Navigating Utah’s Geological Treasures: A Guide to Responsible Rock Collecting
Related Articles: Navigating Utah’s Geological Treasures: A Guide to Responsible Rock Collecting
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Utah’s Geological Treasures: A Guide to Responsible Rock Collecting. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Utah’s Geological Treasures: A Guide to Responsible Rock Collecting

Utah’s landscape is a testament to the power of geological forces, sculpted over millennia into awe-inspiring formations, vibrant canyons, and captivating rock formations. This rich geological heritage offers a unique opportunity for enthusiasts to explore and collect a diverse array of rocks and minerals. However, responsible collection is crucial to ensure the preservation of these natural wonders for future generations. The Utah Division of Natural Resources (DNR) provides invaluable resources and guidelines for navigating the state’s rock collecting landscape.
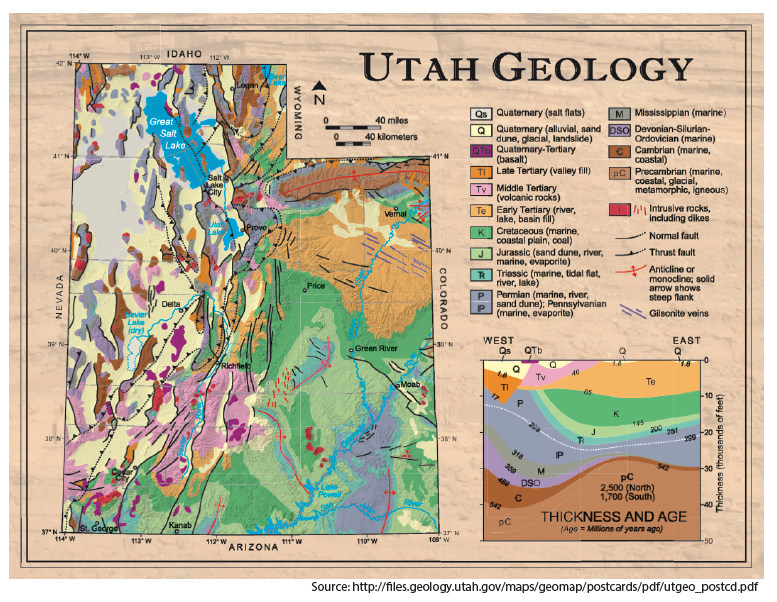
Understanding Utah’s Geology
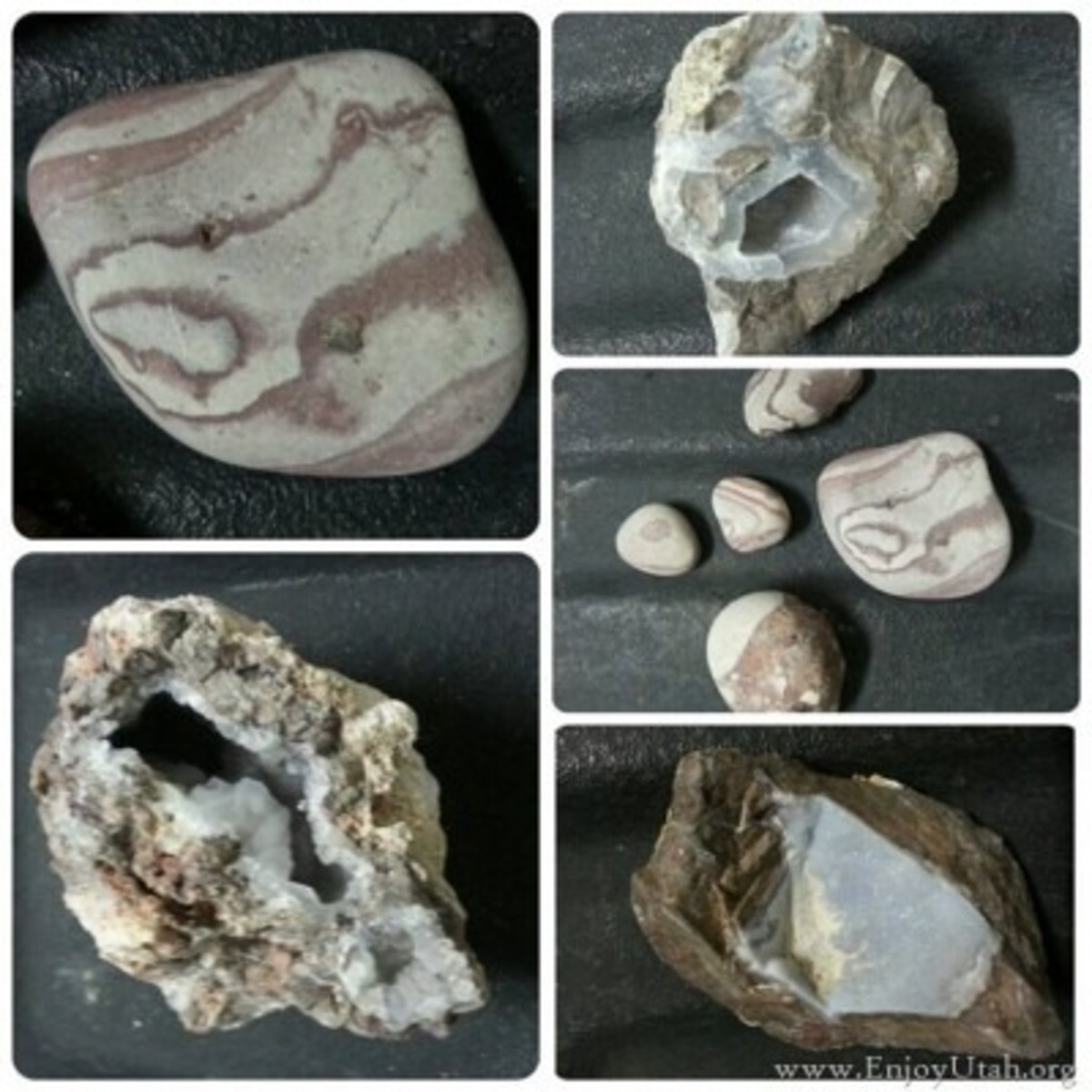
