Navigating the World: Tonga’s Place on the Global Map
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Tonga’s Place on the Global Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Tonga’s Place on the Global Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Tonga’s Place on the Global Map

The world map, a visual representation of our planet’s landmasses and oceans, is an essential tool for understanding global geography, relationships, and interconnectedness. It serves as a visual guide to navigating our world, providing a framework for understanding international politics, trade routes, cultural exchange, and the distribution of resources.
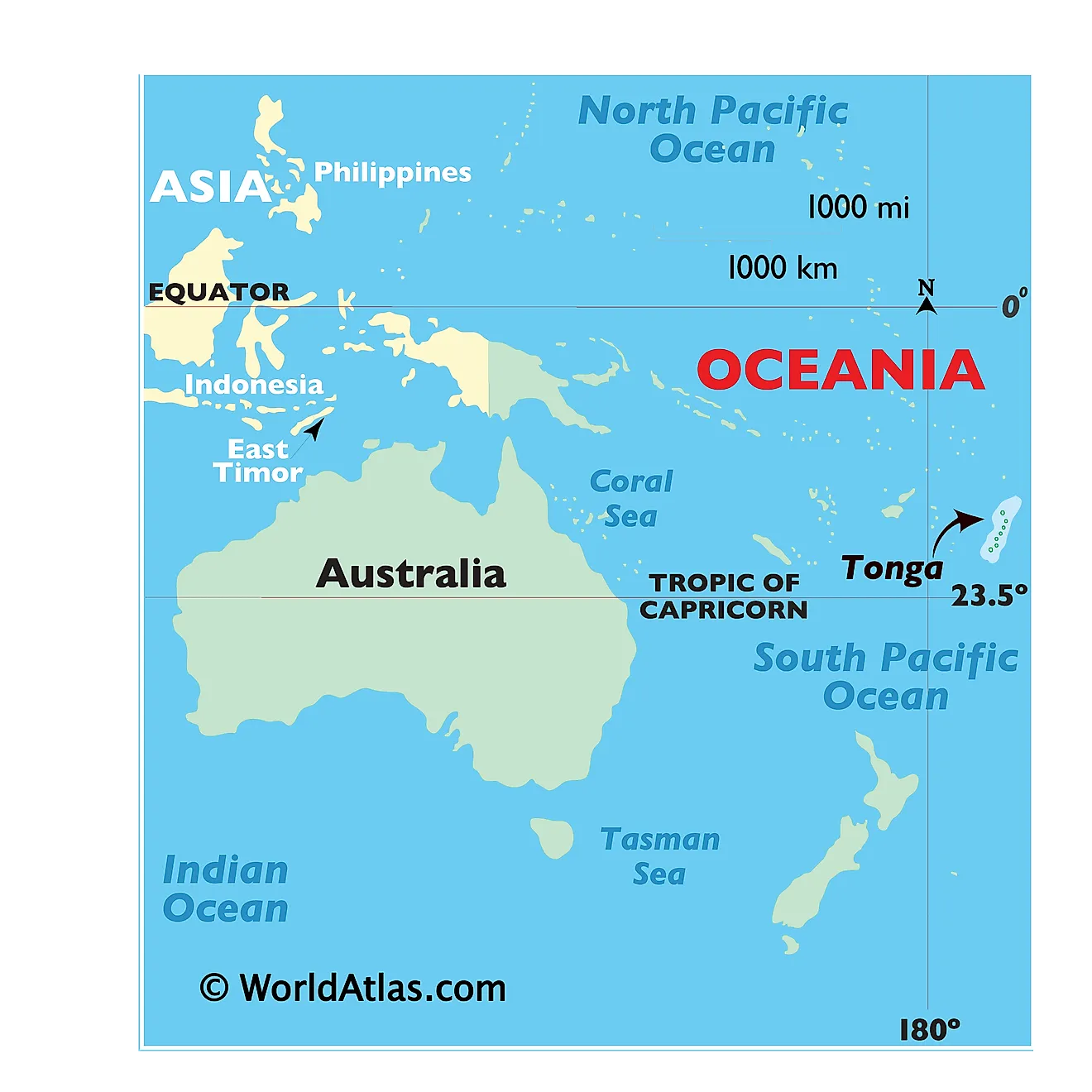
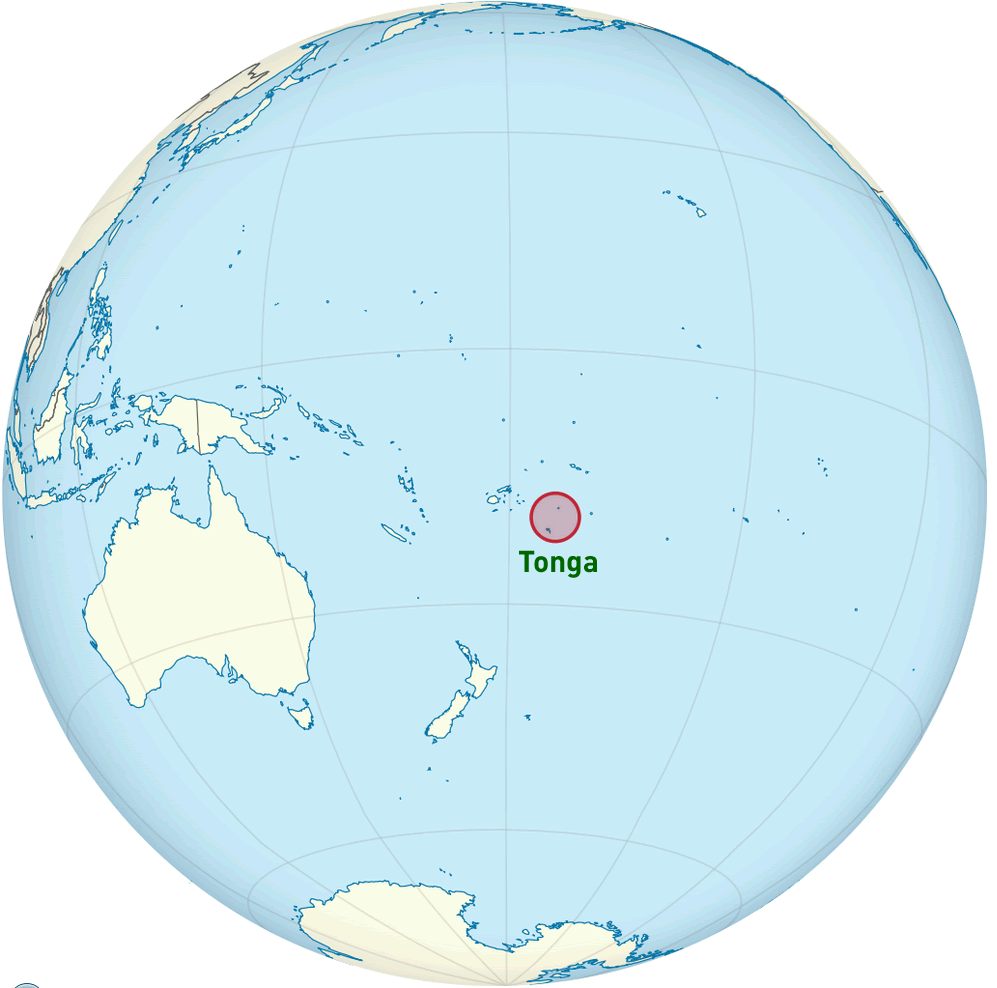
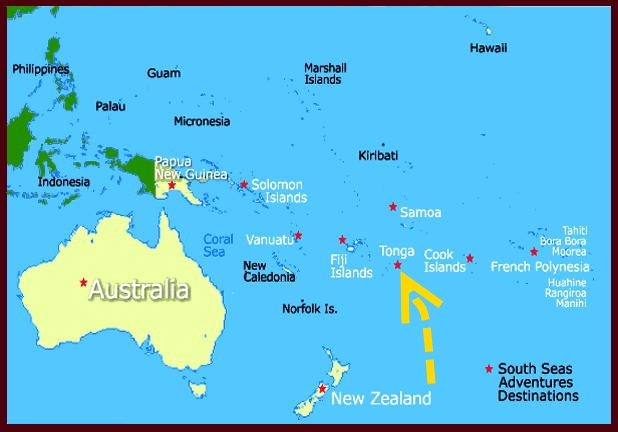
Within this intricate tapestry of continents, islands, and oceans lies Tonga, a Polynesian archipelago nestled in the vast expanse of the South Pacific Ocean. While geographically isolated, Tonga’s presence on the world map is significant, highlighting its unique cultural heritage, rich history, and contributions to the global community.
