Navigating the Waters: Understanding Utah’s Flood Zone Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters: Understanding Utah’s Flood Zone Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters: Understanding Utah’s Flood Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Waters: Understanding Utah’s Flood Zone Map
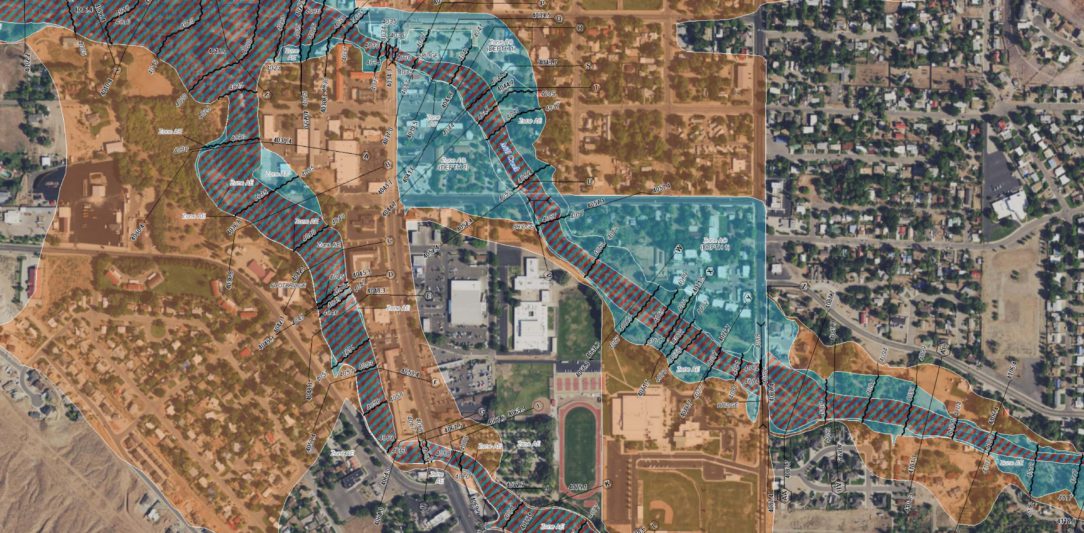
Utah, a state known for its dramatic landscapes and arid climate, is also vulnerable to the destructive force of floods. These events, while often unpredictable, can devastate communities and infrastructure, leaving behind lasting impacts. To mitigate these risks and guide informed decision-making, the state utilizes a comprehensive flood zone map, a critical tool for understanding flood hazards and promoting resilience.
Delving into the Depths: Understanding the Flood Zone Map
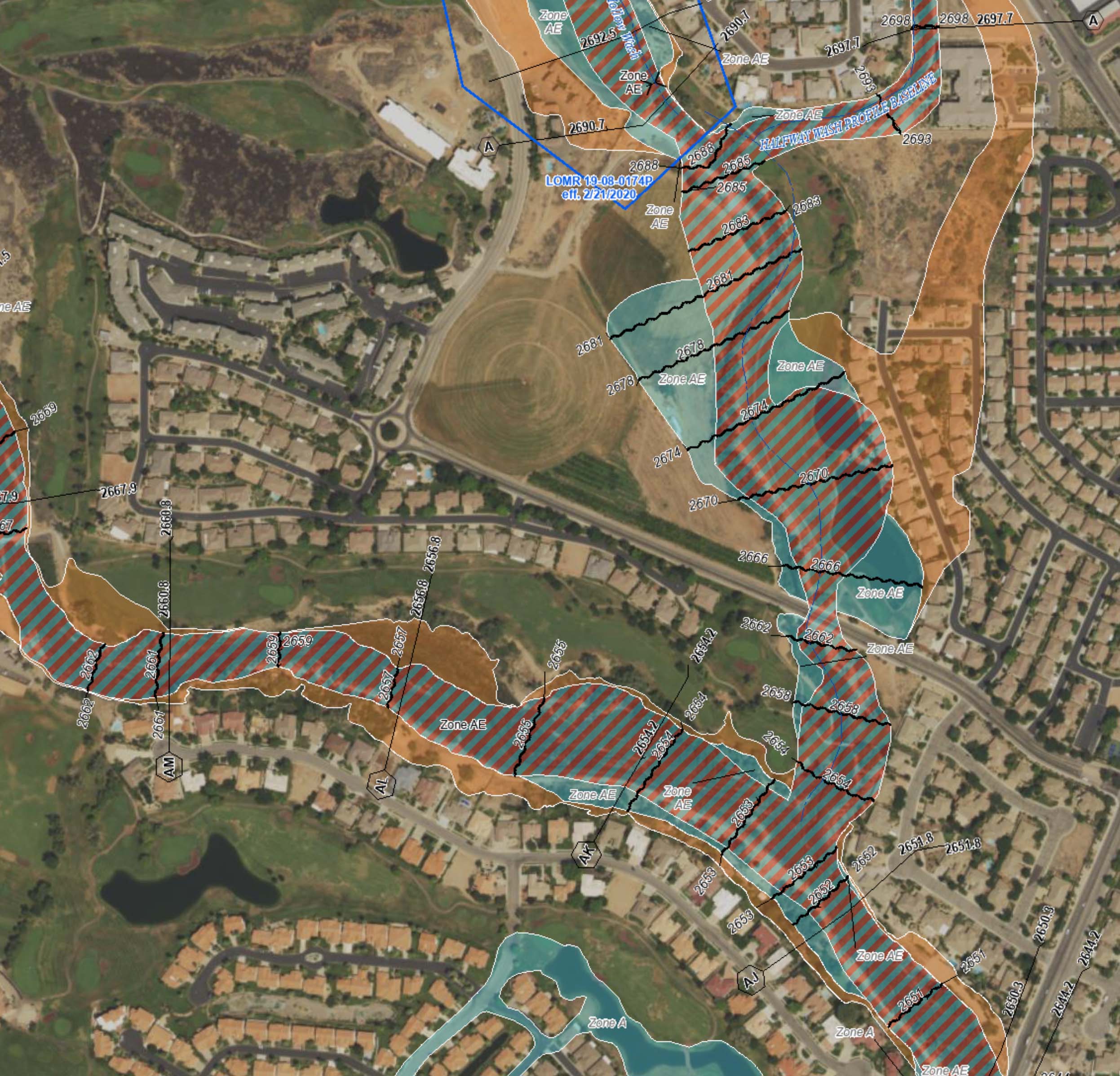
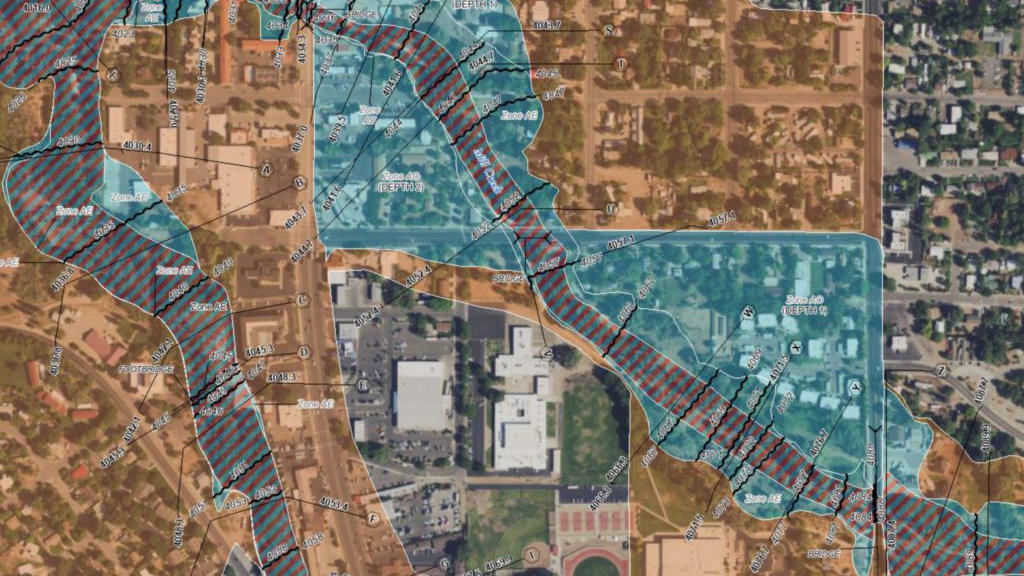
The Utah Flood Zone Map, developed and maintained by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), is a vital resource that delineates areas susceptible to flooding. It categorizes land into different flood zones based on the likelihood of flooding, the depth of potential floodwaters, and the frequency of such events. This map is a cornerstone for understanding flood risk, guiding development, and implementing effective mitigation strategies.
The Anatomy of a Map: Flood Zone Classifications
The flood zone map employs a standardized system to classify areas based on their flood risk. This system utilizes letters and numbers, each representing distinct characteristics:
1. Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHA): These zones represent areas with a 1% chance of experiencing a flood in any given year. This translates to a 26% chance of flooding over a 30-year period. SFHAs are further subdivided into:
- Zone A: Areas where flood hazards are identified but specific flood data is not available.
- Zone AE: Areas with a defined base flood elevation (BFE), representing the highest level of floodwaters expected during a 100-year flood.
