A Geographical Overview: Understanding Turkey’s Neighborhood
Related Articles: A Geographical Overview: Understanding Turkey’s Neighborhood
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Overview: Understanding Turkey’s Neighborhood. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Overview: Understanding Turkey’s Neighborhood
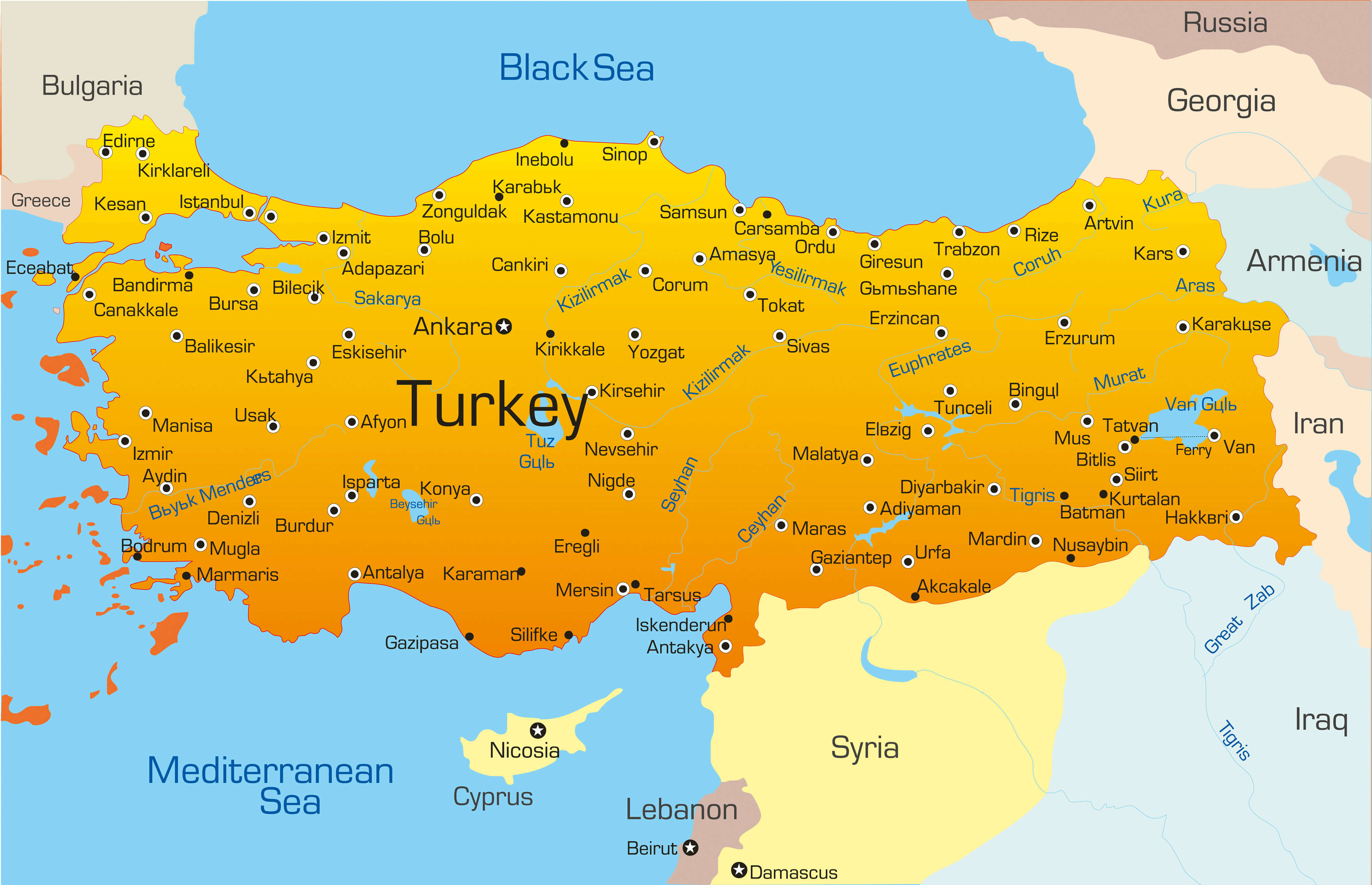
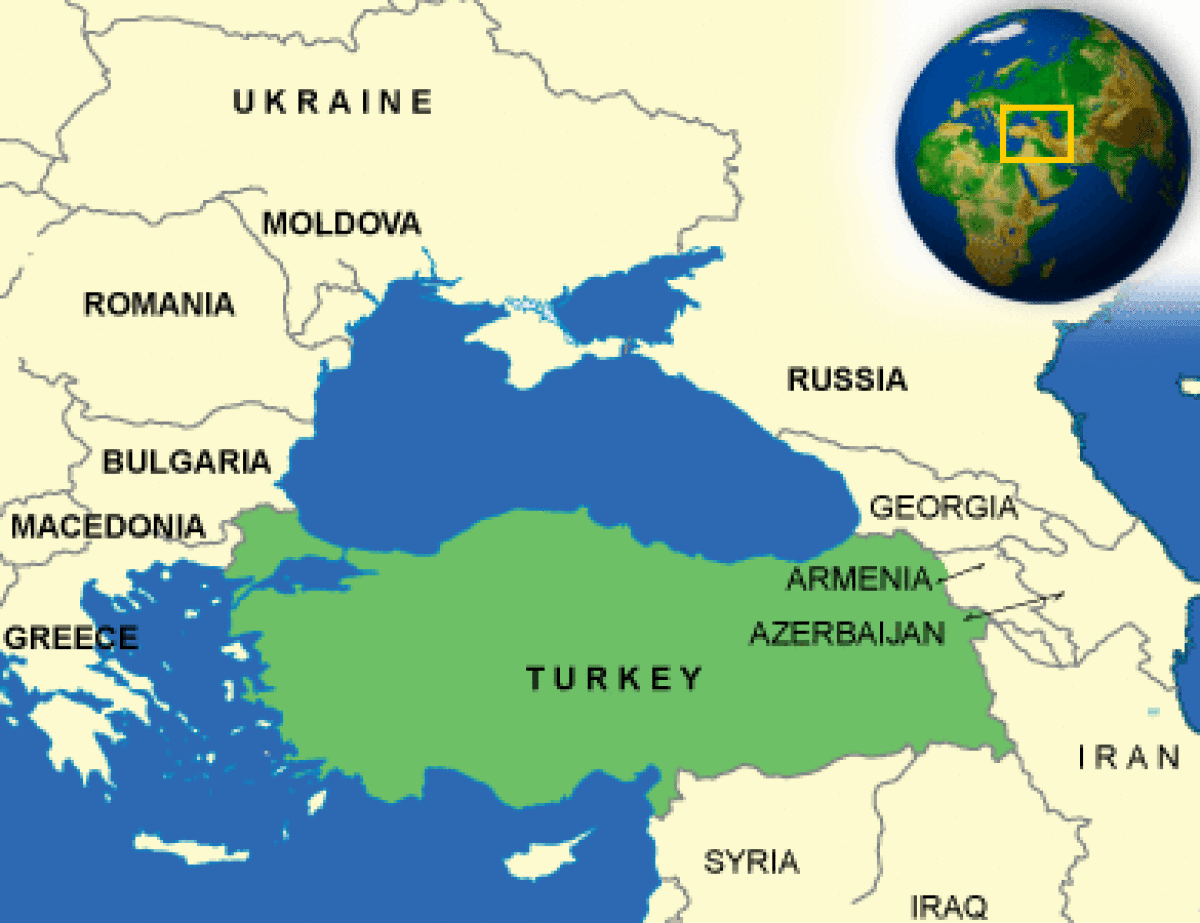
Turkey, a transcontinental nation straddling Europe and Asia, occupies a pivotal position within the Eurasian landmass. Its strategic location, bordering eight countries, has shaped its history, culture, and geopolitical significance. This article delves into the intricate tapestry of Turkey’s neighbors, examining their geographical proximity, historical connections, and contemporary relationships.
A Mosaic of Neighbors:
Turkey shares land borders with eight countries:
- To the north: Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan
- To the east: Iran, Iraq
- To the west: Greece, Bulgaria
- To the south: Syria
The Caucasus Connection:
The Caucasus Mountains, a formidable natural barrier, separate Turkey from Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. This region, historically known as the crossroads of civilizations, witnessed the rise and fall of empires and the confluence of diverse cultures. Turkey’s historical ties with the Caucasus nations are deep-rooted, dating back to the Ottoman Empire, and continue to influence contemporary relations.
