Navigating the Neighborhood: A Geographic Exploration of Turkey’s Surroundings
Related Articles: Navigating the Neighborhood: A Geographic Exploration of Turkey’s Surroundings
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Neighborhood: A Geographic Exploration of Turkey’s Surroundings. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Neighborhood: A Geographic Exploration of Turkey’s Surroundings

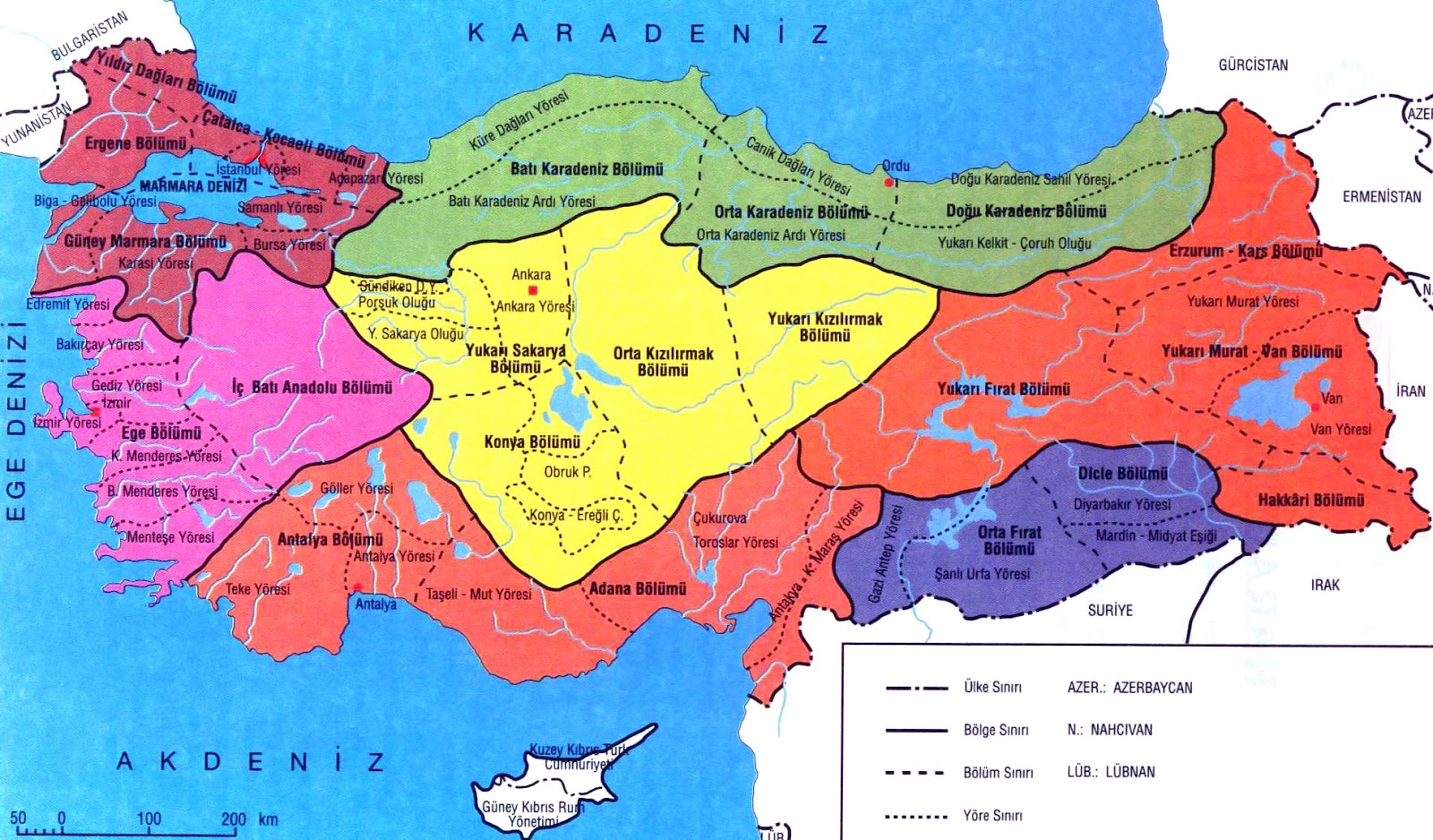
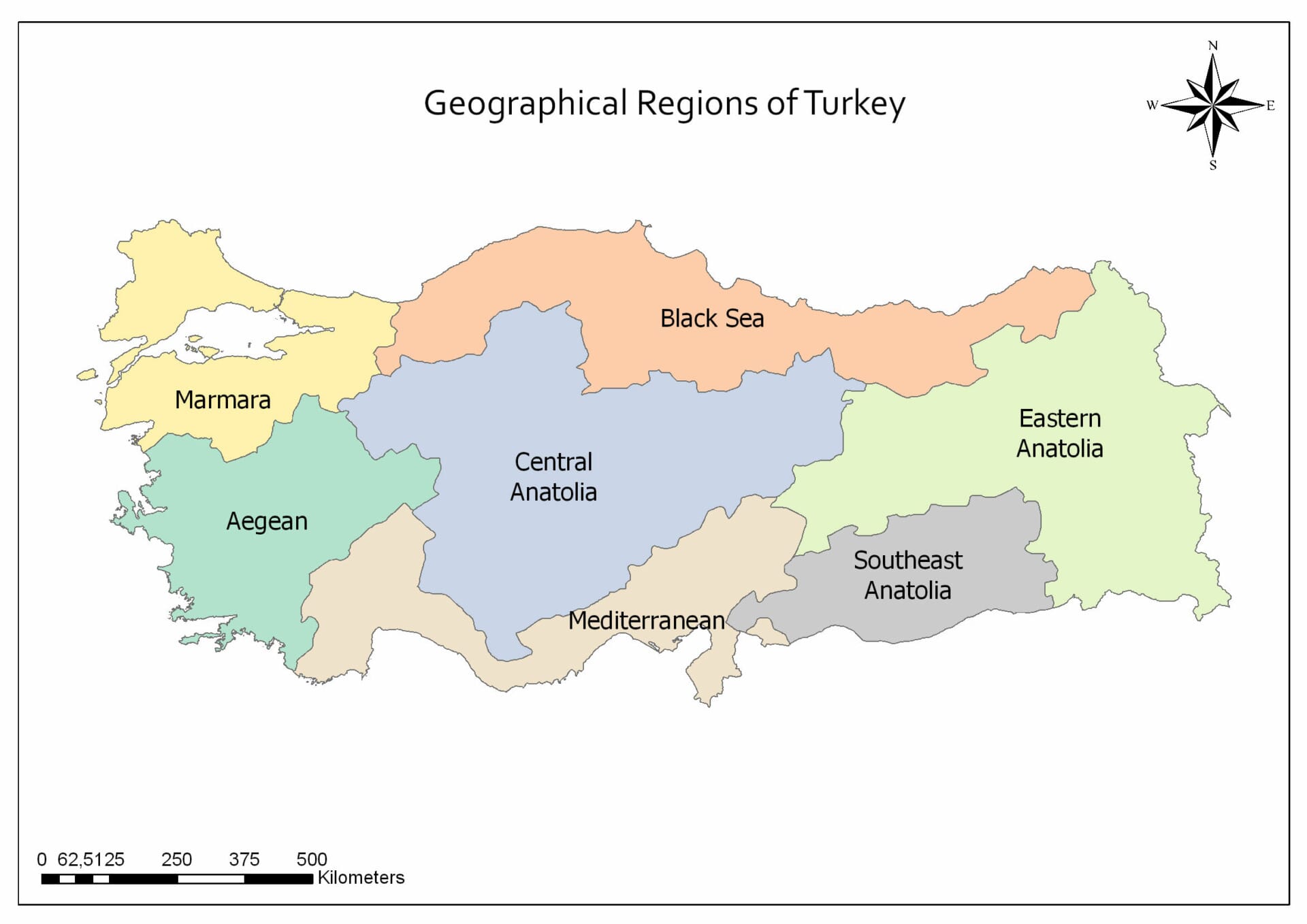
The Republic of Turkey, nestled at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, occupies a strategically vital location. Understanding the geographic relationships of Turkey with its neighboring countries is crucial for comprehending its history, culture, and contemporary challenges. This exploration delves into the map of countries surrounding Turkey, highlighting their unique connections and complexities.
A Tapestry of Borders:
Turkey shares land borders with eight countries, forming a diverse and dynamic regional landscape:
- To the west: Greece and Bulgaria, both European Union members, mark Turkey’s western frontier. These borders, steeped in history and interwoven with cultural exchange, have witnessed periods of both cooperation and tension.
- To the north: Georgia and Armenia, with their distinct cultural identities, lie north of Turkey. The border with Armenia remains closed due to historical disputes, while relations with Georgia have been marked by cooperation in recent years.
