The Power of Transformation: Understanding map in Python
Related Articles: The Power of Transformation: Understanding map in Python
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Transformation: Understanding map in Python. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Transformation: Understanding map in Python
![Python map() — Finally Mastering the Python Map Function [+Video] – Be on the Right Side of Change](https://blog.finxter.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/Map-Python-Kopie.png)
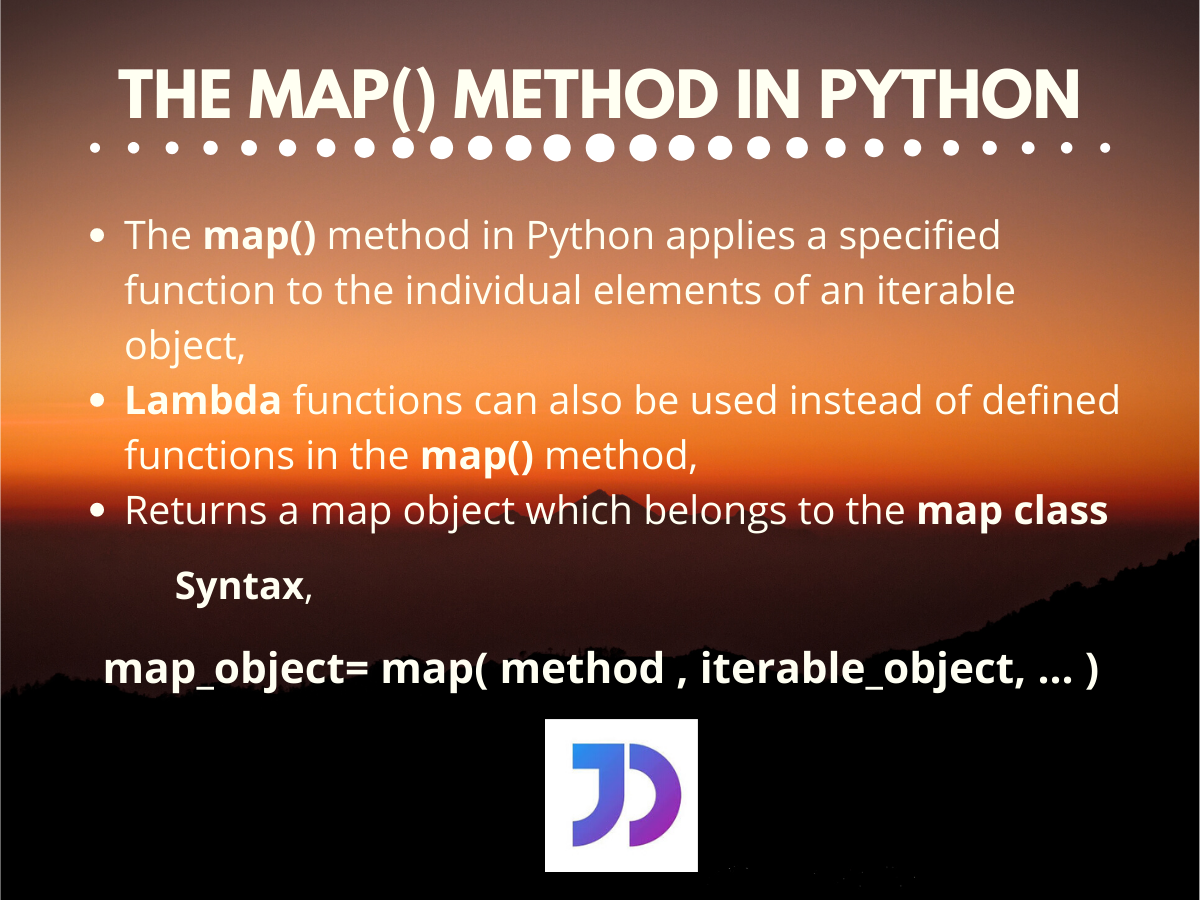
In the realm of Python programming, the map function stands as a powerful tool for efficient data manipulation. It allows developers to apply a specific function to each element of an iterable object, such as a list or tuple, without the need for explicit loops. This inherent efficiency and elegance make map a cornerstone of Pythonic code, enhancing readability and reducing boilerplate.
Understanding the Essence of map
At its core, map is a higher-order function. This means it takes another function as an argument, along with an iterable object. It then iterates over the iterable, applying the provided function to each element and producing a new iterable containing the transformed results.
