The Diverse Topography of India: A Tapestry of Landforms and Their Significance
Related Articles: The Diverse Topography of India: A Tapestry of Landforms and Their Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Diverse Topography of India: A Tapestry of Landforms and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Diverse Topography of India: A Tapestry of Landforms and Their Significance
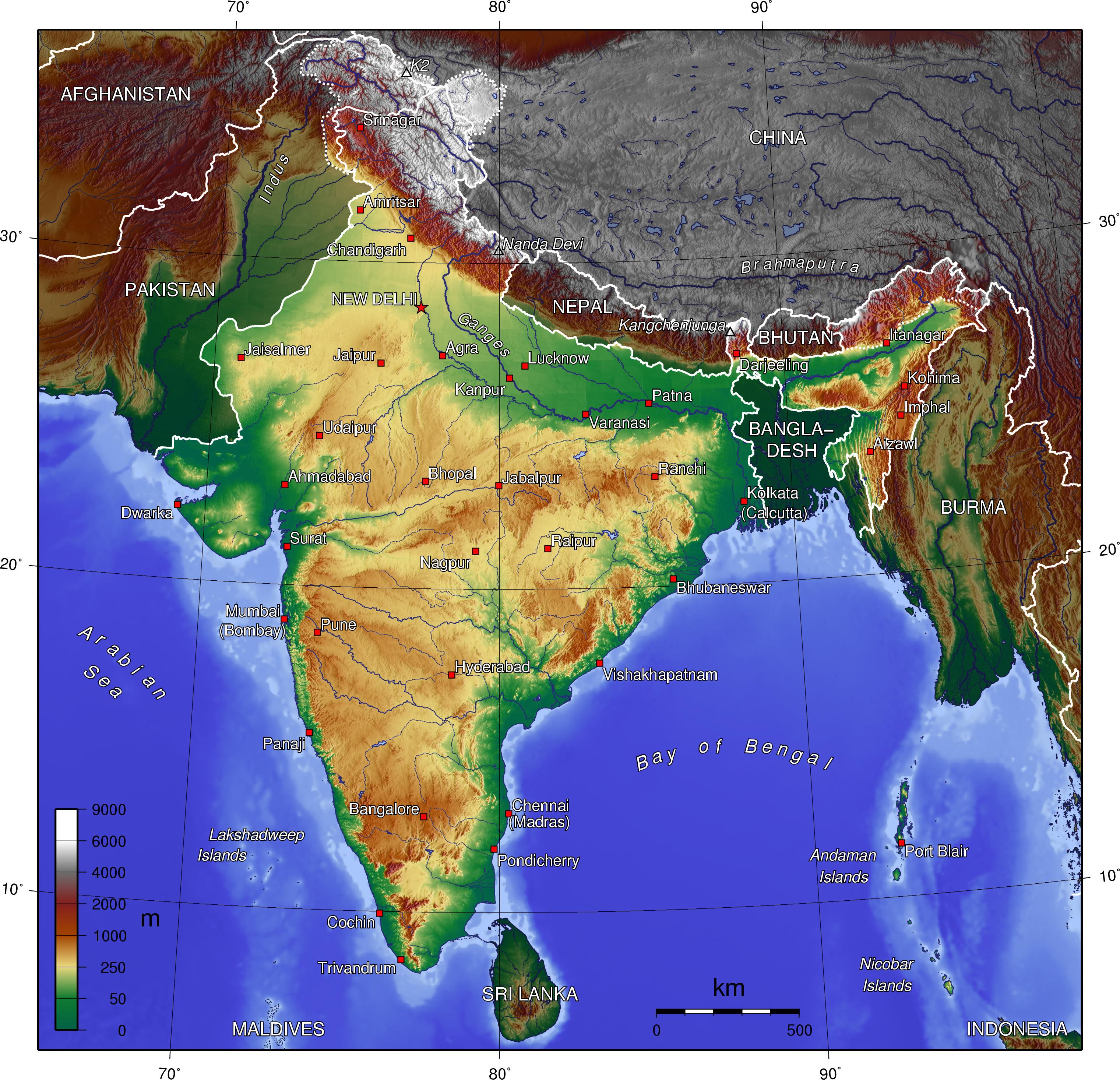
India, a vast and geographically diverse nation, boasts a topography that is as intricate and fascinating as its cultural tapestry. Its landscape, sculpted over millennia by tectonic forces, weathering, and erosion, is a testament to the dynamic nature of the Earth’s surface. Understanding the topography of India is crucial for comprehending its natural resources, climate patterns, agricultural practices, and even its cultural heritage.
