Navigating the Fault Lines of Turkey: A Geological Landscape of Seismic Activity
Related Articles: Navigating the Fault Lines of Turkey: A Geological Landscape of Seismic Activity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Fault Lines of Turkey: A Geological Landscape of Seismic Activity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Fault Lines of Turkey: A Geological Landscape of Seismic Activity

Turkey, a nation straddling the crossroads of continents, is geographically positioned within a complex network of tectonic plates. This unique location, while contributing to its diverse landscapes, also renders it susceptible to seismic activity. Understanding the intricate web of fault lines that crisscross the country is crucial for mitigating the risks associated with earthquakes and fostering a culture of preparedness.
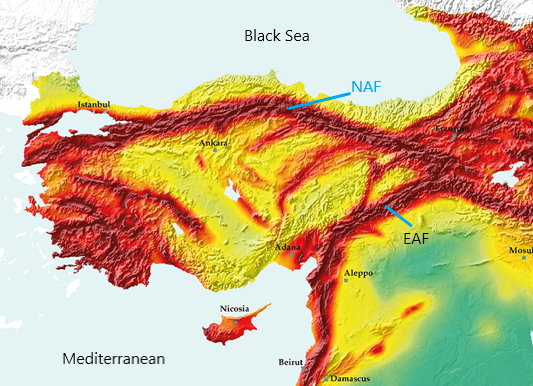
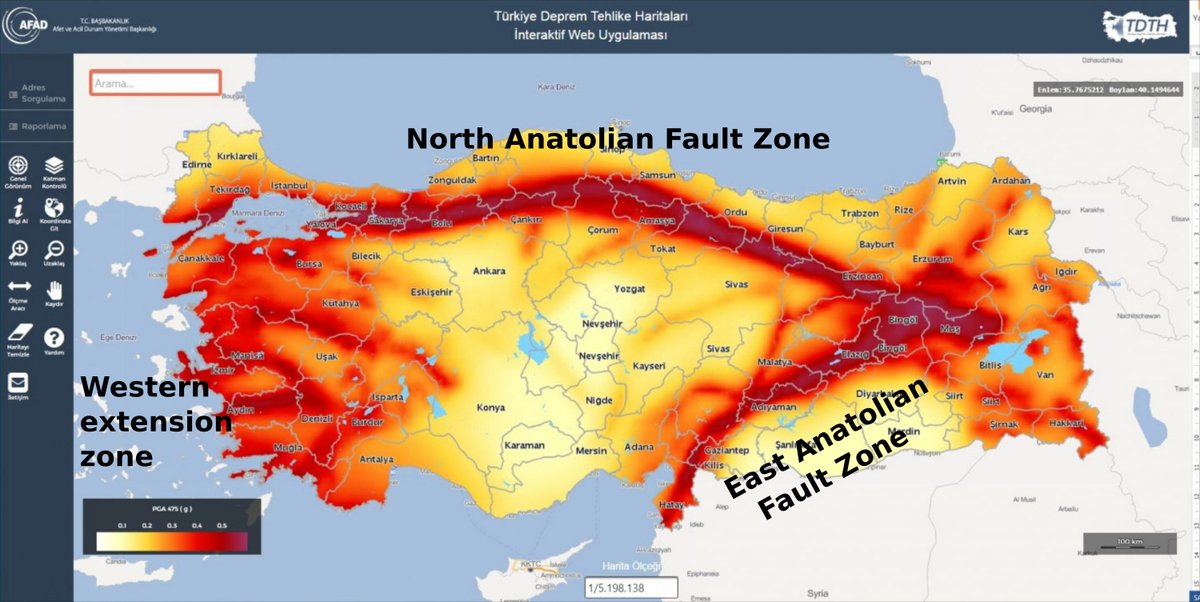
A Tectonic Tapestry: The North Anatolian Fault Zone
The North Anatolian Fault Zone (NAF), a prominent feature in Turkey’s geological landscape, is a right-lateral strike-slip fault stretching over 1,500 kilometers. This fault zone acts as a boundary between the Anatolian Plate and the Eurasian Plate, marking the zone where these massive landmasses grind against each other. The NAF is responsible for numerous historical earthquakes, including the devastating 1999 Izmit earthquake that claimed thousands of lives.
The East Anatolian Fault Zone: A Parallel Path of Seismic Activity
Running parallel to the NAF, the East Anatolian Fault Zone (EAF) is another major fault line traversing eastern Turkey. The EAF is a left-lateral strike-slip fault, where the Anatolian Plate moves westward relative to the Arabian Plate. This fault system is responsible for significant earthquakes, such as the 2011 Van earthquake, which caused widespread damage and loss of life.