Illustrative Example:
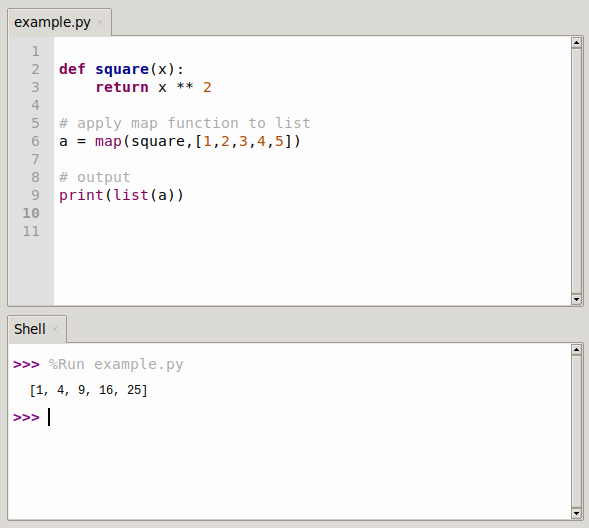
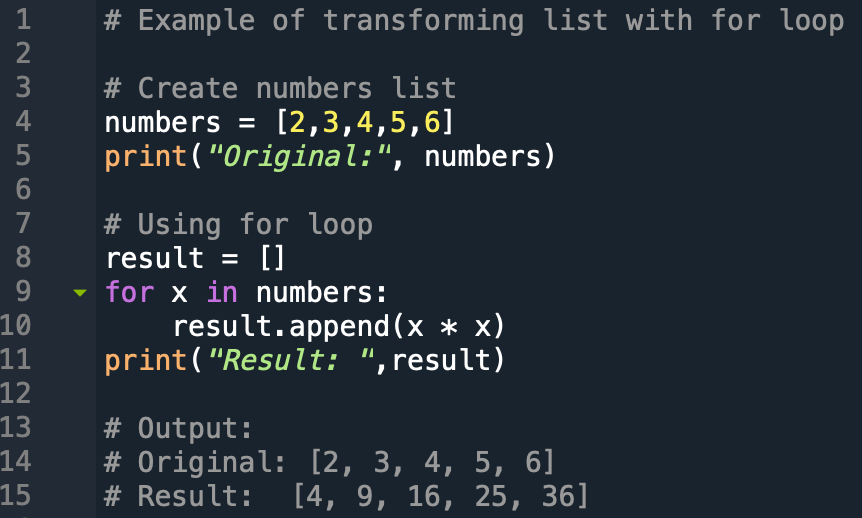
Consider a list of numbers: numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]. Let’s say we want to square each element. Using a traditional loop, this would require:
squared_numbers = []
for number in numbers:
squared_numbers.append(number ** 2)However, map offers a more concise and Pythonic approach:
squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x ** 2, numbers))Here, lambda x: x ** 2 defines an anonymous function that squares its input. map applies this function to each element in numbers, producing a map object. The list() constructor converts this object into a list for easy access.
Benefits of Employing map
The advantages of map extend beyond mere brevity:
-
Readability: The functional style of
mappromotes cleaner and more intuitive code, enhancing understanding and maintainability. - Conciseness: Eliminating explicit loops reduces code length, contributing to improved readability and reducing the potential for errors.
-
Efficiency:
mapis often more efficient than traditional loops, especially for large datasets, as it leverages Python’s internal optimizations. -
Flexibility:
mapcan accept any function as its first argument, enabling diverse transformations on iterable objects.
Beyond Basic Transformations:
While squaring numbers is a simple example, map excels in more complex scenarios. For instance, you could use it to:
-
Convert data types:
map(str, [1, 2, 3])converts a list of integers to a list of strings. -
Apply custom logic:
map(lambda x: x * 2 + 1, [1, 2, 3])applies a custom function to each element. -
Process data from multiple iterables:
map(lambda x, y: x + y, [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])combines elements from two lists.
Understanding the Limitations of map
While powerful, map has certain limitations:
-
Limited Control Flow:
mapprimarily focuses on applying functions to individual elements. It doesn’t provide mechanisms for conditional logic or complex operations within the transformation process. -
Iterables Only:
mapoperates solely on iterable objects. It cannot directly handle non-iterable data structures like dictionaries.
FAQs about map in Python
1. Can map modify the original iterable?
No, map does not modify the original iterable. It creates a new iterable containing the transformed results.
2. What happens if the function and iterable have different lengths?
map iterates until the shortest iterable is exhausted. Any remaining elements in the longer iterable will be ignored.
3. Can I use map with multiple arguments?
Yes, map can accept multiple iterables as arguments, provided the function takes the same number of arguments as the number of iterables.
4. How can I use map with a function that requires multiple arguments?
You can use functools.partial to create a new function that takes only the necessary arguments for map.
5. When should I use map instead of a loop?
Consider map when:
- You need to apply a simple transformation to each element of an iterable.
- You are working with a large dataset.
- You want to improve code readability and conciseness.
Tips for Using map Effectively
-
Choose the right function: Ensure the function you provide to
mapis appropriate for the transformation you intend to perform. -
Use lambda expressions: Lambda expressions offer a concise way to define anonymous functions for use with
map. -
Consider
functools.partial: Utilizefunctools.partialto create functions with fixed arguments for use withmapwhen dealing with functions that require multiple arguments. -
Combine with other functions:
mapcan be combined with other functions likefilterandreduceto create powerful data manipulation pipelines.
Conclusion
map serves as a potent tool in the Python programmer’s arsenal. Its ability to streamline data transformations, promote code clarity, and enhance efficiency makes it an invaluable asset. By understanding its nuances and applying it strategically, developers can elevate their Python code to new heights of elegance and effectiveness.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Transformation: Understanding map in Python. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!