The Landscape of Industrial Growth: A Comprehensive Look at Vietnam’s Industrial Zone Map
Related Articles: The Landscape of Industrial Growth: A Comprehensive Look at Vietnam’s Industrial Zone Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Landscape of Industrial Growth: A Comprehensive Look at Vietnam’s Industrial Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Landscape of Industrial Growth: A Comprehensive Look at Vietnam’s Industrial Zone Map

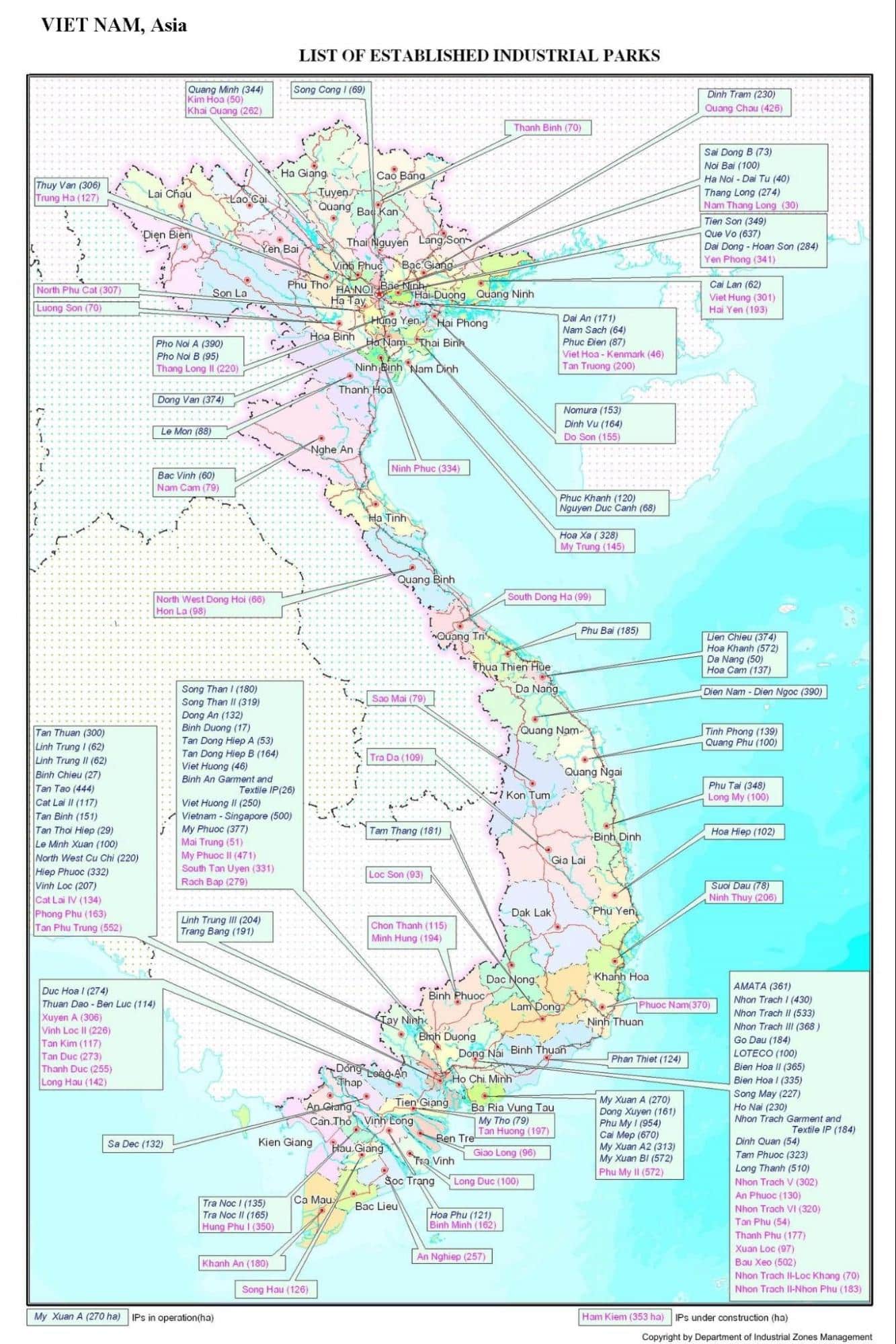
Vietnam’s rapid economic transformation over the past few decades has been fueled by a strategic focus on industrial development. This growth is reflected in the country’s evolving industrial zone map, a vital tool for understanding the spatial distribution of manufacturing and industrial activities across the nation. This map serves as a blueprint for investors, policymakers, and businesses alike, providing insights into the country’s industrial landscape and its potential for further expansion.
