The Indian Topography Map: A Tapestry of Landforms and Its Significance
Related Articles: The Indian Topography Map: A Tapestry of Landforms and Its Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Indian Topography Map: A Tapestry of Landforms and Its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Indian Topography Map: A Tapestry of Landforms and Its Significance
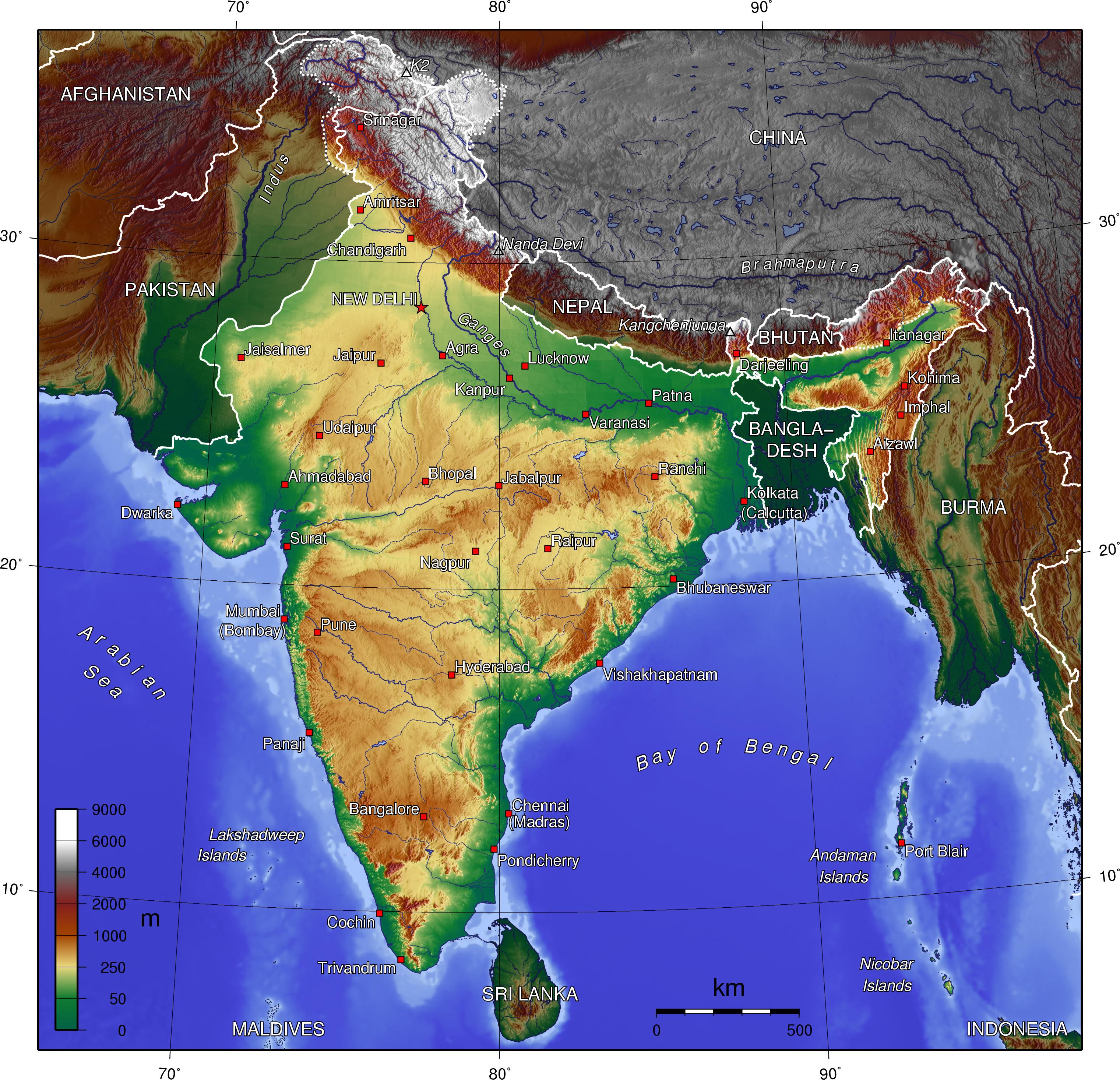
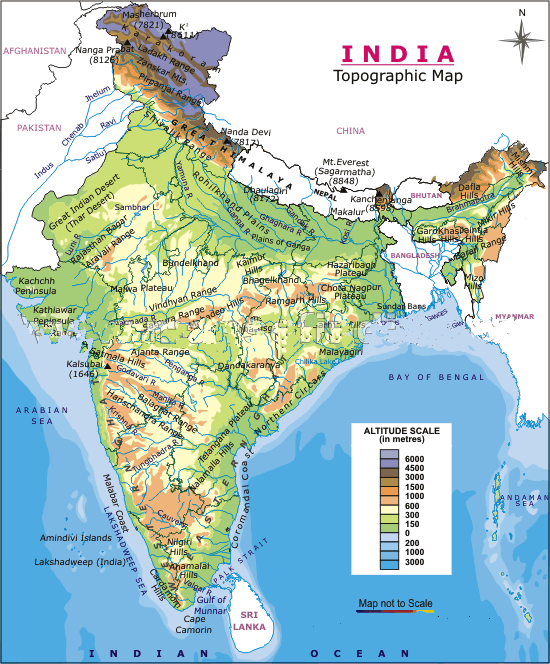
The Indian topography map is a visual representation of the diverse and complex landforms that make up the Indian subcontinent. This intricate tapestry of mountains, plateaus, plains, deserts, and coastal regions has shaped the country’s history, culture, and economy in profound ways. Understanding the topography is crucial for comprehending India’s unique geographical features and their influence on various aspects of life.
