Navigating the Shifting Landscape: The Power of Real-Time Topography
Related Articles: Navigating the Shifting Landscape: The Power of Real-Time Topography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Shifting Landscape: The Power of Real-Time Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Shifting Landscape: The Power of Real-Time Topography
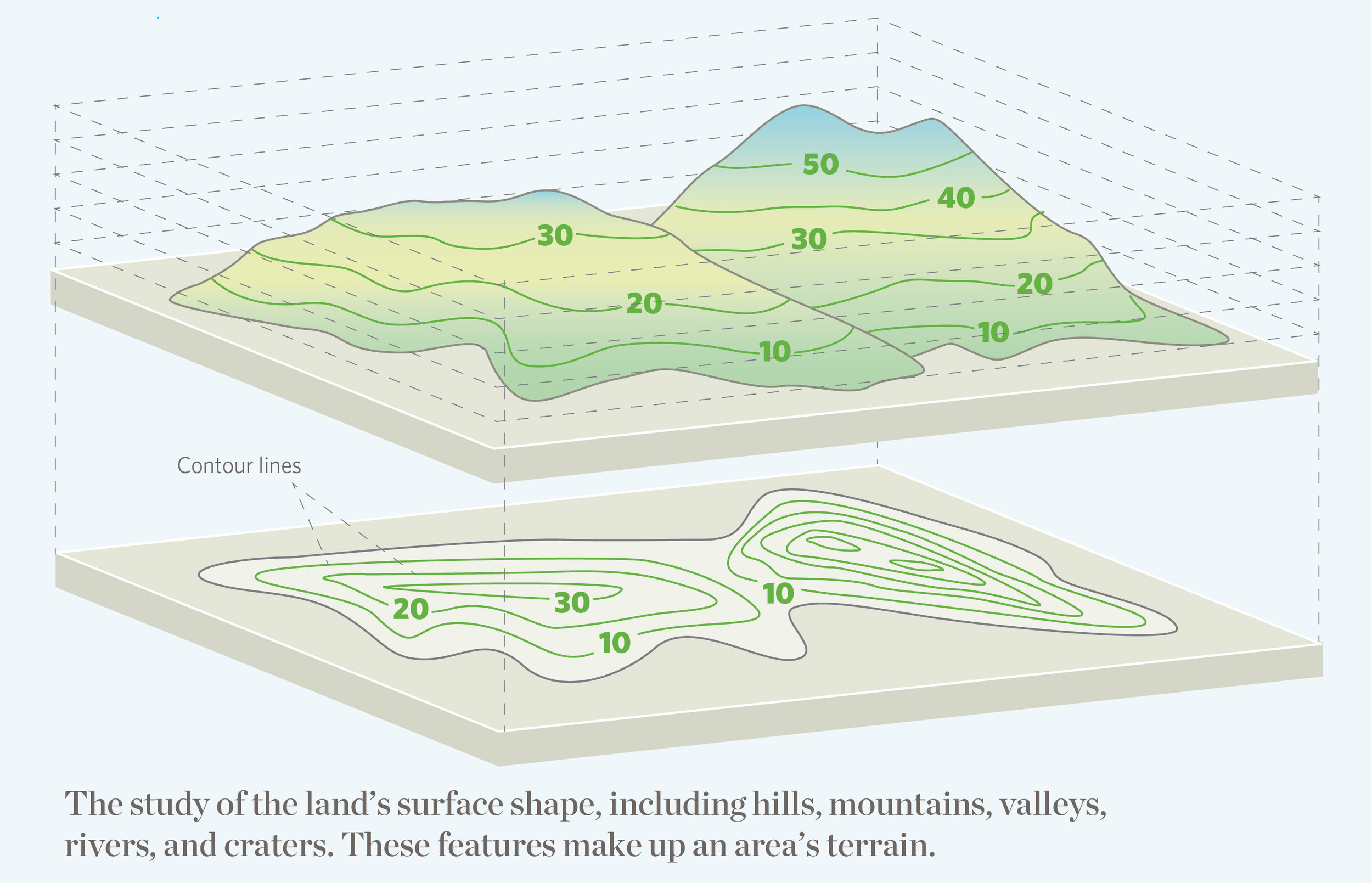
The Earth’s surface is a dynamic entity, constantly evolving under the influence of natural forces and human activities. Understanding these changes in real-time is crucial for a multitude of applications, from disaster response and environmental monitoring to urban planning and infrastructure development. This is where the concept of real-time topography maps comes into play, offering a dynamic and constantly updated picture of the terrain.
