A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Vietnam: Understanding the Land of the Dragon
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Vietnam: Understanding the Land of the Dragon
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Vietnam: Understanding the Land of the Dragon. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Vietnam: Understanding the Land of the Dragon
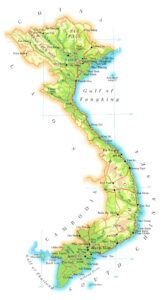
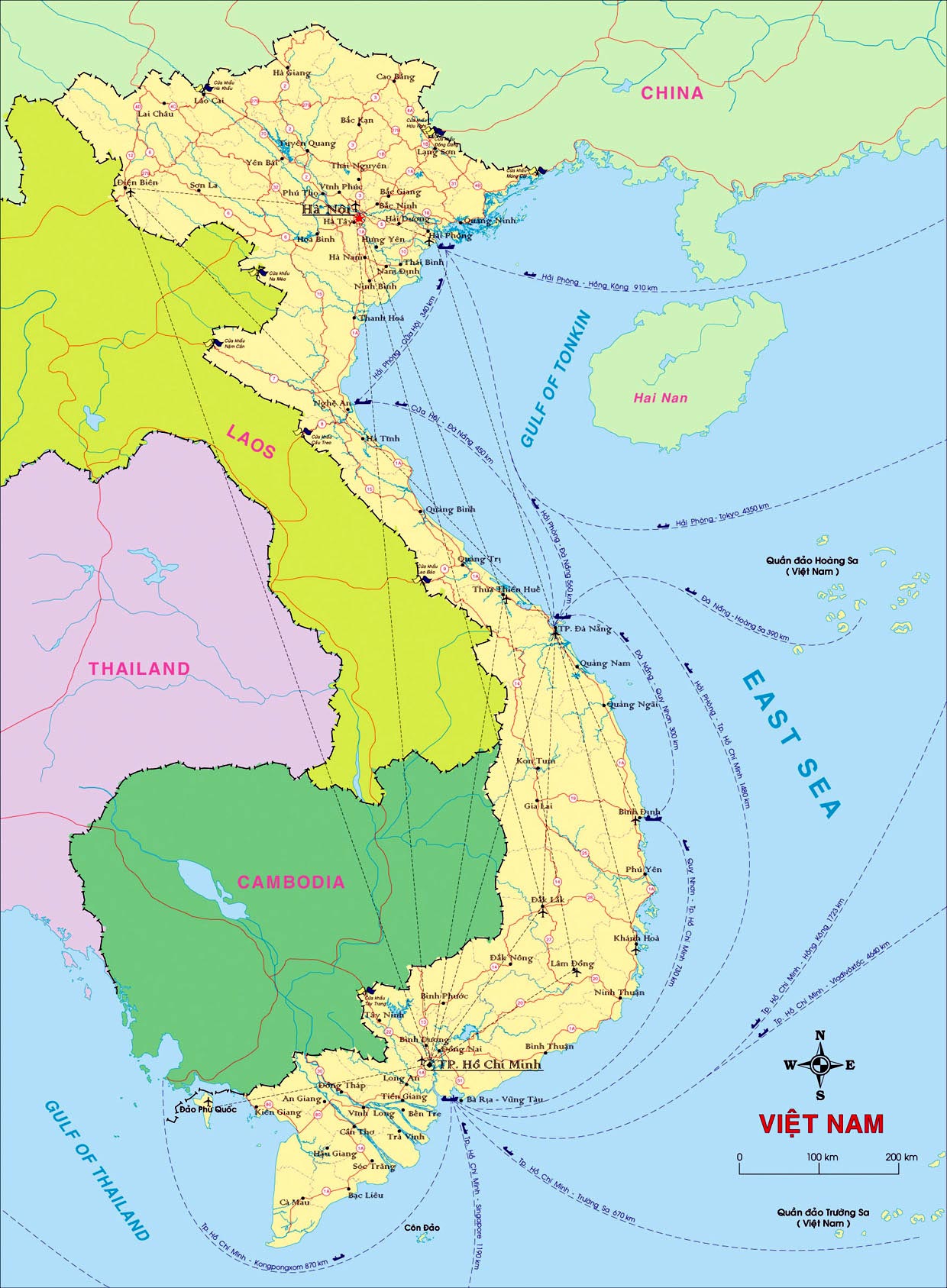
Vietnam, a Southeast Asian nation with a rich history and diverse landscape, holds a captivating allure for travelers and scholars alike. Its geographical features, shaped by millennia of geological and human interaction, have played a pivotal role in shaping its culture, economy, and political landscape. Understanding the map of Vietnam is crucial for appreciating the country’s complexity and appreciating its unique characteristics.