A Diverse Landscape:
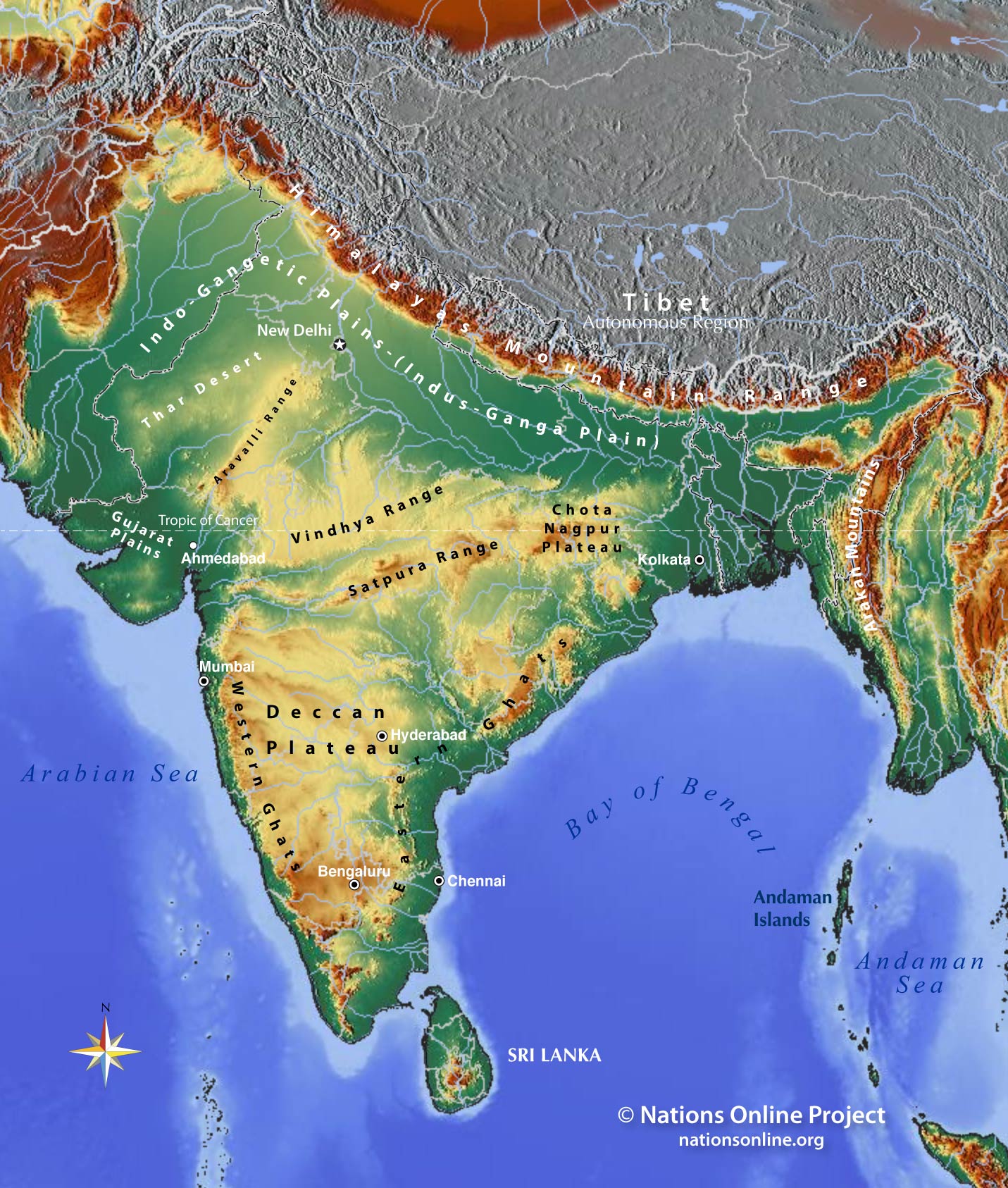
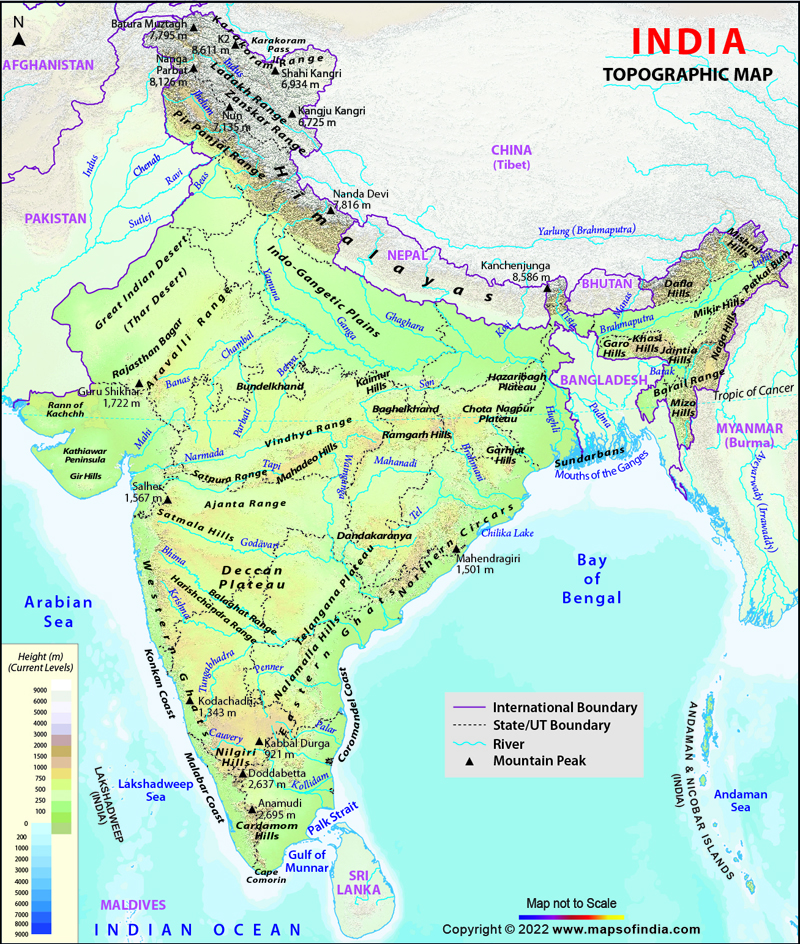
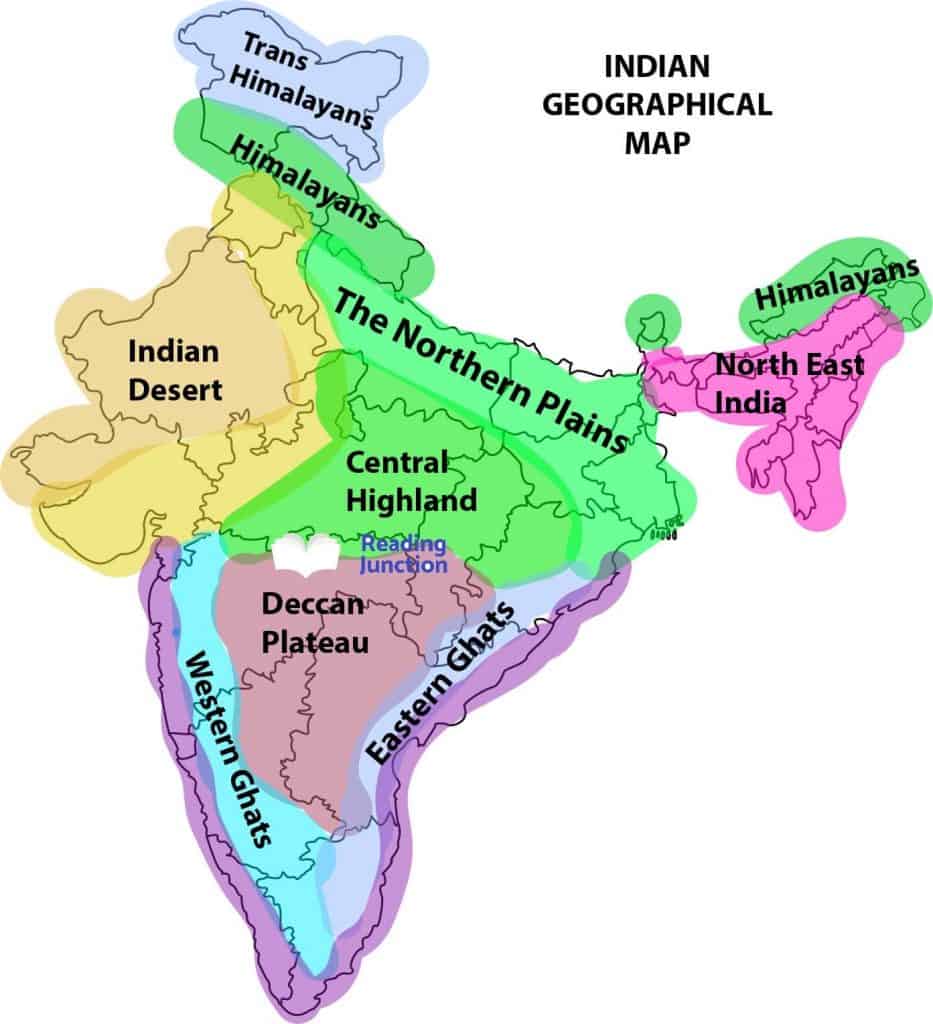
India’s topography is characterized by its remarkable diversity. The towering Himalayan mountain ranges, the highest in the world, dominate the northern frontier, acting as a natural barrier and a source of major rivers. These rivers, such as the Ganga and the Indus, flow through the vast and fertile Indo-Gangetic Plain, a region that has been the cradle of civilization in India for millennia.
Moving south, the topography transitions to the Deccan Plateau, a vast expanse of ancient crystalline rocks that forms the heart of the Indian peninsula. This plateau is characterized by rolling hills, river valleys, and black soil, making it a significant agricultural region.
The western and eastern coastal plains, fringed by the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal respectively, are marked by their fertile alluvial soil and thriving coastal cities. The western coast is home to the Western Ghats, a range of hills that runs parallel to the coast, while the eastern coast features the Eastern Ghats, a less prominent range.
The Significance of Topography:
The varied topography of India has profoundly shaped the country’s history, culture, and economy in numerous ways:
- Agriculture: The fertile Indo-Gangetic Plain, with its rich alluvial soil, is the breadbasket of India, supporting a vast agricultural industry. The Deccan Plateau, with its black soil, is also a significant agricultural region, producing cotton, pulses, and other crops.
- Water Resources: The Himalayan rivers, fed by glacial meltwater, are a crucial source of water for irrigation, drinking, and hydropower generation. These rivers also play a vital role in sustaining the diverse ecosystems of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- Climate: The topography influences India’s diverse climate patterns. The Himalayas act as a barrier, preventing cold winds from the north from reaching the subcontinent. The coastal regions experience a tropical monsoon climate, while the interior regions experience a more arid climate.
- Transportation: The topography has influenced transportation routes and infrastructure development. The plains have facilitated the development of road and rail networks, while the mountains have posed challenges to transportation.
- Biodiversity: The diverse topography has created a wide range of habitats, resulting in a rich biodiversity. The Himalayas are home to a wide variety of flora and fauna, while the coastal regions are characterized by mangroves and coral reefs.
Understanding the Topography: A Tool for Development
The Indian topography map is a valuable tool for understanding the country’s geographical features and their implications for various sectors. It aids in:
- Resource Management: The map helps in identifying areas with abundant water resources, mineral deposits, and fertile land, facilitating efficient resource management.
- Infrastructure Development: It provides insights into the challenges and opportunities associated with infrastructure development, such as road construction, railway lines, and hydropower projects.
- Disaster Management: Understanding the topography helps in predicting and managing natural disasters such as floods, droughts, and earthquakes.
- Tourism: The map highlights the diverse landscapes and scenic beauty of India, attracting tourists and promoting tourism development.
- Environmental Conservation: The map helps in identifying ecologically sensitive areas and formulating strategies for environmental conservation.
FAQs about the Indian Topography Map:
Q: What are the major landforms of India?
A: The major landforms of India include the Himalayan Mountains, the Indo-Gangetic Plain, the Deccan Plateau, the Western Ghats, the Eastern Ghats, the coastal plains, and the Thar Desert.
Q: How does the topography influence India’s climate?
