A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey
Related Articles: A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey
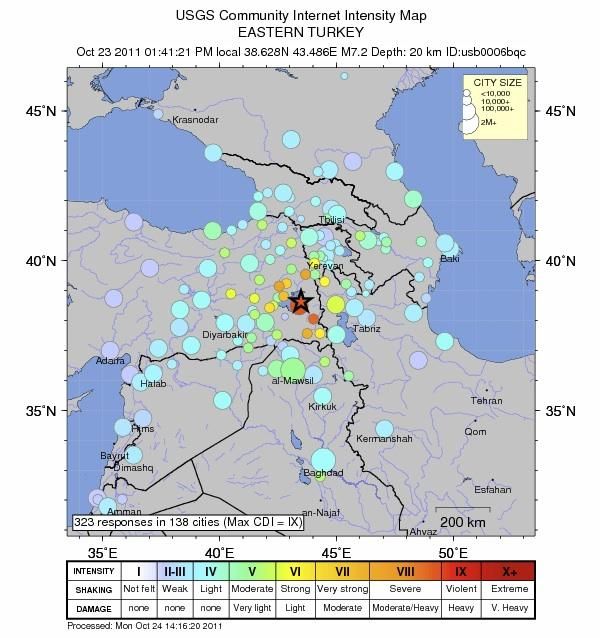
Turkey, a country strategically positioned at the juncture of the Eurasian, Arabian, and African tectonic plates, experiences a high frequency of earthquakes. This geological reality is not a mere academic curiosity; it shapes the nation’s history, infrastructure, and daily life. To understand the seismic vulnerability of Turkey, it is crucial to examine its tectonic setting and the distribution of past earthquakes.
Tectonic Setting: A Collision Zone
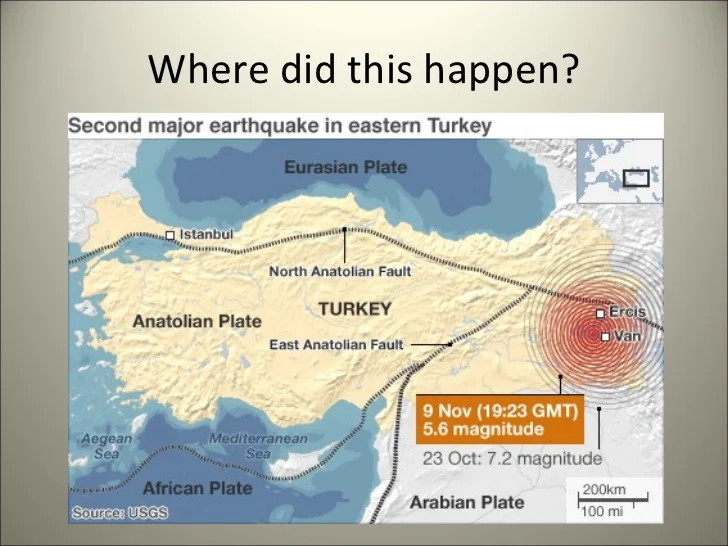
Turkey sits within a complex tectonic environment, characterized by the northward movement of the African and Arabian plates against the Eurasian plate. This collision has resulted in the formation of several major fault lines, acting as zones of weakness within the Earth’s crust. The North Anatolian Fault (NAF) and the East Anatolian Fault (EAF) are prominent examples, stretching across the country and serving as conduits for seismic energy release.
The North Anatolian Fault: A Seismic Highway
The NAF, a 1,500-kilometer-long left-lateral strike-slip fault, traverses Turkey from east to west, dissecting the country into two tectonic blocks. This fault has been responsible for numerous devastating earthquakes throughout history, including the 1939 Erzincan earthquake (magnitude 7.8) and the 1999 İzmit earthquake (magnitude 7.6). The NAF is characterized by a westward migration of earthquake epicenters, a phenomenon known as "fault rupture propagation," where the stress on the fault shifts westward after each major earthquake.
The East Anatolian Fault: A Parallel Threat
The EAF, a right-lateral strike-slip fault, runs parallel to the NAF in eastern Turkey. It has also been responsible for major earthquakes, including the 2020 Elazığ earthquake (magnitude 6.8) and the 2023 Kahramanmaras earthquake (magnitude 7.8). The EAF is characterized by its complex structure, with multiple branches and segments, making seismic hazard assessment more challenging.
Mapping the Seismic History: A Visual Record of Risk
Maps of Turkey depicting the locations of historical earthquakes provide invaluable insights into the seismic hazards faced by the country. These maps highlight the concentration of earthquake activity along the NAF and EAF, emphasizing the importance of these fault lines in shaping the country’s seismic landscape.
