A Geographic Overview of Turkey and its Surrounding Countries
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview of Turkey and its Surrounding Countries
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview of Turkey and its Surrounding Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview of Turkey and its Surrounding Countries

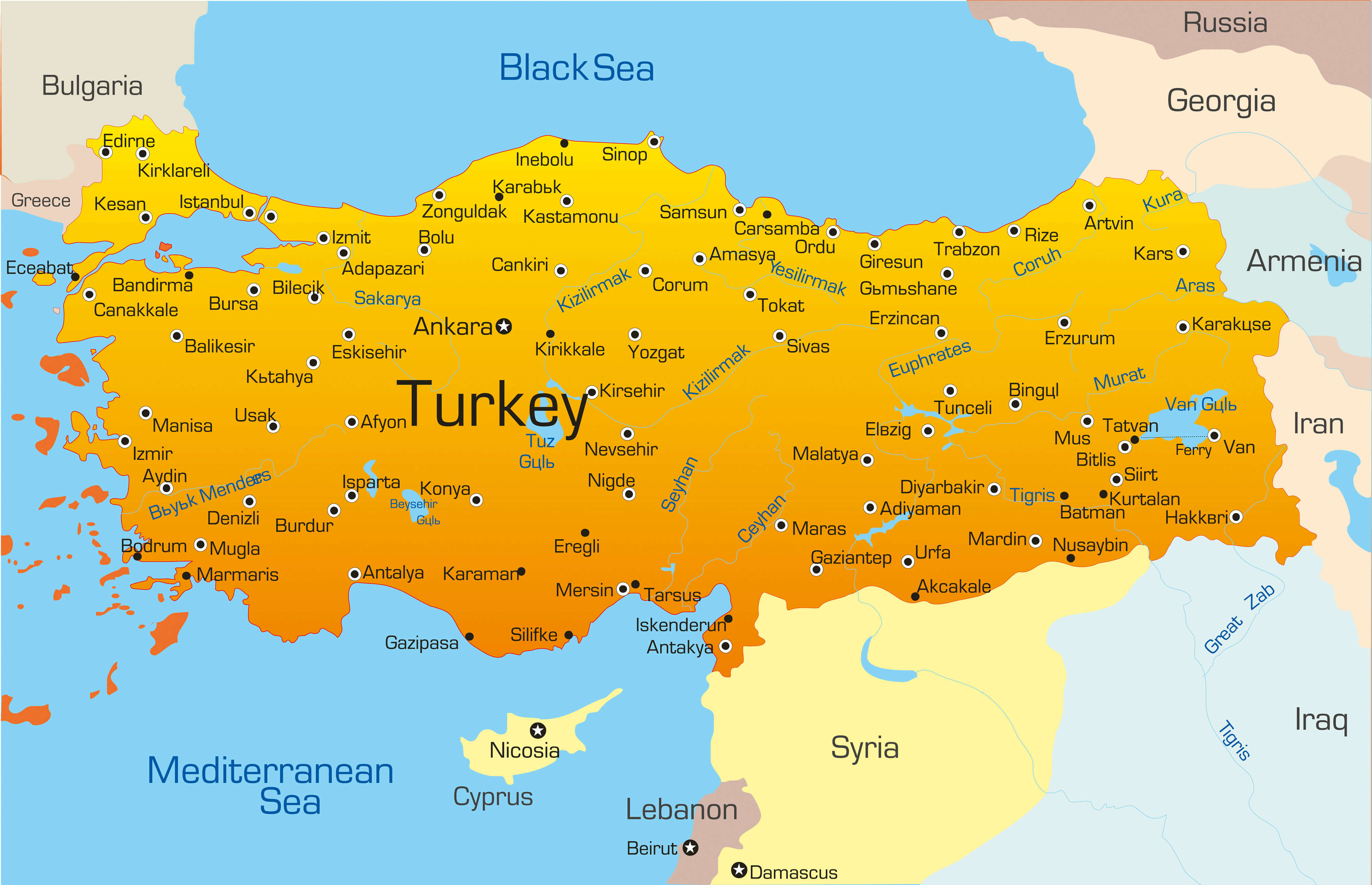
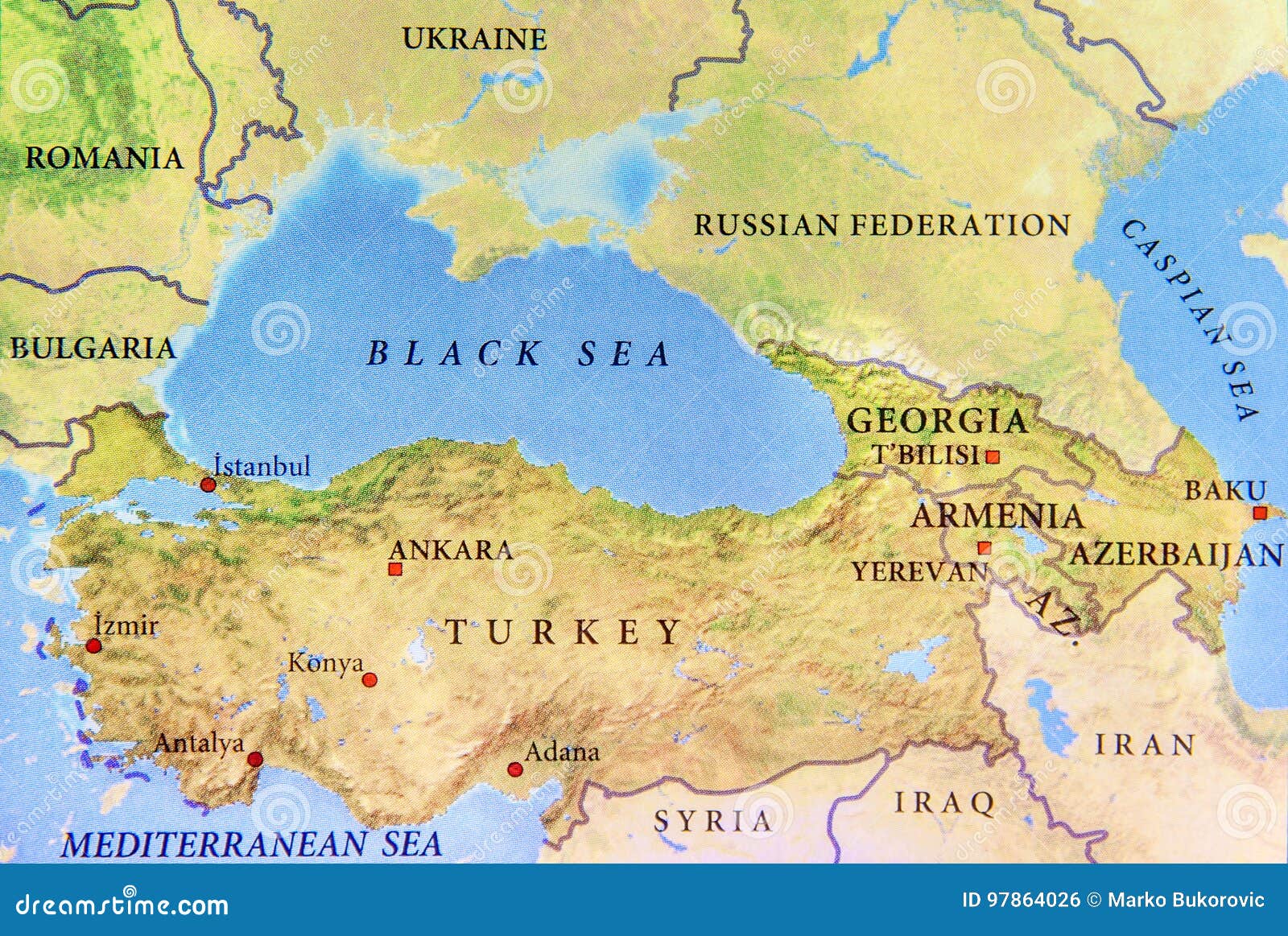
