Charting the Unseen: A Comprehensive Look at Undersea Topography Maps
Related Articles: Charting the Unseen: A Comprehensive Look at Undersea Topography Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Unseen: A Comprehensive Look at Undersea Topography Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Unseen: A Comprehensive Look at Undersea Topography Maps

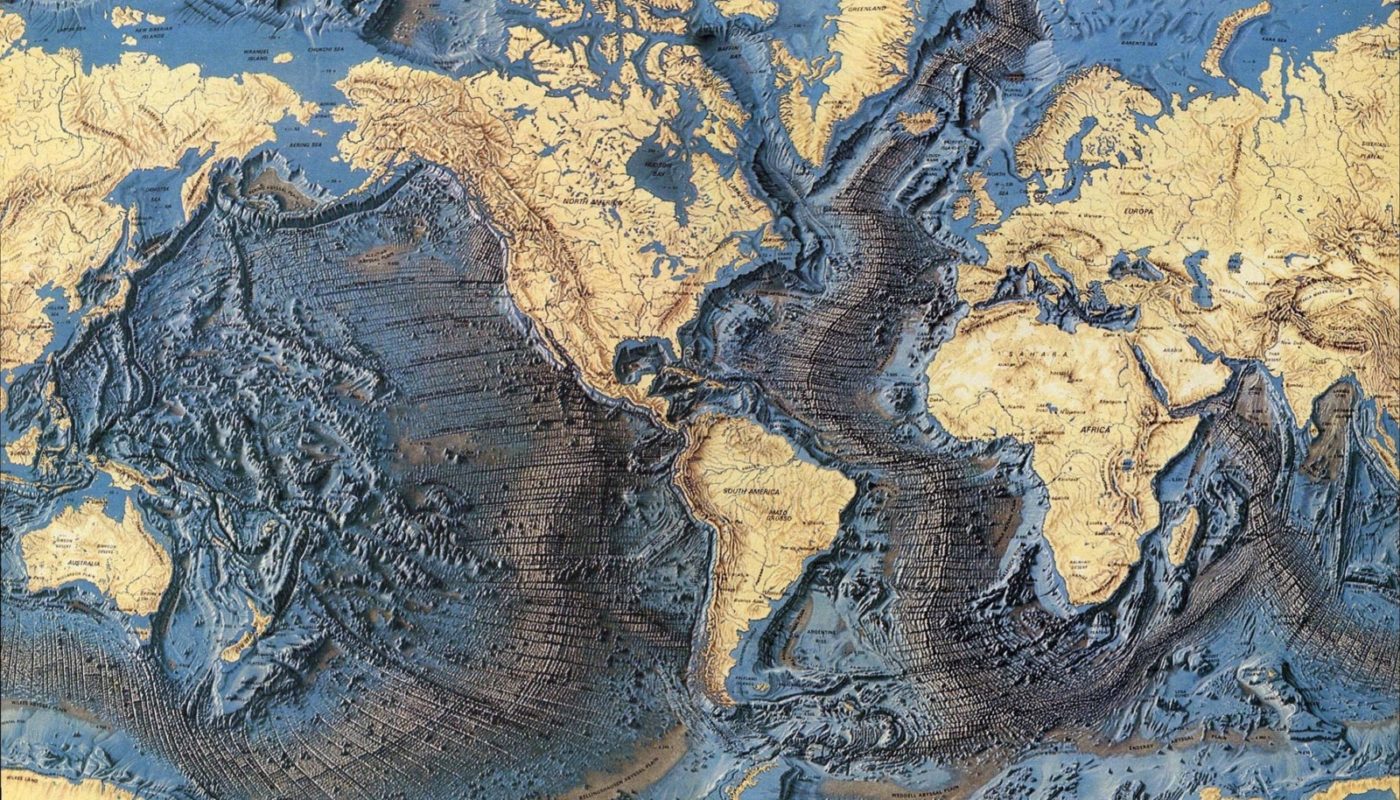
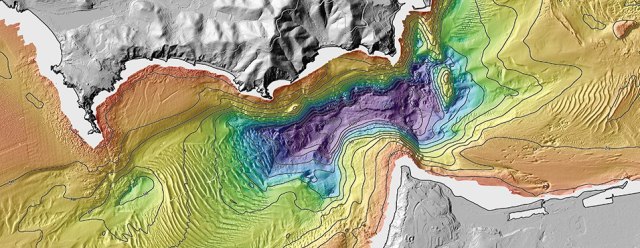
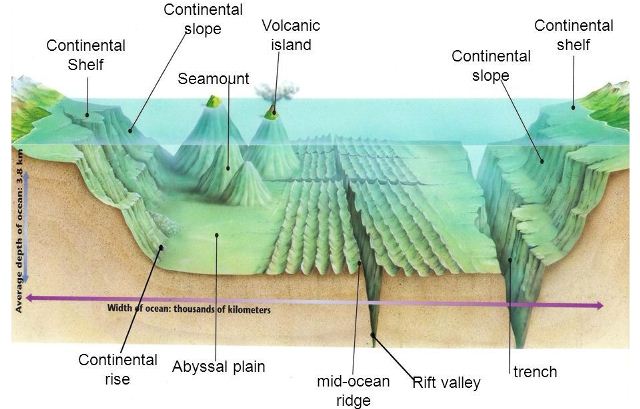
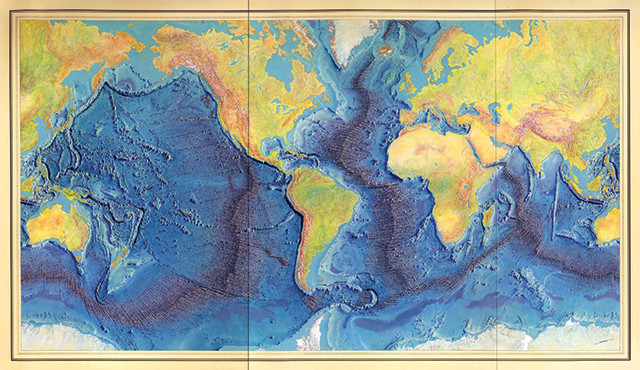
The Earth’s surface is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, with mountains, valleys, and plains shaping our continents. However, beneath the waves lies a hidden world, a vast and intricate underwater topography that remains largely unexplored. Undersea topography maps, also known as bathymetric maps, provide a crucial window into this hidden realm, revealing the intricate features of the ocean floor and shedding light on its geological history, ecological diversity, and potential resources.
Unveiling the Ocean Floor: The Science of Bathymetry
Bathymetry, the study of underwater depths and the shape of the ocean floor, is a fundamental aspect of oceanography. Undersea topography maps, the product of bathymetric surveys, are essential for understanding the ocean’s physical structure, its influence on ocean currents and marine life, and its role in global climate patterns.
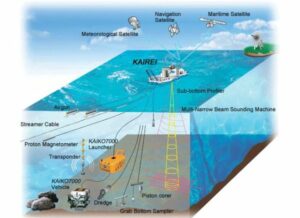
These maps are created using various techniques, each with its own strengths and limitations:
- Echo Sounding: This traditional method, relying on sound waves emitted from a ship, measures the time it takes for the sound to travel to the seabed and return. This technique provides a detailed profile of the ocean floor along a ship’s track.
- Multibeam Sonar: More advanced than echo sounding, multibeam sonar uses multiple beams to map a wider swath of the seabed simultaneously, increasing efficiency and coverage.