The Essence of Real-Time Topography
A real-time topography map is a digital representation of the Earth’s surface that updates itself continuously, reflecting the latest changes in elevation, land cover, and other relevant features. This dynamic visualization is achieved through the integration of various technologies, primarily:
- Remote Sensing: Satellites, drones, and airborne sensors capture images and data about the Earth’s surface, providing a bird’s-eye view of the terrain.
- Ground-Based Sensors: Ground-based sensors, such as laser scanners and GPS receivers, collect detailed information about specific areas, offering high-resolution data for precise mapping.
- Data Processing and Visualization: Sophisticated algorithms process the collected data, generating accurate and visually compelling 3D models of the terrain. These models are then displayed on interactive maps, allowing users to explore the changing landscape in real-time.
Benefits of Real-Time Topography
The ability to monitor and visualize the Earth’s surface in real-time offers a range of benefits across diverse fields:
- Disaster Management: During natural disasters like floods, earthquakes, and landslides, real-time topography maps provide critical information about the affected areas, enabling efficient rescue operations and damage assessment. The ability to track the progression of these events in real-time allows for informed decision-making and swift response.
- Environmental Monitoring: Real-time topography maps play a crucial role in environmental monitoring, enabling the tracking of deforestation, soil erosion, and changes in water bodies. This information is vital for sustainable resource management, biodiversity conservation, and climate change mitigation.
- Infrastructure Development: When planning and constructing infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, real-time topography maps provide accurate data about the terrain, facilitating efficient design, construction, and maintenance.
- Urban Planning: Real-time topography maps contribute to effective urban planning by providing detailed information about land use, population density, and infrastructure development. This data helps optimize urban design, transportation networks, and resource allocation.
- Military Operations: Real-time topography maps are essential for military operations, offering detailed terrain information for planning and executing missions, as well as for navigation and situational awareness.
- Scientific Research: Researchers across various disciplines rely on real-time topography maps for studying geological processes, climate change impacts, and biodiversity distribution.
Real-Time Topography in Action
The applications of real-time topography are diverse and impactful. Here are some prominent examples:
- Flood Monitoring: Real-time topography maps are used to monitor flood events, providing crucial information about water levels, inundation zones, and potential risks. This information is vital for early warning systems and evacuation planning.
- Volcanic Activity: Real-time topography maps help monitor volcanic activity, tracking changes in the terrain and detecting potential eruptions. This information assists in hazard assessment and mitigation efforts.
- Landslide Prediction: By analyzing the terrain and detecting changes in elevation, real-time topography maps can help predict and prevent landslides, ensuring public safety and infrastructure stability.
- Forest Management: Real-time topography maps allow for the monitoring of deforestation rates, tracking changes in forest cover and identifying areas prone to illegal logging. This information is essential for sustainable forest management and biodiversity conservation.
- Construction and Mining: Real-time topography maps are used in construction and mining operations to monitor progress, track material movement, and ensure safety. This information optimizes efficiency and minimizes environmental impact.
FAQs about Real-Time Topography Maps
Q: What are the different types of real-time topography maps?
A: Real-time topography maps can be categorized based on the data sources and the level of detail:
- Satellite-based maps: These maps utilize data from satellites, offering wide coverage and frequent updates.
- Drone-based maps: Drones equipped with sensors capture high-resolution data, providing detailed information about specific areas.
- Ground-based maps: These maps are generated using ground-based sensors, offering the highest level of detail and precision.
Q: What are the limitations of real-time topography maps?
A: Real-time topography maps are not without limitations:
- Data availability: Data availability and frequency can vary depending on the location and the technology used.