A: The Himalayas act as a barrier, preventing cold winds from the north from reaching the subcontinent. The coastal regions experience a tropical monsoon climate, while the interior regions experience a more arid climate.
Q: What is the significance of the Indo-Gangetic Plain?
A: The Indo-Gangetic Plain is the breadbasket of India, supporting a vast agricultural industry. It is also a densely populated region and the cradle of ancient Indian civilizations.
Q: How does the topography impact transportation in India?
A: The plains have facilitated the development of road and rail networks, while the mountains have posed challenges to transportation.
Q: What are the environmental implications of India’s topography?
A: The diverse topography has created a wide range of habitats, resulting in a rich biodiversity. However, deforestation, pollution, and climate change pose threats to these ecosystems.
Tips for Using the Indian Topography Map:
- Study the map carefully: Pay attention to the different landforms, their relative locations, and their elevation.
- Use the map in conjunction with other resources: Combine the map with information on climate, population density, and economic activities for a comprehensive understanding.
- Focus on specific regions: Analyze the topography of different regions to understand their unique characteristics and challenges.
- Consider the impact of topography on various sectors: Analyze how topography influences agriculture, transportation, water resources, and environmental conservation.
- Use the map for research and planning: The map can be a valuable tool for research projects, development plans, and disaster management strategies.
Conclusion:
The Indian topography map is a powerful visual representation of the country’s diverse and complex landforms. Understanding this topography is crucial for comprehending India’s unique geographical features and their influence on various aspects of life. From shaping its history and culture to influencing its agriculture, climate, and economy, the topography plays a vital role in defining the Indian landscape. By studying and analyzing the Indian topography map, we gain a deeper understanding of the country’s natural resources, challenges, and opportunities, paving the way for sustainable development and responsible resource management.
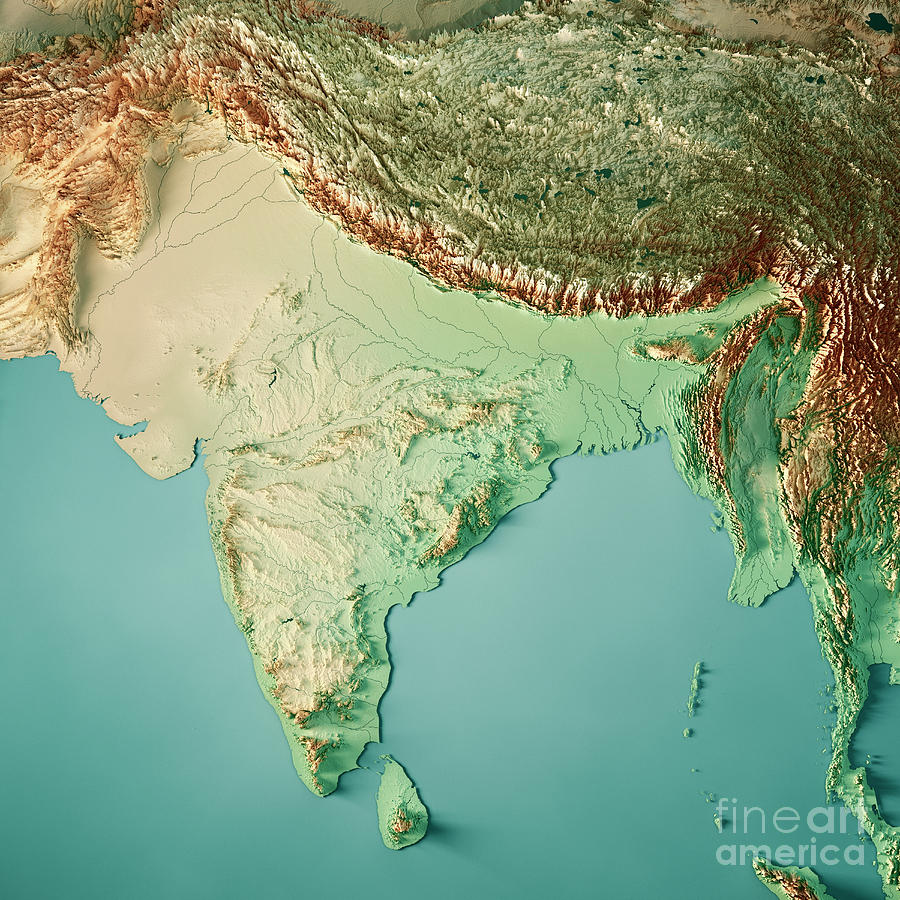




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indian Topography Map: A Tapestry of Landforms and Its Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!