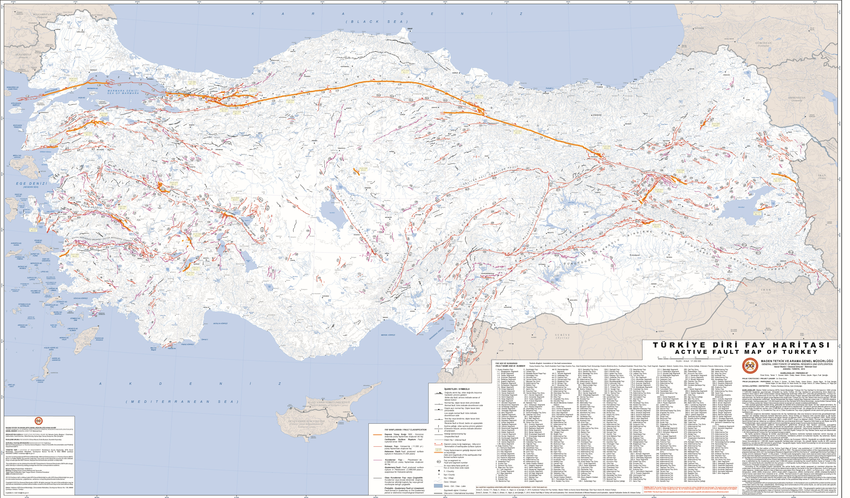
Beyond the Major Fault Zones: A Network of Secondary Faults
The NAF and EAF are not isolated entities but are part of a wider network of interconnected fault lines. Numerous secondary faults branch off from these major zones, contributing to the overall seismic activity in the region. These secondary faults, while less prominent, can still generate earthquakes with significant destructive potential.
The Importance of Understanding Fault Lines: A Foundation for Preparedness
The intricate network of fault lines in Turkey highlights the inherent seismic risk the country faces. Understanding the distribution, characteristics, and activity of these faults is paramount for:
- Earthquake Prediction and Early Warning Systems: By analyzing historical earthquake data, studying fault line geometry, and monitoring ground deformation, scientists can improve earthquake prediction models and develop early warning systems. This information can provide precious time for evacuation and mitigation efforts, potentially saving lives.
- Seismic Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation: Mapping and characterizing fault lines enable the assessment of seismic hazards in different regions. This information is crucial for urban planning, building codes, and infrastructure design. By incorporating earthquake resilience into building regulations and infrastructure development, the impact of future earthquakes can be significantly reduced.
- Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about seismic risks and promoting earthquake preparedness practices is essential for mitigating the consequences of earthquakes. By understanding the underlying geological factors, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure their safety and the safety of their communities.
FAQs about Turkey’s Fault Lines
Q: What is the most active fault line in Turkey?
A: The North Anatolian Fault Zone (NAF) is considered the most active and potentially dangerous fault line in Turkey, responsible for numerous devastating earthquakes throughout history.
Q: Are there any areas in Turkey that are less prone to earthquakes?
A: While the entire country is vulnerable to earthquakes, the westernmost regions of Turkey, particularly those far from the major fault zones, tend to experience lower seismic activity.
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Turkey?
A: Turkey experiences a significant number of earthquakes annually, ranging from minor tremors to major destructive events. The frequency and intensity of earthquakes vary depending on the specific location and the activity of nearby fault lines.
Q: What steps are being taken to address the earthquake risk in Turkey?
A: Turkey has implemented various measures to mitigate earthquake risk, including:
- Stricter Building Codes: Regulations have been strengthened to ensure buildings are designed and constructed to withstand seismic forces.
- Seismic Hazard Mapping: Detailed maps of earthquake risk zones are being developed to guide infrastructure development and urban planning.
- Earthquake Early Warning Systems: Efforts are underway to establish comprehensive early warning systems that can provide timely alerts to the population.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educational programs and public awareness campaigns are being conducted to promote earthquake preparedness and safety practices.
Tips for Earthquake Preparedness in Turkey
- Secure Heavy Objects: Securely fasten heavy objects like bookcases and mirrors to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Create a Family Emergency Plan: Develop a plan that outlines evacuation routes, meeting points, and communication strategies in case of an earthquake.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies like water, food, first-aid supplies, a flashlight, and a battery-powered radio.
- Learn First Aid and CPR: Basic first-aid and CPR skills can be crucial in providing immediate assistance during an earthquake.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on earthquake warnings and safety guidelines through official sources like the Disaster and Emergency Management Presidency (AFAD).
Conclusion: A Nation in Constant Motion
Turkey’s unique geological setting, characterized by a complex network of fault lines, makes it a region of significant seismic activity. Understanding the nature and behavior of these fault lines is essential for mitigating earthquake risks, promoting preparedness, and ensuring the safety of the Turkish population. By continuously researching, monitoring, and adapting to the dynamic geological landscape, Turkey can navigate the challenges of seismic activity and build a more resilient future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Fault Lines of Turkey: A Geological Landscape of Seismic Activity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!