- Zone AO: Areas with a defined flood depth, indicating the expected depth of floodwaters during a 100-year flood.
- Zone AH: Areas with a defined base flood elevation (BFE) and a specific flood depth.
- Zone AR: Areas with a defined base flood elevation (BFE) and a specific flood depth, indicating a special flood hazard due to the presence of a dam.
2. Areas of Minimal Flood Hazard (X Zone): These zones represent areas with a lower risk of flooding, generally outside the 100-year flood plain. However, they may still be susceptible to flooding from smaller, less frequent events.
3. Areas of Undetermined Flood Hazard (D Zone): These zones represent areas where flood hazard data is incomplete or unavailable. They require further study to determine their flood risk.
Navigating the Map: Importance and Benefits
The Utah Flood Zone Map serves as a vital tool for various stakeholders, offering crucial information for:
1. Development Planning: Developers and builders rely on the map to assess flood risks and incorporate appropriate mitigation measures into their projects. This includes elevating structures, using flood-resistant materials, and designing drainage systems to minimize flood impacts.
2. Insurance Considerations: The map plays a crucial role in determining insurance premiums. Properties located within SFHAs are typically required to purchase flood insurance, ensuring financial protection against potential losses.
3. Emergency Response: First responders and emergency management agencies utilize the map to understand potential flood impacts and plan effective evacuation routes, resource allocation, and disaster relief efforts.
4. Community Awareness: The map serves as a valuable educational tool, raising public awareness about flood risks and promoting proactive measures to enhance community resilience.
5. Environmental Stewardship: The map helps identify sensitive ecosystems vulnerable to flooding, guiding land management practices and conservation efforts to protect these valuable resources.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What is the difference between a 100-year flood and a 500-year flood?
A 100-year flood has a 1% chance of occurring in any given year, while a 500-year flood has a 0.2% chance. This means that a 100-year flood is statistically more likely to occur than a 500-year flood, but both represent significant flood events with potentially catastrophic consequences.
2. Can I build a structure in a flood zone?
Building in a flood zone is typically allowed, but it requires adherence to specific building codes and regulations designed to mitigate flood risks. These regulations may include elevation requirements, flood-resistant construction materials, and drainage system specifications.
3. How can I access the Utah Flood Zone Map?
The Utah Flood Zone Map is readily available online through the FEMA website or the Utah Division of Emergency Management website. The map can be accessed via interactive online tools or downloaded as a PDF file.
4. What should I do if my property is located in a flood zone?
If your property is located in a flood zone, it is crucial to take proactive measures to mitigate flood risks. These measures include:
- Purchasing flood insurance.
- Elevating structures and belongings above the base flood elevation.
- Installing flood-resistant materials in your home.
- Maintaining proper drainage systems.
- Developing a flood preparedness plan and evacuation route.
Tips for Flood Mitigation and Preparedness
1. Elevate Structures: Raising structures above the base flood elevation significantly reduces flood damage potential.
2. Use Flood-Resistant Materials: Incorporating flood-resistant materials in construction, such as waterproof drywall and concrete floors, enhances resilience.
3. Install Flood Vents: These vents allow floodwaters to enter a structure without causing significant structural damage.
4. Maintain Drainage Systems: Regularly cleaning gutters, downspouts, and drainage ditches ensures efficient water flow and reduces flooding risks.
5. Develop a Flood Preparedness Plan: This plan should outline evacuation routes, communication strategies, and essential supplies to ensure safety and minimize disruption.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Resilience
The Utah Flood Zone Map serves as a vital tool for understanding and mitigating flood risks in the state. By providing accurate information about flood hazards, it empowers individuals, businesses, and communities to make informed decisions, plan for potential floods, and enhance their resilience to these devastating events. Recognizing the importance of this resource and utilizing its insights is crucial for safeguarding lives, property, and the well-being of Utah’s communities.

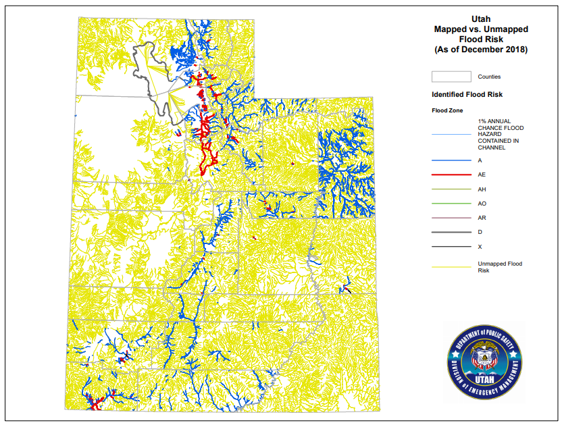

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters: Understanding Utah’s Flood Zone Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
