The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Eruption: A Global Impact
Related Articles: The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Eruption: A Global Impact
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Eruption: A Global Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Eruption: A Global Impact

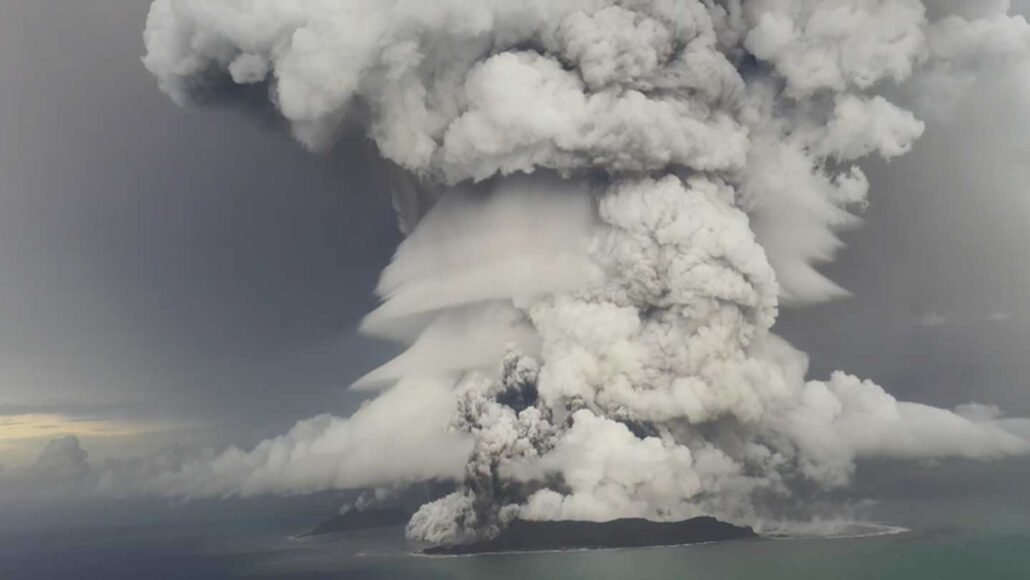
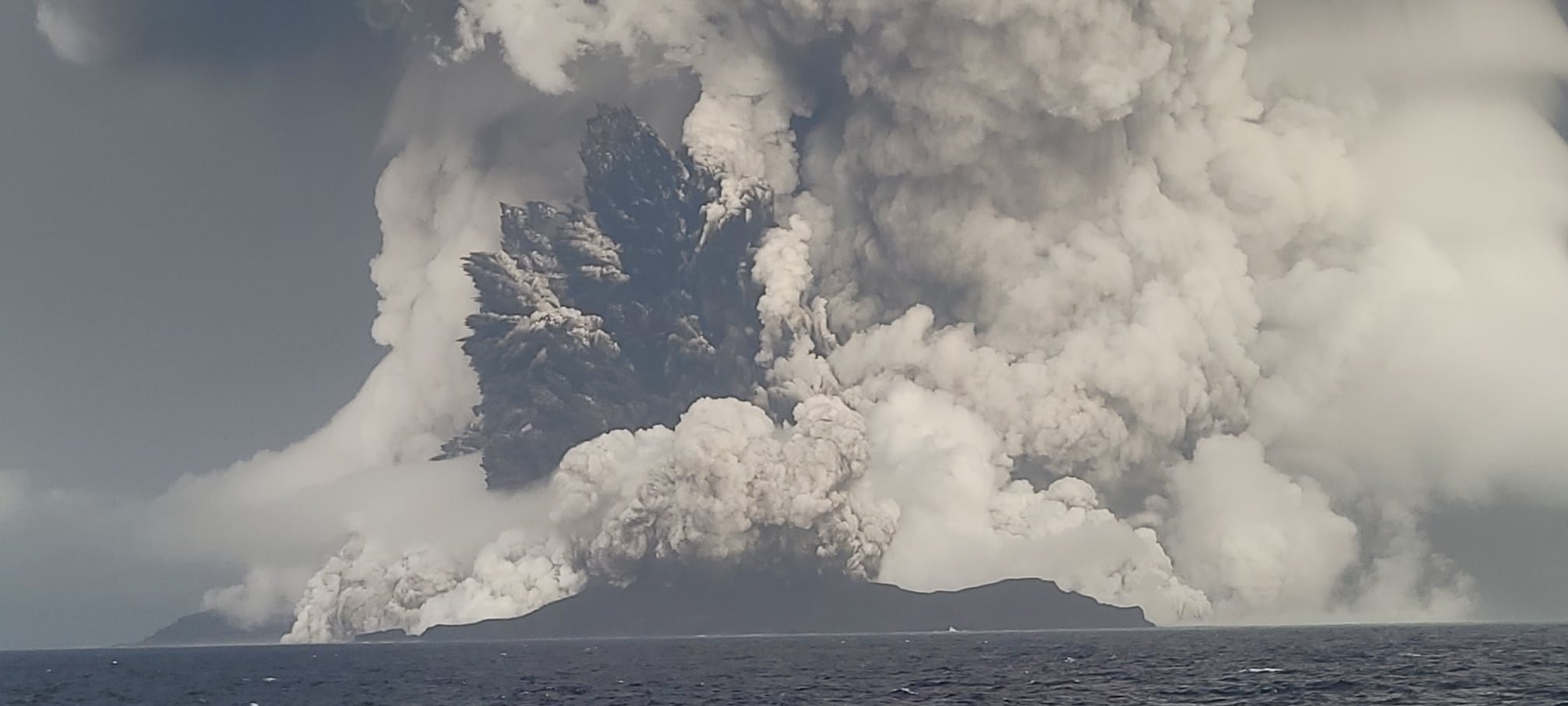