The 1999 İzmit Earthquake: A Turning Point
The 1999 İzmit earthquake, which struck near Istanbul, was a stark reminder of Turkey’s seismic vulnerability. The earthquake caused widespread destruction, claiming thousands of lives and highlighting the need for robust earthquake preparedness measures. This event spurred significant advancements in earthquake engineering, building codes, and disaster management strategies.
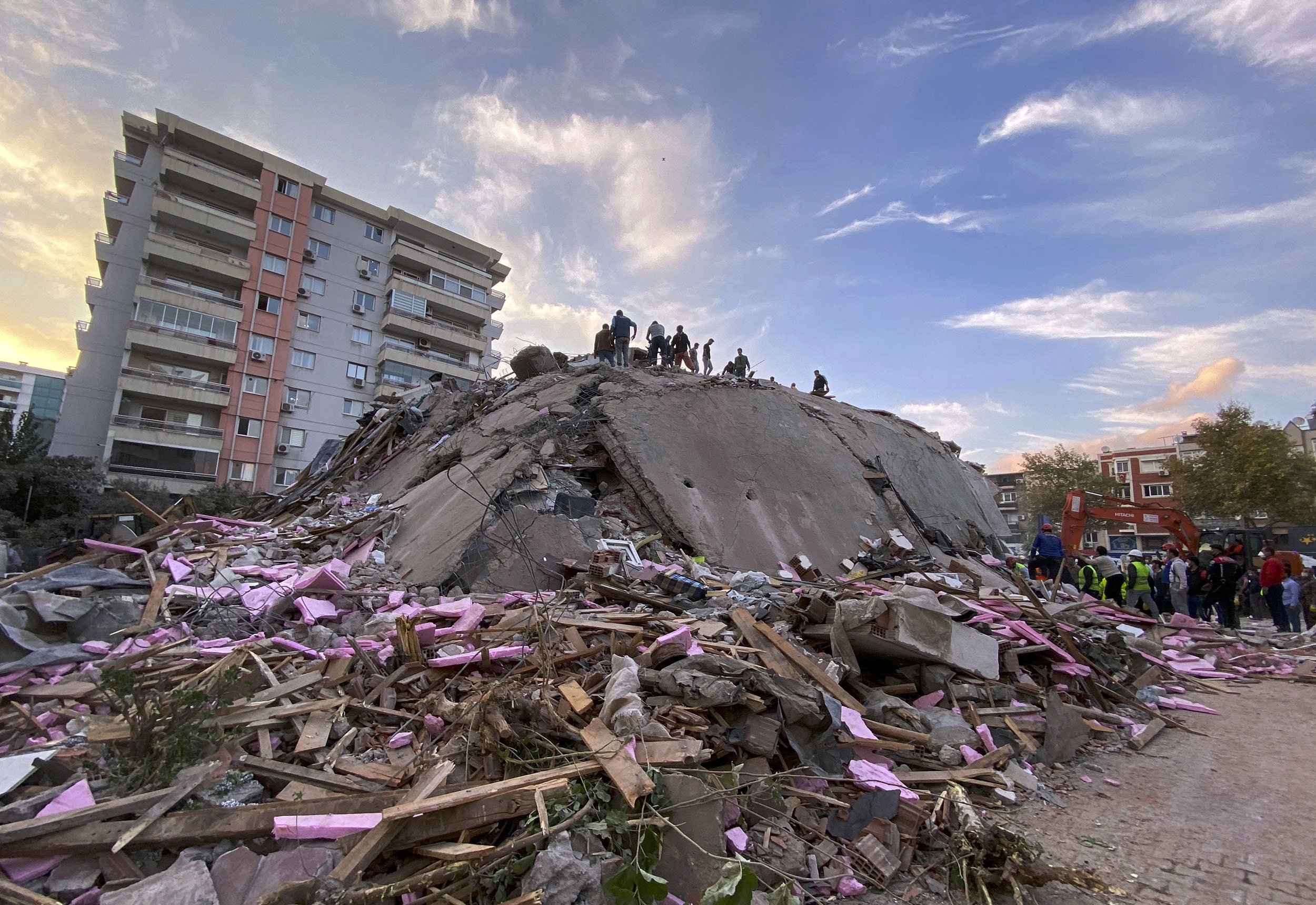
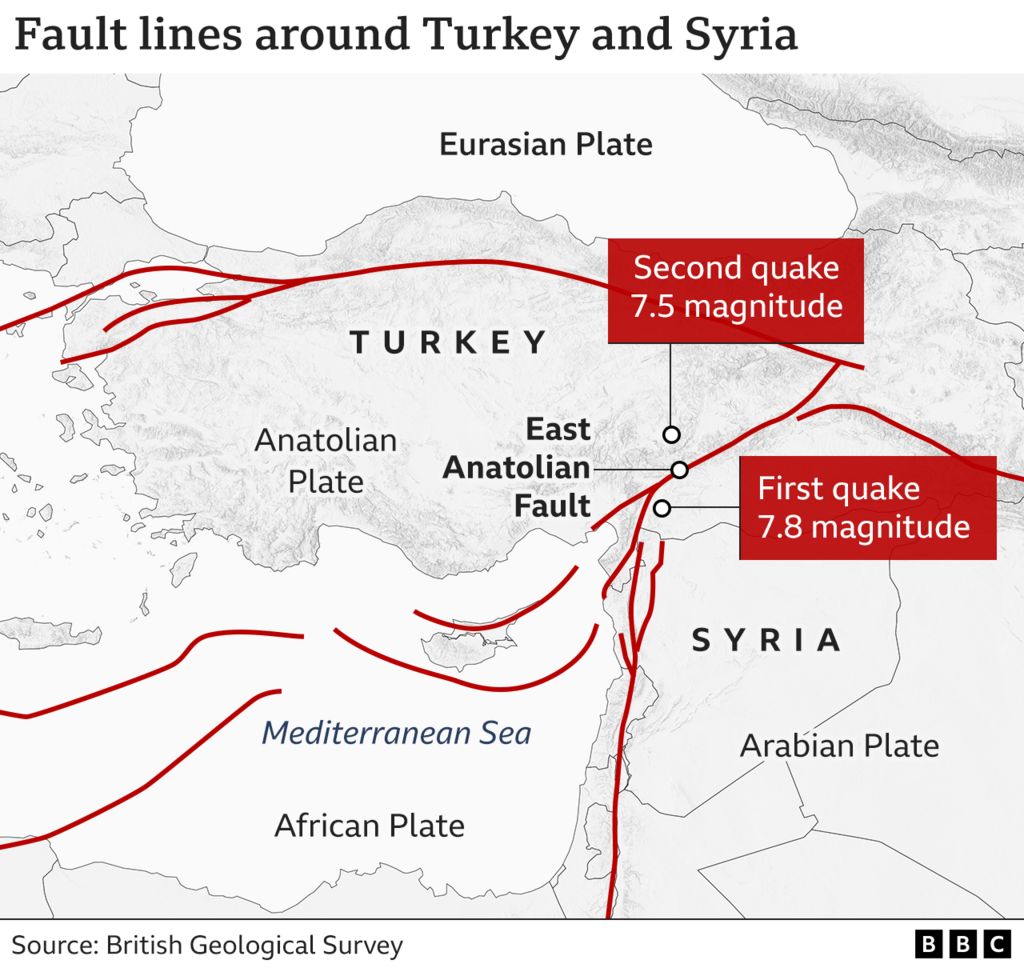
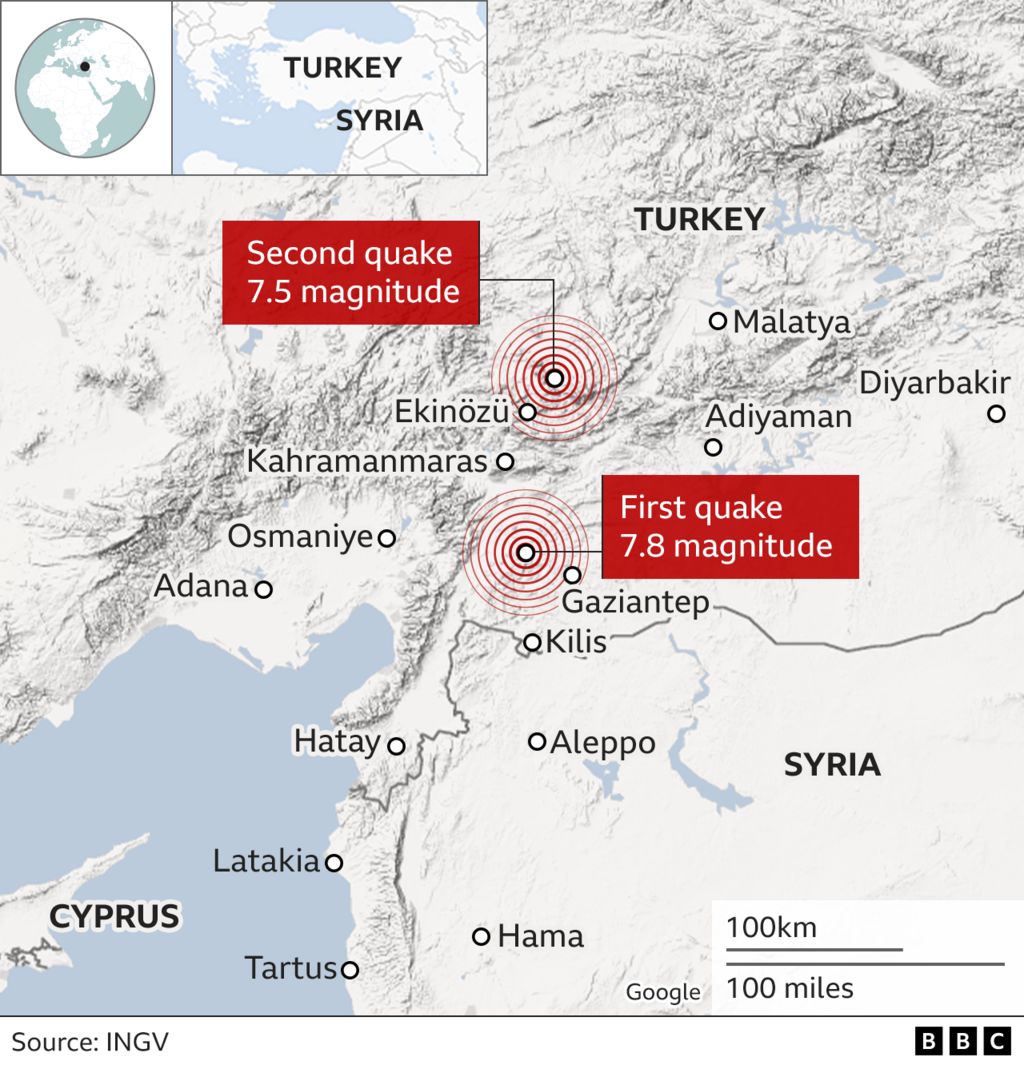
The 2023 Kahramanmaras Earthquakes: A Recent Tragedy
The devastating earthquakes that struck Turkey and Syria in February 2023, centered near the city of Kahramanmaras, underscore the ongoing seismic threat faced by the region. These earthquakes, with magnitudes of 7.8 and 7.5, caused widespread damage, loss of life, and displacement, highlighting the urgent need for continued efforts in earthquake preparedness and resilience.
Understanding the Importance of Seismic Maps
Maps depicting earthquake epicenters, fault lines, and historical seismic activity play a crucial role in:
- Seismic hazard assessment: By analyzing the distribution of past earthquakes, seismologists can identify areas at higher risk of future seismic events.
