A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of South America
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of South America
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of South America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of South America

South America, a continent of breathtaking diversity, is not only home to vibrant cultures and rich biodiversity but also possesses a captivating landscape sculpted by geological forces over millennia. Understanding the continent’s topography, the arrangement of its physical features, is crucial for comprehending its natural processes, resource distribution, and human interactions with the environment. This exploration delves into the intricate details of South America’s topography, highlighting its key features, their implications, and the insights they provide.
A Continent of Contrasts: The Major Topographic Features
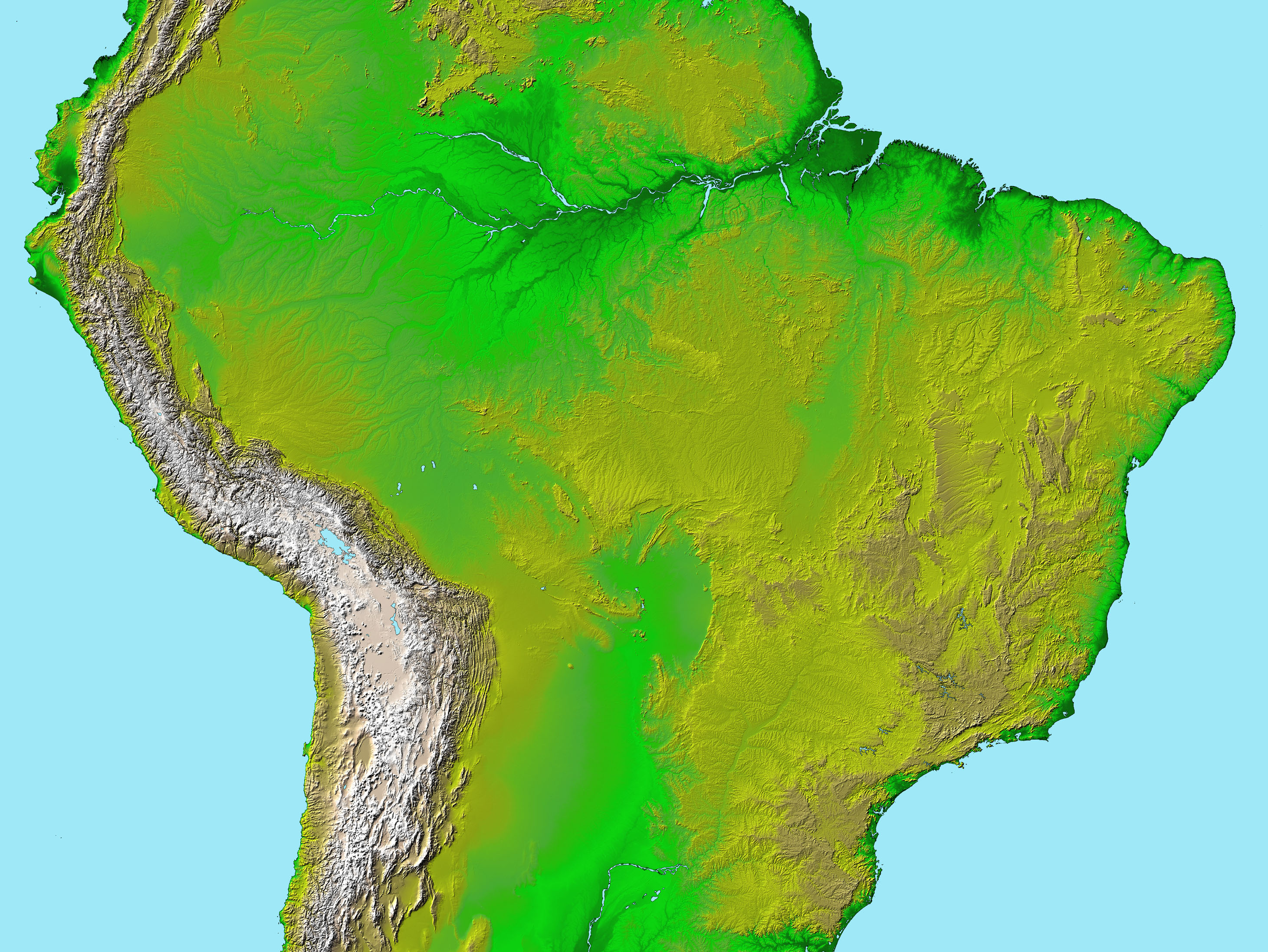
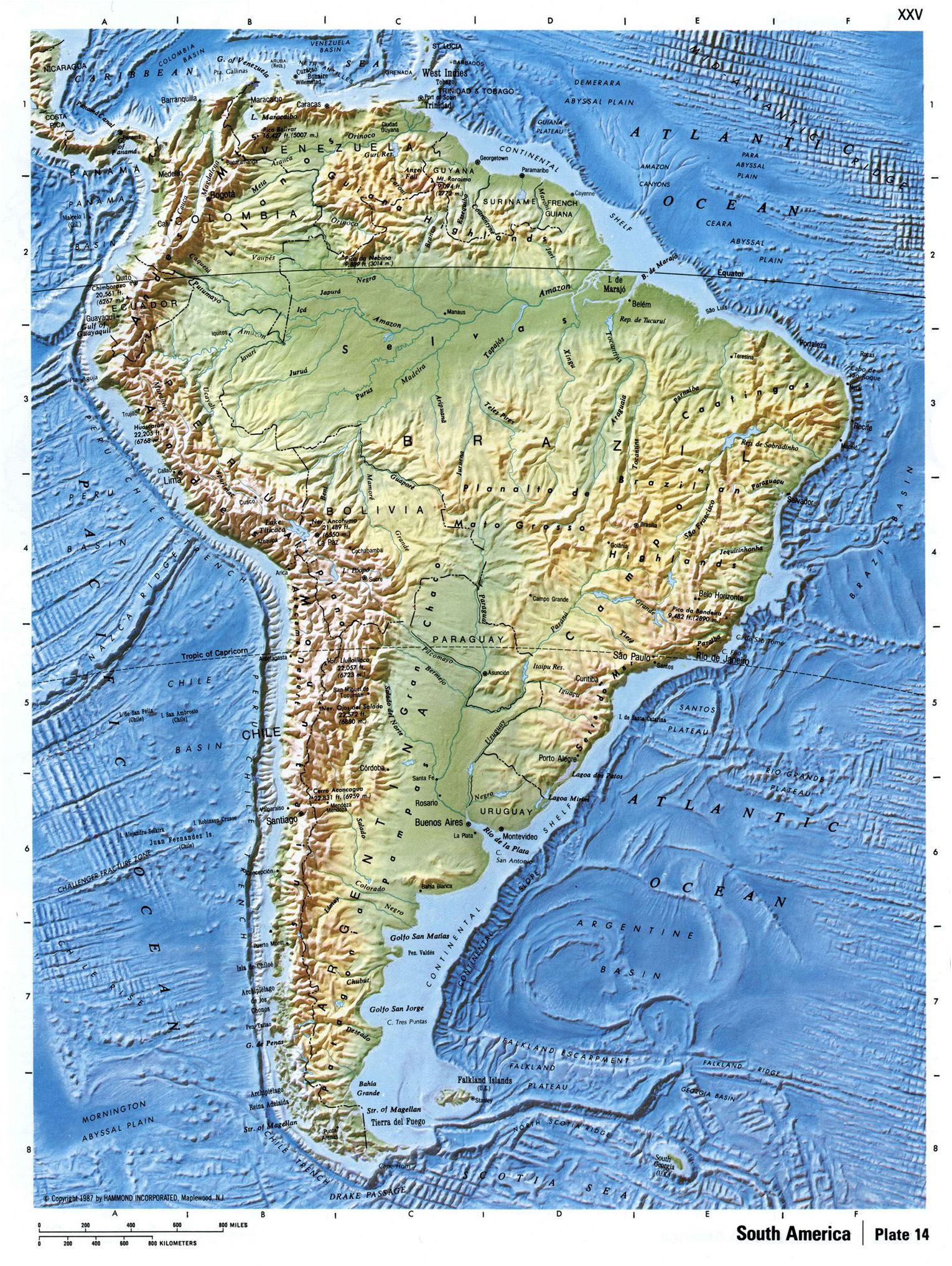
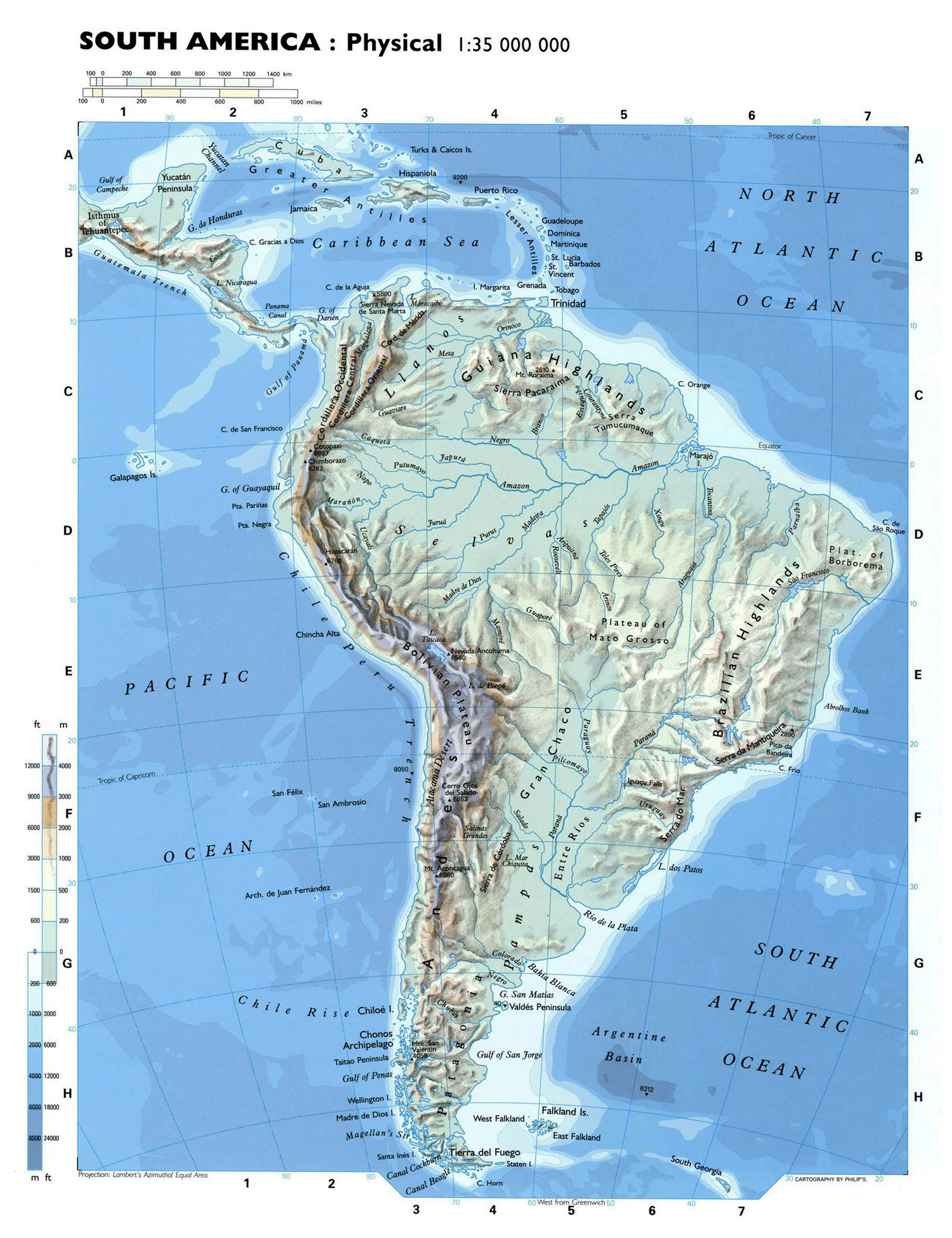
South America’s topography is a tapestry woven with contrasting threads, each contributing to the continent’s unique character. The Andes Mountains, a majestic spine running along the western edge, stand as a defining feature. This young mountain range, formed by the collision of the Nazca and South American tectonic plates, boasts the highest peaks outside Asia, including Aconcagua, the tallest mountain in the Americas. The Andes’ influence extends far beyond their imposing presence, shaping the continent’s climate, influencing river systems, and creating diverse ecosystems.
East of the Andes, the landscape transitions to vast plains and lowlands. The Amazon Basin, the world’s largest rainforest, stretches across a vast, low-lying area, fed by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The basin’s fertile soil and abundant rainfall support a rich ecosystem teeming with life. Further south, the Gran Chaco, a semi-arid region characterized by grasslands and scrublands, stretches across Argentina, Paraguay, and Bolivia.
The continent’s eastern edge is marked by a distinct plateau, the Brazilian Highlands. This region, characterized by rolling hills and deep valleys, is home to several major river systems, including the São Francisco River. The highlands also feature the world’s largest waterfall, Iguazu Falls, a spectacle of raw natural power.
