A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey through Mapping
Related Articles: A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey through Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey through Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey through Mapping

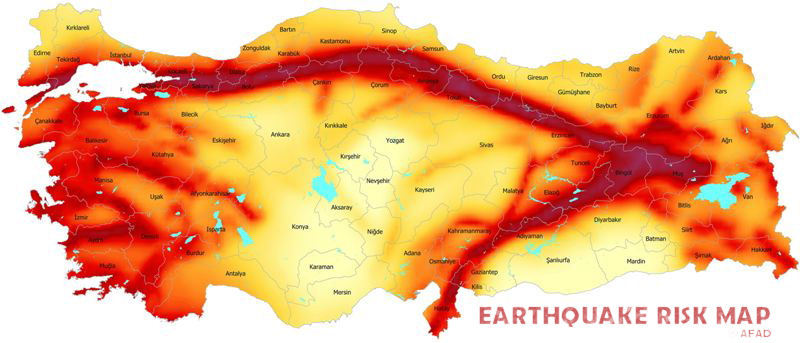
Turkey occupies a geologically complex region, situated at the intersection of the Eurasian, African, and Arabian tectonic plates. This dynamic interplay of tectonic forces makes Turkey one of the most seismically active countries in the world, susceptible to frequent and powerful earthquakes. Mapping these seismic events provides a critical tool for understanding the country’s earthquake hazards, informing disaster preparedness strategies, and guiding infrastructure development.
Tectonic Setting and Earthquake Distribution
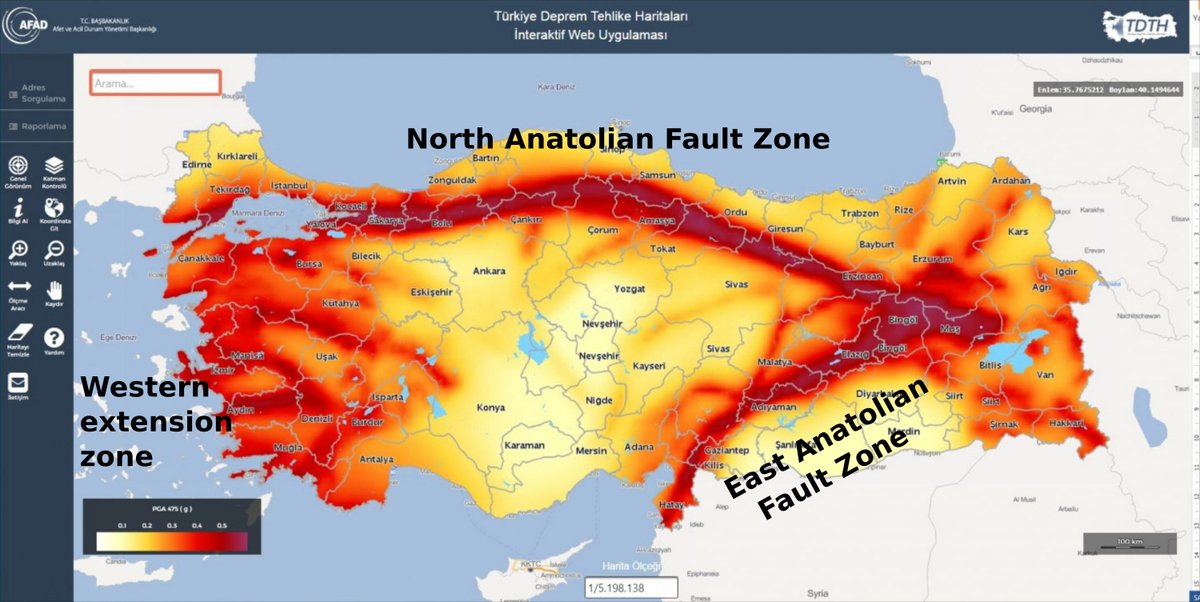
The Anatolian Plate, a smaller tectonic plate sandwiched between the larger Eurasian, African, and Arabian plates, is the primary driver of Turkey’s seismic activity. The Anatolian Plate is being squeezed and pushed westward by the Arabian Plate, while the Eurasian Plate exerts pressure from the north. This compressional force leads to the formation of numerous fault lines across Turkey, which act as zones of weakness where earthquakes originate.