A Dynamic Network of Industrial Hubs
Vietnam’s industrial zone map is not static; it is a dynamic entity reflecting the country’s evolving economic priorities and the changing needs of global investors. The map is characterized by a diverse network of industrial zones, each with its own unique strengths and specialization. These zones are strategically located across the country, taking advantage of geographical advantages such as proximity to ports, access to skilled labor, and availability of essential infrastructure.
Key Features of the Industrial Zone Map:
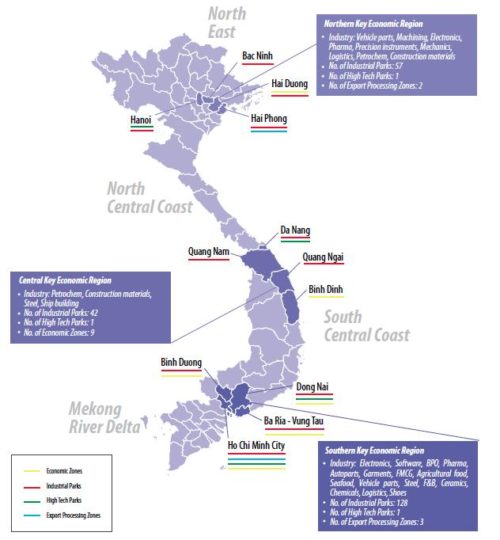
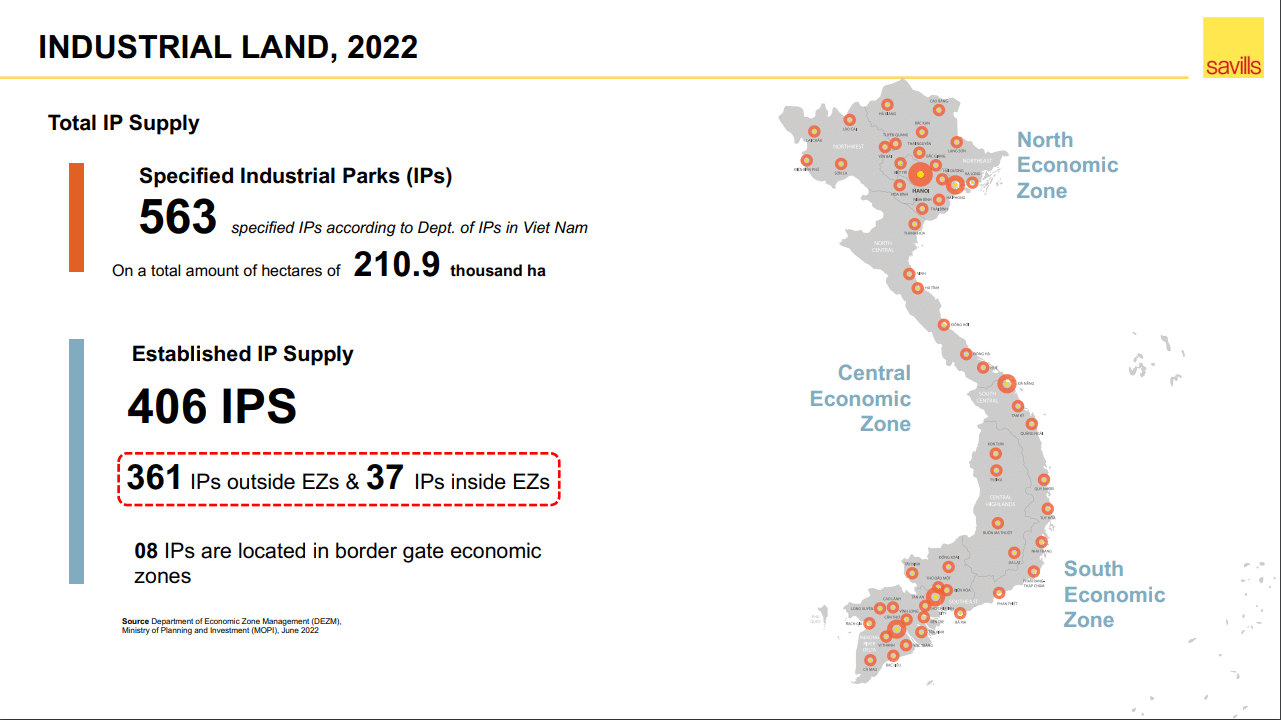
- Geographic Distribution: Industrial zones are spread across all regions of Vietnam, with a concentration in the Southeast region, particularly in Ho Chi Minh City and surrounding provinces. This concentration is driven by the region’s strong infrastructure, proximity to major ports, and established industrial base.
