Delineating Vietnam’s Borders: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
Related Articles: Delineating Vietnam’s Borders: A Geographical and Historical Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delineating Vietnam’s Borders: A Geographical and Historical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delineating Vietnam’s Borders: A Geographical and Historical Perspective

Vietnam, a nation steeped in history and cultural richness, occupies a unique position on the Southeast Asian peninsula. Its borders, both terrestrial and maritime, have been shaped by centuries of political and social transformations, leaving an indelible mark on the country’s identity and its relationships with neighboring states. Understanding these borders, their evolution, and the complexities they embody provides a crucial lens through which to analyze Vietnam’s past, present, and future.
A Tapestry of Borders: Land and Sea
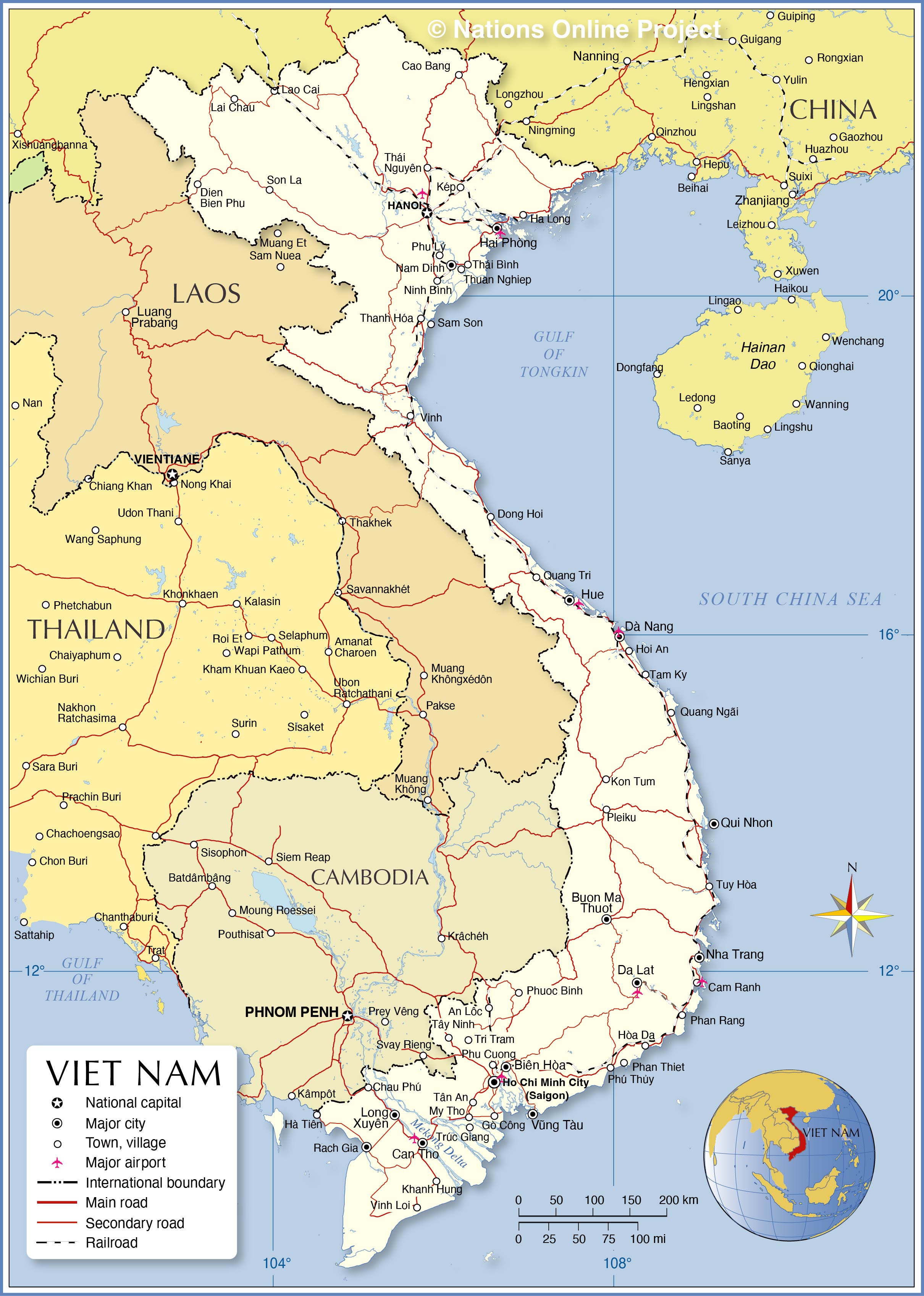
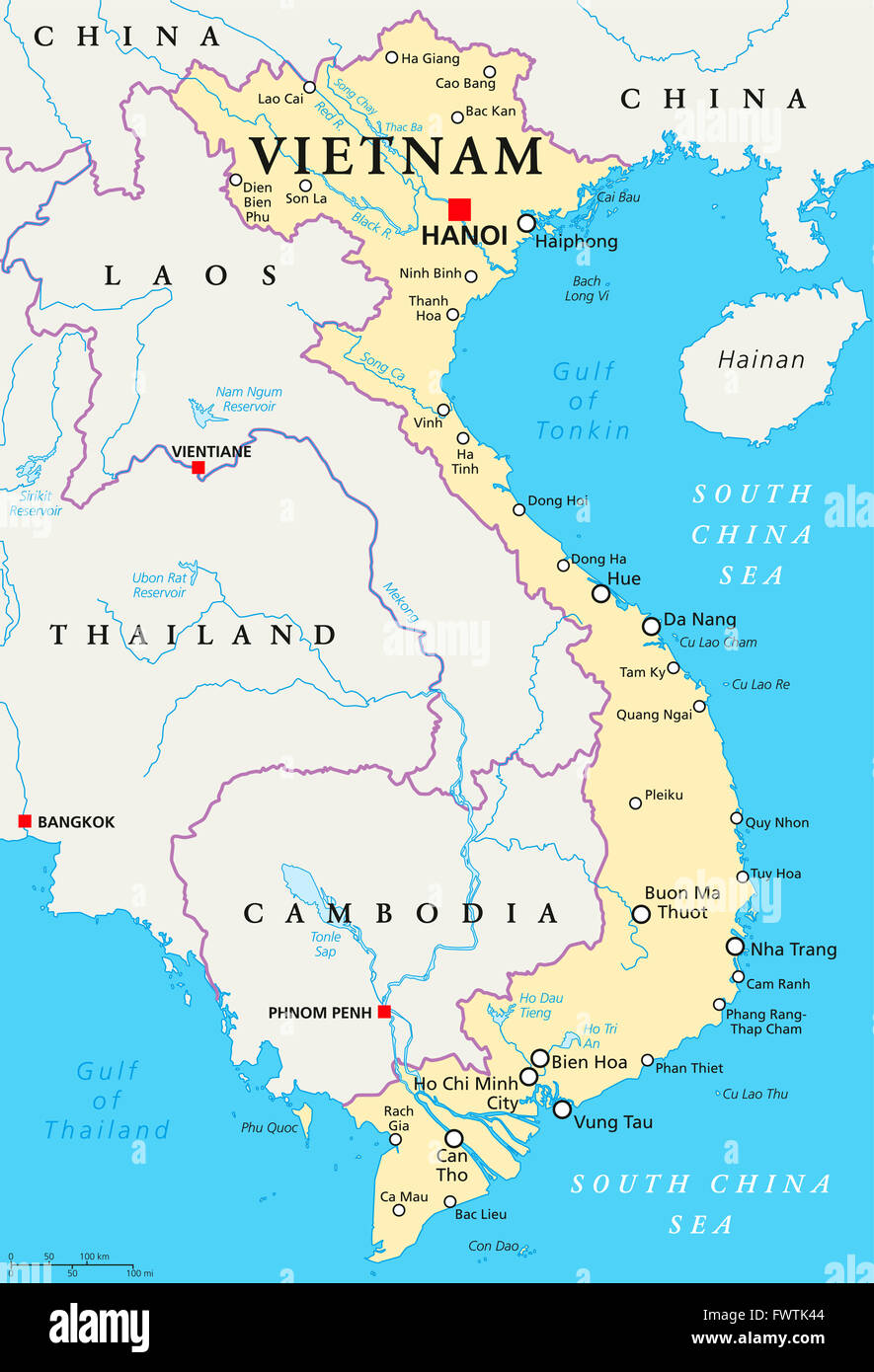
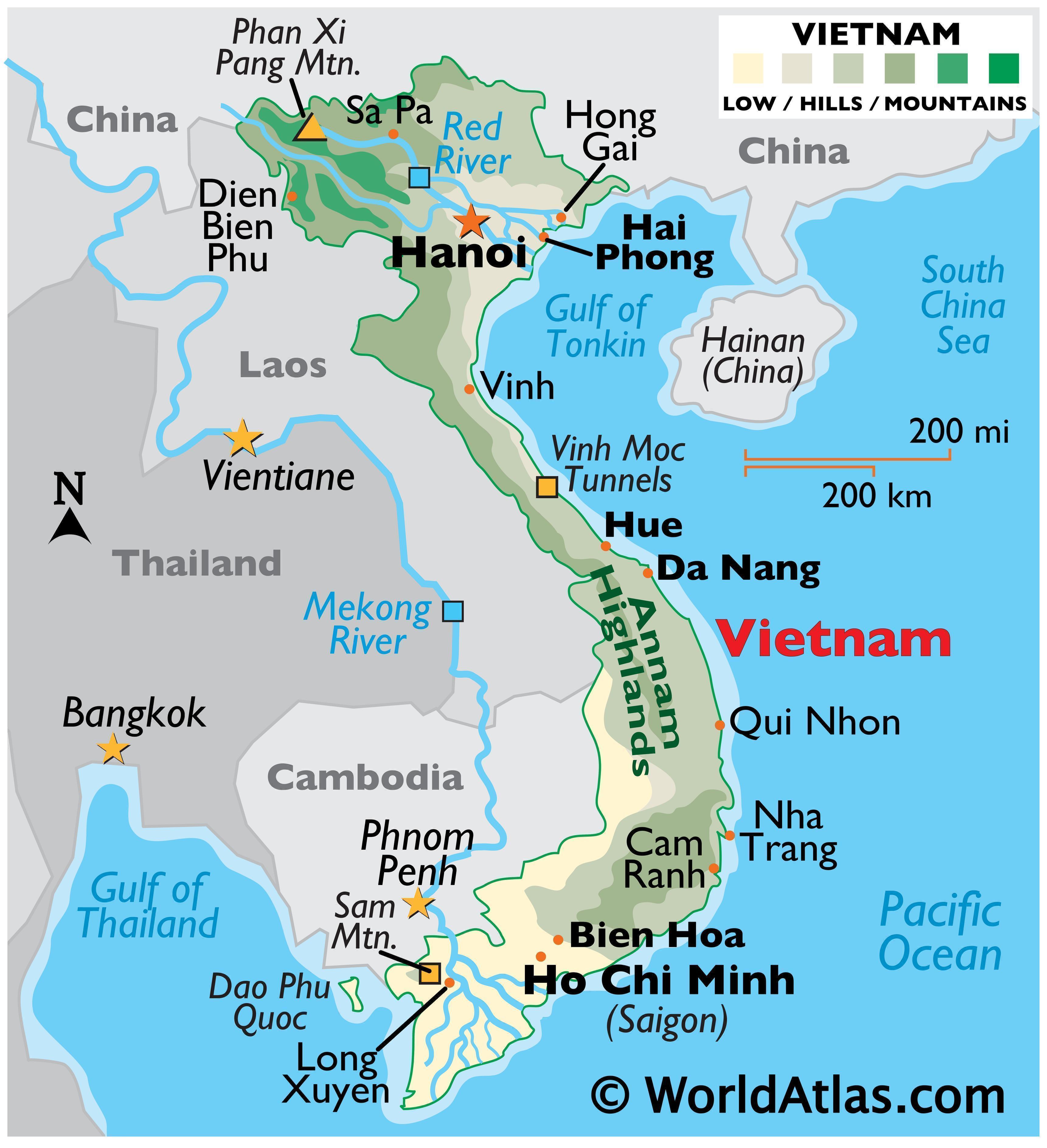
Vietnam’s land borders stretch for over 4,600 kilometers, encompassing a diverse array of landscapes, from the rugged peaks of the Annamite Cordillera to the verdant plains of the Mekong Delta. The country shares borders with five nations:
- China: In the north, a 1,450 kilometer border runs along the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, marked by the Red River and the rugged terrain of the Guangxi-Vietnam border region. This border has witnessed historical conflicts and periods of cooperation, shaping the political and economic dynamics between the two nations.
- Laos: The western border, spanning 2,130 kilometers, follows the Mekong River and traverses the mountainous Annamite Range. This shared border has been a point of contact for centuries, facilitating cultural exchange and economic ties between the two countries.