Utah’s geological history is a tapestry woven with diverse rock types and formations. From the towering sandstone cliffs of Zion National Park to the ancient petrified forests of the Escalante National Monument, the state boasts a remarkable array of geological wonders.
- Sedimentary Rocks: Utah’s landscape is dominated by sedimentary rocks, formed from the accumulation and compression of sediments over millions of years. These include sandstone, limestone, shale, and conglomerate, each with distinctive characteristics and colors.
- Igneous Rocks: Volcanic activity has also left its mark on Utah, shaping the landscape with igneous rocks like granite, basalt, and rhyolite. These rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of molten magma or lava.
- Metamorphic Rocks: Deep beneath the Earth’s surface, intense heat and pressure transform existing rocks into metamorphic rocks. Examples in Utah include marble, slate, and gneiss, often displaying intricate patterns and textures.
The Importance of Responsible Rock Collecting
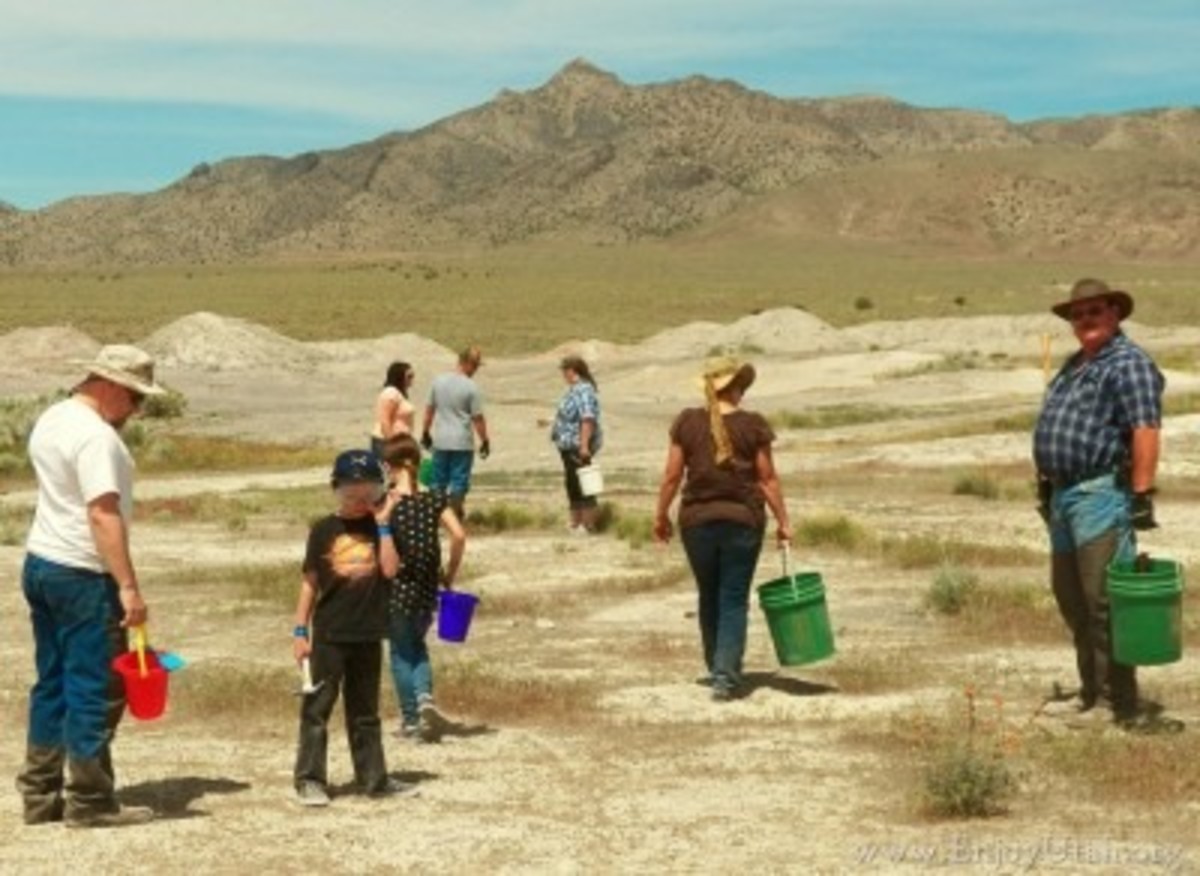
While collecting rocks can be a rewarding and educational experience, it is crucial to practice responsible collection to ensure the sustainability of Utah’s geological heritage.
