Charting a Course: A Comprehensive Look at the Future of Climate Change Mitigation to 2050
Related Articles: Charting a Course: A Comprehensive Look at the Future of Climate Change Mitigation to 2050
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting a Course: A Comprehensive Look at the Future of Climate Change Mitigation to 2050. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting a Course: A Comprehensive Look at the Future of Climate Change Mitigation to 2050
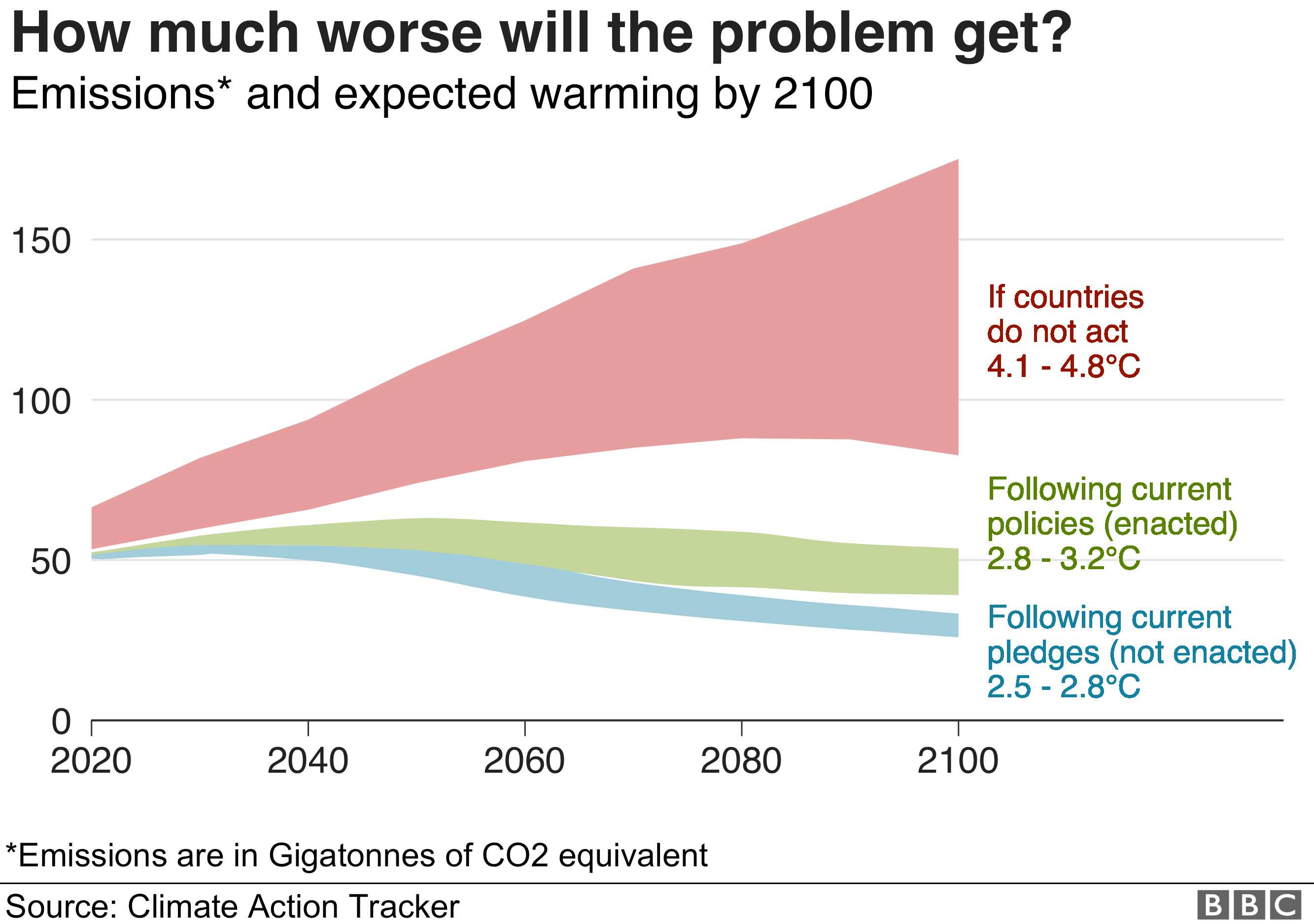
The Earth’s climate is changing at an unprecedented rate, driven by human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This change is already manifesting in rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and shifts in ecosystems. To avert the most catastrophic impacts, global efforts to mitigate climate change are paramount. This article explores the trajectory of climate change mitigation efforts towards 2050, examining the challenges, opportunities, and key pathways for achieving a sustainable future.
