Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Topography Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Topography Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Topography Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Topography Maps

Topography maps, often referred to as contour maps, are essential tools for understanding and navigating the natural world. They provide a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, capturing the intricate details of elevation, terrain features, and other geographical elements. Understanding these maps is crucial for various disciplines, from outdoor recreation and exploration to urban planning and environmental management. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed exploration of topography maps, their significance, and practical applications.
The Essence of Topography Maps
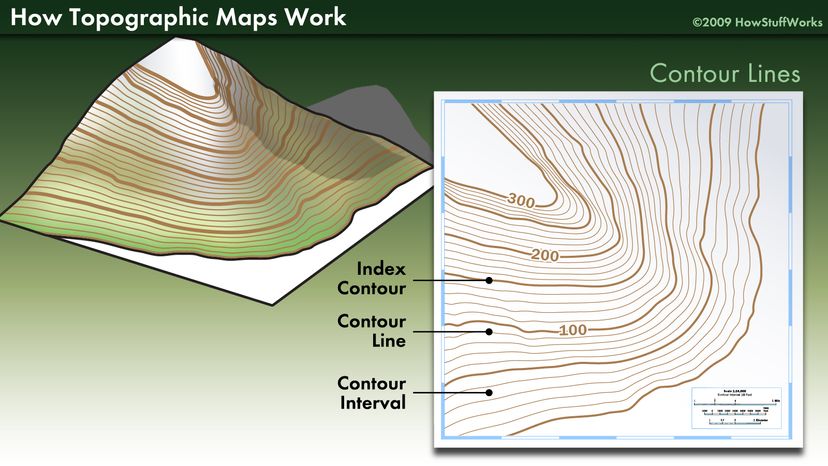
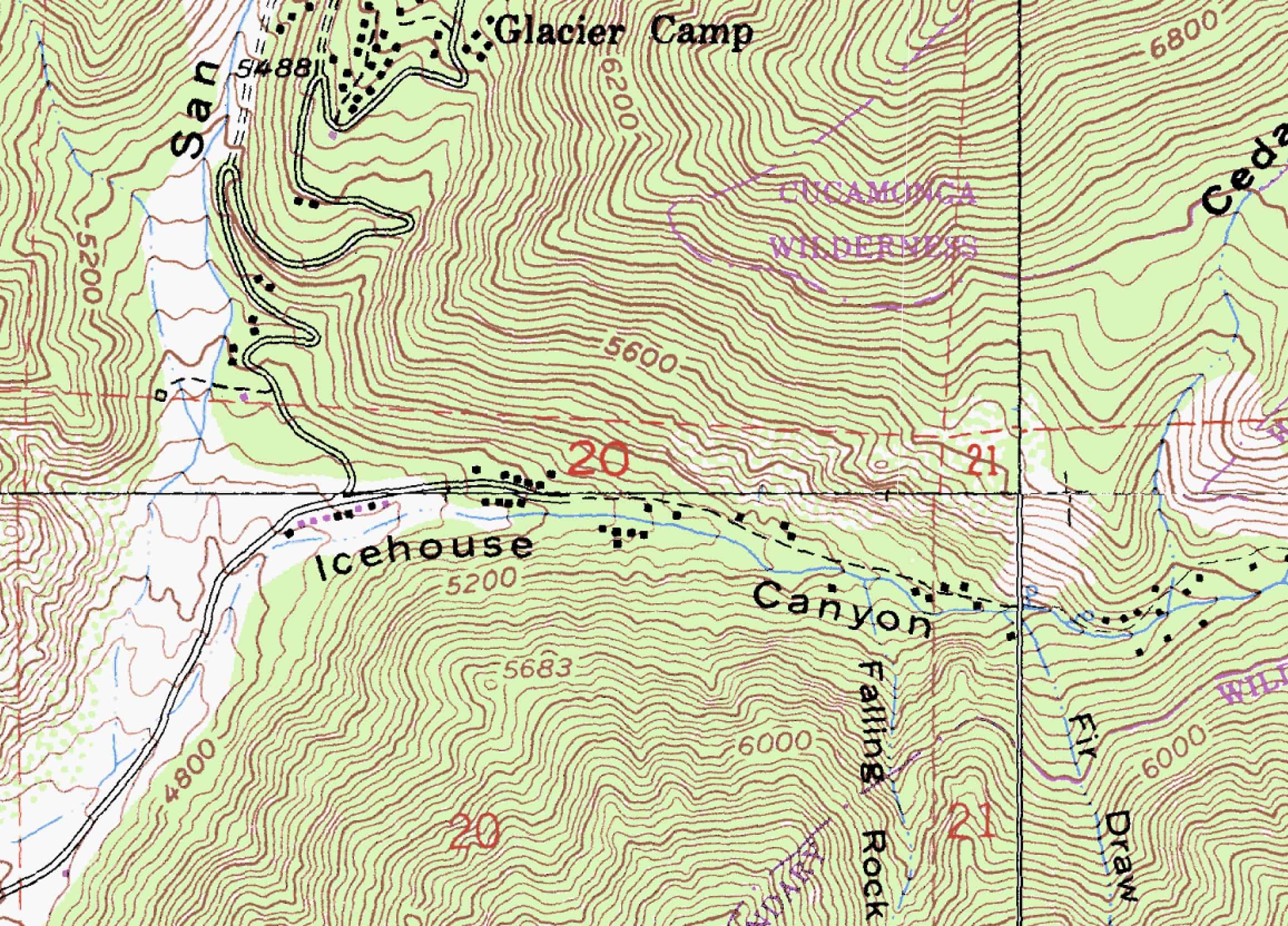
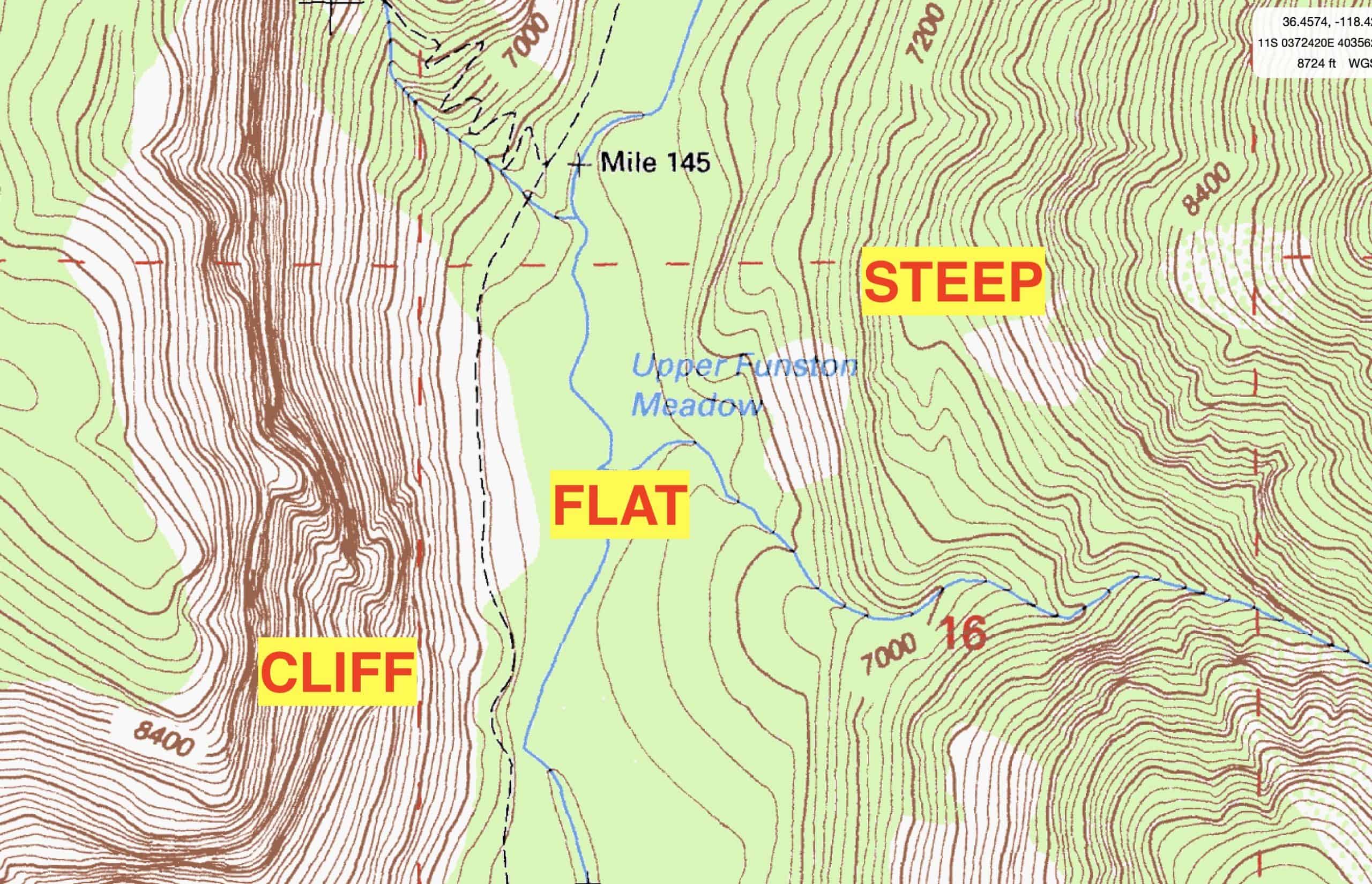
At their core, topography maps utilize contour lines to depict the shape and form of the land. Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, creating a visual representation of the terrain’s ups and downs. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; conversely, widely spaced lines indicate a gentler incline. This system allows for a precise understanding of the landscape’s three-dimensional structure, even on a two-dimensional map.
Components of a Topography Map
Beyond contour lines, topography maps incorporate various elements to enhance their utility and readability:
- Elevation: The map’s legend typically displays a scale representing the elevation intervals between contour lines. This information allows for accurate determination of the height of specific points on the map.
