Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Site Topography Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Site Topography Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Site Topography Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Site Topography Maps

A site topography map, often referred to as a topographic survey, is a visual representation of the Earth’s surface at a specific location. It provides a detailed and accurate depiction of the terrain, including elevation changes, natural features, and man-made structures. This crucial tool serves as a foundation for various planning and development activities, offering invaluable insights into the physical characteristics of a site.
The Essence of a Topography Map
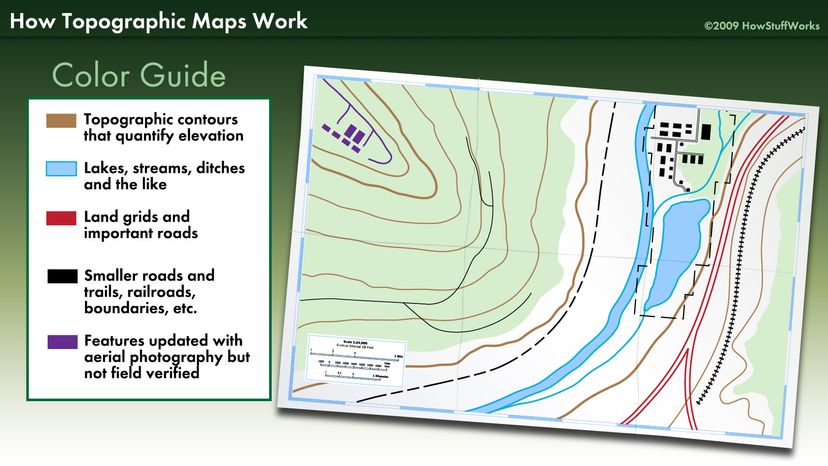
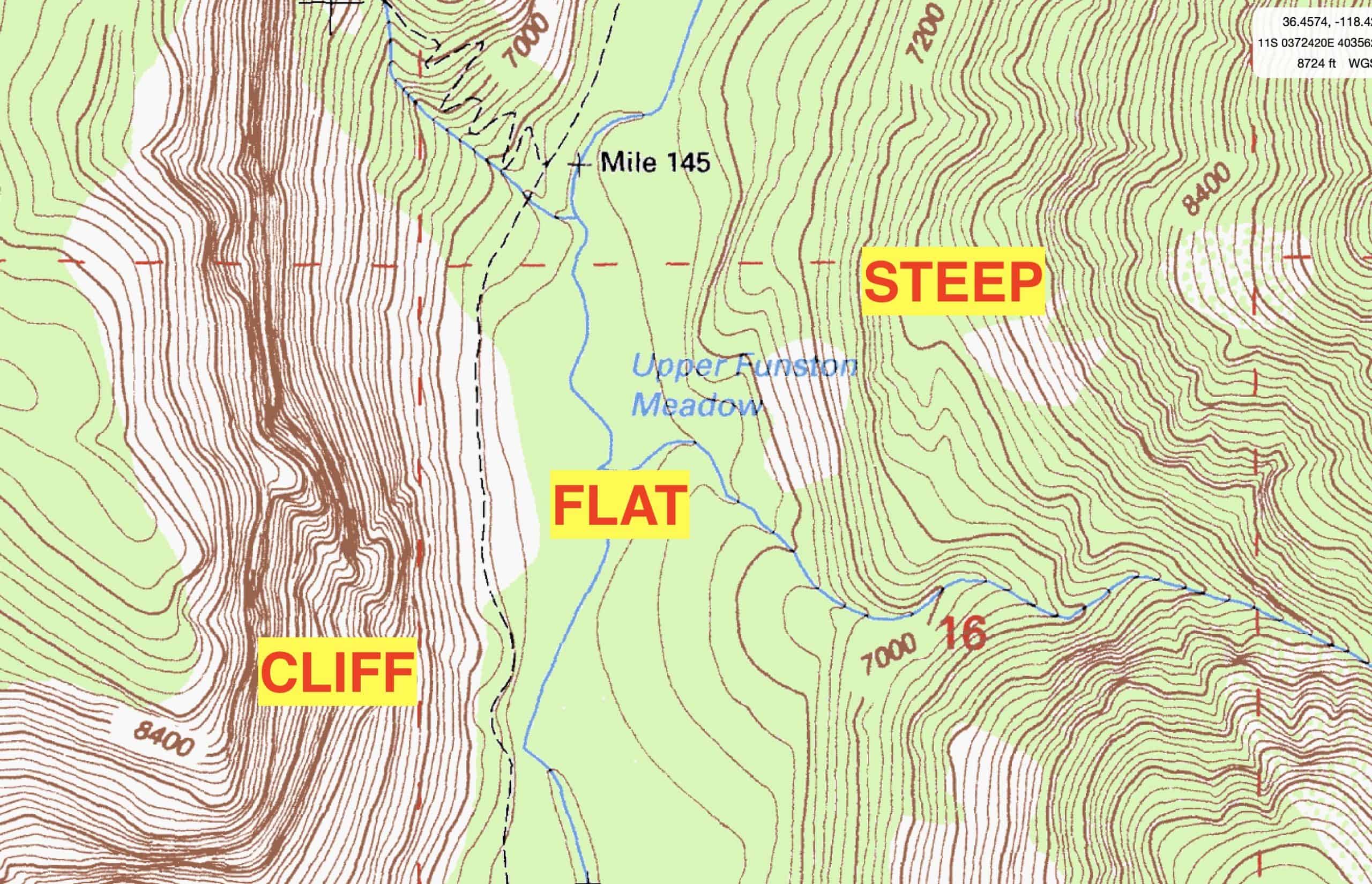
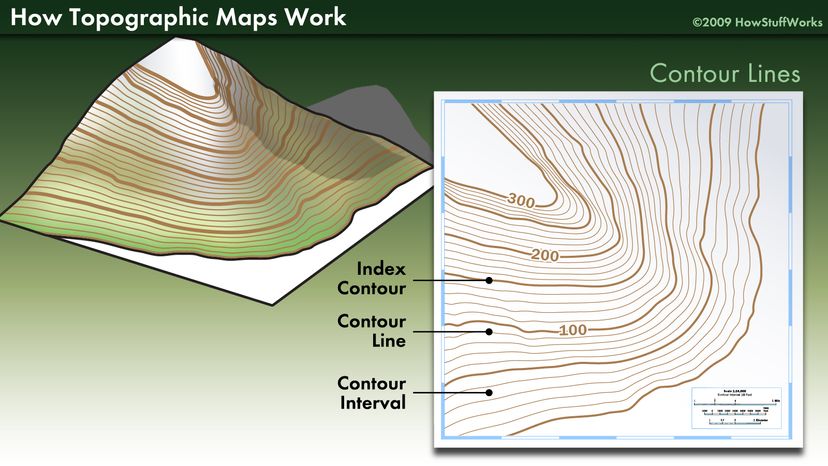
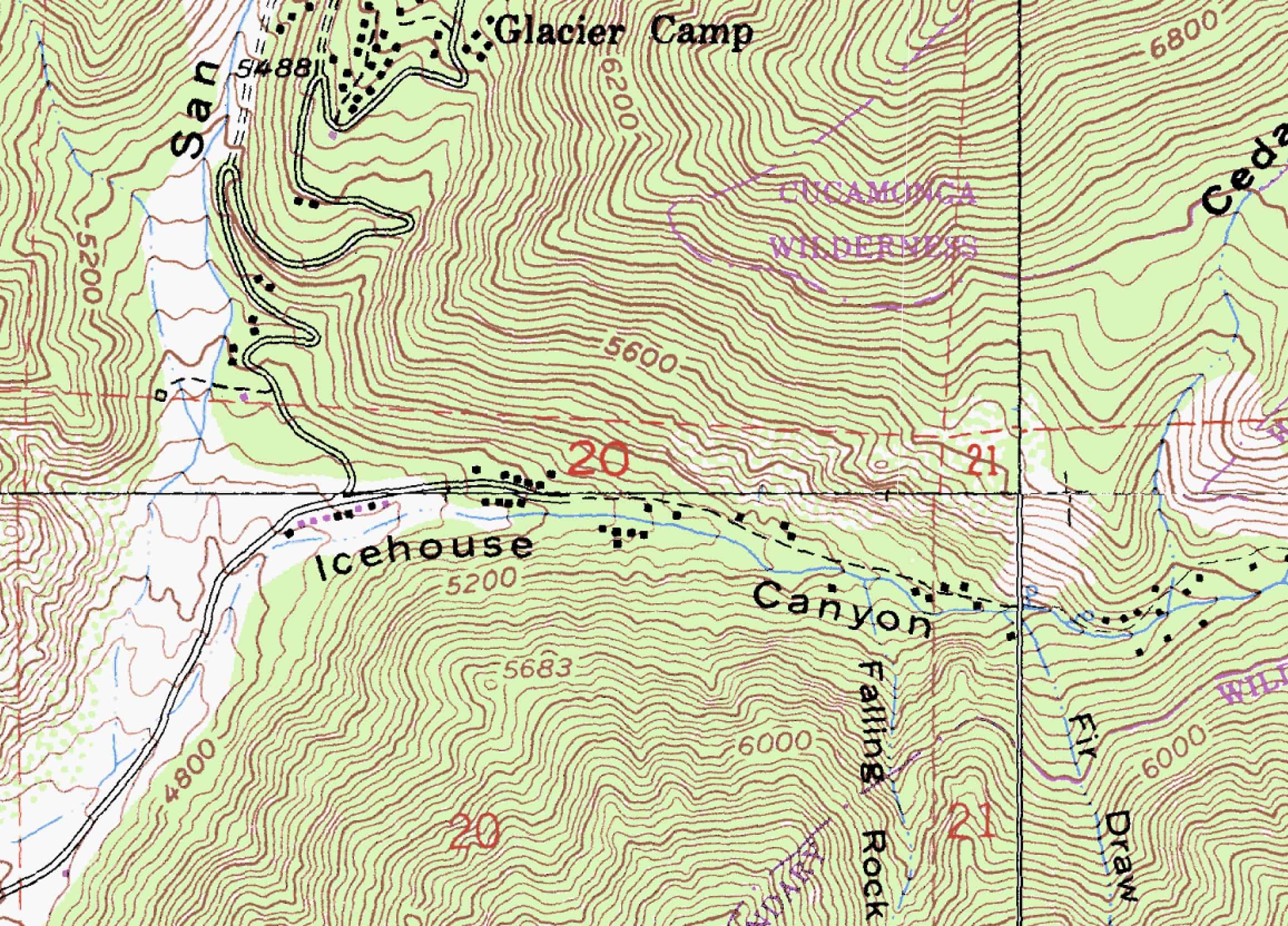
