on water resources. Irrigation systems have transformed arid lands into productive farmland, but they also raise concerns about water depletion and environmental impacts.
-
Mining: Utah has a long history of mining, with resources ranging from coal and copper to uranium and oil shale. Mining operations have had significant impacts on the environment, including habitat loss, air and water pollution, and land disturbance.
-
Urbanization: The state’s population has grown significantly in recent decades, leading to increased development and urbanization. This growth places pressure on natural resources, including water, land, and air quality.
-
Recreation: Utah’s stunning landscapes attract millions of visitors each year, engaging in activities such as hiking, camping, skiing, and rock climbing. While recreation provides economic benefits, it also raises concerns about overuse, habitat disturbance, and the spread of invasive species.
Conservation Efforts
Recognizing the importance of preserving Utah’s unique natural heritage, the state has implemented a range of conservation efforts.
-
National Parks and Monuments: Utah is home to five national parks, including Zion National Park, Bryce Canyon National Park, Canyonlands National Park, Arches National Park, and Capitol Reef National Park. These parks protect some of the state’s most iconic landscapes and provide opportunities for recreation and education.
-
State Parks: Utah also has a network of state parks, offering a variety of recreational experiences, from hiking and camping to fishing and boating.
-
Wildlife Refuges: The state has designated several wildlife refuges to protect endangered and threatened species, including the Great Basin National Park and the Bear River Migratory Bird Refuge.
-
Land Conservation: Non-profit organizations and government agencies are working to conserve land in Utah, protecting open spaces, natural habitats, and scenic views.
Challenges and Opportunities
Utah faces a number of challenges related to its landscape and environment, including:
-
Water scarcity: The state’s semi-arid climate and growing population put pressure on water resources, requiring careful management and conservation efforts.
-
Climate change: Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased wildfire risk are all potential consequences of climate change in Utah, posing challenges for ecosystems and human communities.
-
Population growth: Continued population growth in Utah will place increasing demands on natural resources and infrastructure, requiring thoughtful planning and development strategies.
Despite these challenges, Utah also has significant opportunities for sustainable development and environmental stewardship.
-
Renewable energy: The state has abundant solar and wind resources, providing opportunities to transition to cleaner energy sources.
-
Sustainable agriculture: Innovative farming practices and water conservation technologies can help ensure the long-term sustainability of Utah’s agriculture industry.
-
Ecotourism: Promoting responsible tourism can provide economic benefits while minimizing environmental impacts.
Conclusion
Utah’s landscape is a testament to the power of geological forces and the beauty of natural diversity. The state’s unique features, from towering mountains to vast deserts, offer a tapestry of ecosystems and recreational opportunities. However, Utah faces challenges related to water scarcity, climate change, and population growth. By embracing sustainable practices, conserving natural resources, and promoting responsible development, Utah can ensure that its stunning landscapes and rich heritage are preserved for future generations.
FAQs
Q: What is the highest point in Utah?
A: The highest point in Utah is Kings Peak, located in the Uinta Mountains, at an elevation of 13,528 feet.
Q: What is the most popular national park in Utah?
A: Zion National Park, known for its towering sandstone cliffs and the Virgin River, is the most popular national park in Utah, attracting millions of visitors each year.
Q: What are the major cities in Utah?
A: The major cities in Utah include Salt Lake City, the state capital, as well as Provo, West Valley City, Ogden, and Sandy.
Q: What are the main industries in Utah?
A: Utah’s economy is diverse, with key industries including tourism, technology, manufacturing, mining, and agriculture.
Q: What are some of the unique geological features of Utah?
A: Utah is renowned for its unique geological features, including the canyons of Zion National Park, the hoodoos of Bryce Canyon National Park, the salt flats of the Bonneville Salt Flats, and the arches of Arches National Park.
Tips
-
Visit Utah’s national parks: Experience the awe-inspiring beauty of Zion National Park, Bryce Canyon National Park, Canyonlands National Park, Arches National Park, and Capitol Reef National Park.
-
Explore the Great Salt Lake: Take a boat tour or visit the Antelope Island State Park, home to a herd of wild bison.
-
Hike the Wasatch Range: Discover stunning views and diverse ecosystems on the trails of the Wasatch Mountains.
-
Learn about Utah’s history: Visit historical sites like Temple Square in Salt Lake City and the Brigham Young Historic Park.
-
Support local businesses: Patronize local restaurants, shops, and attractions to contribute to the Utah economy.
Conclusion
Utah, with its diverse landscape, rich history, and vibrant culture, offers a unique travel destination for adventurers, nature enthusiasts, and history buffs alike. By understanding the state’s geographical features, geological processes, and environmental challenges, visitors can appreciate the beauty and fragility of this remarkable corner of the American West.