- Relief Shading: This technique uses shading to create a three-dimensional effect, highlighting areas of high and low elevation. Relief shading enhances the visual clarity of the terrain and facilitates easier identification of prominent features.
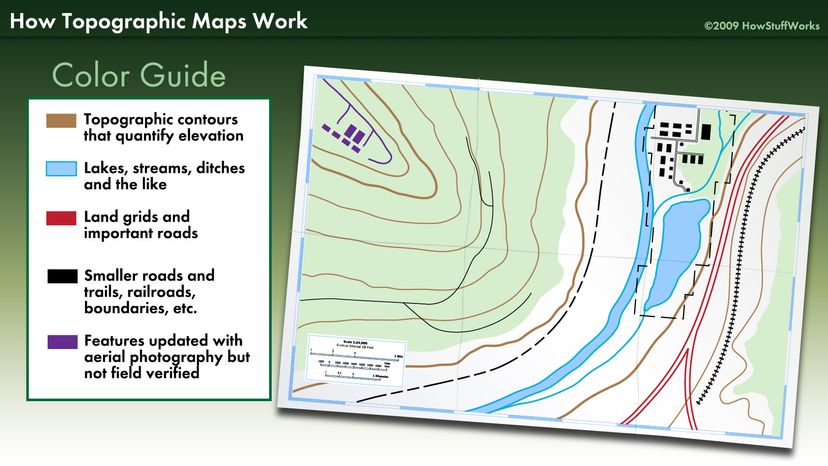
- Symbols and Legends: Topography maps use standardized symbols to represent various features like roads, rivers, buildings, and vegetation. The legend provides a key to these symbols, ensuring consistent interpretation of the map’s information.
- Grid System: Most topography maps utilize a grid system, often based on latitude and longitude, to facilitate precise location identification and measurement. This grid system allows for easy navigation and referencing of specific points on the map.