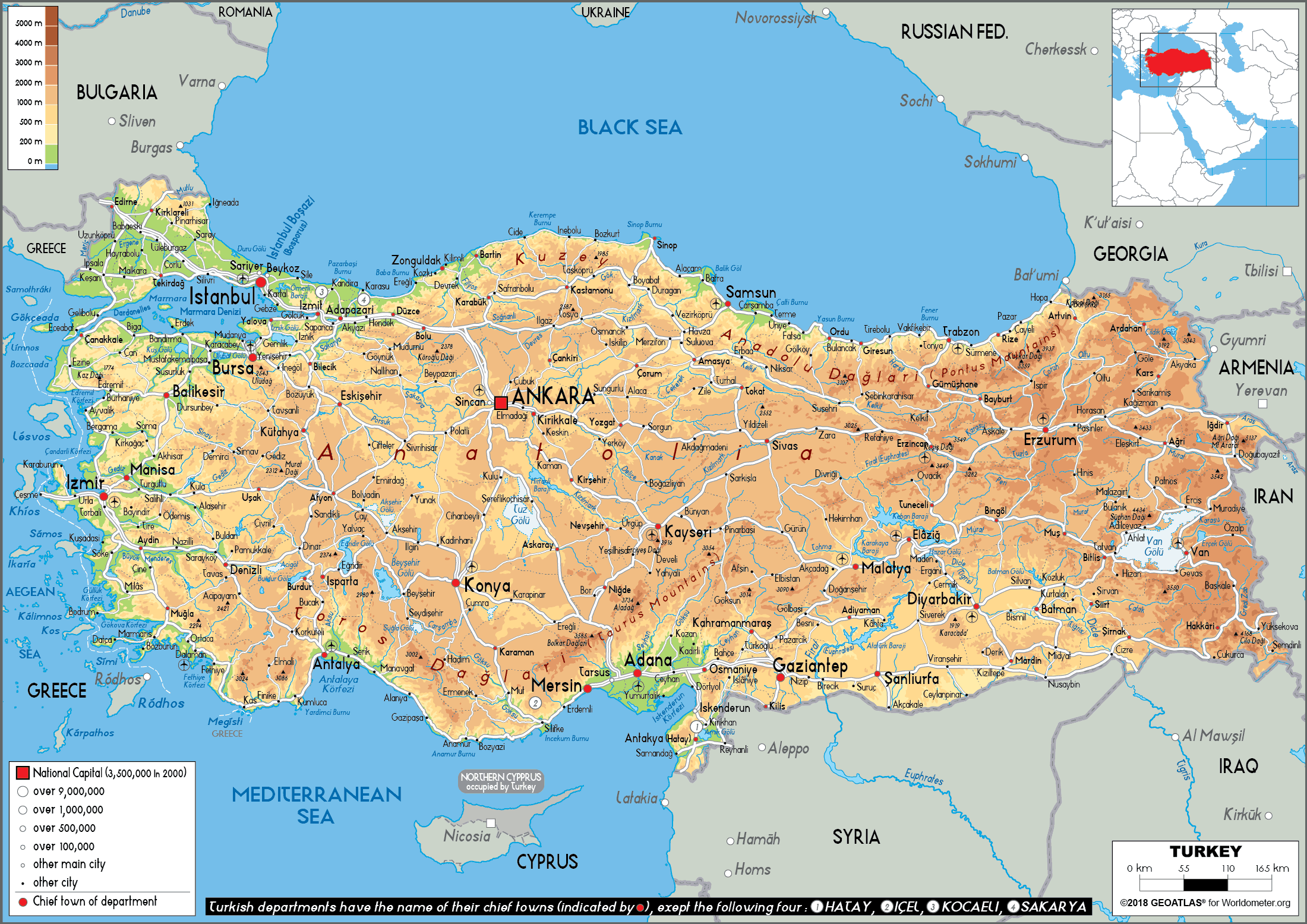
Turkey, a country straddling the crossroads of Europe and Asia, holds a unique position in the global landscape. Its geographic location, bordering eight countries and two seas, has shaped its history, culture, and geopolitical significance. Understanding the map of Turkey and its surroundings provides crucial insights into the region’s complex dynamics, historical influences, and ongoing challenges.
The Strategic Location of Turkey:
Turkey’s strategic location at the juncture of continents, known as the Anatolian Peninsula, has made it a pivotal point for trade, migration, and cultural exchange for millennia. It controls the Bosporus Strait and the Dardanelles Strait, vital waterways connecting the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. This control has historically granted Turkey immense influence over maritime trade and regional security.