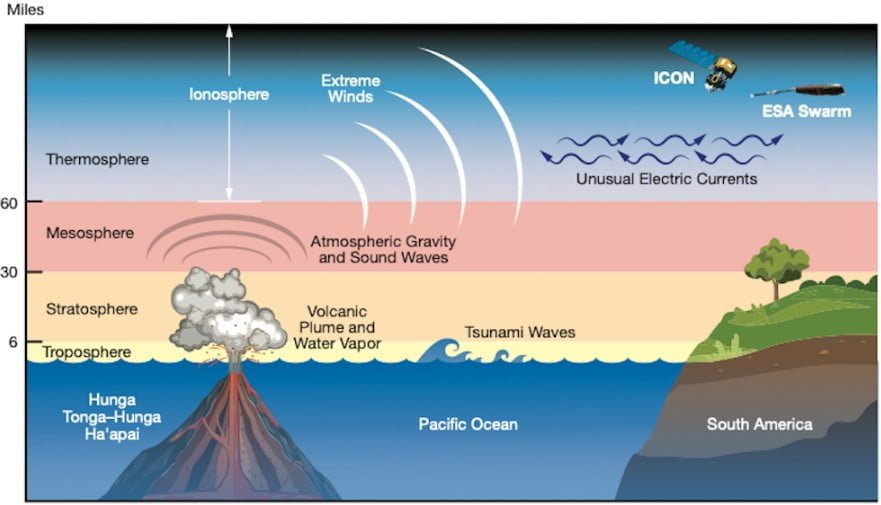
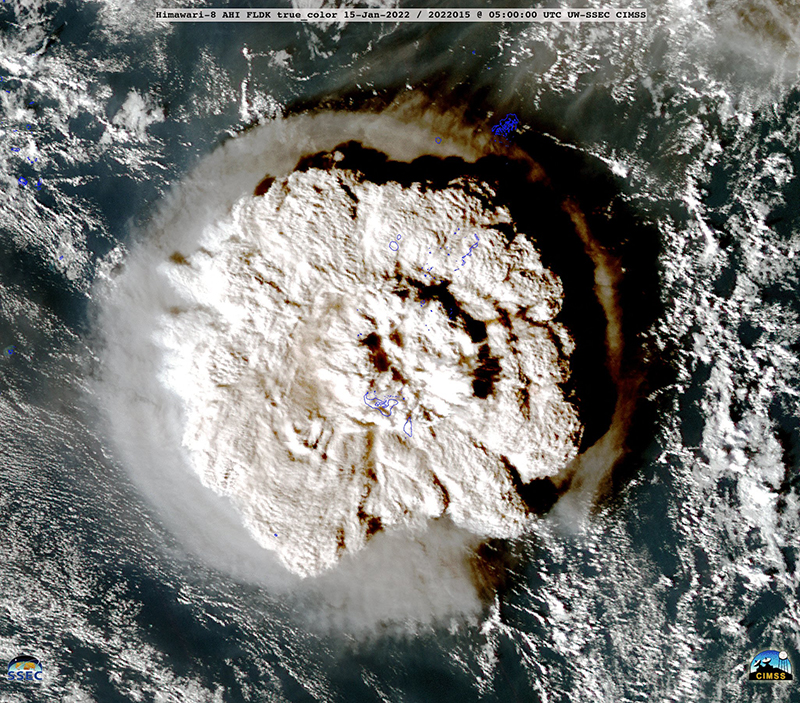
On January 15, 2022, the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano, located in the South Pacific Ocean near the island nation of Tonga, erupted with unprecedented force. This eruption, one of the most powerful volcanic events in recent history, sent shockwaves around the globe, impacting weather patterns, communication systems, and coastal communities.
