A Seismic Landscape: Understanding the Earthquake Turkey Map
Related Articles: A Seismic Landscape: Understanding the Earthquake Turkey Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Seismic Landscape: Understanding the Earthquake Turkey Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Seismic Landscape: Understanding the Earthquake Turkey Map

Turkey, a country situated at the confluence of major tectonic plates, experiences a high frequency of earthquakes. The seismic activity in Turkey is a consequence of the ongoing collision between the Eurasian and African plates, with the Arabian plate also playing a significant role. This dynamic geological setting has shaped the country’s landscape and profoundly impacted its history, resulting in both devastating earthquakes and ongoing efforts to mitigate their impact. The Earthquake Turkey Map, a visual representation of seismic hazard zones, serves as a vital tool for understanding and preparing for these natural disasters.
The Tectonic Jigsaw Puzzle:
Turkey’s earthquake vulnerability is rooted in its geographical location. The Anatolian Plate, a smaller tectonic plate, is sandwiched between the Eurasian Plate to the north and the Arabian Plate to the south and east. The Arabian Plate is pushing northward, forcing the Anatolian Plate westward. This westward movement results in a complex system of faults, zones of weakness in the Earth’s crust, where earthquakes are most likely to occur.
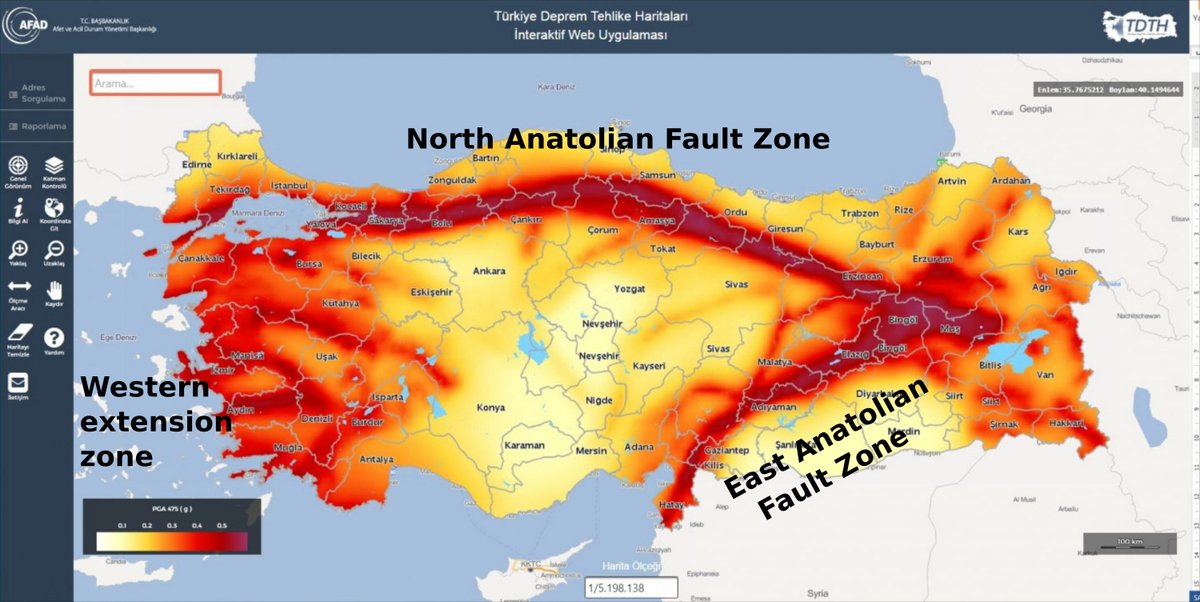
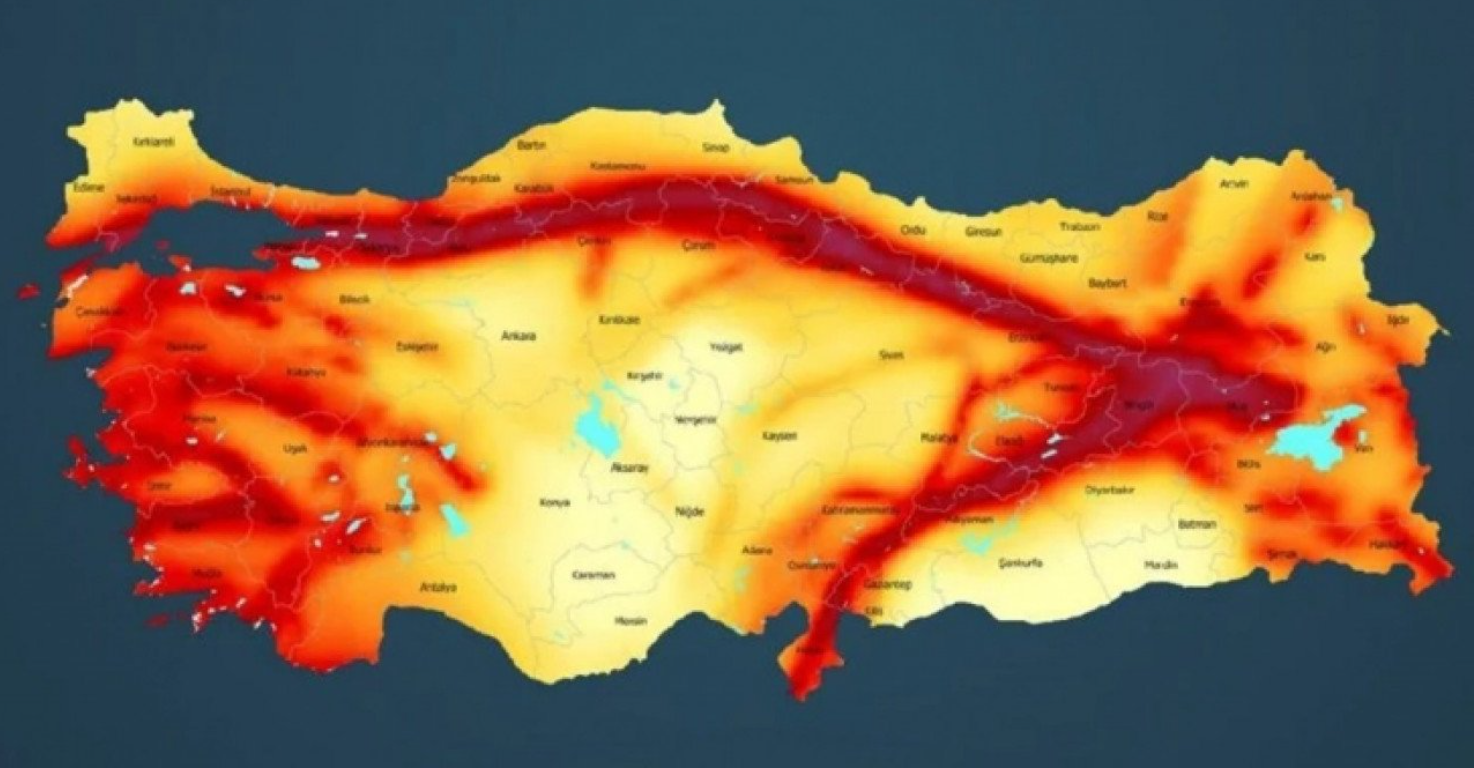
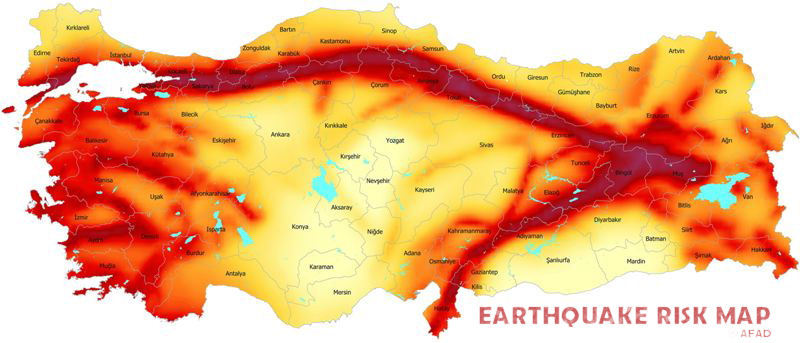
The North Anatolian Fault: A Seismic Hotspot
One of the most prominent features on the Earthquake Turkey Map is the North Anatolian Fault (NAF). This 1,500-kilometer-long fault zone stretches across northern Turkey, from the eastern Black Sea region to the Aegean Sea. The NAF is a strike-slip fault, meaning that the plates move horizontally past each other. The movement along the NAF is responsible for many of Turkey’s most devastating earthquakes, including the 1999 Izmit earthquake (magnitude 7.6) and the 1939 Erzincan earthquake (magnitude 8.0).
