Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Topographic Guide to Hiking Trails
Related Articles: Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Topographic Guide to Hiking Trails
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Topographic Guide to Hiking Trails. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Topographic Guide to Hiking Trails

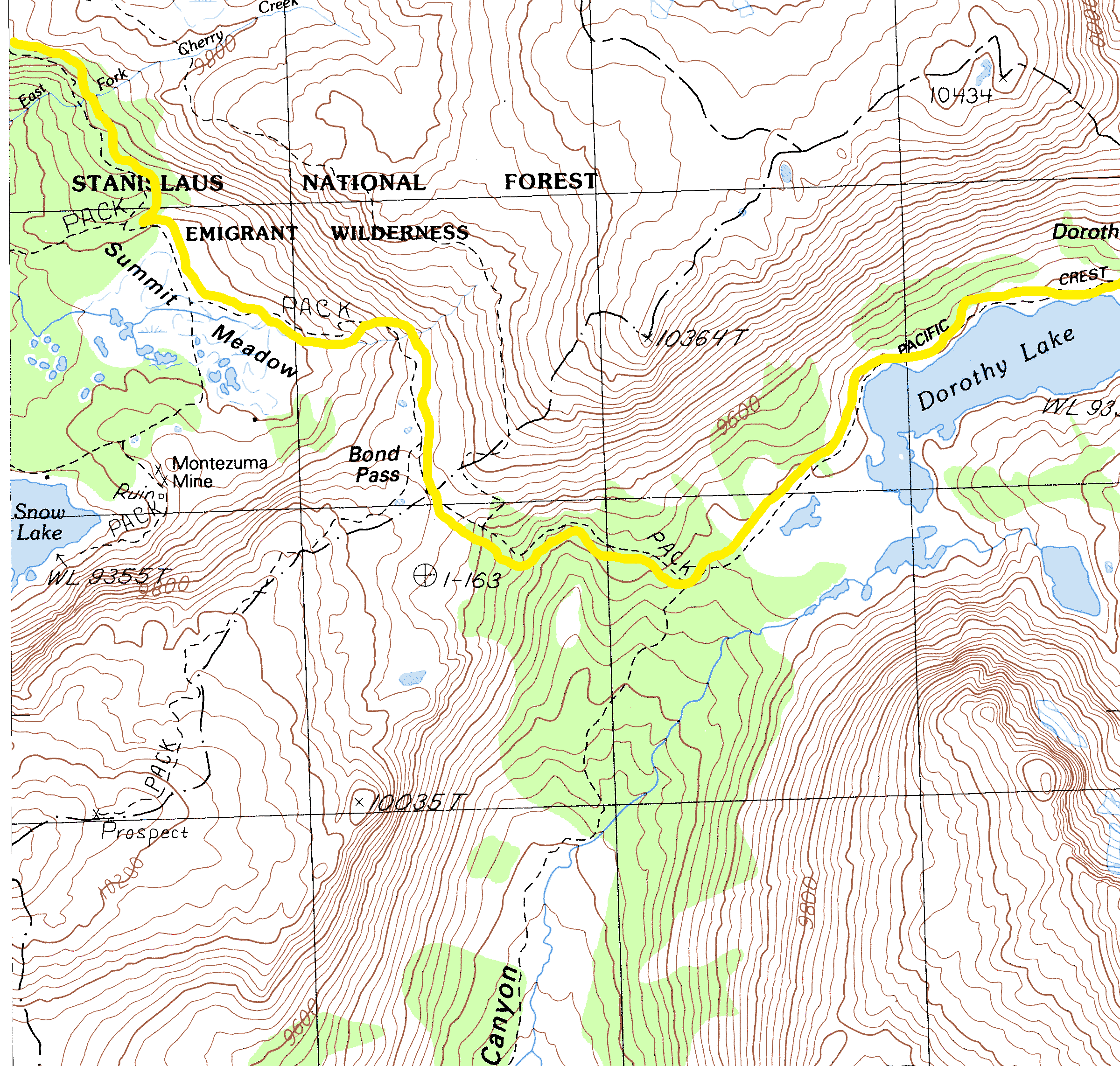
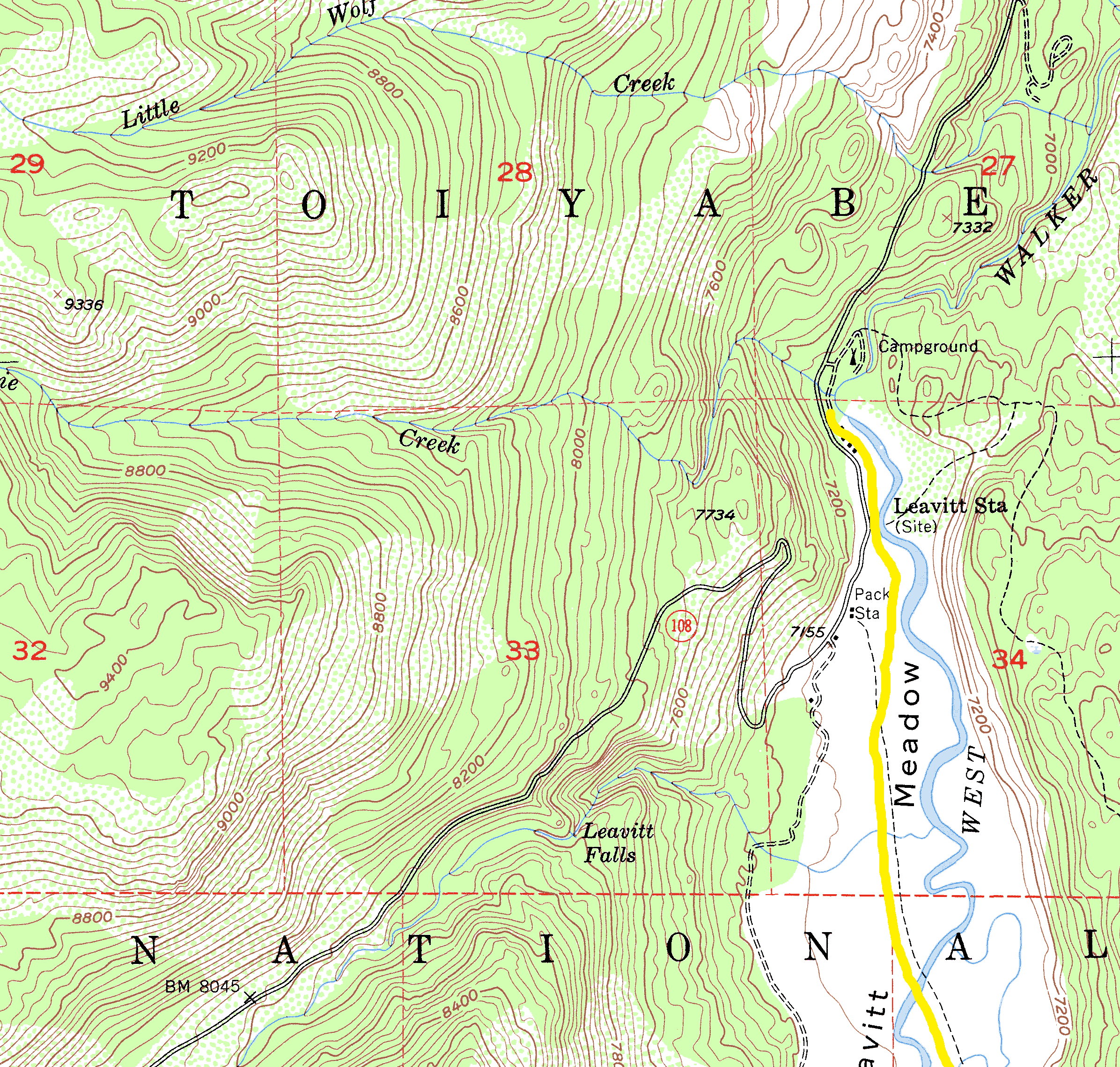
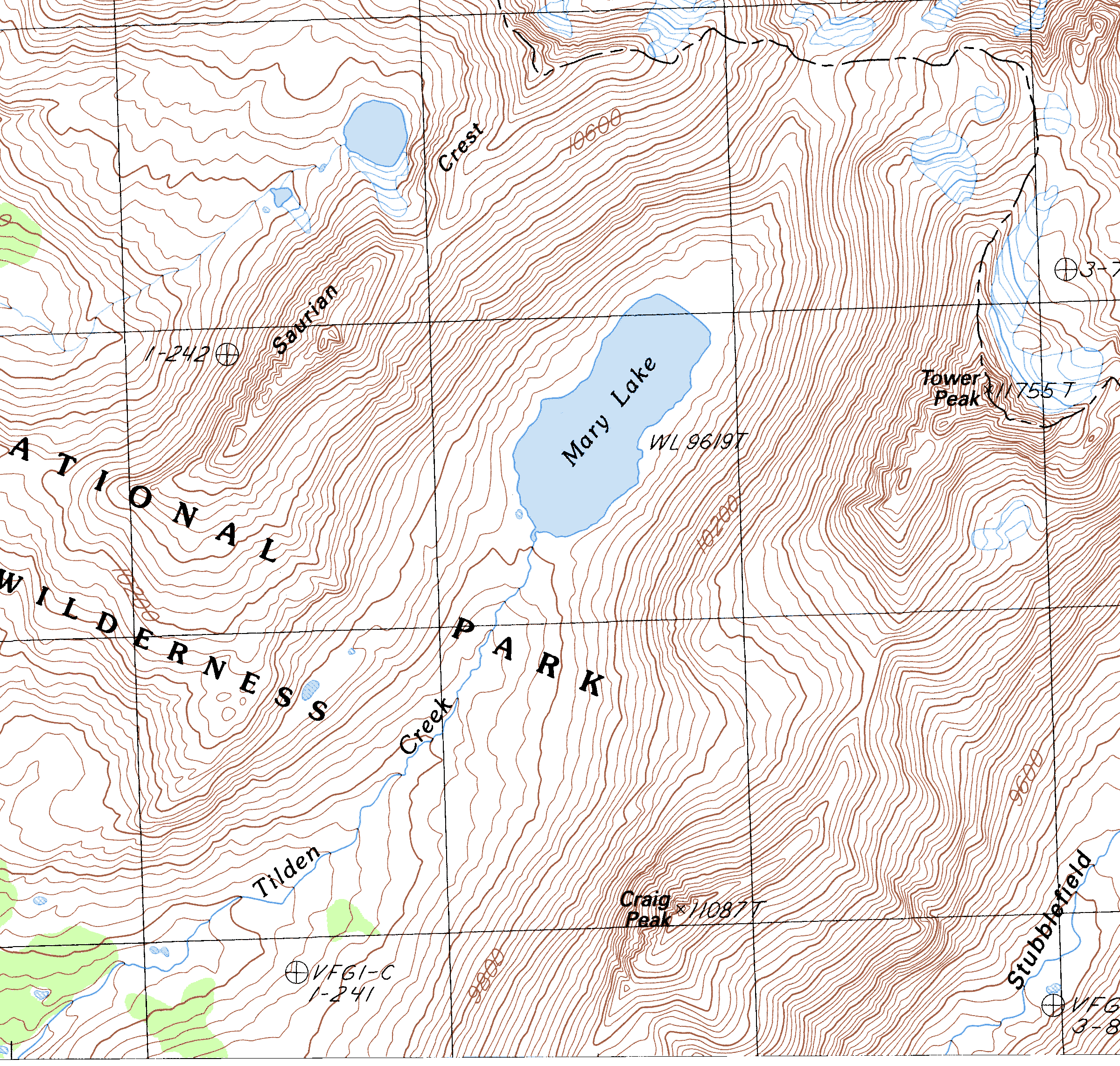
The Sierra Nevada mountain range, a majestic spine running through California, offers a breathtaking landscape of towering granite peaks, deep valleys, and sparkling alpine lakes. This diverse terrain presents a paradise for hikers, each trail offering a unique perspective on the region’s natural beauty. However, navigating this vast and varied landscape requires a thorough understanding of its topography, and that’s where a Sierra Nevada topography hiking trails map becomes an invaluable tool.
Understanding the Sierra’s Topography
The Sierra Nevada’s topography is characterized by dramatic elevation changes, with peaks reaching over 14,000 feet and valleys plunging to elevations below 5,000 feet. This variation in altitude creates a diverse array of ecosystems, ranging from chaparral and oak woodlands at lower elevations to subalpine forests and alpine meadows higher up.
Key Topographic Features:
- Granite Peaks: The Sierra Nevada is renowned for its towering granite peaks, including Mount Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous United States. These peaks are often formed by glacial erosion, resulting in sharp, jagged ridges and deep, U-shaped valleys.
- Glacial Valleys: Glaciers have carved deep valleys through the Sierra Nevada, creating stunning landscapes with cascading waterfalls, alpine meadows, and crystal-clear lakes. Yosemite Valley, with its towering granite cliffs and cascading waterfalls, is a prime example of this glacial influence.