The Middle Eastern Nexus:
Turkey’s southeastern border with Iran, Iraq, and Syria places it at the heart of the Middle East. This region, characterized by political and social complexities, has seen Turkey actively involved in regional conflicts and diplomatic initiatives. The shared history, cultural connections, and economic interdependence between Turkey and its Middle Eastern neighbors underscore the significance of this relationship.
The Balkan Bridge:
Turkey’s western border with Greece and Bulgaria connects it to the Balkans, a region with a turbulent history marked by both conflict and cooperation. Turkey’s historical ties with the Balkan nations, particularly with Greece, are complex and multifaceted, shaped by centuries of political and cultural interactions.
Strategic Importance:
Turkey’s geographical location, situated between Europe and Asia, has made it a crucial player in regional politics and economics. Its strategic importance is amplified by its control over the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits, the only waterways connecting the Black Sea to the Mediterranean. These straits serve as vital trade routes, making Turkey a key player in global maritime commerce.
Beyond Borders: Intertwined Histories:
The history of Turkey and its neighbors is a tapestry woven with threads of conflict and cooperation. From ancient empires to modern alliances, the relationship between these nations has been shaped by a confluence of factors:
- Ottoman Legacy: The Ottoman Empire, at its peak, encompassed vast territories, including many of Turkey’s current neighbors. The legacy of Ottoman rule, including cultural and linguistic influences, continues to shape the region.
- Cold War Rivalry: During the Cold War, Turkey aligned with the West, while some of its neighbors, such as Syria and Iraq, leaned towards the Soviet Union. This geopolitical divide impacted relations between these countries.
- Shared Challenges: The region faces common challenges, including terrorism, instability, and economic disparities. These shared concerns have prompted increased cooperation between Turkey and its neighbors.
Contemporary Relations:
Turkey’s relationships with its neighbors are complex and dynamic, shaped by a confluence of political, economic, and cultural factors.
- EU Aspirations: Turkey’s aspirations to join the European Union have influenced its relations with its European neighbors, particularly Greece and Bulgaria.
- Energy Security: Turkey’s strategic location makes it a key player in energy security, as it serves as a transit route for energy resources from the Caspian Sea and Central Asia.
- Regional Conflicts: The ongoing conflicts in Syria and Iraq have impacted Turkey’s relations with its Middle Eastern neighbors, leading to complex diplomatic and humanitarian challenges.
FAQs
Q: What are the major trade routes connecting Turkey to its neighboring countries?
A: Turkey’s strategic location makes it a hub for trade routes connecting Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. Major trade routes include:
- Trans-European Motorways: Connecting Turkey to Europe via Bulgaria and Greece.
- Silk Road: A historical trade route connecting Turkey to China, with modern-day extensions through Central Asia.
- Trans-Anatolian Pipeline: Transports natural gas from Azerbaijan to Turkey and Europe.
Q: What are the major cultural and linguistic influences shared between Turkey and its neighbors?
A: Turkey and its neighbors share a rich cultural heritage, influenced by:
- Ottoman Legacy: The Ottoman Empire’s influence is evident in the architecture, language, and cuisine of many neighboring countries.
- Persian Influences: Persian culture and language have left a significant mark on Turkey, particularly in its literature and art.
- Greek and Byzantine Influences: The Byzantine Empire’s legacy, particularly in architecture and religious traditions, is visible in Turkey and its Balkan neighbors.
Q: What are the major geopolitical challenges facing Turkey and its neighbors?
A: Turkey and its neighbors face a range of geopolitical challenges, including:
- Regional Instability: The ongoing conflicts in Syria and Iraq pose security threats to the entire region.
- Terrorism: The rise of terrorist groups, such as ISIS and PKK, has destabilized the region and impacted Turkey’s relations with its neighbors.
- Economic Disparities: The region faces significant economic disparities, leading to social unrest and instability.
Tips for Understanding Turkey’s Neighbors
- Study History: Understanding the historical relationships between Turkey and its neighbors provides crucial context for contemporary interactions.
- Explore Culture: Engaging with the diverse cultures of Turkey’s neighbors fosters understanding and appreciation for their unique perspectives.
- Follow Current Events: Staying informed about current events in the region helps to understand the complex dynamics shaping relations between Turkey and its neighbors.
