A Crossroads of History and Conflict: Examining the Geopolitical Landscape of Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey
Related Articles: A Crossroads of History and Conflict: Examining the Geopolitical Landscape of Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Crossroads of History and Conflict: Examining the Geopolitical Landscape of Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Crossroads of History and Conflict: Examining the Geopolitical Landscape of Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Crossroads of History and Conflict: Examining the Geopolitical Landscape of Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey
- 4 FAQs:
- 5 Tips:
- 6 Conclusion:
- 7 Closure
A Crossroads of History and Conflict: Examining the Geopolitical Landscape of Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey
The region encompassing Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey is a complex tapestry woven with threads of history, culture, religion, and geopolitics. This geographically diverse area, nestled at the intersection of Asia, Africa, and Europe, has been a focal point of global attention for centuries, witnessing the rise and fall of empires, the birth of religions, and the eruption of conflicts that continue to shape the world today. Understanding the intricate interplay of these nations, their respective histories, and their current political and economic realities is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of the Middle East and its impact on global affairs.
A Brief Historical Overview:
The region’s history is a testament to its strategic location. Mesopotamia, the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, saw the rise of ancient civilizations like Sumer, Akkad, Babylon, and Assyria, laying the foundation for human civilization itself. The region witnessed the rise and fall of empires, including the Persian Empire, the Roman Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the British Empire, each leaving an indelible mark on the cultural and political landscape.
Iran:
Iran, historically known as Persia, boasts a rich and ancient history. The Achaemenid Empire, established in the 6th century BC, stretched from Egypt to India, making it one of the largest empires of the ancient world. The country’s rich cultural heritage is reflected in its ancient architecture, intricate art, and vibrant traditions. Iran’s strategic location, bordering the Persian Gulf, has made it a key player in global energy markets. However, the country’s political landscape has been marked by instability and conflict, particularly in recent decades.
Iraq:
Iraq, situated in the heart of Mesopotamia, has been a crossroads of civilizations for millennia. The country is home to ancient cities like Babylon and Ur, and its fertile land has supported agriculture and trade for centuries. Iraq’s oil reserves have made it a vital player in the global energy market, but the country has also been plagued by political instability, sectarian violence, and the devastating consequences of war.
Israel:
Israel, a nation with a long and complex history, occupies a strategically important location in the Levant. The country’s history is deeply intertwined with the Bible, and its modern state, established in 1948, has been at the center of a protracted conflict with its Arab neighbors. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has been a major source of tension in the region, with profound implications for international relations.
Jordan:
Jordan, located on the eastern bank of the Jordan River, has a history deeply intertwined with the history of Israel and Palestine. The country’s strategic location, bordering Israel, Saudi Arabia, and Iraq, has made it a key player in regional politics. Jordan’s economy is heavily reliant on foreign aid and tourism, and the country has faced challenges related to water scarcity, political instability, and the ongoing Syrian civil war.
Turkey:
Turkey, straddling the crossroads of Europe and Asia, has a rich and diverse history. The country’s location, encompassing the Anatolian peninsula and the eastern Thrace region, has made it a bridge between continents for millennia. Turkey’s history is marked by the rise and fall of empires, including the Byzantine Empire and the Ottoman Empire. Today, Turkey is a member of NATO and plays a vital role in regional security. The country has also emerged as a major economic power, with a growing industrial sector and a strategic location in global trade routes.
The Geopolitical Landscape:
The region’s geopolitical landscape is characterized by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Religious Diversity: The region is home to a diverse range of religious groups, including Muslims, Christians, Jews, and Zoroastrians. These religious identities have often played a significant role in shaping political and social dynamics.
- Resource Competition: The region is rich in natural resources, particularly oil and gas, which have attracted international interest and sparked competition among regional powers.
- Ethnic and Tribal Divisions: The region is home to a multitude of ethnic and tribal groups, whose identities and aspirations have often been the source of conflict and instability.
- International Rivalries: The region has been a battleground for international rivalries, with the United States, Russia, and China vying for influence and control.