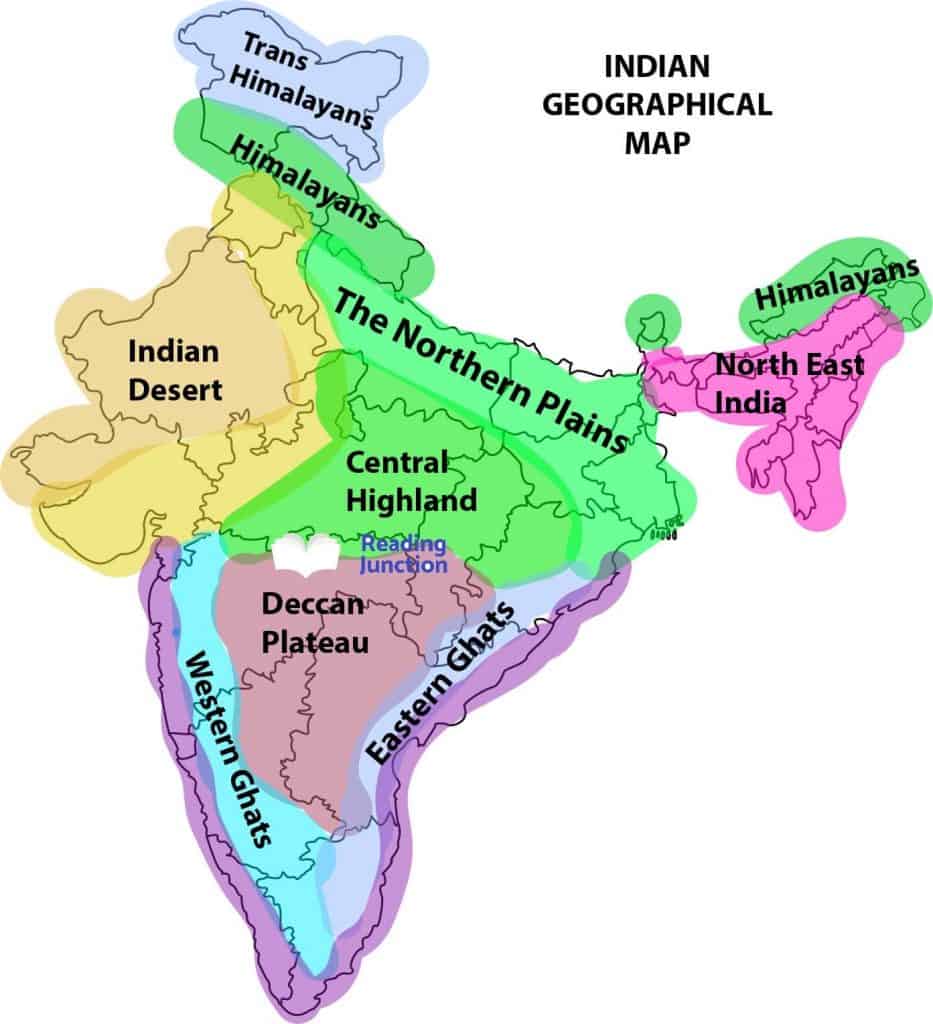
The Himalayan Giants and the Northern Plains:
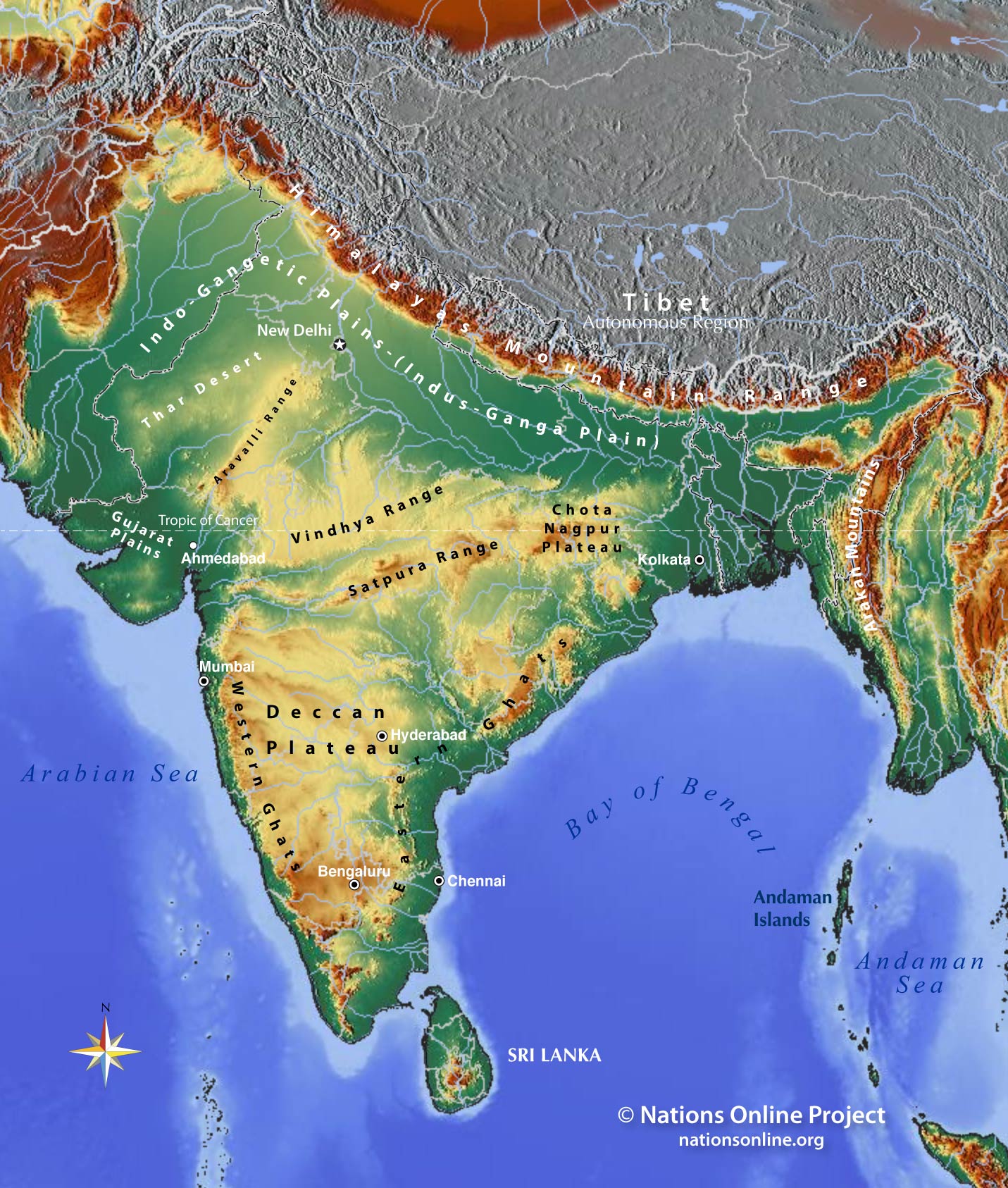
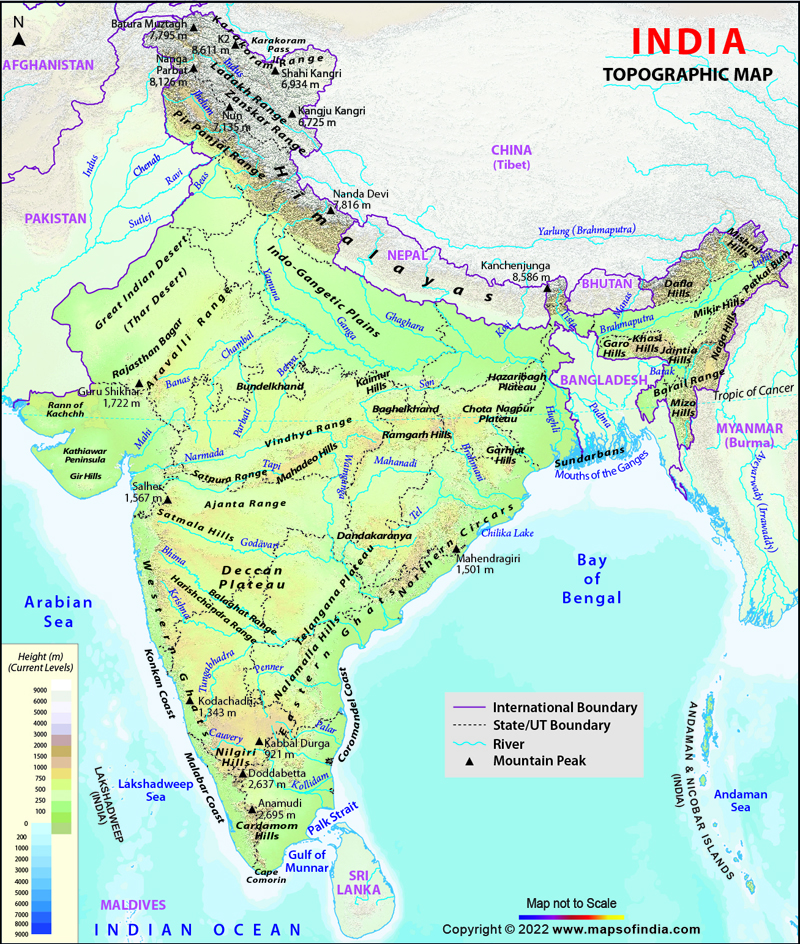
India’s northern frontier is defined by the majestic Himalayas, the world’s youngest and highest mountain range. This formidable wall of rock serves as a natural barrier, protecting the subcontinent from the harsh winds of Central Asia. The Himalayas are a source of major rivers like the Ganga, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra, which flow down to the fertile Indo-Gangetic Plain, a vast expanse of alluvial soil that supports a significant portion of India’s population and agriculture. This plain is characterized by its flatness, making it ideal for farming, and its rich soil, resulting from the deposition of silt from the Himalayan rivers.