At its core, a topography map employs contour lines to depict elevation changes. These lines connect points of equal elevation, forming a network that reveals the shape and form of the land. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; conversely, widely spaced lines indicate gentler inclines.
Beyond elevation, topography maps incorporate a wealth of information, including:
- Natural Features: Rivers, lakes, streams, wetlands, forests, and other natural elements are meticulously mapped, providing context for the surrounding environment.
- Man-made Structures: Buildings, roads, utilities, and other human-made features are included, offering an understanding of existing infrastructure and potential constraints.
- Land Use: The map may indicate current land use, such as residential, commercial, or industrial areas, aiding in understanding the site’s context within the broader landscape.
- Drainage Patterns: Topography maps often illustrate drainage patterns, showcasing the flow of water across the site, which is crucial for understanding potential flooding risks and drainage requirements.
- Vegetation: Vegetation types, such as trees, shrubs, and grasslands, may be depicted, offering insights into the site’s ecological character.
The Significance of Topography Maps
The value of a topography map extends across diverse fields, serving as a critical tool for informed decision-making in:
- Civil Engineering: Topography maps are indispensable for planning and designing infrastructure projects, ensuring roads, bridges, and buildings are constructed with optimal stability and functionality. They aid in determining the most efficient routes, calculating earthwork volumes, and assessing potential environmental impacts.
- Architecture and Landscape Design: Architects and landscape architects rely heavily on topography maps to understand the site’s natural contours and plan buildings and outdoor spaces that seamlessly integrate with the existing terrain. They inform the design of retaining walls, terraces, and other features that harmonize with the site’s natural beauty.