- Sectoral Specialization: Industrial zones often specialize in specific sectors, catering to the demands of particular industries. For instance, some zones focus on electronics manufacturing, while others are dedicated to textiles and garments, automotive components, or food processing. This specialization allows for economies of scale and attracts businesses seeking a supportive ecosystem.
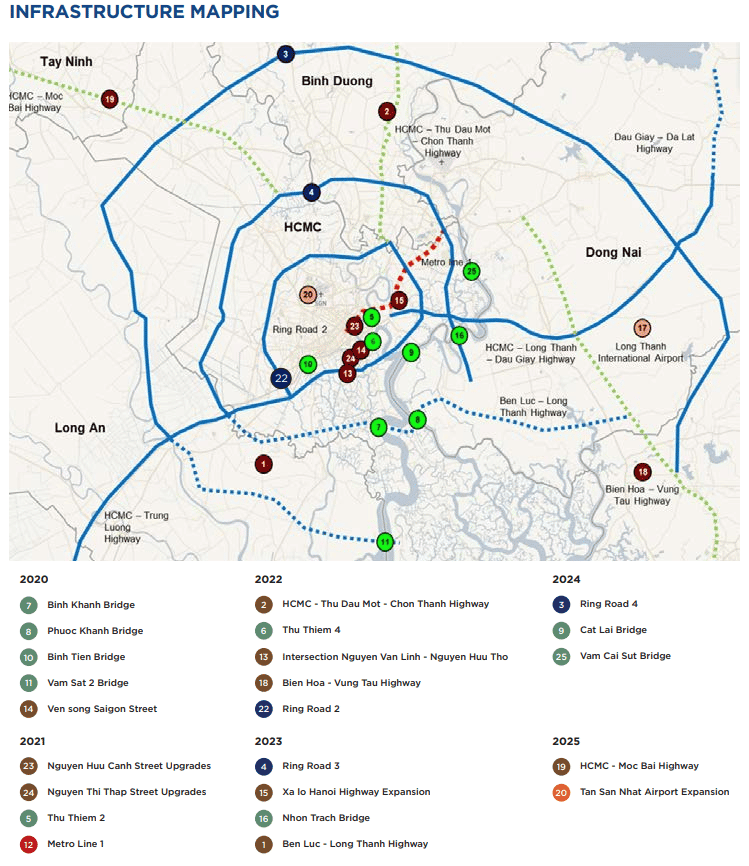
- Infrastructure Development: The success of industrial zones hinges on robust infrastructure, including power supply, transportation networks, telecommunications, and water management systems. The map highlights the development of key infrastructure projects within and around industrial zones, indicating the government’s commitment to supporting industrial growth.
- Investment Incentives: The government offers various investment incentives to attract foreign and domestic companies to industrial zones. These incentives can include tax breaks, land lease concessions, and simplified administrative procedures. The map often incorporates information on these incentives, highlighting the attractive investment environment offered by different zones.
Benefits of a Well-Defined Industrial Zone Map:
- Investment Attraction: The map serves as a valuable tool for attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) by providing a clear overview of available industrial land, infrastructure, and investment incentives. This transparency fosters confidence among potential investors, leading to increased investment in the country.
- Economic Diversification: By promoting the development of different industrial sectors, the map contributes to economic diversification, reducing dependence on any single industry and creating a more resilient economy.
- Job Creation and Skill Development: Industrial zones are major drivers of employment, creating jobs for local communities and contributing to the overall economic well-being of the country. They also stimulate the development of vocational training programs, fostering a skilled workforce.