Understanding the Eruption:
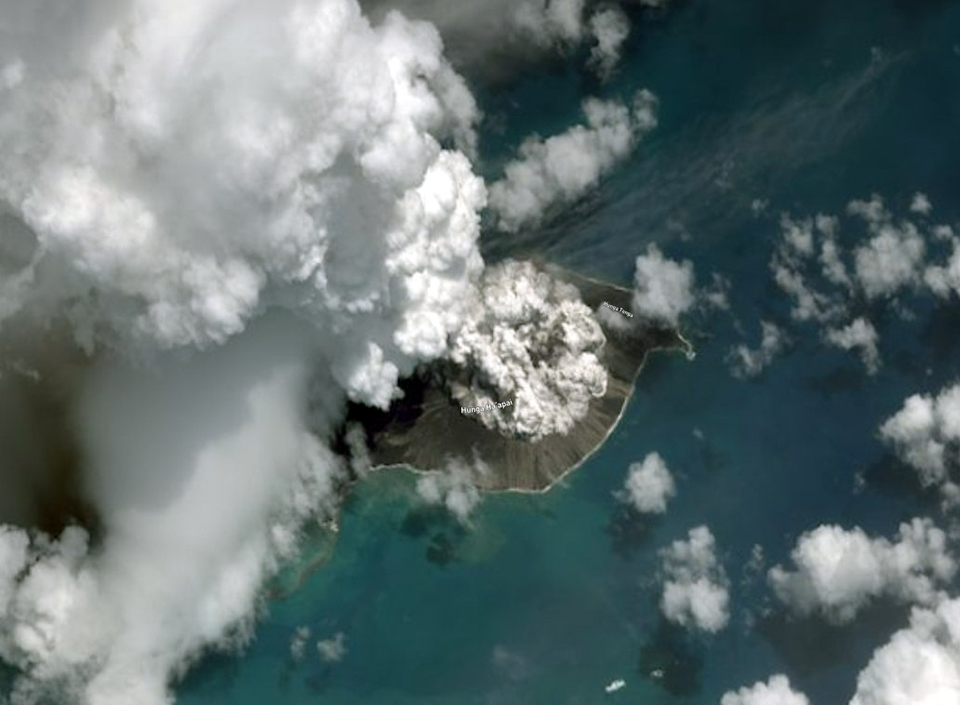
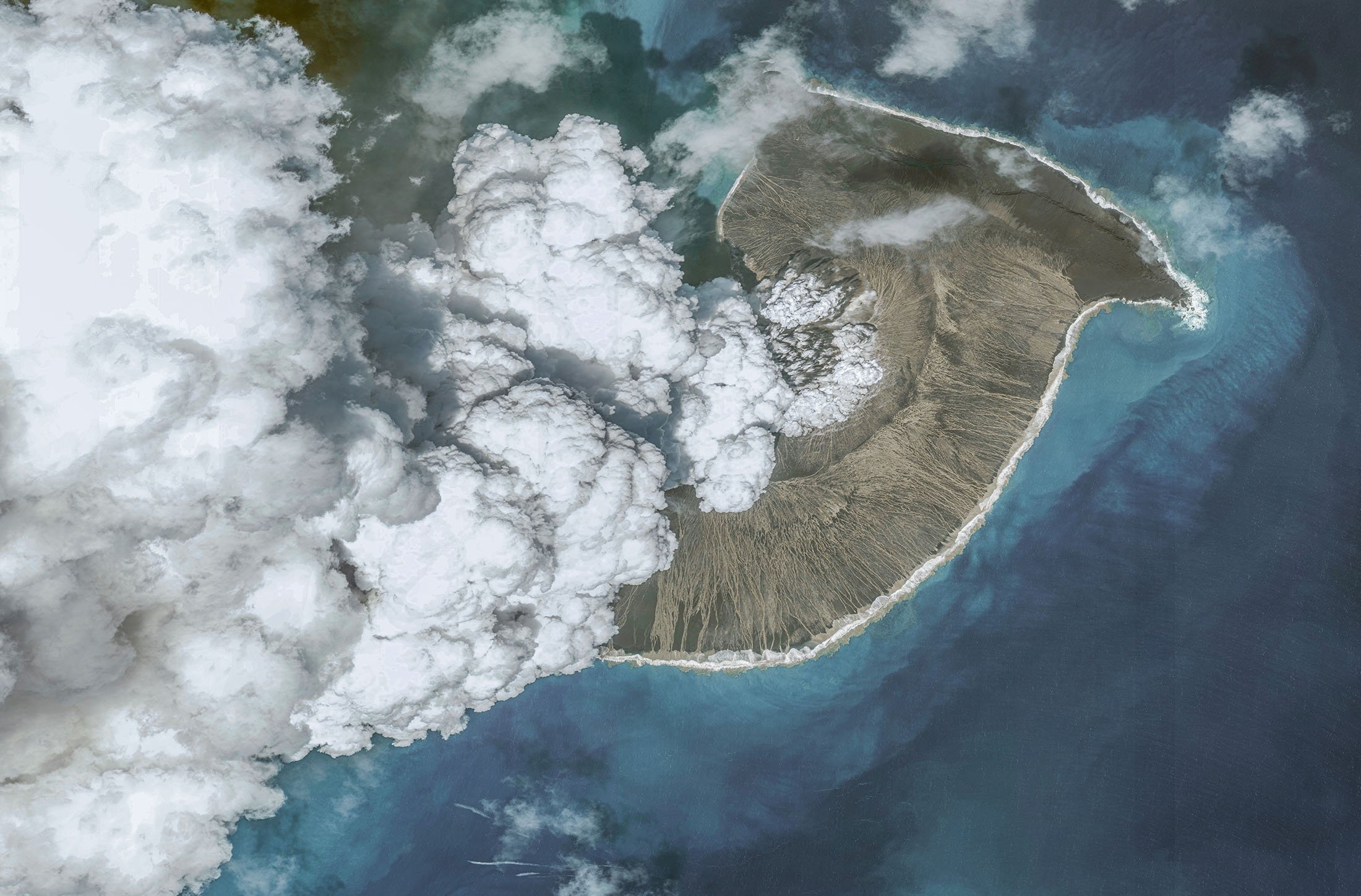
Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai is a submarine volcano, meaning it is largely submerged beneath the ocean’s surface. The volcano has a history of eruptions, with the most recent prior to 2022 occurring in 2014-2015. However, the 2022 eruption surpassed all previous events in its intensity and scale.