Surrounding Countries and Borders:
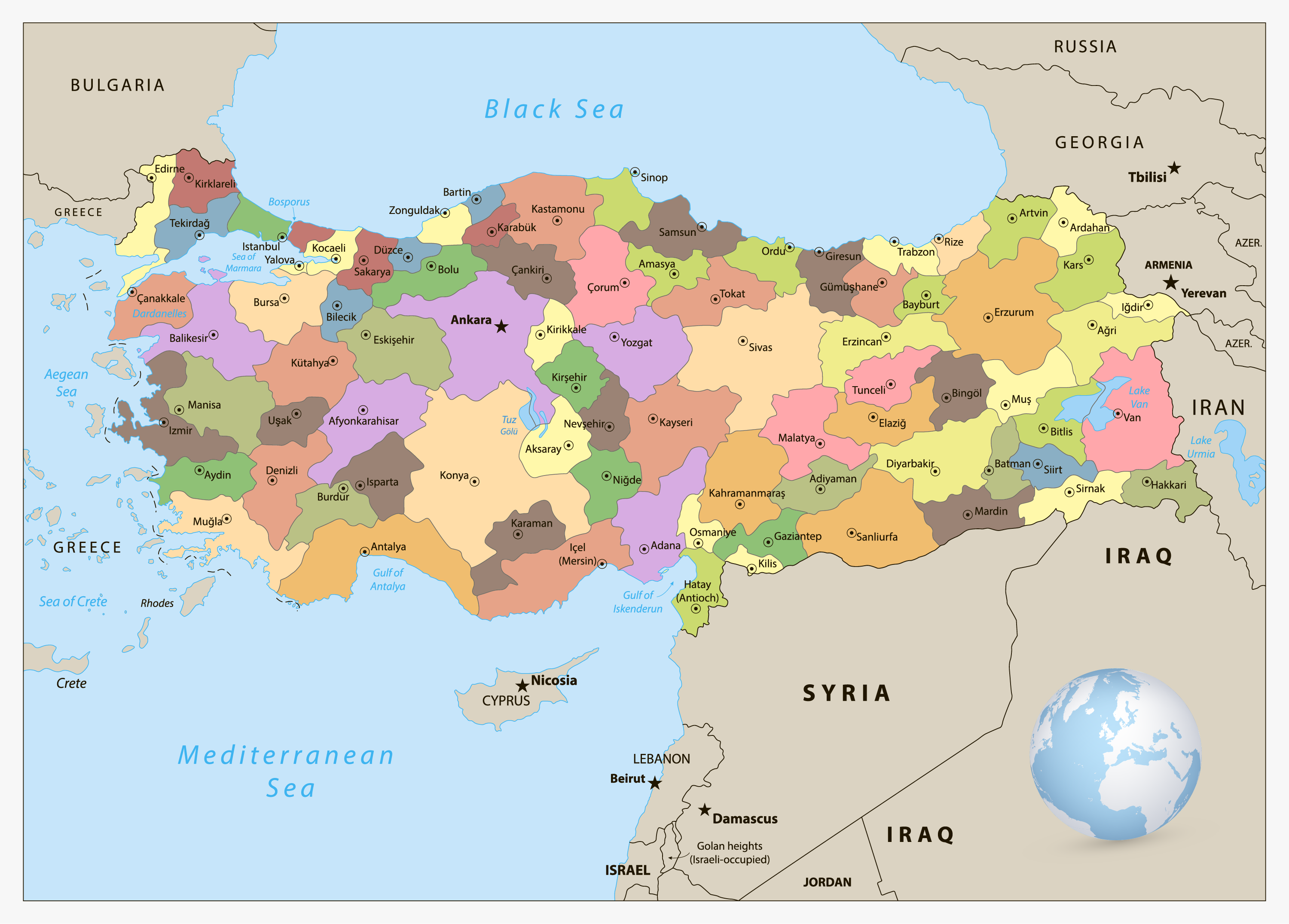
Turkey shares borders with eight countries, each contributing to the country’s diverse cultural tapestry and complex geopolitical landscape:
- Greece: To the west, Turkey shares a land border with Greece, a fellow NATO member and a historical rival. The two countries have a long and complex history, marked by periods of conflict and cooperation.
- Bulgaria: To the northwest, Turkey shares a border with Bulgaria, a member of the European Union. The two countries have historically maintained good relations, fostering economic and cultural ties.
