The Geopolitical Significance of Turkey’s Asian Proximity: A Regional Perspective
Related Articles: The Geopolitical Significance of Turkey’s Asian Proximity: A Regional Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Geopolitical Significance of Turkey’s Asian Proximity: A Regional Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geopolitical Significance of Turkey’s Asian Proximity: A Regional Perspective

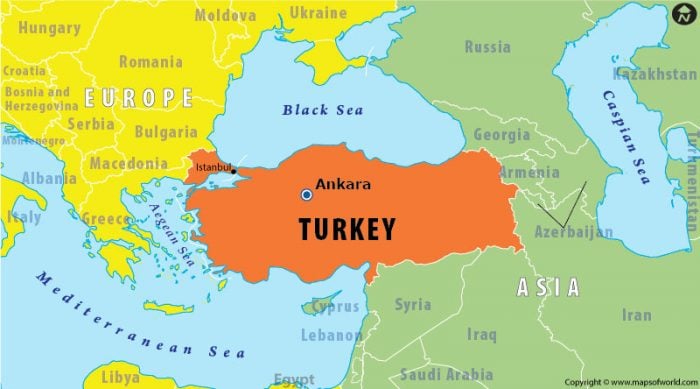
Turkey, a transcontinental nation straddling Europe and Asia, occupies a unique and strategically important position in the world. Its geographic proximity to the Asian continent, specifically the Middle East and the Caucasus region, has profound implications for its history, culture, economy, and geopolitical dynamics. This article delves into the significance of Turkey’s Asian connections, examining its regional relationships, economic ties, and the challenges and opportunities that arise from this geographic reality.
A Crossroads of Civilizations:
Turkey’s geographic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia has shaped its history and cultural identity. The Anatolian peninsula, which forms the core of Turkey, has served as a bridge between the East and West for millennia. This historical crossroads has resulted in a rich tapestry of cultural influences, evident in Turkey’s diverse languages, religions, and artistic traditions.
The region around Turkey has been the stage for countless empires and civilizations, including the Hittites, Persians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans. Each of these empires left its mark on the cultural and political landscape of the region, contributing to Turkey’s complex and multifaceted heritage.
Regional Relationships:
Turkey’s proximity to the Middle East, the Caucasus, and Central Asia gives it significant regional influence. It shares borders with eight countries, including Syria, Iraq, Iran, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Greece, and Bulgaria. This shared geography fosters intricate relationships, marked by both cooperation and conflict.
The Middle East:
Turkey’s relationship with the Middle East is multifaceted. It is a major player in the region’s political and economic dynamics, with its interests ranging from energy security to counterterrorism. Turkey’s support for democratic movements in the region, coupled with its concerns about regional instability, has led to complex interactions with countries like Syria, Iraq, and Iran.
The Caucasus:
Turkey’s ties with the Caucasus region, including Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, are historically and culturally significant. The region is strategically important for Turkey, as it offers access to energy resources and provides a corridor to Central Asia. However, unresolved historical disputes, particularly with Armenia, continue to cast a shadow over these relationships.
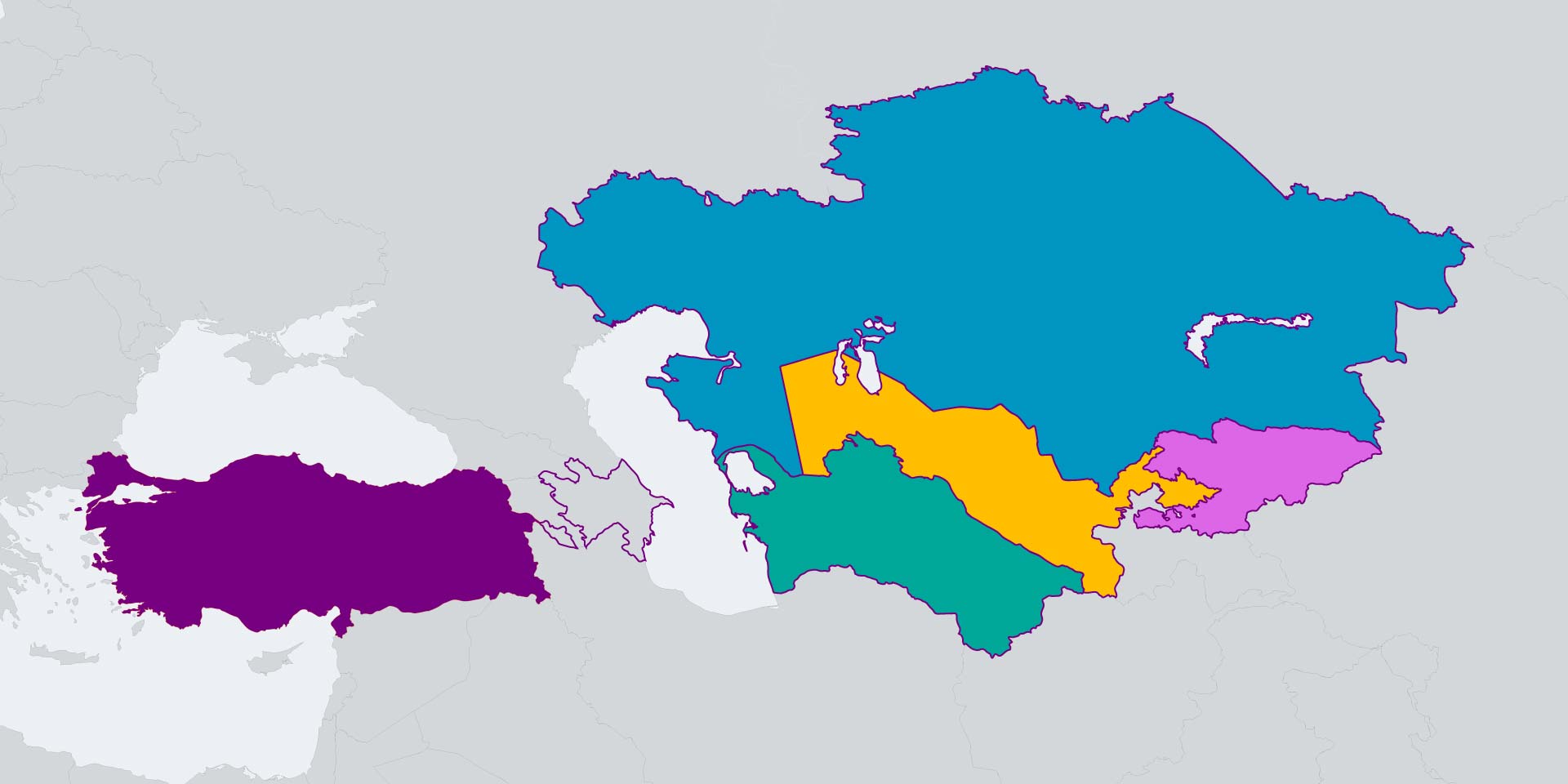
Central Asia:
Turkey has historically maintained close ties with the Turkic republics of Central Asia, sharing cultural and linguistic connections. It has played a role in promoting economic and political cooperation in the region, seeking to strengthen its influence in this strategically important area.
Economic Ties:
Turkey’s geographic proximity to Asia has facilitated economic growth and development. It serves as a vital trade route connecting Europe to Asia, playing a crucial role in the global supply chain. The country’s strategic location has attracted significant foreign investment, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, tourism, and energy.
The Silk Road Revival:
Turkey’s location along the ancient Silk Road, a historic trade route connecting the East and West, has renewed significance in the 21st century. The revival of the Silk Road, through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, offers Turkey the opportunity to become a major hub for trade and transportation, connecting Europe to Asia.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Turkey’s position in Asia presents both challenges and opportunities.
Challenges:
- Regional Instability: The Middle East and the Caucasus are regions marked by political instability, conflict, and terrorism. Turkey’s proximity to these areas exposes it to security threats and economic disruptions.
- Competition for Influence: Turkey faces competition for influence from other regional powers, including Russia, Iran, and the European Union. This competition can lead to geopolitical tensions and complicate Turkey’s efforts to maintain its regional standing.
- Economic Disparities: The economic disparities between Turkey and its neighboring countries in Asia can create challenges in promoting equitable development and cooperation.
Opportunities:
- Economic Growth: Turkey’s geographic location offers significant economic opportunities, particularly in trade, transportation, and energy sectors.
- Cultural Exchange: Turkey’s proximity to Asia facilitates cultural exchange and understanding, promoting regional cooperation and dialogue.
- Strategic Partnerships: Turkey’s strategic location allows it to build strong partnerships with countries in Asia, fostering cooperation in areas like security, energy, and infrastructure development.
FAQs:
Q: What are the key geopolitical challenges facing Turkey in its relations with Asia?
A: Turkey faces several geopolitical challenges in its relations with Asia, including regional instability, competition for influence, and economic disparities. The Middle East and the Caucasus are characterized by conflict and political instability, which pose security threats to Turkey. Additionally, Turkey faces competition for influence from other regional powers, such as Russia, Iran, and the European Union. Economic disparities between Turkey and its neighbors can also create challenges in promoting equitable development and cooperation.
Q: How does Turkey’s location benefit its economy?
A: Turkey’s strategic location benefits its economy in several ways. It serves as a vital trade route connecting Europe to Asia, playing a crucial role in the global supply chain. This location has attracted significant foreign investment, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, tourism, and energy. Turkey’s potential to become a major hub for trade and transportation along the revived Silk Road offers further economic opportunities.
Q: What are the main cultural and historical connections between Turkey and Asia?
A: Turkey shares deep cultural and historical connections with Asia, particularly the Middle East, the Caucasus, and Central Asia. The Anatolian peninsula has served as a bridge between the East and West for millennia, resulting in a rich tapestry of cultural influences in Turkey. Turkey’s language, religion, art, and cuisine reflect these historical connections.
Tips:
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the latest developments in Turkey’s relations with its Asian neighbors. Follow reputable news sources and research institutions specializing in the region.
- Engage in Dialogue: Encourage dialogue and understanding between Turkey and its Asian partners. Participate in cultural exchange programs and support initiatives promoting regional cooperation.
- Support Economic Development: Support projects and initiatives aimed at promoting economic development and integration in the region. This can involve investing in infrastructure, promoting trade, and supporting small and medium enterprises.
Conclusion:
Turkey’s geographic proximity to Asia is a defining factor in its history, culture, and geopolitical standing. Its location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia has shaped its identity and provided it with a unique strategic position in the world. Turkey’s relations with its Asian neighbors are complex and multifaceted, marked by opportunities and challenges. As the region continues to evolve, Turkey’s role in shaping its future will remain significant, requiring careful navigation of geopolitical complexities and a commitment to regional cooperation and stability.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geopolitical Significance of Turkey’s Asian Proximity: A Regional Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!