- Earthquake-resistant design: Architects and engineers use seismic maps to design buildings and infrastructure that can withstand the forces of earthquakes.
- Disaster preparedness: Maps help authorities plan evacuation routes, identify vulnerable communities, and allocate resources for disaster response.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: Are all earthquakes in Turkey caused by the NAF and EAF?
A: While the NAF and EAF are responsible for the majority of major earthquakes in Turkey, other fault lines and smaller seismic events also contribute to the country’s seismic activity.
Q: Can earthquakes be predicted?
A: Currently, scientists cannot predict earthquakes with pinpoint accuracy. However, by studying the history of earthquakes and the movement of tectonic plates, they can assess the probability of future events and identify areas at higher risk.
Q: What can be done to mitigate earthquake risk?
A: Mitigating earthquake risk involves a multi-faceted approach:
- Earthquake-resistant construction: Building codes and regulations should be enforced to ensure that structures are designed to withstand seismic forces.
- Public awareness: Educating the public about earthquake preparedness, safety measures, and evacuation procedures is crucial.
- Disaster response: Efficient disaster response systems, including search and rescue teams, medical facilities, and communication infrastructure, are essential.
Tips for Earthquake Preparedness:
- Secure heavy objects: Anchor heavy furniture and appliances to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Identify safe spots: Determine safe places in your home, such as under sturdy furniture or in doorways, where you can take shelter during an earthquake.
- Prepare an emergency kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies, such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a flashlight.
- Stay informed: Monitor weather reports and earthquake alerts to stay updated on potential seismic activity.
Conclusion: A Continuous Challenge
Living in a seismically active region presents both challenges and opportunities. Understanding the tectonic setting, mapping historical earthquakes, and implementing effective earthquake preparedness measures are crucial steps towards mitigating the risks associated with seismic activity. By fostering awareness, investing in research, and strengthening infrastructure, Turkey can better navigate the challenges posed by its seismic landscape. The map of Turkey, with its intricate network of fault lines and historical earthquake epicenters, serves as a constant reminder of the country’s vulnerability and the need for ongoing vigilance in safeguarding its people and infrastructure.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!