Understanding the Urgency: The Science Behind Climate Change Mitigation
The scientific consensus is clear: human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, are the primary drivers of global warming. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the leading international body for the assessment of climate change, has established that limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial levels, is essential to avoid the most severe consequences of climate change.
Achieving these goals requires a rapid and profound shift in global energy systems and industrial processes. This necessitates a transition towards low-carbon energy sources, enhanced energy efficiency, and a reduction in emissions from deforestation and other land-use changes.
The Path Forward: Key Strategies for Climate Change Mitigation
The roadmap for climate change mitigation involves a multi-pronged approach, encompassing various sectors and incorporating technological advancements, policy changes, and behavioral shifts:
1. Transitioning to Renewable Energy Sources:
- Solar and Wind Power: Harnessing solar and wind energy is crucial for achieving a clean energy future. Technological advancements have significantly reduced costs, making these sources increasingly competitive.
- Hydropower: While hydropower is a mature technology, its potential for expansion is limited by environmental concerns.
- Geothermal Energy: Utilizing heat from the Earth’s interior offers a stable and reliable source of energy, particularly in regions with geothermal activity.
- Bioenergy: Utilizing biomass for energy production can be a sustainable option when managed responsibly, minimizing deforestation and ensuring carbon neutrality.
2. Enhancing Energy Efficiency:
- Building Retrofits: Implementing energy-efficient building materials and technologies can significantly reduce energy consumption for heating, cooling, and lighting.
- Transportation Electrification: Transitioning to electric vehicles and promoting public transport can dramatically reduce emissions from the transportation sector.
- Industrial Efficiency: Optimizing industrial processes and adopting energy-efficient technologies can minimize energy waste and carbon emissions.
3. Carbon Capture and Storage:
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): This technology captures carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and industrial processes, storing them underground or utilizing them for other purposes.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): This emerging technology directly removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, offering a potential solution for addressing historical emissions.
4. Sustainable Land Management:
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees can sequester significant amounts of carbon dioxide, mitigating climate change and enhancing biodiversity.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Practices such as agroforestry, conservation agriculture, and reduced tillage can minimize emissions from agriculture and enhance soil carbon sequestration.
- Sustainable Forestry: Managing forests sustainably, including responsible harvesting and reforestation, can contribute to carbon storage and prevent deforestation-related emissions.
5. Policy and Regulatory Framework:
- Carbon Pricing Mechanisms: Implementing carbon taxes, emissions trading systems, or other pricing mechanisms can incentivize businesses to reduce their emissions.
- Renewable Energy Targets: Setting ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment can drive investment and innovation in the clean energy sector.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Establishing energy efficiency standards for appliances, buildings, and vehicles can promote the adoption of energy-saving technologies.
- International Cooperation: Global collaboration is essential for addressing climate change, particularly in areas like technology transfer, finance, and capacity building.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Path to 2050
The transition to a low-carbon future faces several challenges:
- Cost of Transition: The upfront costs associated with transitioning to renewable energy sources, upgrading infrastructure, and developing new technologies can be significant.
- Technological Barriers: While technological advancements are crucial for climate change mitigation, some technologies are still in their early stages of development and require further research and investment.
- Social and Political Resistance: Resistance to change, particularly from industries reliant on fossil fuels, can hinder the implementation of climate policies and initiatives.
- Equity and Justice: The transition to a low-carbon future must be equitable, ensuring that the benefits are shared widely and that vulnerable communities are not disproportionately affected.