- Cambodia: In the southwest, a 1,228 kilometer border runs along the Mekong River and the Cardamom Mountains. This border has been relatively stable, fostering close cultural and economic ties between Vietnam and Cambodia.
- Thailand: The eastern border, measuring 1,870 kilometers, follows the Mekong River and the Dangrek Mountains. This border has been a point of contention in the past, with territorial disputes resolved through diplomatic efforts.
- Myanmar: A relatively short, 230 kilometer border exists in the westernmost point of Vietnam, following the Mekong River. This border has been less significant historically, but it remains a vital connection point for trade and cultural exchange.
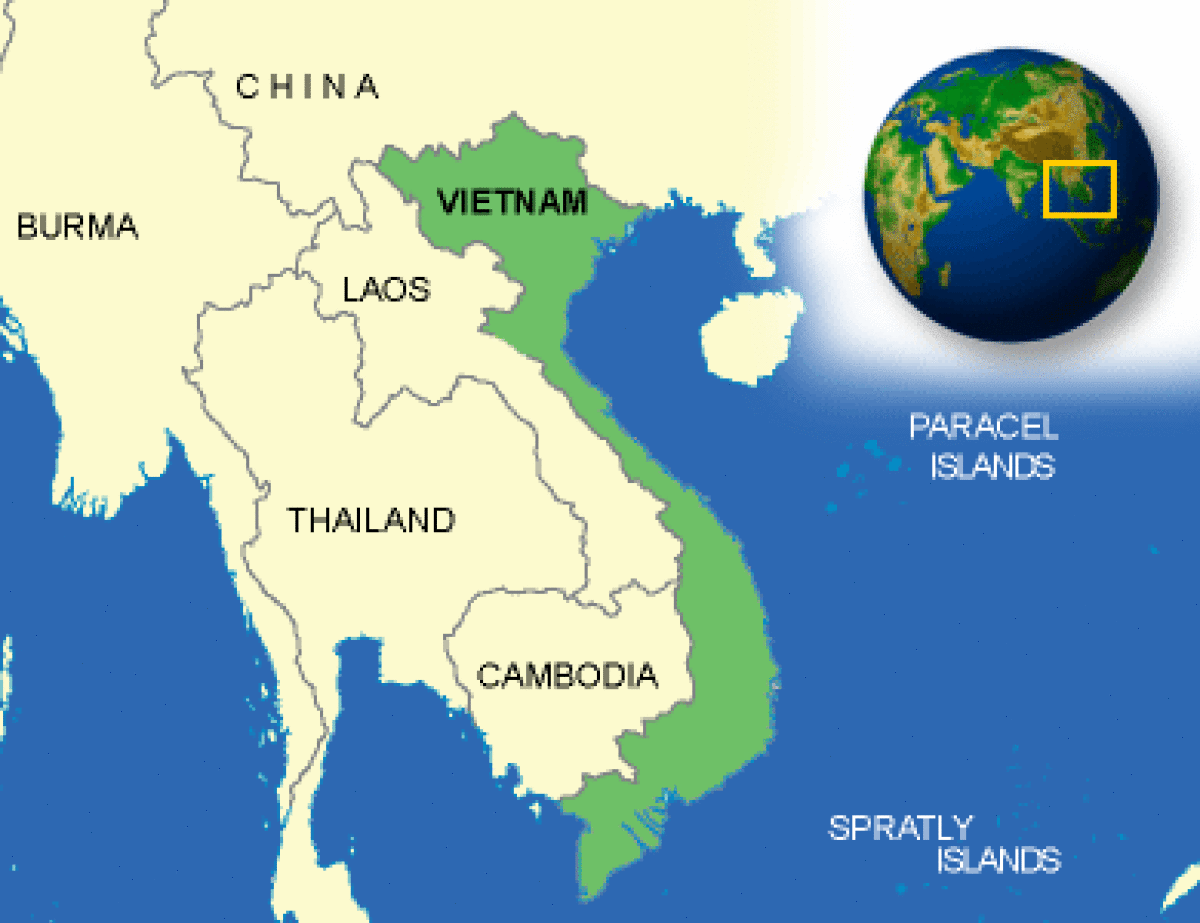
Beyond the terrestrial borders, Vietnam’s maritime boundaries extend into the South China Sea, a region of immense strategic and economic importance. These boundaries have been a source of contention, particularly with China, which claims sovereignty over much of the sea. Vietnam’s maritime claims are based on the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which defines Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) and territorial waters.