- Rivers and Streams: The Sierra Nevada is home to numerous rivers and streams that flow down from the high peaks, carving through the landscape and creating fertile valleys. These waterways are essential for the region’s biodiversity and provide scenic hiking opportunities.
- Forests: The Sierra Nevada boasts a variety of forest types, from the mixed conifer forests at lower elevations to the subalpine forests dominated by pines and firs. These forests provide habitat for a wide range of wildlife and offer a sense of serenity to hikers.
- Alpine Meadows: At higher elevations, above the treeline, lie alpine meadows, characterized by wildflowers, stunning views, and a unique microclimate. These meadows are often home to rare plant and animal species.
The Importance of a Topographic Map
A Sierra Nevada topography hiking trails map is more than just a simple guide; it’s a critical tool for safe and enjoyable hiking. It provides crucial information about:
- Elevation: The map clearly depicts elevation contours, allowing hikers to assess the difficulty of the trail and plan accordingly.
- Trail Gradient: Knowing the gradient of the trail helps hikers anticipate challenging climbs and descents, allowing them to pace themselves and bring appropriate gear.
- Water Sources: The map often indicates the location of streams, rivers, and lakes, essential for staying hydrated during long hikes.
- Terrain Features: The map highlights key terrain features like cliffs, canyons, and steep slopes, enabling hikers to avoid potential hazards.
- Trail Junctions: Navigating complex trail systems is simplified with a map that clearly marks junctions and alternative routes.
Benefits of Using a Topographic Hiking Trails Map:
- Increased Safety: Understanding the terrain and potential hazards through the map helps hikers make informed decisions and avoid dangerous situations.
- Enhanced Planning: By studying the map, hikers can plan their routes, estimate hiking times, and pack appropriate gear for the anticipated conditions.
- Improved Navigation: The map provides clear landmarks and trail markings, allowing hikers to stay on course and avoid getting lost.
- Enriched Experience: By understanding the topography, hikers gain a deeper appreciation for the landscape’s beauty and the forces that shaped it.
FAQs about Sierra Nevada Topography Hiking Trails Maps:
Q: What types of maps are available for Sierra Nevada hiking trails?
A: Several types of maps are available, including:
- Topographic Maps: These maps, often published by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), provide detailed elevation contours and terrain features.
- Trail Maps: These maps focus specifically on hiking trails, often including information about trail difficulty, distance, and points of interest.
- Online Mapping Tools: Websites and apps like Gaia GPS, AllTrails, and Google Maps offer digital versions of topographic and trail maps.
Q: How do I choose the right map for my hike?
A: Consider the following factors:
- Trail Difficulty: Choose a map with detailed elevation contours and trail markings for challenging hikes.
- Area of Interest: Select a map that covers the specific area you plan to hike.
- Personal Preference: Some hikers prefer paper maps, while others prefer digital versions.
Q: How do I read a topographic map?
A: Topographic maps use contour lines to represent elevation. Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, and the closer the lines, the steeper the terrain.
Q: What other resources should I use in conjunction with a map?
A: In addition to a map, consider using:
- Compass: A compass is essential for navigation, especially in areas with limited landmarks.
- GPS Device: A GPS device can provide precise location information and help track your progress.
- Guidebook: A guidebook can offer additional information about the trail, including historical facts, points of interest, and wildlife sightings.
Tips for Using a Sierra Nevada Topography Hiking Trails Map:
- Study the Map Beforehand: Familiarize yourself with the trail route, elevation changes, and potential hazards before starting your hike.
- Mark Your Route: Use a pen or marker to highlight your planned route on the map.
- Check for Updates: Maps can become outdated, so check for recent updates or revisions before using them.
- Carry a Map with You: Always bring a physical or digital copy of the map with you on your hike.
- Know How to Use a Compass: Learn the basics of compass navigation in case you need to find your way back to the trail.
Conclusion:
A Sierra Nevada topography hiking trails map is an essential tool for anyone venturing into this majestic mountain range. By providing detailed information about elevation, terrain, and trail features, it empowers hikers to plan their routes, assess risks, and navigate safely. Understanding the topography of the Sierra Nevada not only enhances the hiking experience but also fosters a deeper appreciation for this unique and awe-inspiring landscape.


![↪PDF Pacific Crest Trail: Sierra Nevada North [Sierra Buttes to Devil's Postpile] (National](https://www.yumpu.com/fr/image/facebook/66430193.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Sierra Nevada: A Topographic Guide to Hiking Trails. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