The Influence of Topography: Shaping Climate, Resources, and Human Life
South America’s topography plays a critical role in shaping the continent’s climate, resources, and the distribution of human populations. The Andes Mountains act as a formidable barrier, blocking moisture-laden winds from the Pacific Ocean and creating a rain shadow effect on the eastern slopes. This results in a stark contrast in rainfall patterns, with the western slopes receiving abundant precipitation while the eastern slopes experience arid conditions.
The continent’s topography also influences the flow of rivers and the distribution of water resources. The Amazon Basin, with its low elevation and abundant rainfall, receives water from numerous tributaries, making it the world’s largest river system. The Andes Mountains, on the other hand, act as a source of numerous rivers that flow eastward, providing water for agriculture and industry.
The varied topography of South America has also shaped human settlement patterns. The fertile valleys and plains of the Amazon Basin and the Gran Chaco have attracted populations for centuries, supporting agricultural activities. The Andes Mountains, while challenging to inhabit, have also provided refuge and opportunities for communities adapted to high altitudes.
Understanding the Importance of Topography: A Multifaceted Perspective
Understanding South America’s topography is crucial for various fields of study and practical applications.
-
Geography and Geology: Topography maps provide essential data for geographers and geologists to understand the continent’s geological history, landform evolution, and the forces that shaped its landscape.
-
Climate Science: The relationship between topography and climate is fundamental in understanding regional climate patterns, rainfall distribution, and the impact of climate change on the continent.
-
Resource Management: Topography maps are essential for identifying and managing natural resources, including water resources, mineral deposits, and fertile land for agriculture.
-
Infrastructure Development: The topography of South America presents challenges and opportunities for infrastructure development, influencing the construction of roads, railways, and hydroelectric dams.
-
Environmental Conservation: Understanding the topography is crucial for conservation efforts, allowing for the identification of sensitive ecosystems, biodiversity hotspots, and areas vulnerable to environmental degradation.
Exploring Further: Frequently Asked Questions about the Topography of South America
Q: What are the major geological processes that shaped South America’s topography?
A: The continent’s topography is a product of tectonic plate movements, volcanic activity, and erosion. The collision of the Nazca and South American plates resulted in the formation of the Andes Mountains. Volcanic activity has also played a significant role, creating volcanic peaks and shaping the landscape. Erosion by wind, water, and ice has further sculpted the continent’s features over time.
Q: How does the topography of South America impact its biodiversity?
A: The varied topography of South America has created a wide range of habitats, supporting a rich biodiversity. The Andes Mountains, with their diverse elevations and microclimates, host a unique array of flora and fauna. The Amazon Basin, with its vast rainforest, is home to an incredible diversity of species. The Gran Chaco, with its grasslands and scrublands, supports a distinct ecosystem.
Q: What are some of the challenges presented by South America’s topography for human development?
A: The mountainous terrain of the Andes presents challenges for transportation, communication, and infrastructure development. The Amazon Basin’s dense rainforest poses difficulties for accessing resources and managing deforestation. The Gran Chaco’s arid conditions present challenges for agriculture and water management.
Q: How is the topography of South America being impacted by climate change?
A: Climate change is impacting South America’s topography in several ways. Rising temperatures are accelerating glacial melt in the Andes Mountains, affecting water resources. Changes in rainfall patterns are impacting river systems and potentially leading to increased erosion. Sea-level rise is threatening coastal areas, particularly in low-lying regions.
Navigating the Landscape: Tips for Understanding and Using Topography Maps
- Familiarize yourself with topographic symbols: Understand the symbols used on maps to represent different features such as mountains, valleys, rivers, and elevation contours.
- Pay attention to elevation: Contour lines indicate elevation changes, providing insights into the steepness of slopes and the height of mountains.
- Analyze the relationship between topography and other features: Consider how topography influences climate, vegetation, and human settlements.
- Utilize online resources: Online platforms offer interactive topographic maps, providing detailed information and visualization tools.
- Combine maps with other data sources: Integrate topographic maps with satellite imagery, climate data, and demographic information for a comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
Conclusion: A Continent in Motion, Shaped by Time and Geology
The topography of South America is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped our planet. From the majestic Andes Mountains to the vast Amazon Basin, each feature contributes to the continent’s unique character and ecological diversity. Understanding the intricate interplay of topography, climate, resources, and human activities is crucial for sustainable development, resource management, and environmental conservation in this vibrant and diverse continent. As we continue to explore and learn from South America’s remarkable landscape, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our planet and the importance of preserving its natural wonders for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of South America. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!