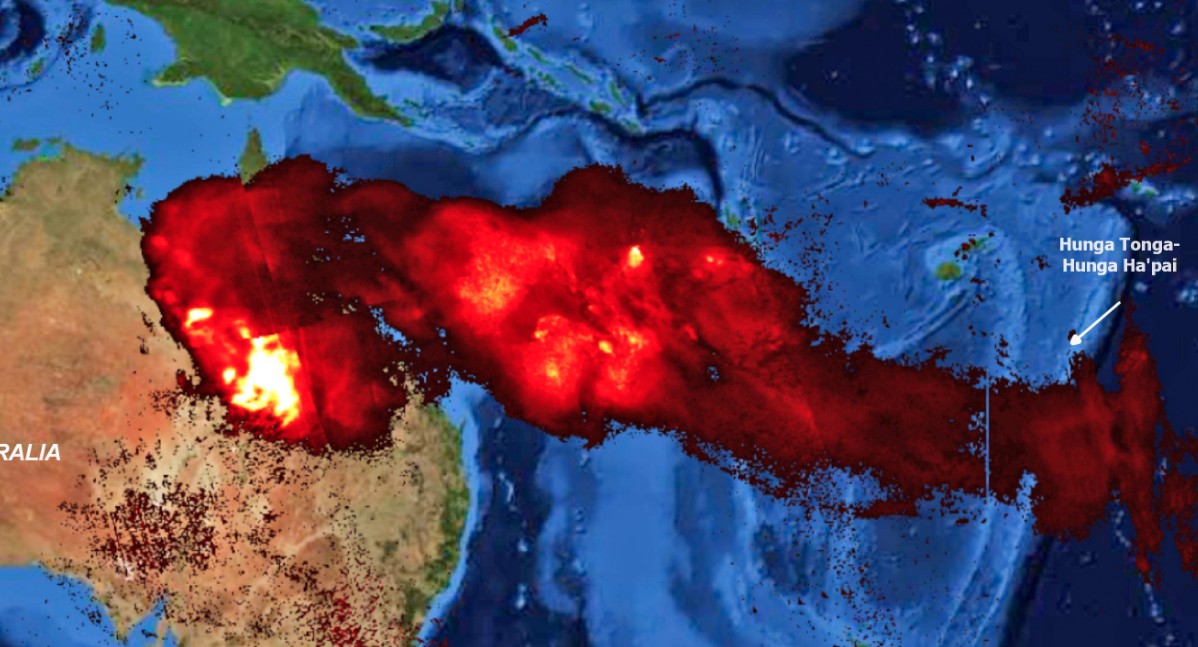
The eruption began with a series of underwater explosions, culminating in a massive, explosive event that sent a plume of ash, steam, and gas skyward. The eruption’s energy was equivalent to hundreds of atomic bombs, creating a shockwave that circled the globe multiple times. This shockwave triggered tsunamis across the Pacific, causing significant damage in Tonga and other island nations.