- To the east: Azerbaijan, a nation with strong cultural ties to Turkey, shares a border along the Caucasus Mountains. The border with Azerbaijan serves as a crucial conduit for trade and cultural exchange.
- To the south: Iran, Iraq, and Syria, all countries with complex internal dynamics, form Turkey’s southern borders. These borders have been impacted by regional conflicts and the influx of refugees, presenting significant challenges for Turkey.
Beyond Borders: A Network of Connections:
While land borders define immediate proximity, Turkey’s influence and connections extend far beyond these physical boundaries. The country’s strategic location on trade routes linking Europe, Asia, and the Middle East has historically made it a vital hub for commerce and cultural exchange.
The Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean:
Turkey’s coastline along the Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean Sea connects it to numerous island nations and coastal states. This maritime connection fosters trade, tourism, and cultural exchange with countries like Greece, Cyprus, and Egypt.
The Black Sea:
Turkey’s northern coast borders the Black Sea, connecting it to countries like Ukraine, Russia, and Romania. This maritime route plays a vital role in regional trade and energy transportation.
Understanding the Significance:
The map of countries surrounding Turkey reveals a complex interplay of historical, cultural, and economic factors. This geographic context sheds light on:
- Historical Influences: Turkey’s location has been shaped by the confluence of empires and civilizations, resulting in a rich cultural heritage and diverse population.
- Strategic Importance: Turkey’s strategic position at the crossroads of continents has made it a significant player in regional politics and international relations.
- Economic Ties: Turkey’s location facilitates trade and economic cooperation with its neighbors, making it a vital economic hub in the region.
- Security Concerns: The volatile nature of some neighboring countries, coupled with the presence of terrorist groups and regional conflicts, presents significant security challenges for Turkey.
FAQs:
1. What are the major geopolitical challenges facing Turkey due to its location?
Turkey’s location at the intersection of Europe, Asia, and the Middle East exposes it to various geopolitical challenges, including:
- Regional Conflicts: Turkey’s proximity to ongoing conflicts in Syria, Iraq, and the Caucasus region poses significant security risks and strains on its resources.
- Refugee Crisis: The influx of refugees fleeing conflict zones in neighboring countries has placed immense pressure on Turkey’s social and economic systems.
- Terrorist Threats: Turkey faces threats from various terrorist groups operating in the region, posing a significant challenge to its national security.
2. How does Turkey’s location impact its cultural identity?
Turkey’s location has been instrumental in shaping its unique cultural identity, characterized by:
- Cultural Fusion: Turkey’s history as a crossroads of civilizations has resulted in a rich tapestry of cultural influences, blending elements of European, Asian, and Middle Eastern traditions.
- Linguistic Diversity: The presence of various languages and dialects within Turkey reflects its diverse population and historical interactions.
- Religious Pluralism: Turkey is home to a range of religious communities, including Muslims, Christians, and Jews, reflecting its historical tolerance and diversity.
3. What are the economic opportunities and challenges arising from Turkey’s location?
Turkey’s strategic location offers significant economic opportunities, but also presents challenges:
- Trade Hub: Turkey’s location at the crossroads of continents makes it a vital hub for trade, connecting Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
- Infrastructure Development: Turkey’s strategic location necessitates robust infrastructure development, including transportation networks, energy pipelines, and communication systems.
- Economic Competition: Turkey faces competition from other regional economic powers, requiring it to enhance its competitiveness and attract foreign investment.
Tips:
- Study the history and culture of Turkey’s neighboring countries: Understanding their historical interactions and cultural nuances provides valuable context for comprehending Turkey’s own identity and relationships.
- Follow current events in the region: Staying informed about political developments, economic trends, and security issues in Turkey’s surrounding countries is crucial for understanding the dynamics at play.
- Explore Turkey’s diverse geography: From the snow-capped peaks of the Caucasus Mountains to the vibrant coastal cities of the Aegean Sea, Turkey’s varied landscape offers a captivating journey of discovery.
Conclusion:
The map of countries surrounding Turkey reveals a complex and dynamic regional landscape. Turkey’s location has been both a blessing and a challenge, shaping its history, culture, and contemporary realities. Understanding the intricate relationships between Turkey and its neighbors is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the region and its impact on global affairs. As Turkey navigates the challenges and opportunities presented by its strategic location, its relationship with its surrounding countries will continue to be a defining factor in its future trajectory.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Neighborhood: A Geographic Exploration of Turkey’s Surroundings. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!