I. The Shape of the Dragon: A Geographical Overview
Vietnam’s elongated S-shape, stretching over 1,650 kilometers from north to south, is a defining feature. The country is bordered by China to the north, Laos and Cambodia to the west, and the South China Sea to the east. This elongated form contributes to a diverse range of climates, ecosystems, and cultural influences.
A. The North: Mountains and Rice Fields
The north of Vietnam is dominated by the Annamite Cordillera, a rugged mountain range that forms a natural barrier between Vietnam and Laos. The Red River Delta, a fertile plain formed by the Red River, is a major agricultural region, renowned for its rice production. This region is also home to Hanoi, the country’s capital, and other historical cities like Ha Long Bay, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
B. The Central Coast: Beaches, Mountains, and Rivers
The central coast of Vietnam is characterized by a narrow coastal plain interspersed with mountain ranges and rivers. This region is known for its stunning beaches, including the popular destinations of Da Nang and Nha Trang. The Central Highlands, also known as the Tay Nguyen, are a plateau region with coffee plantations and indigenous cultures.
C. The Mekong Delta: The Rice Bowl of Vietnam
The southernmost region of Vietnam is dominated by the Mekong Delta, a vast network of rivers, canals, and rice paddies. This region is the heart of Vietnam’s rice production, earning it the moniker "the rice bowl of Vietnam." The Mekong Delta is also home to Ho Chi Minh City, the country’s largest city and economic hub.
II. Beyond the Boundaries: The Importance of Vietnam’s Geography
A. Economic Potential: A Land of Abundance
Vietnam’s diverse geography has bestowed upon it a rich array of natural resources, including fertile land, abundant rivers, and coastal access. These resources have contributed significantly to the country’s agricultural and fisheries sectors, forming the backbone of its economy. The Mekong Delta, for instance, produces a significant portion of Vietnam’s rice, while the coastal regions are home to a thriving fishing industry.
B. Cultural Diversity: A Tapestry of Traditions
The diverse landscapes of Vietnam have fostered a vibrant and multifaceted culture. Each region boasts unique traditions, languages, and customs, reflecting the influence of historical interactions and geographical isolation. The north, with its long history of Chinese influence, has a distinct cultural heritage. The central coast, with its blend of coastal and mountainous influences, has a unique cultural identity. The Mekong Delta, with its diverse ethnic groups and agricultural traditions, has a rich and vibrant culture.
C. Strategic Significance: A Crossroads of Trade and Conflict
Vietnam’s strategic location has made it a crossroads of trade and conflict throughout history. Situated at the heart of Southeast Asia, Vietnam has served as a gateway between China and the rest of the region. This strategic importance has also led to periods of conflict, particularly during the Vietnam War, which had a profound impact on the country’s landscape and society.
III. Understanding the Map: A Guide to Navigating Vietnam’s Complexity
A. Key Cities and Towns
The map of Vietnam clearly shows the distribution of major cities and towns, providing a glimpse into the country’s urban centers. Hanoi, the capital, is located in the north, while Ho Chi Minh City, the largest city, is located in the south. Other important cities include Da Nang, Hue, Hai Phong, and Can Tho.