Tonga’s Geographical Significance
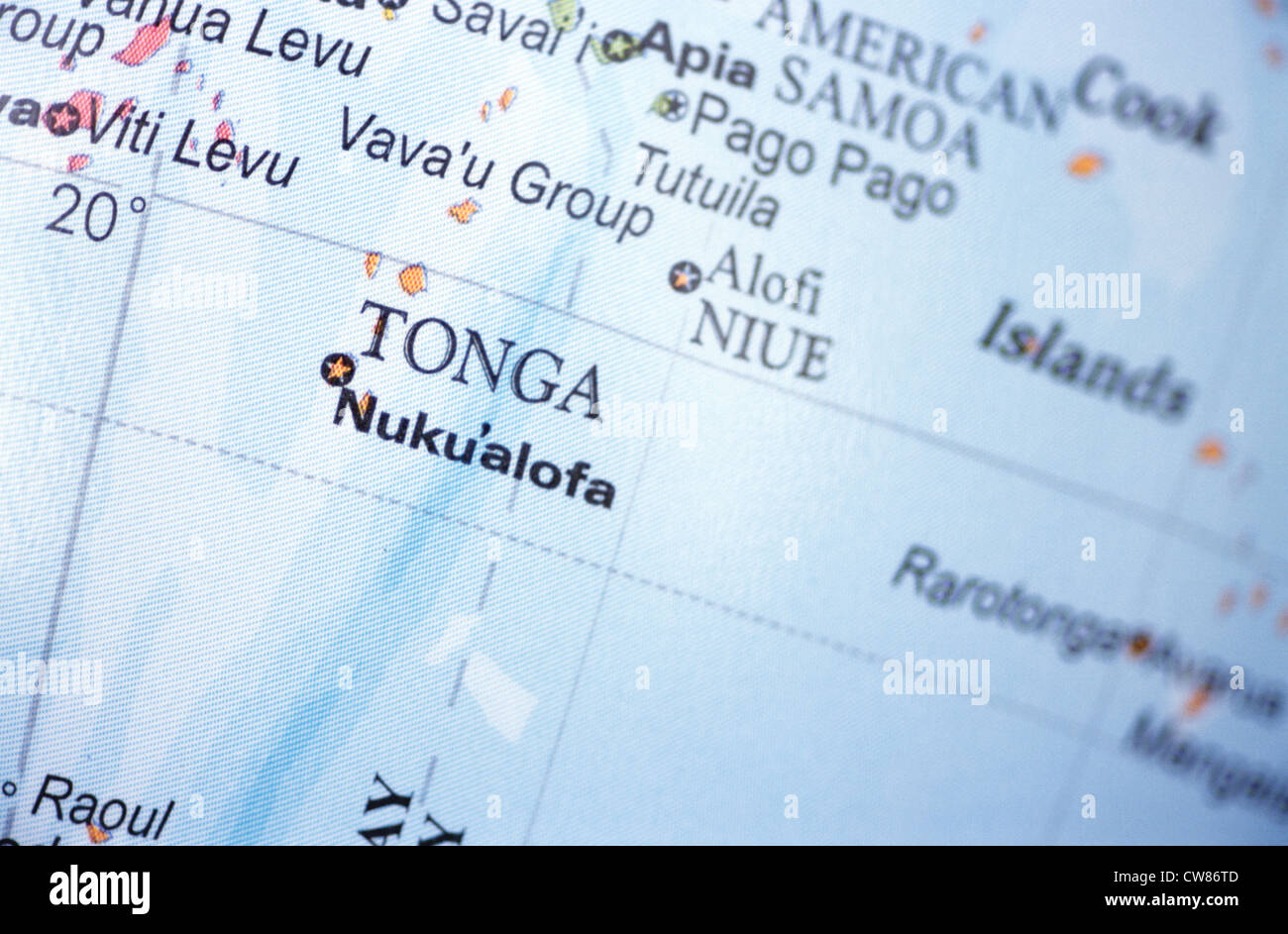
Tonga’s location in the South Pacific Ocean places it at a crucial intersection of geographical and cultural influences. The archipelago comprises over 170 islands and islets, with only 36 inhabited. This geographical configuration has shaped Tonga’s culture, economy, and interactions with the wider world.
-
Island Nation: Tonga’s island nature has fostered a strong maritime tradition, with fishing and navigation playing central roles in its history and culture. The islanders developed sophisticated seafaring skills, enabling them to navigate the vast Pacific Ocean and establish trade routes with other island nations.