Global Impacts:
The eruption’s effects were felt far beyond the immediate vicinity of the volcano. The massive plume of ash and gas injected into the atmosphere created a global "dust cloud" that impacted weather patterns worldwide. The eruption also disrupted communication systems, causing widespread internet outages in Tonga and neighboring islands.
The Tsunami:
The eruption triggered a series of tsunamis, the most significant of which struck Tonga’s main island, Tongatapu. The tsunami caused widespread damage to coastal infrastructure, including homes, businesses, and vital infrastructure. The waves also contaminated freshwater supplies, posing a significant health risk to the population.
Environmental Impacts:
The eruption’s environmental impacts are still being assessed. The ash cloud, composed of volcanic particles and gases, dispersed across the Pacific region, potentially impacting air quality and agricultural productivity. The eruption also released significant amounts of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, which can contribute to acid rain and ozone depletion.
Recovery and Resilience:
The eruption had devastating consequences for Tonga, leaving the nation facing a long and arduous recovery process. The international community responded with aid and support, providing essential supplies, medical assistance, and technical expertise. The people of Tonga demonstrated remarkable resilience, working tirelessly to rebuild their lives and communities.
Scientific Significance:
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption provided scientists with an unprecedented opportunity to study volcanic processes and their global impacts. The eruption’s scale and intensity allowed researchers to gather valuable data on the dynamics of volcanic eruptions, tsunami generation, and atmospheric interactions. This data will contribute to a deeper understanding of these natural phenomena and enhance our ability to predict and mitigate their risks.
FAQs about the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Eruption:
Q: What caused the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption?
A: The eruption was caused by the interaction of magma, seawater, and tectonic forces. As magma rose from the Earth’s mantle, it encountered seawater, causing explosive reactions. The eruption was also influenced by the volcano’s location near a tectonic plate boundary, where the Pacific and Australian plates are converging.
Q: How powerful was the eruption?
A: The eruption was one of the most powerful volcanic events in recent history. Its energy was estimated to be equivalent to hundreds of atomic bombs. The eruption’s force generated a shockwave that circled the globe multiple times and triggered tsunamis across the Pacific Ocean.
Q: What were the long-term impacts of the eruption?
A: The eruption’s long-term impacts are still being assessed. However, it is clear that the eruption will have significant environmental, social, and economic consequences for Tonga and the surrounding region. The ash cloud and volcanic gases released into the atmosphere could impact weather patterns, air quality, and agricultural productivity for years to come.
Q: How did the eruption affect communication systems?
A: The eruption caused widespread internet outages in Tonga and neighboring islands. The underwater cables that connect Tonga to the global internet network were damaged by the eruption and subsequent tsunamis. The disruption to communication systems hindered relief efforts and hampered the flow of information during the immediate aftermath of the eruption.
Q: What lessons can be learned from the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption?
A: The eruption highlights the importance of understanding volcanic processes and their potential impacts on our planet. It underscores the need for robust early warning systems, effective communication strategies, and coordinated international responses to natural disasters. The eruption also underscores the vulnerability of island nations to natural hazards and the importance of investing in disaster preparedness and resilience.
Tips for Understanding Volcanic Eruptions:
- Learn about the different types of volcanic eruptions: Different types of eruptions have varying levels of intensity and impact. Understanding the different types of eruptions can help you better assess the potential risks posed by volcanic activity.
- Stay informed about volcanic activity in your region: Monitor news reports and official government websites for updates on volcanic activity.
- Develop an emergency plan: In the event of a volcanic eruption, it is crucial to have a plan in place to ensure your safety and well-being. This plan should include evacuation routes, communication protocols, and essential supplies.
- Be prepared for volcanic ashfall: Volcanic ash can pose a health risk and disrupt transportation systems. If you live in a volcanic region, it is important to have a plan for dealing with ashfall.
Conclusion:
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption was a monumental event that demonstrated the power and unpredictability of nature. While the eruption had devastating consequences for Tonga, it also provided a valuable opportunity for scientific research and global collaboration. As we continue to study the eruption’s impacts and learn from the lessons it provides, we can strive to better understand and mitigate the risks posed by volcanic activity and other natural hazards.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Eruption: A Global Impact. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!