The Deccan Plateau and the Western Ghats:
To the south of the Indo-Gangetic Plain lies the Deccan Plateau, a massive triangular plateau formed by ancient volcanic activity. The plateau is characterized by its relatively flat terrain, interspersed with hills and plateaus. The Deccan Plateau is home to a variety of ecosystems, including dry deciduous forests, grasslands, and scrublands. The Western Ghats, a range of mountains that runs parallel to the west coast of India, rise abruptly from the coastal plain, forming a barrier between the plateau and the Arabian Sea. These mountains are a significant source of rainfall, contributing to the unique biodiversity of the Western Ghats region.
The Eastern Ghats and the Coastal Plains:
The Eastern Ghats, a series of discontinuous ranges that run along the eastern coast of India, are less elevated than the Western Ghats. They are known for their rich biodiversity and the presence of numerous waterfalls and gorges. The coastal plains, located between the Eastern Ghats and the Bay of Bengal, are characterized by their fertile soil and extensive deltaic regions. These plains are important for agriculture, fishing, and transportation.
The Thar Desert and the Islands:
The Thar Desert, located in the northwestern part of India, is the largest desert in India and one of the world’s largest subtropical deserts. This arid region is characterized by its shifting sand dunes, sparse vegetation, and extreme temperatures. India also encompasses a number of islands, including the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea. These islands offer unique ecosystems and contribute to the country’s biodiversity.