- Respecting Public Lands: The majority of Utah’s land is managed by federal, state, or local agencies, each with specific regulations regarding rock collecting. It is essential to obtain necessary permits and adhere to these regulations.
- Minimizing Impact: Rock collecting should be done in a way that minimizes impact on the environment. Avoid damaging fragile formations, removing large quantities of rocks, or leaving behind litter.
- Preserving for Future Generations: Responsible collection ensures that future generations can continue to enjoy the beauty and wonder of Utah’s geological treasures.
Utah DNR’s Role in Guiding Responsible Collection
The Utah DNR plays a vital role in promoting responsible rock collecting and protecting the state’s geological resources. Their efforts encompass several key aspects:
- Providing Information: The DNR website and publications provide comprehensive information about rock collecting regulations, permitted areas, and best practices.
- Issuing Permits: For specific areas or types of collection, the DNR may require permits to ensure sustainable harvesting.
- Educating the Public: The DNR conducts outreach programs and workshops to educate the public about responsible rock collecting and the importance of conservation.
- Enforcing Regulations: DNR officers enforce regulations to protect geological resources and ensure compliance with permitting requirements.
Navigating Utah’s Rock Collecting Landscape: A Map-Based Approach
The DNR’s website provides a valuable resource for navigating Utah’s rock collecting landscape: an interactive map that showcases areas where rock collecting is permitted. This map offers a clear visual guide, enabling collectors to identify potential locations while respecting designated boundaries and regulations.
- Understanding the Map: The map features different color-coded areas, each representing a specific level of rock collecting access.
- Permitted Areas: Green areas indicate locations where rock collecting is permitted with a valid permit.
- Restricted Areas: Red areas represent areas where rock collecting is prohibited, often due to environmental sensitivity or cultural significance.
- Limited Access: Yellow areas indicate locations where rock collecting is allowed with specific restrictions, such as limitations on the quantity or type of rocks collected.
FAQs on Rock Collecting in Utah
1. What are the general rules for rock collecting in Utah?
- Always obtain necessary permits from the managing agency for the area.
- Respect designated boundaries and avoid collecting in restricted areas.
- Minimize environmental impact by collecting only small quantities and leaving the area clean.
2. Do I need a permit to collect rocks in Utah?
- Permits are often required for specific areas or types of rock collecting. The DNR website provides information on permit requirements and application procedures.
3. What are the consequences of violating rock collecting regulations?
- Violations can result in fines, citations, or even imprisonment.
4. How can I learn more about the geology of Utah?
- The DNR website and publications offer valuable information about Utah’s geological history, rock types, and formations.
- Local museums, geological societies, and universities often provide educational resources and workshops.
5. What are some tips for identifying rocks and minerals?
- Utilize field guides and online resources to familiarize yourself with common rock types and their identifying characteristics.
- Observe the rock’s color, texture, hardness, and crystal structure.
- Consult with experts at local museums or geological societies for identification assistance.
Tips for Responsible Rock Collecting
- Plan Ahead: Research the area you intend to visit, understand the regulations, and obtain necessary permits.
- Pack Light: Bring only essential equipment, such as a backpack, hand tools, and a field guide.
- Leave No Trace: Pack out all trash and leave the area as you found it.
- Respect the Environment: Avoid disturbing fragile formations, disturbing wildlife, or removing large quantities of rocks.
- Educate Others: Share your knowledge about responsible rock collecting and encourage others to follow best practices.
Conclusion
Utah’s geological diversity offers a unique opportunity to connect with the Earth’s history and appreciate the beauty of natural formations. By adhering to responsible collecting practices and utilizing the resources provided by the Utah DNR, individuals can ensure that these treasures remain accessible for generations to come. Understanding the regulations, respecting designated boundaries, and minimizing environmental impact are essential for preserving Utah’s geological heritage and ensuring its continued enjoyment for all.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Utah’s Geological Treasures: A Guide to Responsible Rock Collecting. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!