- Georgia: To the northeast, Turkey borders Georgia, a former Soviet republic. The two countries have experienced growing economic and political cooperation in recent years, with Turkey playing a significant role in Georgia’s economic development.
- Armenia: To the east, Turkey shares a border with Armenia, a country with which it has no diplomatic relations. The two countries have a long-standing dispute over the Armenian Genocide, which has strained relations for decades.
- Azerbaijan: To the east, Turkey shares a border with Azerbaijan, a country with strong cultural and historical ties. The two countries have a close relationship, based on shared language, culture, and religious beliefs.
- Iran: To the east, Turkey borders Iran, a country with a complex relationship with Turkey. The two countries have historical and cultural ties, but also political and economic differences.
- Iraq: To the south, Turkey shares a border with Iraq, a country with which it has experienced periods of both cooperation and conflict. The two countries have worked together on issues of security and trade, but also have disagreements over the Kurdish issue.
- Syria: To the south, Turkey shares a border with Syria, a country with which it has experienced significant political and security challenges in recent years. The Syrian Civil War has had a profound impact on Turkey, leading to a large influx of refugees and a complex security situation along the border.
The Impact of Geography on Turkey’s History and Culture:
Turkey’s strategic location has played a crucial role in shaping its history and culture. The country has been home to numerous empires and civilizations, including the Hittites, the Romans, the Byzantines, and the Ottomans. Each of these empires left a lasting mark on Turkey’s cultural landscape, contributing to its diverse heritage and rich history.
The proximity to Europe and the Middle East has also made Turkey a cultural crossroads, fostering a unique blend of Eastern and Western influences. Turkish cuisine, art, and music reflect this cultural fusion, making Turkey a fascinating and diverse country.
Geopolitical Importance and Challenges:
Turkey’s strategic location also presents significant geopolitical challenges. The country’s position between Europe and Asia, its control of key waterways, and its historical role in regional affairs make it a vital player in global politics.
However, this strategic importance also comes with challenges. Turkey faces internal tensions related to its Kurdish population, its relationship with the European Union, and its complex relationship with its neighbors. The Syrian Civil War and the rise of ISIS have also presented significant security challenges for Turkey.
The Future of Turkey and its Surrounding Countries:
The future of Turkey and its surrounding countries is intertwined and complex. The region faces a range of challenges, including political instability, economic disparities, and social tensions. However, there is also potential for cooperation and progress.
The development of regional trade and infrastructure projects, such as the Trans-Anatolian Natural Gas Pipeline (TANAP) and the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline, could contribute to economic growth and stability. Increased cooperation on issues of security, migration, and cultural exchange could also foster a more stable and prosperous region.
FAQs about Turkey and its Surrounding Countries:
1. What is the significance of Turkey’s location?
Turkey’s location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, controlling vital waterways, has made it a crucial point for trade, migration, and cultural exchange throughout history.
2. What are the main challenges faced by Turkey and its surrounding countries?
Challenges include political instability, economic disparities, social tensions, the Syrian Civil War, and the rise of ISIS.
3. What are some potential solutions to these challenges?
Potential solutions include regional trade and infrastructure development, increased cooperation on security, migration, and cultural exchange.
4. How has Turkey’s geography influenced its culture?
Turkey’s location has led to a unique blend of Eastern and Western influences, evident in its cuisine, art, and music.
5. What are the key historical events that have shaped Turkey’s current situation?
Key events include the rise and fall of empires, including the Ottomans, and the formation of the modern Turkish republic.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Turkey and its Surrounding Countries:
- Study the historical context: Understanding the region’s history, including the rise and fall of empires, can provide insights into current political and cultural dynamics.
- Focus on key geographical features: Pay attention to the strategic waterways, mountain ranges, and key cities that shape the region’s geography.
- Consider the geopolitical context: Analyze the relationships between countries, including alliances, rivalries, and conflicts.
- Explore cultural and economic connections: Investigate shared cultural traditions, trade routes, and economic interdependence between countries.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep up with news and analysis of the region to understand evolving political and economic trends.
Conclusion:
The map of Turkey and its surrounding countries reveals a region of immense historical, cultural, and geopolitical significance. Understanding the complex dynamics of this region is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. By studying the region’s geography, history, and current events, we can gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shape the lives of millions of people in this vital part of the world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview of Turkey and its Surrounding Countries. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!