Despite these challenges, there are also significant opportunities:
- Economic Growth: Investing in clean energy and sustainable technologies can create new industries, jobs, and economic opportunities.
- Innovation and Technological Advancements: The drive to mitigate climate change is spurring innovation and technological advancements, leading to breakthroughs in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and carbon capture technologies.
- Improved Public Health: Reducing air pollution from fossil fuel combustion can significantly improve public health, leading to lower rates of respiratory diseases and other health problems.
- Enhanced Environmental Sustainability: Climate change mitigation efforts can contribute to biodiversity conservation, ecosystem restoration, and sustainable land management practices.
The Role of Innovation and Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are crucial for achieving climate change mitigation goals. Continued research and development in areas like renewable energy, energy efficiency, carbon capture and storage, and sustainable land management are essential.
- Renewable Energy Technologies: Advancements in solar and wind power technologies are continuously reducing costs and increasing efficiency. The development of new storage technologies, such as batteries and hydrogen, is crucial for addressing the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
- Energy Efficiency Technologies: Innovations in building materials, appliances, and transportation systems are leading to significant improvements in energy efficiency. The development of smart grids and energy management systems can optimize energy use and reduce waste.
- Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies: Research and development in carbon capture and storage technologies are advancing, with potential for large-scale deployment in the coming decades.
- Sustainable Land Management Technologies: Innovations in agricultural practices, forestry management, and soil carbon sequestration technologies are crucial for mitigating emissions from land-use change.
FAQs on Climate Change Mitigation to 2050
1. What are the key milestones for climate change mitigation to 2050?
- 2025: Achieving significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions from major economies.
- 2030: Reaching peak emissions globally, with a clear trajectory towards net-zero emissions by 2050.
- 2040: Transitioning to a predominantly renewable energy system, with significant investments in energy efficiency and carbon capture technologies.
- 2050: Achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions globally, with a resilient and sustainable energy system.
2. What are the potential impacts of failing to achieve climate change mitigation goals?
- Increased Frequency and Intensity of Extreme Weather Events: Heat waves, droughts, floods, and wildfires will become more frequent and intense, leading to significant economic and social disruption.
- Rising Sea Levels: Coastal communities will face increased risks from sea level rise, resulting in displacement, infrastructure damage, and ecosystem loss.
- Food and Water Security Challenges: Climate change will disrupt agricultural production and water resources, leading to food shortages and water scarcity.
- Biodiversity Loss and Ecosystem Degradation: Climate change will exacerbate biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation, impacting human health and well-being.
3. What are the key roles of governments, businesses, and individuals in climate change mitigation?
- Governments: Implementing strong climate policies, investing in research and development, and providing financial support for climate action.
- Businesses: Reducing emissions from their operations, investing in clean energy technologies, and developing sustainable products and services.
- Individuals: Adopting sustainable lifestyles, reducing energy consumption, supporting climate-friendly businesses, and advocating for climate action.
Tips for Climate Change Mitigation
- Reduce Energy Consumption: Use energy-efficient appliances, turn off lights when leaving a room, and consider using public transportation or cycling.
- Adopt a Sustainable Diet: Reduce meat consumption and prioritize locally-sourced, seasonal produce.
- Support Climate-Friendly Businesses: Choose businesses that prioritize sustainability and invest in clean energy.
- Advocate for Climate Action: Contact your elected officials and support organizations working to address climate change.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Stay informed about climate change and share your knowledge with others.
Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable Future
The path towards 2050 presents both challenges and opportunities for mitigating climate change. Achieving a sustainable future requires a collective effort from governments, businesses, and individuals. By embracing innovative technologies, implementing robust policies, and making responsible choices, we can create a world where climate change is effectively addressed, ensuring a healthy and prosperous future for generations to come. The time for action is now, and the choices we make today will shape the future of our planet.
