Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps
The Earth’s surface is not a flat expanse. It is a dynamic landscape sculpted by geological processes, human activity, and the relentless forces of nature. Capturing this intricate three-dimensional reality on a two-dimensional surface requires a specialized map: a topographic map.
Topographic maps, often referred to as "topo maps," are essential tools for understanding and navigating the Earth’s varied terrain. They go beyond simple representations of location, providing a detailed depiction of elevation, landforms, and physical features. This information is conveyed through a system of contour lines, a unique language that translates the ups and downs of the landscape into a visual representation.
The Language of Contour Lines
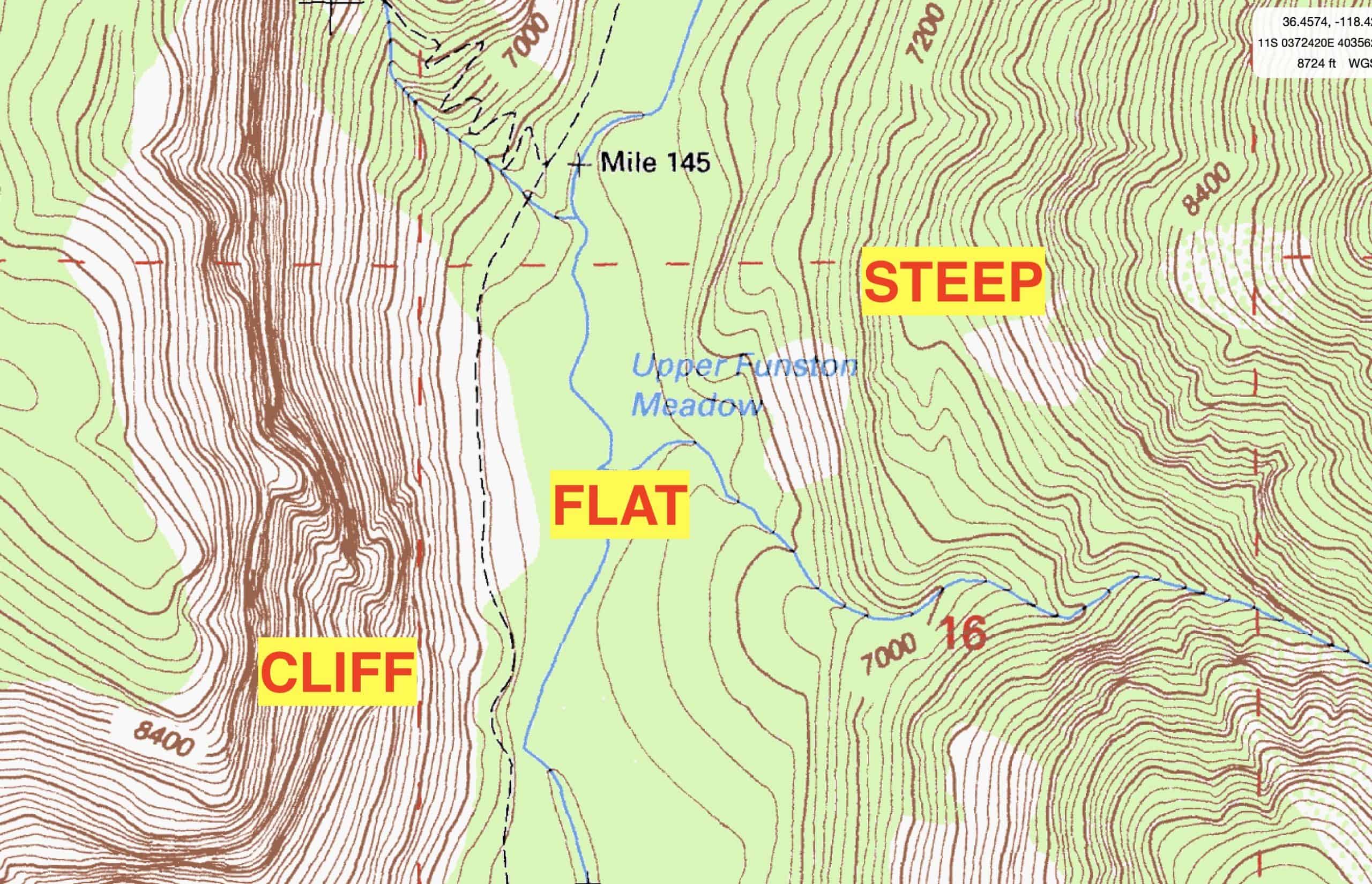
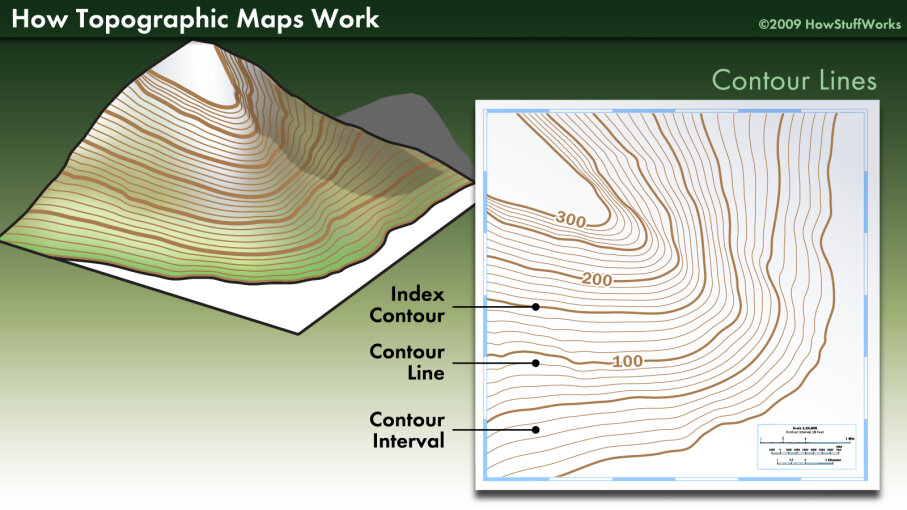
Contour lines are the heart of topographic maps. They are imaginary lines that connect points of equal elevation on the Earth’s surface. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the incline.