Mapping Earthquake Activity
Mapping earthquake activity in Turkey involves plotting the locations, magnitudes, and depths of past earthquakes. This data is collected through seismological networks, which consist of sensitive instruments called seismometers strategically placed across the country. These instruments detect ground vibrations caused by earthquakes and transmit the data to central monitoring stations.
Understanding the Maps
Earthquake maps typically display the following information:
- Epicenter: The point on the Earth’s surface directly above the earthquake’s focus (the point of origin underground).
- Magnitude: The measure of the earthquake’s strength, typically represented on the Richter scale or the Moment Magnitude Scale.
- Depth: The distance from the Earth’s surface to the earthquake’s focus.
- Fault Lines: The major geological structures where earthquakes occur.
Importance of Earthquake Maps
Earthquake maps serve as crucial tools for a variety of purposes:
- Hazard Assessment: Identifying areas with high seismic risk, aiding in the development of building codes and land use regulations.
- Disaster Preparedness: Providing valuable information for emergency response teams, enabling them to anticipate potential damage and develop effective evacuation plans.
- Infrastructure Planning: Guiding the construction of earthquake-resistant structures and infrastructure, minimizing potential damage and loss of life.
- Scientific Research: Contributing to our understanding of earthquake mechanisms, fault behavior, and seismic hazard prediction.
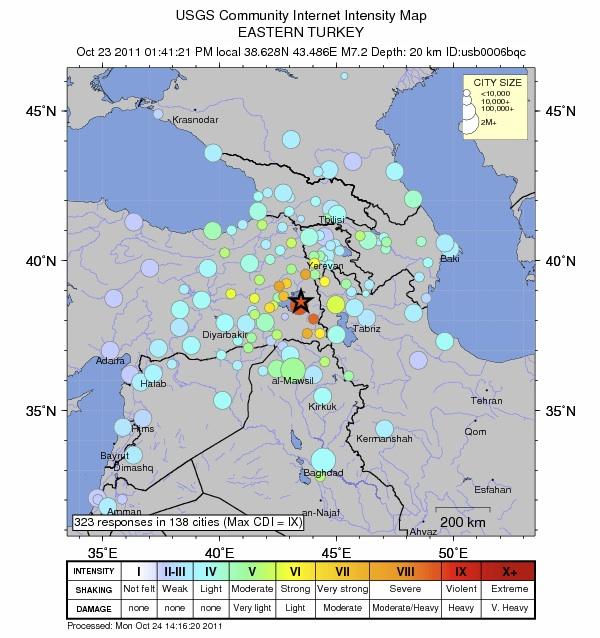
Notable Earthquakes in Turkey
Turkey has experienced numerous devastating earthquakes throughout history, with some of the most impactful events including:
- 1939 Erzincan Earthquake (M 8.0): The deadliest earthquake in Turkish history, causing over 30,000 fatalities.
- 1999 İzmit Earthquake (M 7.6): A major earthquake that struck near Istanbul, resulting in over 17,000 deaths and significant damage.
- 2020 Elazığ Earthquake (M 6.8): A significant earthquake that caused widespread damage and loss of life in eastern Turkey.
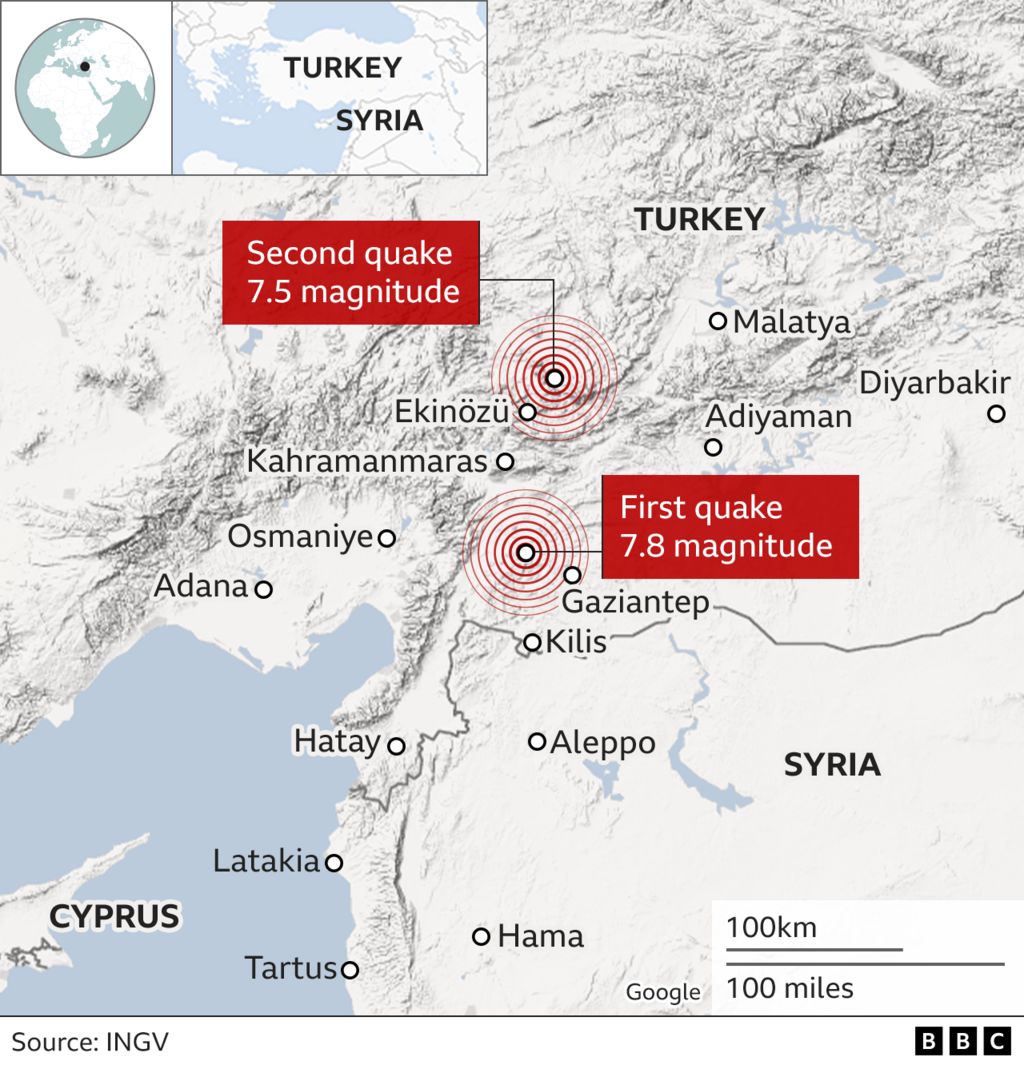
- 2023 Kahramanmaraş Earthquakes (M 7.8 and 7.5): Two devastating earthquakes that struck southern Turkey and northern Syria, causing widespread destruction and claiming thousands of lives.