Types of Topography Maps
Topography maps come in various formats and scales, each tailored to specific purposes:
- Large-Scale Maps: These maps cover smaller areas with greater detail, typically used for local planning, surveying, and recreational activities.
- Small-Scale Maps: These maps cover larger areas with less detail, commonly used for regional planning, navigation, and general overview.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These are digital representations of elevation data, often used in computer-aided design (CAD) and geographic information systems (GIS) applications.
- Topographic Profiles: These are cross-sectional views of the terrain, showing the elevation changes along a specific line. Topographic profiles are valuable for visualizing slope gradients and identifying potential obstacles.
Benefits of Utilizing Topography Maps
Topography maps offer numerous benefits across a wide range of applications:
- Navigation and Exploration: They provide a detailed understanding of the terrain, aiding in route planning, identifying potential hazards, and navigating challenging landscapes.
- Land Management and Planning: They serve as valuable tools for urban planning, infrastructure development, and environmental management by providing crucial information about terrain features, slope gradients, and water flow patterns.
- Scientific Research: Topography maps are essential for various scientific disciplines, including geology, hydrology, and ecology, providing valuable data for research and analysis.
- Outdoor Recreation: They are invaluable for hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts, enabling them to plan routes, estimate travel times, and identify points of interest.
Reading a Topography Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding the intricacies of topography maps requires a systematic approach:
- Identify the Map’s Scale: This information, usually found in the map’s legend, indicates the ratio between the map’s distance and the actual distance on the ground.
- Locate the Key: The map’s legend provides a key to the symbols used to represent different features, ensuring accurate interpretation of the map’s information.
- Analyze Contour Lines: Pay close attention to the spacing and direction of contour lines to understand the terrain’s shape and slope. Closely spaced lines indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced lines represent gentler inclines.
- Interpret Elevation: Use the elevation scale and contour lines to determine the height of specific points on the map.
- Identify Features: Utilize the map’s symbols and legends to identify various features, such as roads, rivers, buildings, and vegetation.
- Plan Routes: Use the terrain information provided by the map to plan routes, taking into account elevation changes, potential obstacles, and desired points of interest.
FAQs about Topography Maps
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A: A topographic map specifically focuses on depicting the terrain’s elevation and shape using contour lines, while a regular map primarily displays geographical features like roads, cities, and boundaries.
Q: How are topography maps created?
A: Traditionally, topography maps were created through surveying techniques involving measuring distances and elevations. Today, advanced technologies like aerial photography, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and satellite imagery are utilized to generate highly accurate and detailed digital elevation models.
Q: What are the limitations of topography maps?
A: Topography maps represent a snapshot in time, and the terrain can change due to natural processes or human activities. Additionally, they may not accurately depict certain features like dense vegetation or underground structures.
Q: How can I find topography maps for a specific area?
A: Numerous resources are available for accessing topography maps, including government agencies like the United States Geological Survey (USGS), online mapping platforms like Google Earth, and specialized map providers catering to specific industries.
Tips for Effective Use of Topography Maps
- Study the Map’s Legend: Thoroughly understand the symbols and conventions used on the map to ensure accurate interpretation.
- Consider the Map’s Scale: Choose a map scale appropriate for your intended use, ensuring sufficient detail for your needs.
- Use a Compass and GPS: These tools aid in navigating the terrain and pinpointing your location on the map.
- Practice Reading Contour Lines: Develop an understanding of how contour lines represent elevation changes and slope gradients.
- Combine with Other Resources: Integrate topography maps with other resources like guidebooks, online tools, and local knowledge for a comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
Conclusion
Topography maps are invaluable tools for understanding, navigating, and managing the Earth’s surface. Their ability to represent the intricate details of elevation, terrain features, and other geographical elements makes them essential for various disciplines, from outdoor recreation and exploration to urban planning and environmental management. By understanding the principles behind topography maps and developing proficiency in reading and interpreting them, individuals can unlock a deeper understanding of the natural world and utilize this information for informed decision-making and effective planning.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Landscape: A Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Topography Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!