A Historical Journey: The Making of Vietnam’s Borders
The borders of modern-day Vietnam are a product of historical events, political struggles, and diplomatic negotiations.
- Pre-Colonial Era: Prior to the arrival of European powers, Vietnam’s borders were fluid and often subject to change due to shifting power dynamics between different kingdoms and empires. The Vietnamese kingdom of Đại Việt, for example, expanded its territory southwards, incorporating areas that are now part of Laos and Cambodia.
- Colonial Era: The French colonization of Vietnam in the 19th century marked a significant shift in the country’s borders. France, seeking to establish a unified Indochina, imposed its own boundaries, often ignoring pre-existing historical and cultural ties. The borders drawn by the French colonial administration, particularly those with Laos and Cambodia, have had lasting implications for the region’s political and social landscape.
- Post-Independence: Following Vietnam’s independence from France in 1954, the country was divided into North and South Vietnam. This division, along the 17th parallel, was a product of the Cold War and the competing interests of the United States and the Soviet Union. The reunification of Vietnam in 1975 marked the end of this division, but the legacy of the border continues to influence the country’s political and social fabric.
- Modern Era: In the post-Cold War era, Vietnam has focused on strengthening its relations with neighboring countries and resolving long-standing border disputes. The country has signed numerous border treaties and agreements, aiming to establish clear and stable boundaries and promote regional cooperation.
The Significance of Vietnam’s Borders
Understanding the geography and history of Vietnam’s borders is crucial for appreciating the country’s complex relationship with its neighbors. These borders:
- Shape Vietnam’s Identity: The borders define the country’s geographical limits and its cultural interactions with neighboring states. They have played a significant role in shaping Vietnamese identity and national consciousness.
- Influence Regional Security: The borders are a point of contact for various security concerns, including territorial disputes, transnational crime, and the flow of refugees. Vietnam’s relationship with its neighbors is intricately linked to its border security strategy.
- Facilitate Economic Development: The borders are crucial for trade, investment, and cultural exchange. They provide access to regional markets and facilitate the flow of goods, services, and people.
- Promote Regional Cooperation: Vietnam’s borders are a platform for fostering cooperation with neighboring countries on issues of mutual interest, such as environmental protection, infrastructure development, and disaster management.
FAQs on Vietnam’s Borders
Q: What are the major border disputes involving Vietnam?
A: The most significant border dispute involves Vietnam and China in the South China Sea. Both countries claim sovereignty over the Paracel and Spratly Islands, leading to tensions and military posturing in the region.
Q: How have Vietnam’s borders influenced its culture?
A: Vietnam’s borders have facilitated cultural exchange with neighboring countries, resulting in a blend of influences in its language, cuisine, religion, and art. The country’s cultural landscape is a testament to its diverse interactions with its neighbors.
Q: What role do Vietnam’s borders play in its economic development?
A: Vietnam’s borders are vital for its economic growth, facilitating trade with neighboring countries, attracting foreign investment, and providing access to regional markets.
Q: How is Vietnam managing its border security?
A: Vietnam has implemented a multi-layered approach to border security, including strengthening its border patrol, enhancing cooperation with neighboring countries, and investing in border infrastructure.
Tips for Understanding Vietnam’s Borders
- Study Maps: Consult detailed maps of Vietnam and its surrounding region to visualize the country’s borders and their relationship to neighboring countries.
- Research Historical Events: Explore the history of Vietnam’s borders, focusing on key events, treaties, and agreements that have shaped their evolution.
- Engage with News and Media: Stay informed about current events related to Vietnam’s borders, including political developments, economic partnerships, and security concerns.
- Travel to Border Regions: If possible, visit border regions in Vietnam to gain firsthand experience of the country’s geographical and cultural diversity.
Conclusion
Vietnam’s borders are more than just geographical lines on a map; they are a reflection of the country’s historical journey, its cultural identity, and its relationships with neighboring states. Understanding these borders, their complexities, and their significance is crucial for appreciating the dynamics of Southeast Asia and the challenges and opportunities that Vietnam faces in the 21st century. As Vietnam continues to navigate the complexities of its regional relationships, the understanding and management of its borders will remain central to its future success.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delineating Vietnam’s Borders: A Geographical and Historical Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!