-
Strategic Location: Tonga’s position in the South Pacific Ocean has made it a strategic location for trade and communication. The archipelago lies along important shipping routes connecting Asia, Australia, and the Americas, making it a vital link in the global trade network.
-
Vulnerability to Climate Change: As a low-lying island nation, Tonga faces significant threats from climate change, particularly rising sea levels and increasingly intense storms. The archipelago’s vulnerability highlights the global impact of climate change and underscores the need for international cooperation to address this pressing issue.
Tonga’s Cultural Significance
Tonga boasts a rich and vibrant culture, deeply rooted in Polynesian traditions. Its cultural heritage is characterized by:
-
Polynesian Roots: Tonga’s culture is intrinsically linked to its Polynesian ancestry. The archipelago shares a common cultural heritage with other Polynesian islands, including Samoa, Fiji, and Hawaii. This shared heritage is evident in Tonga’s music, dance, language, and traditional beliefs.
-
Unique Identity: Despite its shared heritage, Tonga has developed its own distinct cultural identity. The archipelago’s unique history and geographical location have fostered a unique blend of Polynesian traditions and influences from other cultures.
-
Cultural Preservation: Tonga has actively sought to preserve its cultural heritage, recognizing its importance to national identity and a sense of belonging. The archipelago’s government and communities have implemented various initiatives to promote traditional arts, language, and customs.
Tonga’s Economic Significance
While geographically isolated, Tonga plays a vital role in the global economy. Its economic activities are primarily based on:
-
Agriculture: Agriculture is a major contributor to Tonga’s economy, with crops like bananas, coconuts, and vanilla being key exports. The archipelago’s fertile volcanic soils and tropical climate provide favorable conditions for agricultural production.
-
Tourism: Tourism is an increasingly important sector of Tonga’s economy, with its pristine beaches, coral reefs, and rich cultural heritage attracting visitors from around the world.
-
Fishing: Fishing is a traditional industry in Tonga, with tuna being a major export. The archipelago’s waters are abundant with tuna, making it a significant player in the global tuna industry.
-
Remittances: Remittances from Tongans living abroad play a significant role in the archipelago’s economy, providing a crucial source of income for many families.
Tonga’s Role in the Global Community
Tonga’s engagement in the global community is multifaceted, encompassing:
-
International Relations: Tonga is an active member of the United Nations and other international organizations. The archipelago participates in global discussions on issues such as climate change, sustainable development, and human rights.
-
Regional Cooperation: Tonga is a member of the Pacific Islands Forum, a regional organization that promotes cooperation and development among Pacific Island nations. The archipelago actively engages in regional initiatives on issues such as trade, climate change, and disaster preparedness.
-
Cultural Exchange: Tonga plays a significant role in fostering cultural exchange with other nations. The archipelago’s participation in international cultural events and festivals promotes understanding and appreciation of its unique heritage.
FAQs
Q: What is Tonga’s capital city?
A: Tonga’s capital city is Nuku’alofa, located on the island of Tongatapu.
Q: What is Tonga’s official language?
A: Tonga’s official language is Tongan, a Polynesian language. English is also widely spoken.
Q: What is Tonga’s currency?
A: Tonga’s currency is the Tongan pa’anga (TOP).
Q: What is Tonga’s population?
A: Tonga’s population is estimated to be around 105,000 people.
Q: What is Tonga’s main industry?
A: Tonga’s main industries include agriculture, tourism, fishing, and remittances.
Tips for Understanding Tonga’s Significance
-
Study a world map: Familiarize yourself with Tonga’s location in the South Pacific Ocean and its relationship to other countries in the region.
-
Explore Tonga’s cultural heritage: Learn about Tonga’s unique traditions, music, dance, and language.
-
Read about Tonga’s history: Understand the archipelago’s historical development and its interactions with the wider world.
-
Follow Tonga’s news and current events: Stay informed about Tonga’s political, economic, and social developments.
-
Engage with Tonga’s people: Connect with Tongans living in your community or online to learn about their perspectives and experiences.
Conclusion
Tonga’s presence on the world map signifies its unique cultural heritage, rich history, and contributions to the global community. Despite its geographical isolation, the archipelago plays a vital role in the Pacific region and the world. Understanding Tonga’s significance requires appreciating its cultural heritage, its economic contributions, and its engagement in international affairs. As we navigate the complexities of our interconnected world, it is crucial to recognize the importance of every nation, however small, and to appreciate the unique perspectives and contributions they bring to the global stage.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Tonga’s Place on the Global Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!