- Political Instability: The region has experienced widespread political instability, characterized by revolutions, coups, and civil wars.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The region faces a number of challenges, including:
- The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: This protracted conflict has been a major source of instability and violence in the region, with profound implications for international relations.
- Terrorism: The region has been a breeding ground for terrorism, with groups like ISIS and al-Qaeda posing a significant threat to regional security.
- Water Scarcity: The region faces a growing water crisis, driven by population growth, climate change, and unsustainable water management practices.
- Economic Inequality: The region is characterized by significant economic inequality, with a small elite controlling a disproportionate share of wealth.
Despite these challenges, the region also presents a number of opportunities:
- Economic Growth: The region’s rich natural resources, strategic location, and growing population present opportunities for economic growth and development.
- Cultural Exchange: The region’s diverse cultures offer opportunities for cultural exchange and cooperation.
- Regional Integration: The region’s nations have the potential to work together to address common challenges and foster regional integration.
Conclusion:
The region encompassing Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey is a complex and dynamic area, shaped by a confluence of historical, cultural, religious, and geopolitical factors. Its history is a testament to its strategic location, its diverse cultures, and its enduring struggles. The region’s future is uncertain, but its potential for peace, prosperity, and stability is undeniable. Understanding the region’s complex dynamics is essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
FAQs:
1. What is the role of religion in the region’s politics?
Religion plays a significant role in the region’s politics, shaping identities, values, and political ideologies. The region is home to a diverse range of religious groups, including Muslims, Christians, Jews, and Zoroastrians, and their respective beliefs have often influenced political discourse, social norms, and regional conflicts.
2. How has the discovery of oil impacted the region?
The discovery of vast oil reserves in the region has had a profound impact, transforming economies, attracting international interest, and fueling regional rivalries. While oil wealth has brought economic benefits, it has also contributed to political instability, corruption, and environmental degradation.
3. What are the major sources of conflict in the region?
The region is characterized by a multitude of conflicts, including:
- The Israeli-Palestinian conflict: This protracted conflict has been a major source of instability and violence in the region, with profound implications for international relations.
- The Syrian Civil War: This ongoing conflict has destabilized the region, creating a humanitarian crisis and fueling regional tensions.
- The conflict in Yemen: This ongoing conflict has created a humanitarian catastrophe and exacerbated regional instability.
4. What are the prospects for peace and stability in the region?
The prospects for peace and stability in the region are uncertain, with a multitude of challenges hindering progress. However, there are also opportunities for cooperation and dialogue. Resolving the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, addressing the root causes of terrorism, and fostering economic development are crucial steps towards achieving lasting peace and stability.
5. What is the role of the United States and other international powers in the region?
The United States, Russia, and China are major players in the region, vying for influence and control. Their involvement has often been controversial, contributing to instability and conflict. However, they also play a vital role in promoting peace, security, and economic development.
Tips:
- Stay informed: Follow reputable news sources and engage with academic literature to gain a deeper understanding of the region’s complexities.
- Be critical: Approach information with a critical eye, recognizing the biases and agendas that may influence reporting.
- Engage in dialogue: Engage in respectful dialogue with people from different backgrounds and perspectives to foster understanding and empathy.
- Support peace initiatives: Support organizations working towards peace and reconciliation in the region.
- Promote cultural exchange: Seek opportunities to learn about and appreciate the diverse cultures of the region.
Conclusion:
The region encompassing Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey is a microcosm of global challenges, reflecting the complexities of history, religion, culture, and geopolitics. Understanding this region is crucial for navigating a world increasingly defined by interdependence and interconnectedness. The region’s future hinges on the ability of its nations to overcome historical animosities, address shared challenges, and embrace the potential for cooperation and prosperity.