The Significance of India’s Topography:
The diverse topography of India has profound implications for the country’s natural resources, climate patterns, and human activities.
- Water Resources: The Himalayas, with their snow-capped peaks and glaciers, are the source of major rivers that sustain India’s agriculture and provide drinking water to millions. These rivers also contribute to the formation of fertile alluvial plains, which are crucial for food production.
- Climate Patterns: The Himalayas act as a natural barrier, preventing cold winds from Central Asia from reaching the subcontinent. The Western Ghats intercept the monsoon winds, resulting in heavy rainfall on the western coast, while the eastern coast receives less rainfall. This variation in rainfall contributes to the diverse ecosystems found across India.
- Agriculture: The Indo-Gangetic Plain, with its fertile soil and ample water resources, is a major agricultural hub. The Deccan Plateau, while less fertile, is suitable for growing drought-resistant crops. The coastal plains, with their fertile soil and proximity to water bodies, are also important for agriculture.
- Biodiversity: India’s diverse topography has given rise to a rich and varied biodiversity. The Himalayas, the Western Ghats, and the Eastern Ghats are all home to unique flora and fauna, including numerous endemic species.
- Cultural Heritage: The topography of India has also shaped its cultural heritage. The Himalayas have inspired numerous myths and legends, while the Indo-Gangetic Plain has been a cradle of civilization for millennia. The Deccan Plateau, with its ancient rock-cut temples and monuments, is a testament to the rich cultural heritage of India.
FAQs on India’s Topography:
Q: What are the major topographic features of India?
A: India’s major topographic features include the Himalayas, the Indo-Gangetic Plain, the Deccan Plateau, the Western Ghats, the Eastern Ghats, the Thar Desert, and the islands.
Q: What is the significance of the Himalayas for India?
A: The Himalayas are crucial for India’s water resources, climate patterns, and biodiversity. They act as a natural barrier, provide the source of major rivers, and support a unique ecosystem.
Q: What is the role of the Indo-Gangetic Plain in India’s economy?
A: The Indo-Gangetic Plain is a major agricultural hub, supporting a significant portion of India’s population and contributing to the country’s food security.
Q: What are the unique features of the Deccan Plateau?
A: The Deccan Plateau is characterized by its relatively flat terrain, interspersed with hills and plateaus, and is home to a variety of ecosystems. It is also known for its ancient rock-cut temples and monuments.
Q: What are the ecological and economic importance of the Western Ghats?
A: The Western Ghats are a significant source of rainfall, contribute to the unique biodiversity of the region, and are home to a variety of endemic species. They also play a role in regulating the flow of rivers and supporting agriculture.
Q: How does the Thar Desert impact India’s environment?
A: The Thar Desert is a unique ecosystem, but its arid conditions can lead to desertification and dust storms, affecting the environment and human activities in neighboring regions.
Tips for Understanding India’s Topography:
- Use a physical map of India: A physical map will show the elevation and relief of the land, providing a clear visual representation of the country’s topography.
- Read about the different regions: Each region of India has its unique topographic features and associated ecosystems. Reading about the specific characteristics of each region will enhance your understanding of India’s topography.
- Visit different parts of India: Traveling to different parts of India will provide firsthand experience of the country’s diverse topography.
- Explore online resources: There are numerous online resources, such as websites and documentaries, that provide detailed information about India’s topography.
Conclusion:
The topography of India is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped the Earth’s surface over millennia. From the towering Himalayas to the vast Indo-Gangetic Plain, the Deccan Plateau, and the coastal plains, India’s landscape is as diverse and fascinating as its people. Understanding the topography of India is crucial for comprehending its natural resources, climate patterns, agricultural practices, and cultural heritage. By appreciating the intricate relationship between the land and its inhabitants, we can better understand the unique challenges and opportunities facing this vast and complex nation.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Diverse Topography of India: A Tapestry of Landforms and Their Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