Imagine walking across a hill. As you ascend, you encounter a series of steps, each representing a change in elevation. Contour lines on a map mimic these steps, creating a visual representation of the terrain’s profile.
Beyond Elevation: A Rich Tapestry of Information
Topographic maps do not simply depict elevation; they offer a comprehensive understanding of the landscape’s physical characteristics. They incorporate a range of symbols and conventions to represent:
- Water features: Rivers, lakes, streams, and even marshes are meticulously mapped, providing valuable insights into water flow and drainage patterns.
- Vegetation: Forests, grasslands, and agricultural areas are differentiated by specific symbols, offering a glimpse into the land’s ecological diversity.
- Cultural features: Roads, railroads, bridges, and buildings are included, providing context for human activity and infrastructure development.
- Landform details: Canyons, valleys, ridges, and other distinctive features are depicted, providing a nuanced understanding of the landscape’s geological history.
The Importance of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps are indispensable tools for a wide range of applications, playing crucial roles in:
- Navigation: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic maps to navigate unfamiliar terrain, identifying safe routes, potential hazards, and points of interest.
- Land use planning: Urban planners, engineers, and architects utilize topographic maps to assess site suitability for development, infrastructure projects, and environmental impact assessments.
- Environmental studies: Geographers, ecologists, and environmental scientists utilize topographic maps to understand the distribution of natural resources, analyze land cover changes, and conduct ecological research.
- Military operations: Topographic maps are essential for military planning, allowing for the identification of strategic locations, the assessment of terrain challenges, and the development of tactical maneuvers.
- Disaster preparedness: Topographic maps are critical for disaster response and mitigation efforts, aiding in identifying areas at risk from floods, landslides, and other natural hazards.
FAQs about Topographic Maps
1. How do I read a topographic map?
Reading a topographic map requires understanding the language of contour lines. The closer the lines, the steeper the slope. Look for symbols representing water features, vegetation, and cultural features to gain a comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
2. What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A regular map primarily focuses on location and political boundaries. A topographic map goes beyond location, providing detailed information about elevation, landforms, and physical features.
3. Are topographic maps still relevant in the age of GPS?
While GPS technology provides accurate location data, topographic maps offer a more comprehensive understanding of the terrain, including elevation changes, landforms, and potential hazards. They remain valuable for navigation, planning, and environmental studies.
4. Where can I find topographic maps?
Topographic maps are available from various sources, including government agencies (like the United States Geological Survey), online mapping services, and specialized retailers.
5. Can I create my own topographic map?
Creating a topographic map requires specialized equipment and software. However, readily available mapping tools allow users to generate basic topographic representations using elevation data.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps
- Study the map legend: Understand the symbols and conventions used to represent different features.
- Identify contour intervals: The difference in elevation between adjacent contour lines.
- Look for steep slopes: Closely spaced contour lines indicate steep terrain.
- Analyze landforms: Identify ridges, valleys, and other landform features.
- Plan your route: Use the map to choose a safe and efficient path.
Conclusion
Topographic maps are essential tools for navigating, understanding, and managing the Earth’s diverse landscapes. They provide a unique perspective on the three-dimensional world, offering detailed information about elevation, landforms, and physical features. From hikers and climbers to urban planners and environmental scientists, topographic maps continue to play a vital role in a wide range of disciplines, empowering us to explore, analyze, and protect our planet.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depths: Understanding Topographic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!