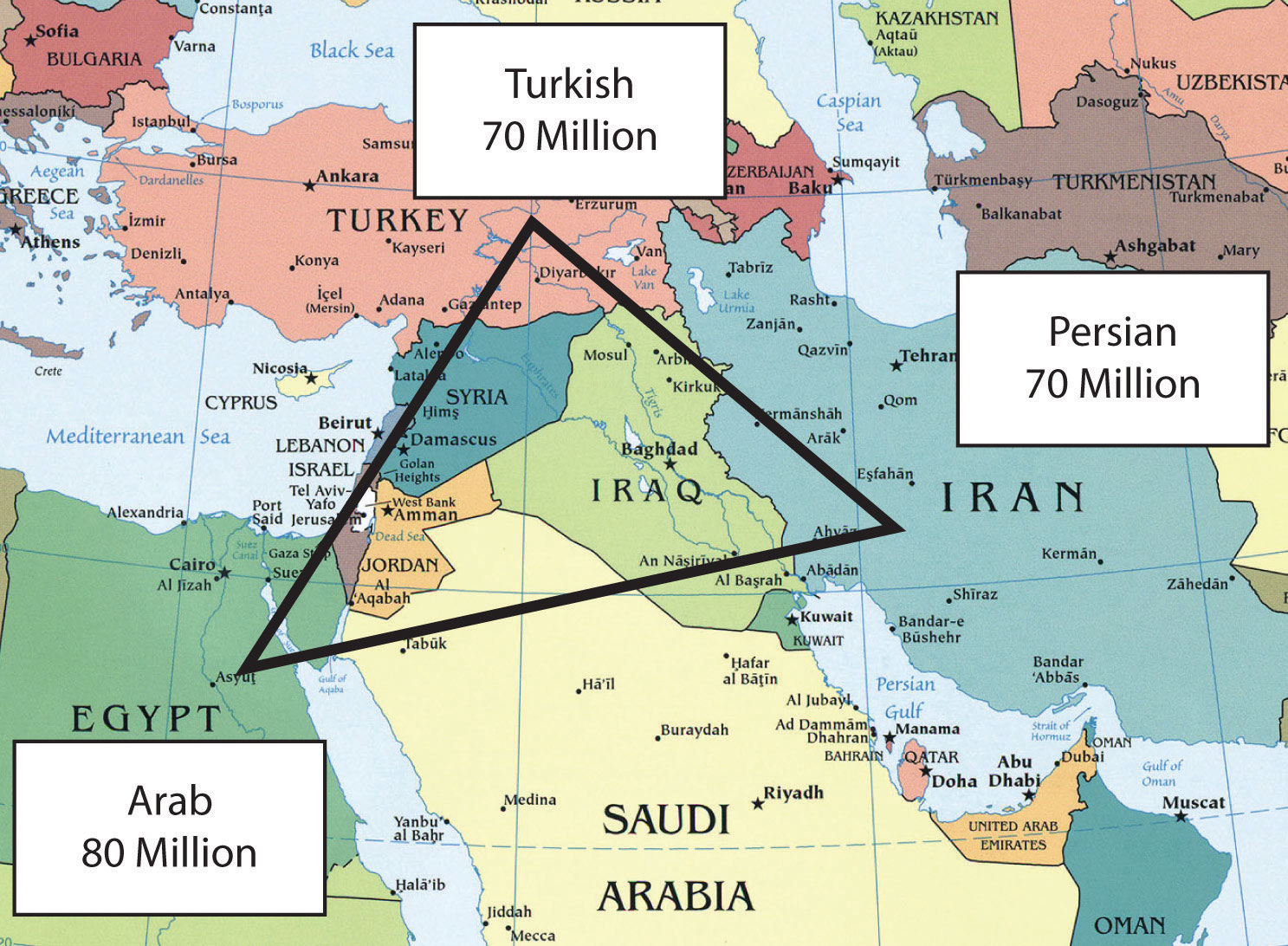
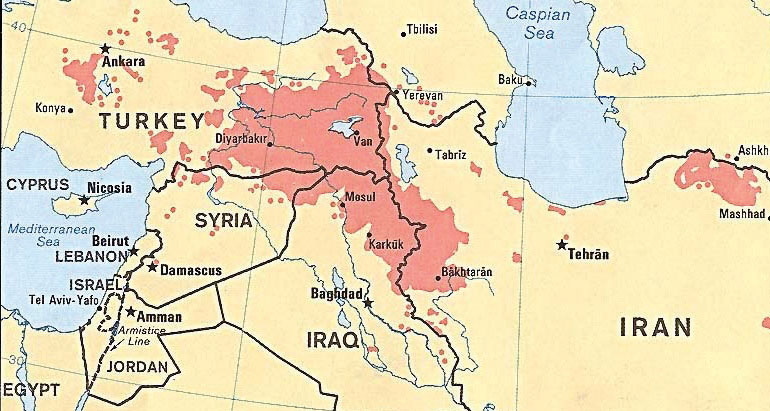
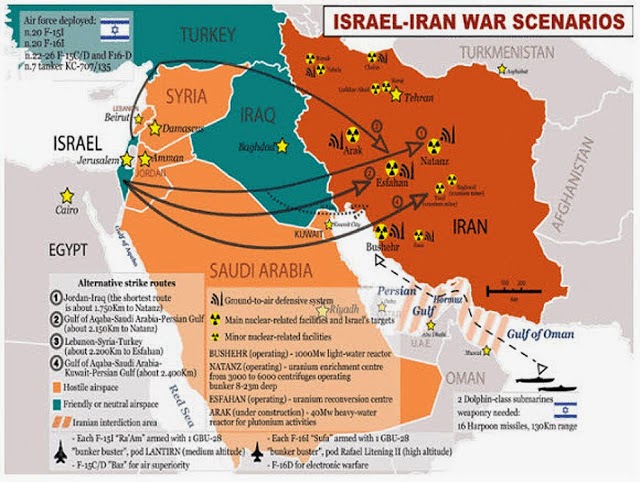