B. Major Rivers and Waterways
Vietnam’s network of rivers and waterways is a defining feature of its geography. The Red River, the Mekong River, and the Thu Bon River are some of the most important waterways, playing a crucial role in transportation, agriculture, and cultural development.
C. Mountain Ranges and National Parks
The map of Vietnam highlights the country’s mountainous terrain, particularly the Annamite Cordillera and the Central Highlands. These regions are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, as well as numerous national parks, such as Phong Nha-Ke Bang National Park and Cuc Phuong National Park.
D. Coastal Zones and Islands
Vietnam has a long coastline stretching over 3,260 kilometers, featuring numerous beaches, bays, and islands. The South China Sea, which borders Vietnam’s east coast, is a vital source of fishing and a potential source of energy resources. The map highlights major islands like Phu Quoc Island and Con Dao Island, popular tourist destinations.
IV. FAQs about the Map of Vietnam
Q: What is the most populous city in Vietnam?
A: Ho Chi Minh City is the most populous city in Vietnam.
Q: What is the highest mountain in Vietnam?
A: Fansipan, located in the Annamite Cordillera, is the highest mountain in Vietnam.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Vietnam?
A: The major religions practiced in Vietnam include Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, and Islam.
Q: What are the major languages spoken in Vietnam?
A: The official language of Vietnam is Vietnamese. Other languages spoken include Khmer, Hmong, and Chinese.
Q: What are the major economic activities in Vietnam?
A: The major economic activities in Vietnam include agriculture, fishing, manufacturing, tourism, and services.
V. Tips for Using the Map of Vietnam
1. Familiarize yourself with the major geographical features: This will help you understand the country’s diverse landscapes and cultural influences.
2. Identify key cities and towns: This will provide a framework for planning your itinerary and understanding the country’s urban centers.