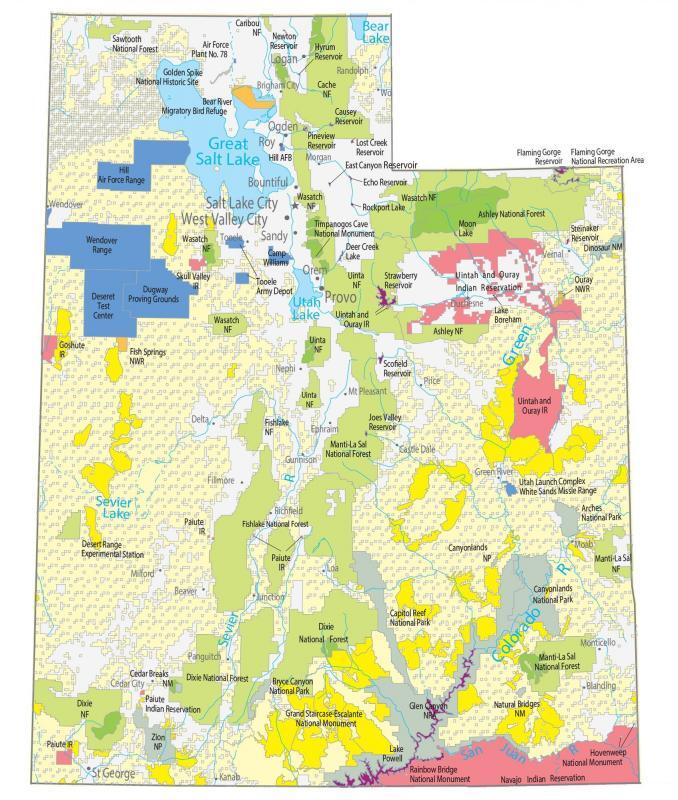

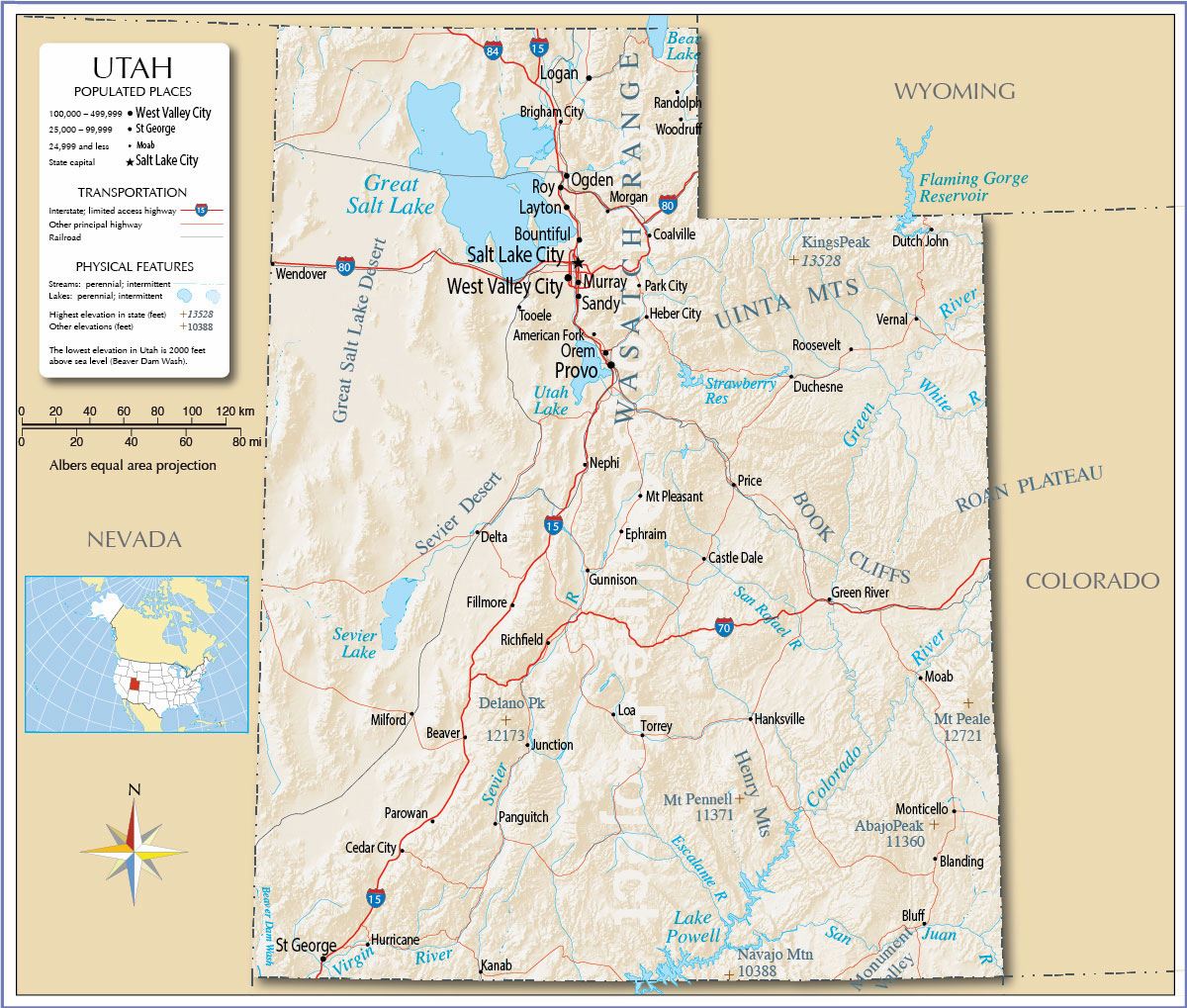

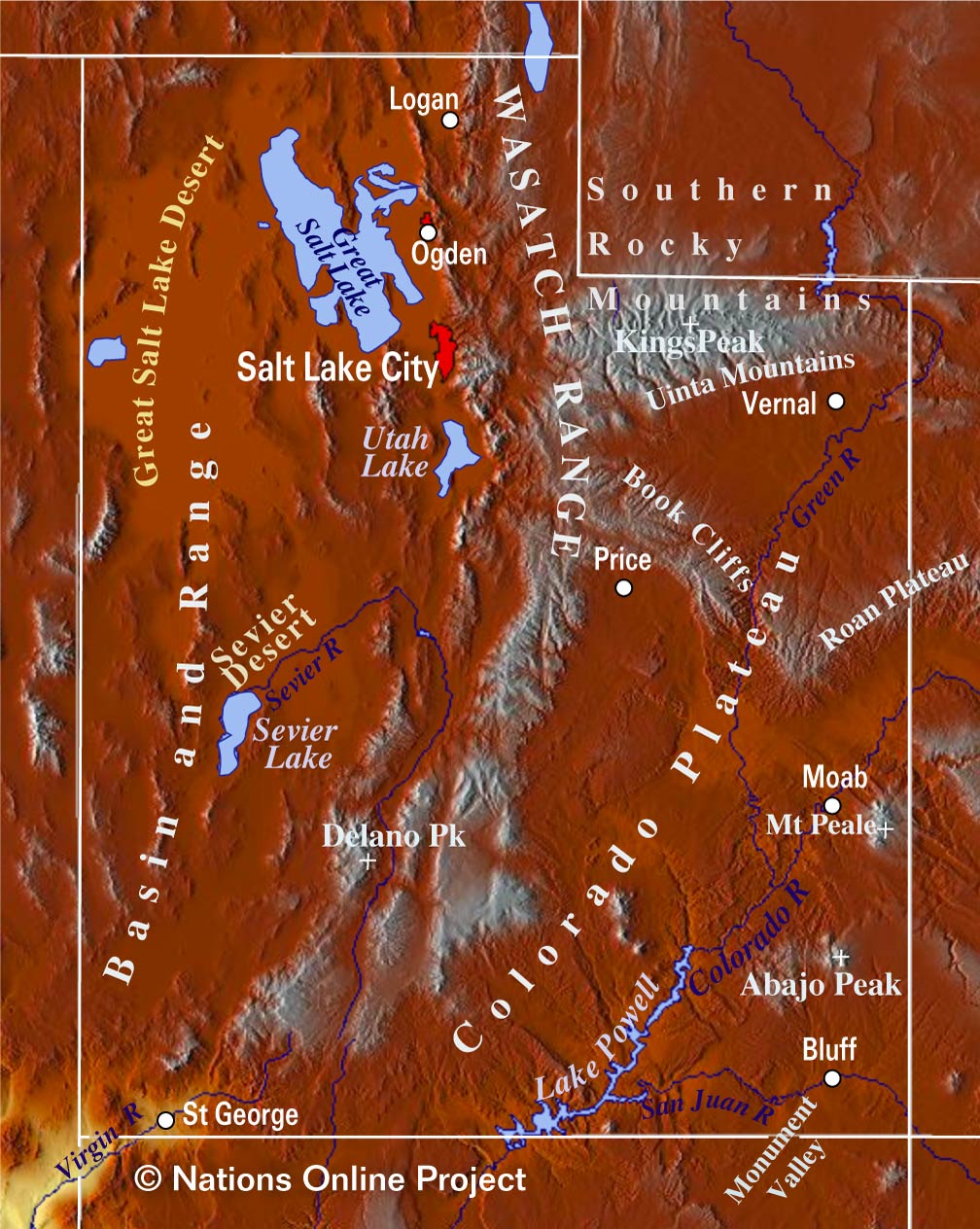


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography and Landscape of Utah. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!