The East Anatolian Fault: Another Zone of Risk
Another significant fault zone on the Earthquake Turkey Map is the East Anatolian Fault (EAF). This 600-kilometer-long fault runs along the eastern border of Turkey, from the southern Black Sea region to the eastern Mediterranean Sea. The EAF is also a strike-slip fault, and its movement has caused numerous earthquakes, including the 2011 Van earthquake (magnitude 7.2) and the 2020 Elazig earthquake (magnitude 6.8).
The Aegean Region: A Complex Seismic Landscape
The Aegean region of Turkey, located in the southwest, is also seismically active. The region is characterized by a complex system of faults, including the North Aegean Trench and the Hellenic Arc. These faults are responsible for a significant number of earthquakes, many of which have caused significant damage and loss of life.
Mapping Seismic Hazards: The Earthquake Turkey Map
The Earthquake Turkey Map provides a visual representation of the seismic hazard zones across the country. It categorizes regions based on their seismic risk, ranging from low to high. The map highlights areas with a higher frequency and intensity of earthquakes, allowing for targeted mitigation efforts and informed urban planning.
Benefits of the Earthquake Turkey Map:
- Seismic Hazard Assessment: The map serves as a crucial tool for assessing the potential for earthquakes in different regions of Turkey. This information is vital for urban planning, infrastructure development, and disaster preparedness.
- Earthquake-Resistant Construction: The map helps guide the design and construction of earthquake-resistant buildings and infrastructure. By understanding the seismic risk in specific areas, engineers can design structures that can withstand strong ground shaking.
- Disaster Response Planning: The Earthquake Turkey Map is essential for planning and coordinating disaster response efforts. It helps authorities identify areas that are most vulnerable to earthquakes and allocate resources accordingly.
- Public Awareness: The map serves as a valuable educational tool to raise public awareness about earthquake risks and promote preparedness measures. This includes understanding the importance of earthquake drills, having emergency kits, and knowing evacuation routes.
FAQs Regarding the Earthquake Turkey Map:
Q: What are the most seismically active regions in Turkey?
A: The most seismically active regions in Turkey are the North Anatolian Fault Zone, the East Anatolian Fault Zone, and the Aegean region.
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Turkey?
A: Turkey experiences a high frequency of earthquakes. On average, there are several hundred earthquakes each year, with a few significant events occurring every decade.
Q: How is the Earthquake Turkey Map updated?
A: The Earthquake Turkey Map is regularly updated based on new scientific data and research. The Turkish government and other relevant institutions monitor seismic activity and update the map accordingly.
Q: What are some of the measures being taken to mitigate earthquake risks in Turkey?
A: Turkey has implemented several measures to mitigate earthquake risks, including:
- Building Codes: The country has strict building codes that require new structures to be earthquake-resistant.
- Seismic Retrofitting: Existing buildings are being retrofitted to improve their seismic resistance.
- Early Warning Systems: The development and implementation of early warning systems to provide advance notice of earthquakes.
- Public Education and Awareness Campaigns: Public education campaigns to raise awareness about earthquake preparedness and safety measures.
Tips for Earthquake Preparedness in Turkey:
- Secure Heavy Objects: Secure heavy objects such as bookcases and mirrors to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Create an Emergency Kit: Assemble an emergency kit that includes essential supplies like water, food, first-aid supplies, and a flashlight.
- Develop an Evacuation Plan: Create a family evacuation plan and practice it regularly.
- Learn CPR and First Aid: Learn basic CPR and first aid skills to be prepared to help yourself and others in an emergency.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about earthquake risks and preparedness measures by following official sources like the Turkish Disaster and Emergency Management Presidency (AFAD).
Conclusion:
The Earthquake Turkey Map is a vital tool for understanding and mitigating the risks associated with earthquakes in Turkey. It provides a clear visual representation of seismic hazard zones, allowing for informed urban planning, earthquake-resistant construction, and effective disaster response. By understanding the geological forces at play and taking necessary precautions, Turkey can strive to minimize the impact of future earthquakes and build a more resilient society.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Seismic Landscape: Understanding the Earthquake Turkey Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!