- Satellite Altimetry: By measuring the height of the sea surface, satellites can indirectly infer the shape of the ocean floor. This technique provides a broad overview of large-scale features.
- Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs): These unmanned vehicles equipped with sonar systems can navigate and map the ocean floor autonomously, providing detailed data for specific areas.
Beyond the Depths: The Importance of Undersea Topography Maps
The benefits of undersea topography maps extend far beyond scientific curiosity. They play a crucial role in various fields, including:
- Navigation and Safety: Accurate bathymetric data is essential for safe navigation of ships, especially in coastal areas and shallow waters. It allows for the identification of potential hazards like reefs, shipwrecks, and underwater mountains.
- Resource Exploration and Management: Undersea topography maps are vital for locating and managing marine resources, including oil and gas deposits, mineral resources, and fishing grounds. They help to identify areas with high potential for resource extraction while minimizing environmental impact.
- Climate Change Research: Understanding the ocean floor’s topography is crucial for studying ocean currents, which play a significant role in regulating global climate. Bathymetric data helps researchers model ocean circulation and predict the effects of climate change.
- Marine Biology and Conservation: Undersea topography maps reveal the intricate habitat structure of the ocean floor, providing valuable insights into the distribution and diversity of marine life. This information is crucial for marine conservation efforts and the management of marine protected areas.
- Tsunami and Earthquake Prediction: Understanding the topography of the ocean floor, particularly in subduction zones, is crucial for predicting the potential impact of tsunamis and earthquakes. Bathymetric data helps scientists model the propagation of tsunami waves and assess their potential destructive power.