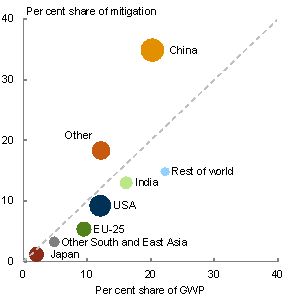

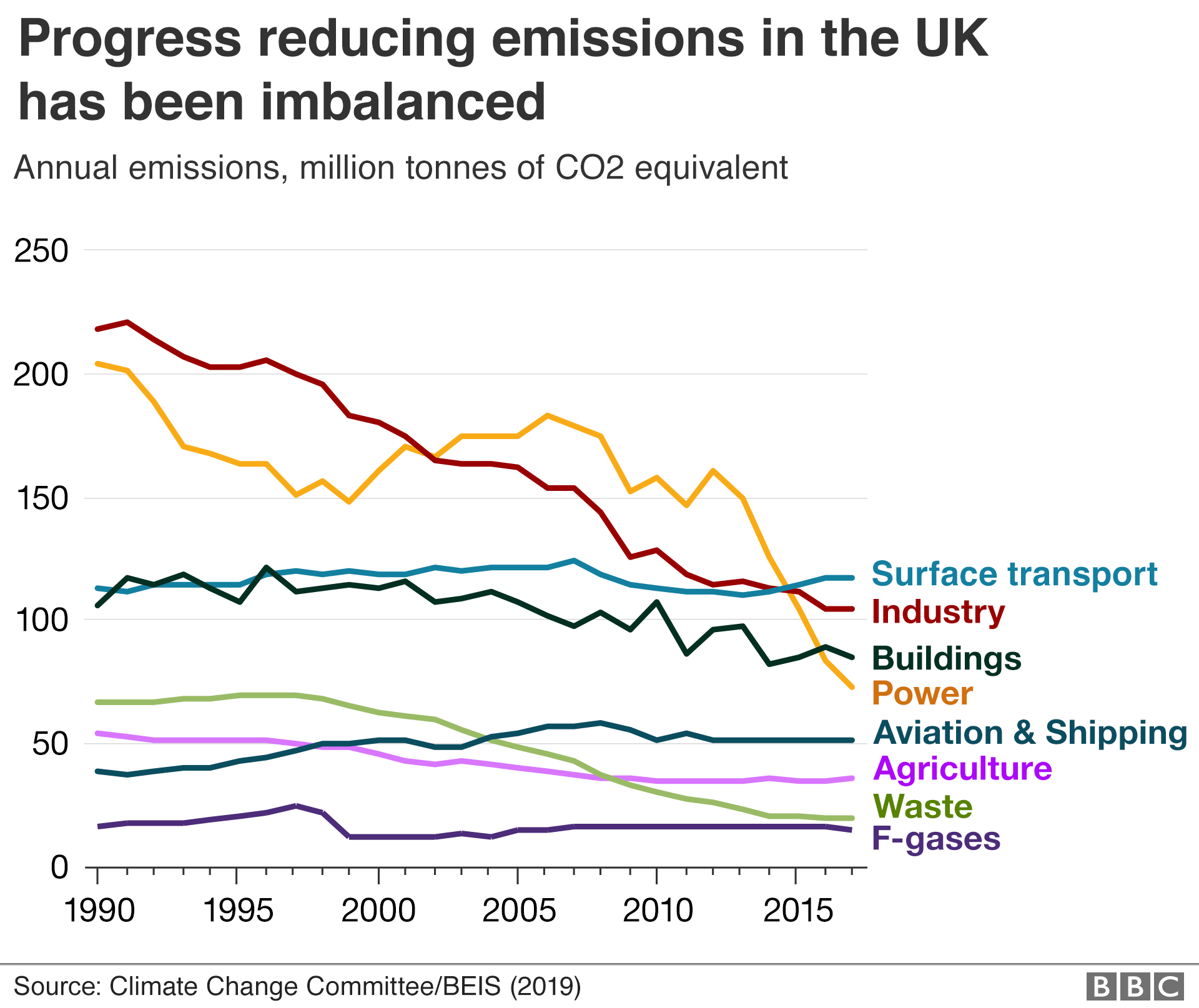
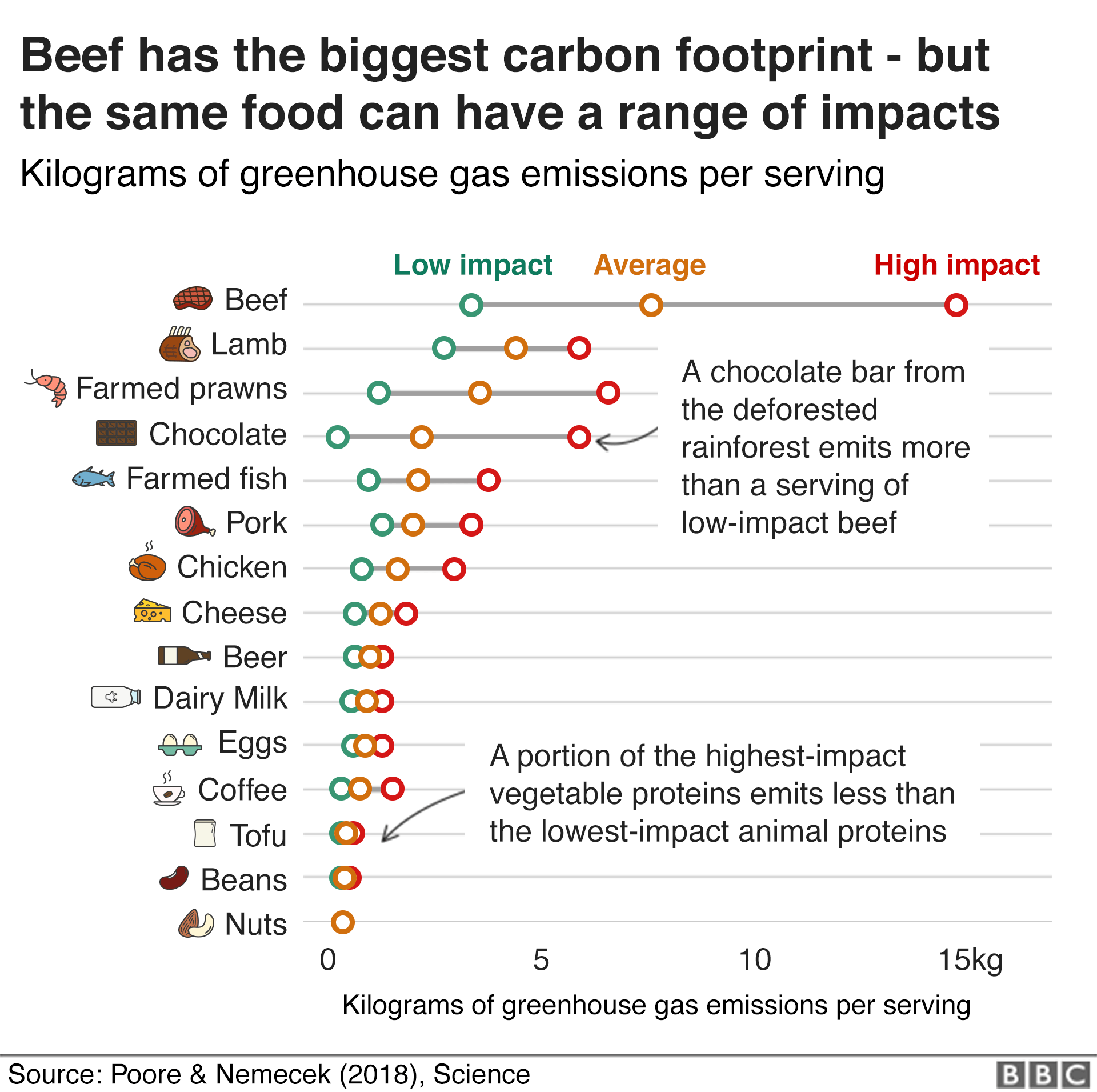

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting a Course: A Comprehensive Look at the Future of Climate Change Mitigation to 2050. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!