- Regional Development: The strategic location of industrial zones helps promote balanced regional development by creating economic opportunities in different parts of the country. This reduces regional disparities and fosters a more equitable society.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite its significant progress, Vietnam’s industrial zone map faces several challenges:
- Environmental Sustainability: The rapid industrial growth needs to be balanced with environmental protection. Sustainable practices and pollution control measures are crucial to ensure the long-term viability of industrial zones.
- Infrastructure Gaps: While infrastructure development has been a priority, some zones still face limitations in terms of power supply, transportation, and water management. Addressing these gaps is essential for attracting more investment and ensuring the smooth functioning of industrial activities.
- Skilled Labor Shortages: As industries become more sophisticated, the demand for skilled labor is increasing. The country needs to invest in education and training programs to ensure a sufficient supply of qualified workers.
Looking ahead, the industrial zone map will play a key role in Vietnam’s continued economic growth. The government is actively working to address the challenges mentioned above and to further optimize the map by:
- Developing Special Economic Zones (SEZs): SEZs offer a more liberal investment environment and are designed to attract high-value industries and technology-driven companies.
- Promoting Green Industrial Zones: The focus is shifting towards creating environmentally sustainable industrial zones, utilizing renewable energy sources and implementing green technologies.
- Strengthening Infrastructure Connectivity: Improving connectivity between industrial zones and major transportation hubs is essential for facilitating the efficient movement of goods and services.
FAQs about Vietnam’s Industrial Zone Map:
Q: What are the most important industrial zones in Vietnam?
A: Some of the most prominent industrial zones include:
- Tan Thuan Export Processing Zone (SEZ) in Ho Chi Minh City: Known for its strong infrastructure, diverse industries, and proximity to the port.
- Thuan An Industrial Zone in Binh Duong Province: A major hub for electronics manufacturing, automotive components, and textiles.
- Nong Son Industrial Zone in Hai Phong City: Specializes in shipbuilding, heavy industries, and logistics.
- Van Phong Economic Zone in Khanh Hoa Province: Focuses on high-tech industries, tourism, and logistics.
Q: How can I access information about specific industrial zones?
A: Information on industrial zones can be found on various online platforms, including:
- Vietnam Industrial Zones Authority (VIZIPA): The official website provides detailed information on all industrial zones in Vietnam, including their location, infrastructure, and investment incentives.
- Vietnam Investment Review: This publication regularly features articles on industrial zone development and investment opportunities.
- Foreign investment agencies: Embassies and consulates of various countries in Vietnam provide information on industrial zones relevant to their respective investors.
Q: What are the main challenges faced by Vietnam’s industrial zones?
A: Challenges include:
- Environmental sustainability: Balancing economic growth with environmental protection is a constant concern.
- Infrastructure gaps: Some zones lack adequate power supply, transportation, and water management systems.
- Skilled labor shortages: The demand for skilled workers is increasing, requiring investments in education and training.
Q: How is the government working to improve the industrial zone map?
A: The government is taking several steps to optimize the map:
- Developing special economic zones (SEZs): Offering more liberal investment conditions and attracting high-value industries.
- Promoting green industrial zones: Focusing on environmental sustainability and utilizing green technologies.
- Strengthening infrastructure connectivity: Improving transportation links between industrial zones and major hubs.
Tips for Businesses Interested in Investing in Vietnam’s Industrial Zones:
- Conduct thorough research: Study the map, understand the strengths and weaknesses of different zones, and assess their suitability for your specific business needs.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with legal and financial advisors specializing in Vietnam to navigate the investment landscape and understand the legal and regulatory framework.
- Network with local businesses: Connect with existing businesses operating in industrial zones to gain insights into the local market and potential partnerships.
- Explore government incentives: Familiarize yourself with the various investment incentives offered by the government and how they can benefit your business.
Conclusion:
Vietnam’s industrial zone map is a testament to the country’s commitment to economic growth and its strategic vision for industrial development. It provides a valuable roadmap for investors, businesses, and policymakers, showcasing the country’s potential as a manufacturing hub in Southeast Asia. By addressing the challenges and continuing to optimize the map, Vietnam can further enhance its attractiveness as an investment destination and secure its place as a key player in the global supply chain.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Landscape of Industrial Growth: A Comprehensive Look at Vietnam’s Industrial Zone Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!