Unveiling the Unknown: The Ongoing Quest for Complete Mapping
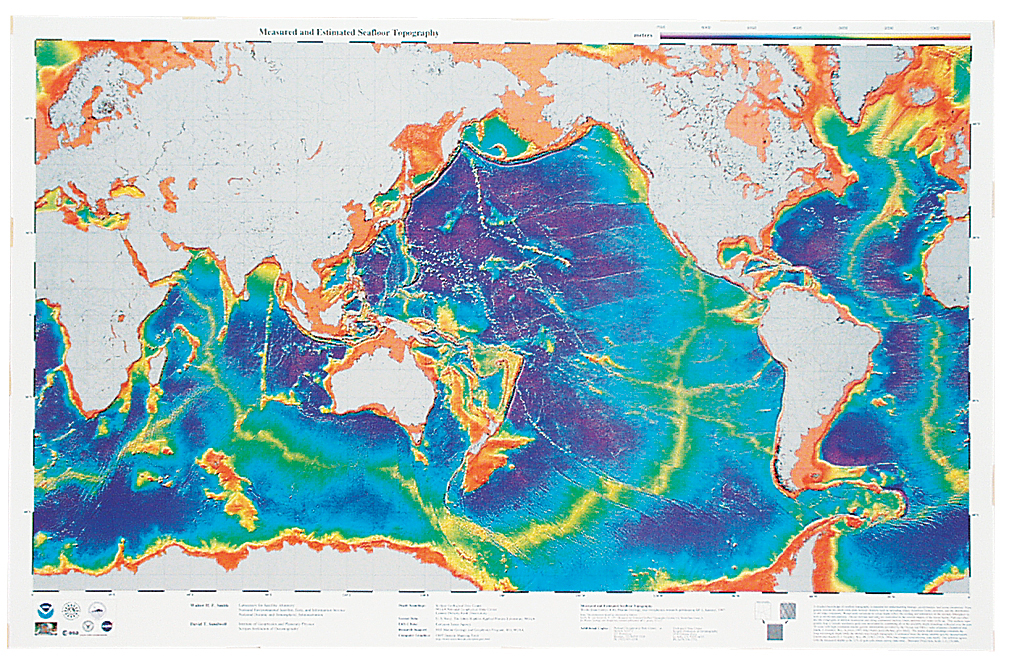
Despite significant progress in bathymetric mapping, vast portions of the ocean floor remain unexplored. The challenges are immense, including the vastness of the ocean, the harsh environment, and the cost of data acquisition. However, the scientific community is constantly working to improve mapping techniques and expand coverage.
The Seabed 2030 project, a collaborative effort led by the Nippon Foundation and GEBCO, aims to map the entire ocean floor by 2030. This ambitious project relies on data from various sources, including research institutions, government agencies, and the private sector.
FAQs About Undersea Topography Maps
1. What is the difference between a bathymetric map and a topographic map?
A bathymetric map depicts the depths and shape of the ocean floor, while a topographic map represents the elevation and features of land.
2. How accurate are undersea topography maps?
The accuracy of bathymetric maps varies depending on the mapping technique used and the specific area being mapped. Modern multibeam sonar systems can provide highly accurate data, while satellite altimetry offers a broader but less precise overview.
3. What are the limitations of undersea topography maps?
Undersea topography maps are limited by the availability of data and the technical challenges of mapping the ocean floor. Deep trenches and areas with complex topography can be difficult to map accurately.
4. How are undersea topography maps used in marine conservation?
Bathymetric data helps identify critical marine habitats, such as coral reefs, seamounts, and hydrothermal vents, allowing for targeted conservation efforts and the establishment of marine protected areas.
5. What are the future prospects for undersea topography mapping?
The future of bathymetric mapping is promising, with advancements in technology, increased funding, and growing international collaboration. The Seabed 2030 project aims to revolutionize our understanding of the ocean floor and unlock its potential for scientific research, resource management, and conservation.
Tips for Using Undersea Topography Maps
- Consider the scale and resolution of the map: Different maps are designed for different purposes. Choose a map that provides the level of detail you need.
- Understand the mapping technique used: Each method has its strengths and limitations. Be aware of the potential for inaccuracies or gaps in data.
- Look for additional information: Many bathymetric maps include additional layers, such as geological features, marine life distribution, or resource locations.
- Use online tools and resources: Several online platforms and databases provide access to bathymetric data and visualization tools.
- Consult with experts: If you need detailed information or assistance interpreting bathymetric data, consult with oceanographers or marine scientists.
Conclusion
Undersea topography maps are essential tools for understanding the hidden world beneath the waves. They provide a foundation for scientific research, resource management, navigation safety, and marine conservation. As our knowledge of the ocean floor continues to expand, these maps will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping our relationship with the planet’s largest and least explored ecosystem. The ongoing quest to map the entire ocean floor is a testament to our enduring curiosity and the vital need to understand and protect this vast and complex environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Unseen: A Comprehensive Look at Undersea Topography Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!