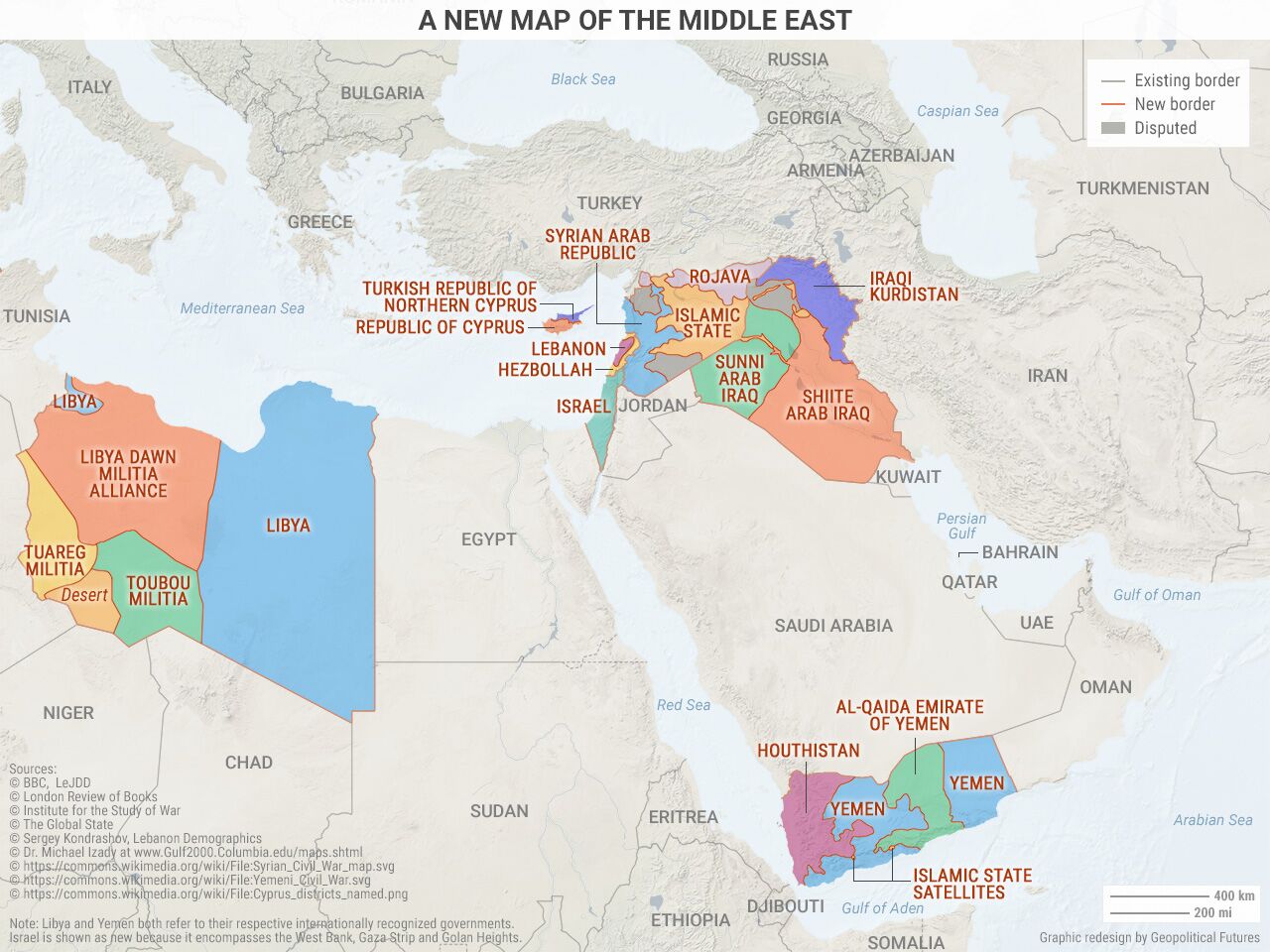
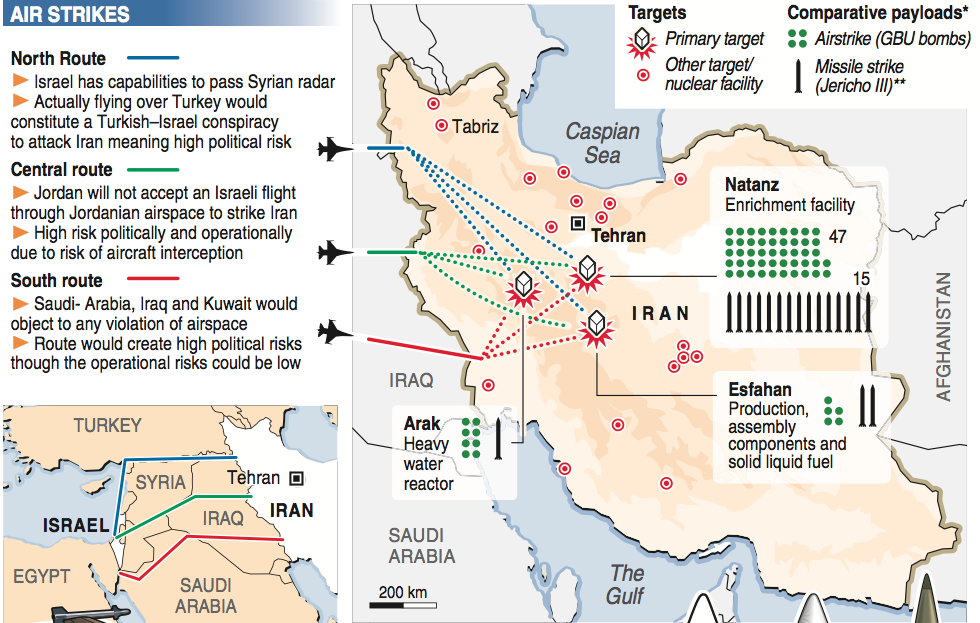
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Crossroads of History and Conflict: Examining the Geopolitical Landscape of Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!