- Urban Planning: Topography maps play a pivotal role in urban planning, informing the development of infrastructure, transportation systems, and urban green spaces. They help in identifying areas suitable for residential, commercial, or industrial development while minimizing environmental impact.
- Environmental Studies: Researchers and environmental consultants utilize topography maps to study the impact of human activities on the landscape, assess potential environmental risks, and develop conservation strategies. They aid in understanding soil erosion, water quality, and wildlife habitat.
- Real Estate Development: Topography maps provide crucial insights for real estate developers, aiding in identifying suitable land for construction, understanding the feasibility of specific projects, and assessing the potential value of a site.
Creating a Topography Map
The process of creating a topography map typically involves the following steps:
- Site Survey: A surveyor utilizes specialized equipment, such as total stations and GPS devices, to meticulously measure the site’s elevation at numerous points.
- Data Collection: The surveyor records the elevation data along with the coordinates of each point, creating a comprehensive dataset.
- Data Processing: The collected data is then processed using computer software to generate contour lines, which represent the elevation changes across the site.
- Map Creation: The processed data is then used to create the final topography map, which may include various layers of information, such as natural features, man-made structures, and land use.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Applications
Topography maps serve as a foundation for advanced applications, further enhancing their utility in various fields:
- 3D Modeling: Topography maps can be used to create 3D models of the site, offering a more immersive and comprehensive understanding of the terrain. These models are invaluable for visualizing construction projects, landscape designs, and potential environmental impacts.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Topography maps are integral components of GIS systems, allowing for the integration of spatial data with other layers of information, such as demographics, land ownership, and environmental data. This integration provides a powerful tool for analysis and decision-making.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Topography maps are readily incorporated into CAD software, enabling architects and engineers to design structures and infrastructure that seamlessly integrate with the existing terrain. This integration enhances the accuracy and efficiency of design processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the different types of topography maps?
Topography maps can be categorized based on their scale and purpose. Some common types include:
- Large-scale maps: These maps depict detailed information over a small area, often used for site planning and development.
- Small-scale maps: These maps cover larger areas with less detail, often used for regional planning and environmental studies.
- Contour maps: These maps primarily use contour lines to represent elevation changes.
- Planimetric maps: These maps focus on horizontal features, such as roads and buildings, but do not include elevation information.
2. How accurate are topography maps?
The accuracy of a topography map depends on the survey methods used and the required level of detail. Modern surveying techniques, such as GPS and total stations, provide highly accurate data, typically within a few centimeters.
3. How can I obtain a topography map?
Topography maps can be obtained from various sources, including:
- Professional surveyors: Surveyors can conduct site surveys and generate custom topography maps.
- Government agencies: Many government agencies, such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS), provide publicly available topographic maps.
- Online mapping services: Websites such as Google Maps and Bing Maps offer interactive maps with basic topographic information.
4. What are the limitations of topography maps?
While valuable tools, topography maps have limitations:
- Static representation: They depict a snapshot of the terrain at a specific point in time and do not reflect dynamic changes, such as erosion or construction.
- Scale limitations: Large-scale maps may not capture the full context of a region, while small-scale maps may lack sufficient detail for specific projects.
- Data interpretation: Interpretation of contour lines and other features requires technical knowledge and experience.
Tips for Utilizing Topography Maps
- Understand the scale: Ensure the map’s scale aligns with the project’s requirements.
- Identify key features: Pay attention to natural features, man-made structures, and elevation changes.
- Consider the context: Analyze the site’s location within the broader landscape.
- Consult with experts: Seek guidance from surveyors, engineers, or other professionals for accurate interpretation.
Conclusion
Topography maps serve as indispensable tools for understanding the physical characteristics of a site, providing essential information for planning, design, and development. From civil engineering and architecture to urban planning and environmental studies, these maps offer a comprehensive and accurate representation of the terrain, enabling informed decision-making across diverse fields. As technology advances, topography maps continue to evolve, incorporating advanced applications and enhancing their utility for navigating and shaping the landscape. By understanding the nuances of topography maps, individuals and organizations can unlock the potential of the land, fostering sustainable development and responsible stewardship of the environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Site Topography Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!