Conclusion
Turkey’s geographical location, at the crossroads of continents and civilizations, makes it a key player in regional and global affairs. Its diverse neighbors, each with unique histories and challenges, contribute to the complex and dynamic tapestry of relationships surrounding Turkey. Understanding these relationships is crucial for navigating the intricacies of the region and fostering cooperation for a more stable and prosperous future.


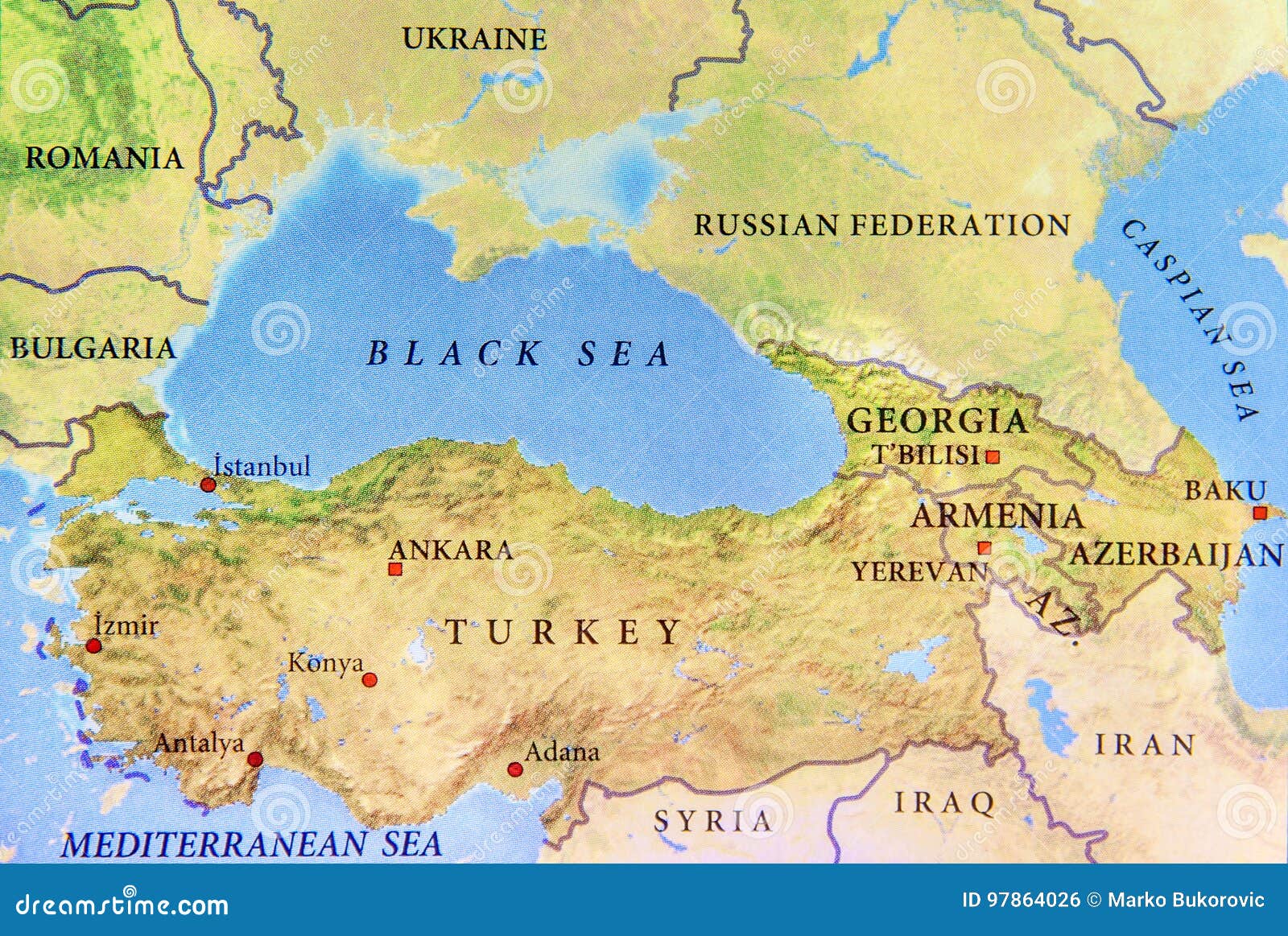

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Overview: Understanding Turkey’s Neighborhood. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!