FAQs about Earthquake Maps in Turkey:
Q: What is the significance of the North Anatolian Fault Zone?
A: The North Anatolian Fault Zone is a major fault system extending across northern Turkey. It is responsible for numerous powerful earthquakes, including the 1939 Erzincan and 1999 İzmit earthquakes. This zone represents a significant seismic hazard for Turkey.
Q: How are earthquake maps used to predict future earthquakes?
A: While earthquake prediction remains a complex and elusive goal, earthquake maps provide valuable insights into the recurrence rates and potential magnitudes of earthquakes in specific regions. This information can help researchers identify areas with a higher likelihood of future seismic events.
Q: What are the limitations of earthquake maps?
A: Earthquake maps are based on historical data and cannot predict the exact timing, location, or magnitude of future earthquakes. The accuracy of these maps can be influenced by the availability of historical data and the complexity of tectonic processes.
Tips for Earthquake Safety:
- Prepare an emergency kit: Include essentials like food, water, first aid supplies, and a flashlight.
- Secure heavy objects: Secure shelves, cabinets, and heavy objects to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Learn evacuation routes: Familiarize yourself with the safest evacuation routes from your home, school, or workplace.
- Practice earthquake drills: Conduct regular earthquake drills to ensure everyone knows what to do in case of an earthquake.
Conclusion
Earthquake maps play a crucial role in understanding and mitigating the risks associated with earthquakes in Turkey. By providing valuable insights into historical seismic activity, fault locations, and potential earthquake hazards, these maps empower researchers, policymakers, and communities to make informed decisions regarding disaster preparedness, infrastructure development, and public safety. Continued research and investment in seismological monitoring networks are essential to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of earthquake maps, ultimately contributing to a safer and more resilient Turkey.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Seismic Landscape: Understanding Earthquakes in Turkey through Mapping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!