3. Study the major rivers and waterways: These waterways are essential for transportation, agriculture, and cultural development.
4. Explore the mountain ranges and national parks: These areas offer stunning natural beauty and opportunities for adventure.
5. Discover the coastal zones and islands: Vietnam’s coastline is a paradise for beach lovers and water sports enthusiasts.
VI. Conclusion: The Map as a Window into Vietnamese Identity
The map of Vietnam is more than just a geographical representation; it is a reflection of the country’s history, culture, and identity. It reveals the intricate interplay of mountains, rivers, and coastlines that have shaped the nation’s destiny. By understanding the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for Vietnam’s unique characteristics and the enduring spirit of its people.
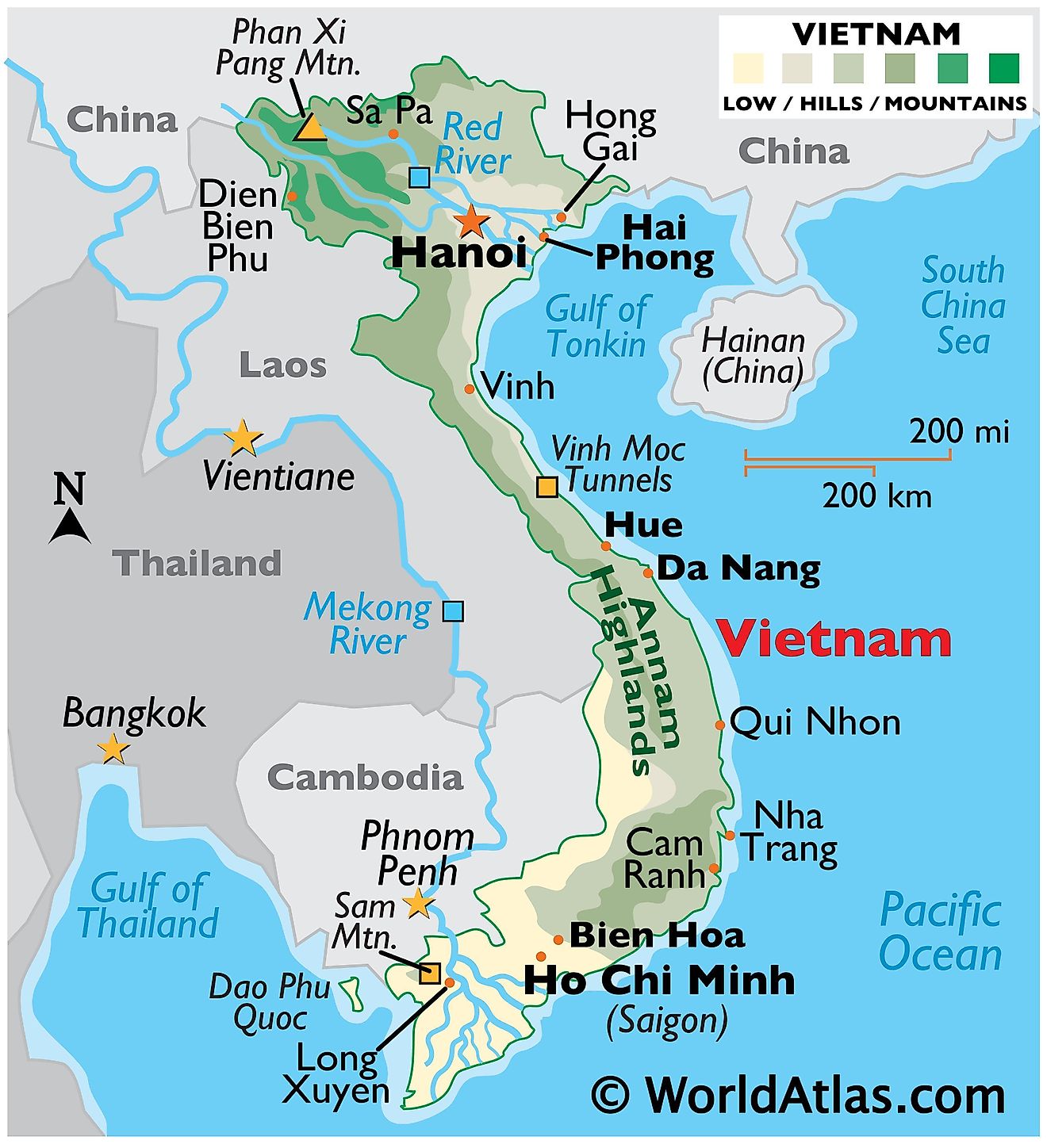

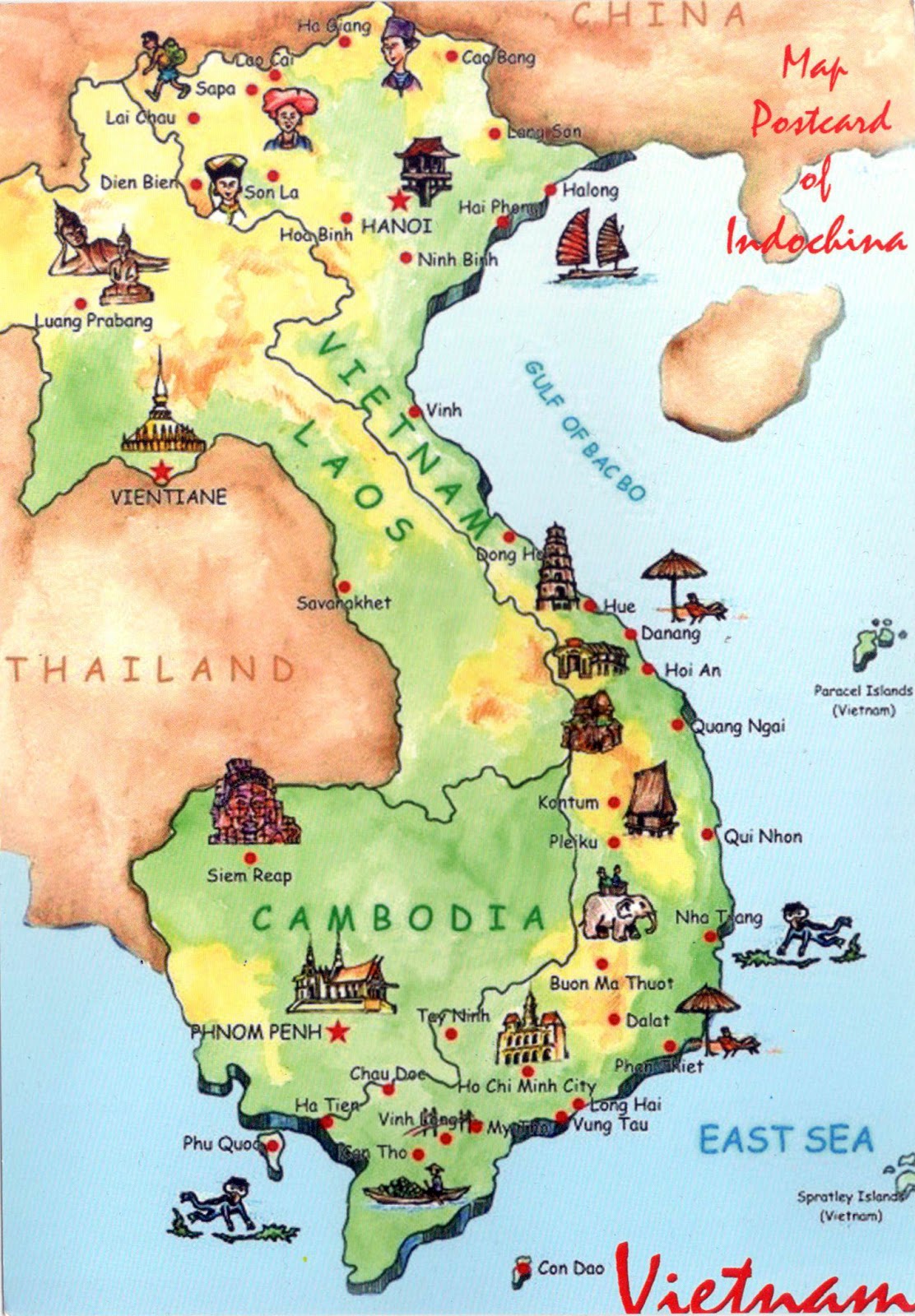
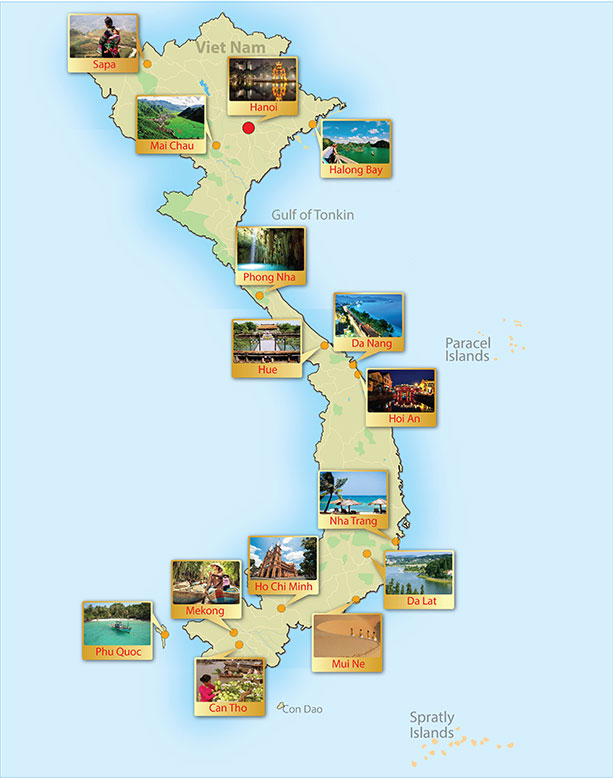



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Vietnam: Understanding the Land of the Dragon. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!