- Cost: Developing and maintaining real-time topography systems can be expensive.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of real-time topography maps depends on the quality of the data sources and the processing algorithms.
- Privacy concerns: The use of aerial imagery and ground-based sensors can raise privacy concerns.
Q: What are the future trends in real-time topography?
A: The future of real-time topography is promising:
- Increased data availability: Advancements in remote sensing technologies and sensor networks will lead to increased data availability and higher frequency updates.
- Improved accuracy: The development of more sophisticated algorithms and data processing techniques will improve the accuracy of real-time topography maps.
- Integration with other technologies: Real-time topography maps will be integrated with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to provide more comprehensive and insightful information.
- Wider adoption: The increasing availability and affordability of real-time topography technologies will lead to wider adoption across various industries and applications.
Tips for Using Real-Time Topography Maps Effectively
- Identify the specific needs: Determine the specific application and the level of detail required for the desired outcome.
- Choose the right technology: Select the appropriate data sources and mapping technology based on the specific needs and budget.
- Validate the data: Ensure the accuracy of the data by comparing it with other sources and verifying the information.
- Interpret the data correctly: Understand the limitations of the data and interpret the information correctly to avoid misinterpretations.
- Stay updated: Keep up with the latest advancements in real-time topography technologies and data sources.
Conclusion
Real-time topography maps are a powerful tool for understanding and managing the ever-changing landscape of our planet. By providing a dynamic and constantly updated picture of the terrain, these maps empower decision-making across diverse fields, from disaster response and environmental monitoring to infrastructure development and scientific research. As technology continues to advance, real-time topography maps will play an increasingly vital role in shaping a more sustainable and resilient future.
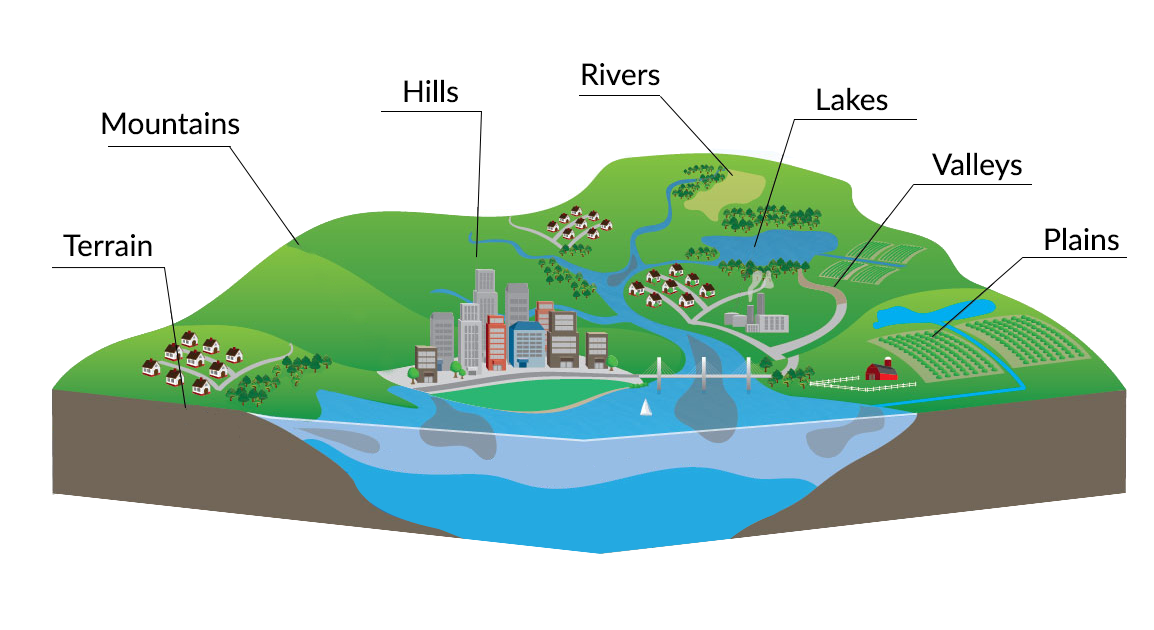






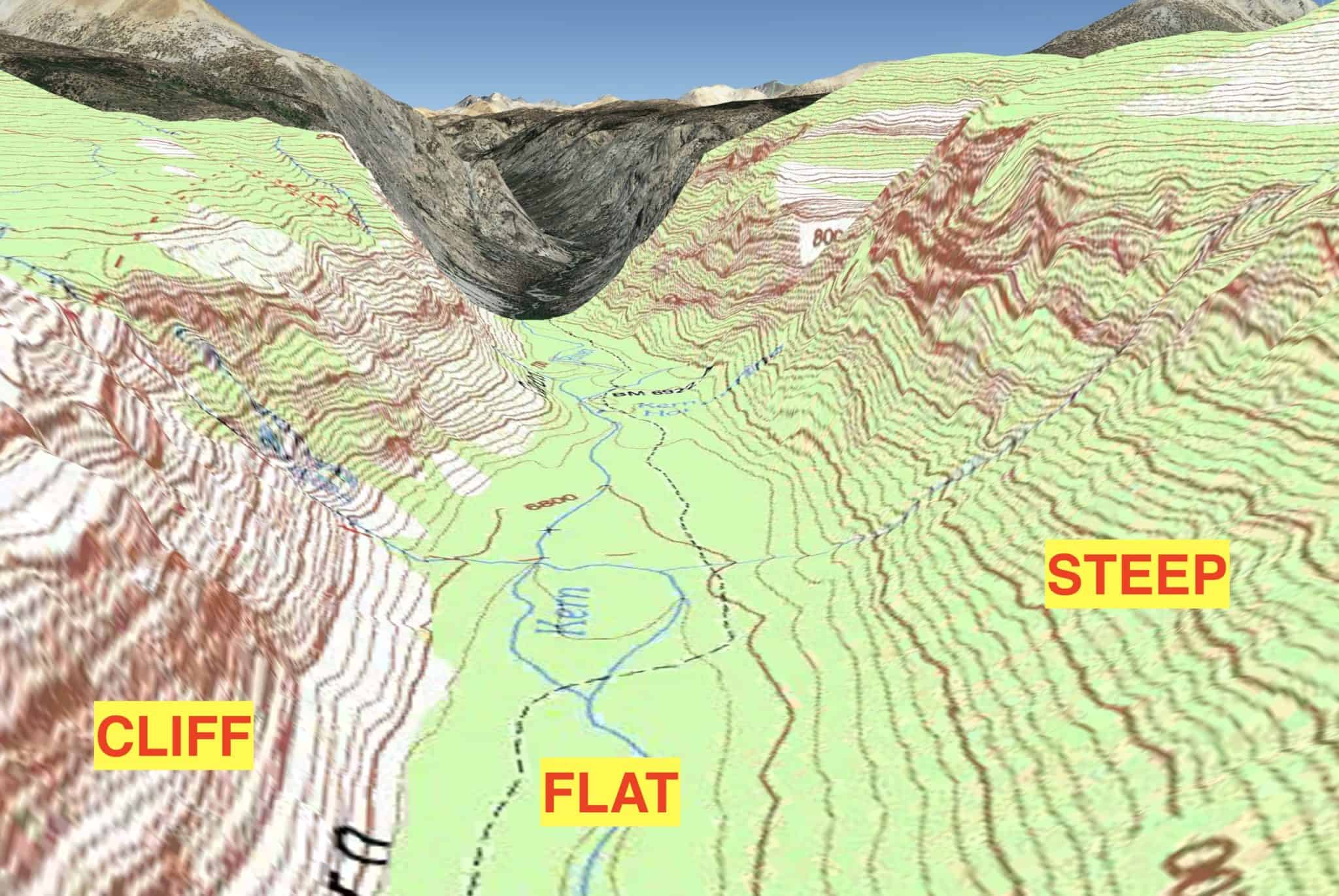
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Shifting Landscape: The Power of Real-Time Topography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!