The Topographical Landscape of Yemen: A Journey Through Diverse Terrain
Related Articles: The Topographical Landscape of Yemen: A Journey Through Diverse Terrain
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Topographical Landscape of Yemen: A Journey Through Diverse Terrain. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Topographical Landscape of Yemen: A Journey Through Diverse Terrain
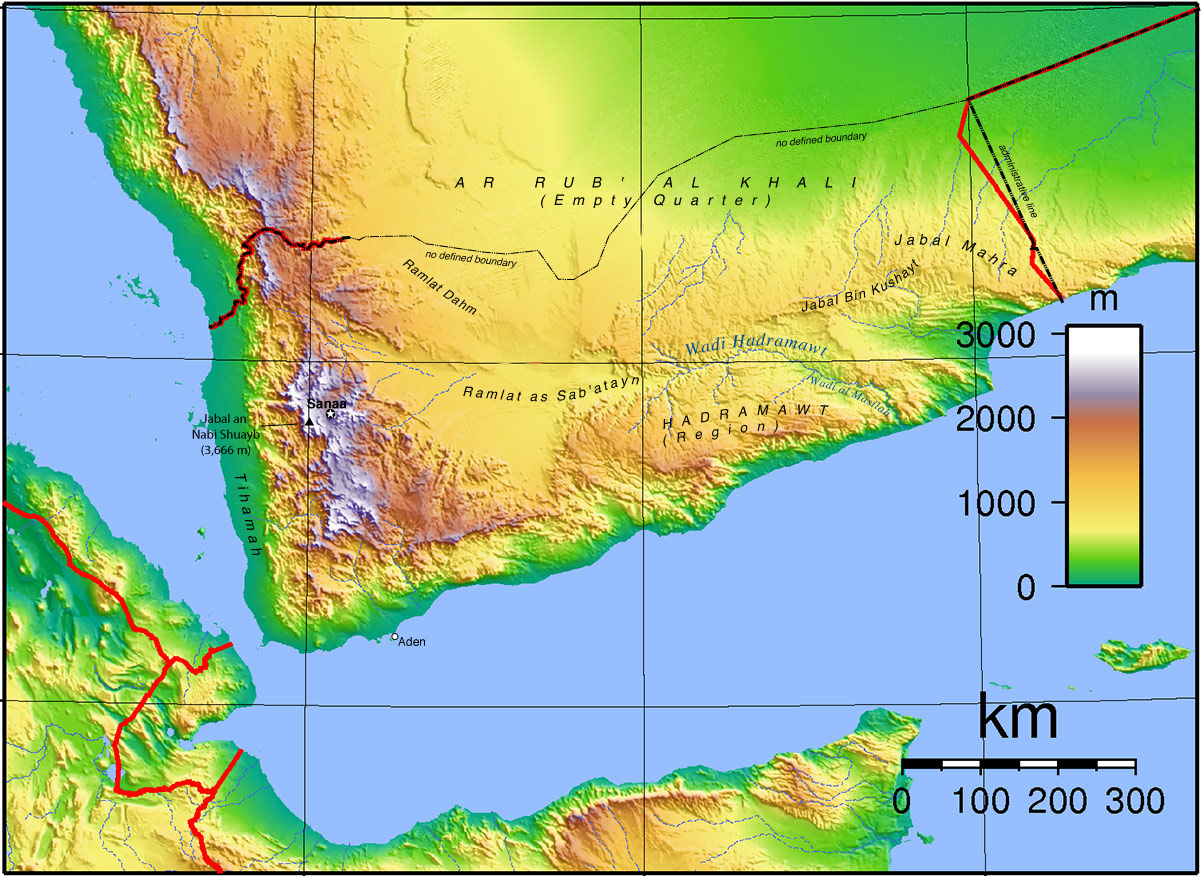
Yemen, nestled at the southern tip of the Arabian Peninsula, boasts a remarkably diverse and challenging topography. Its geographical makeup, a tapestry woven from rugged mountains, vast deserts, fertile valleys, and coastal plains, has profoundly shaped the country’s history, culture, and societal dynamics. Understanding the intricate interplay of these features is crucial for comprehending Yemen’s present and envisioning its future.
A Mountainous Backbone:
The most prominent feature of Yemen’s topography is its towering mountain ranges, forming a backbone that traverses the country from north to south. The Sarawat Mountains, stretching for over 1,200 kilometers, rise dramatically from the coastal plains, culminating in Jabal Nabi Shu’ayb, the highest peak in the Arabian Peninsula at 3,666 meters. These mountains, with their steep slopes and deep gorges, create a challenging environment for transportation and communication, isolating communities and hindering development.
Desert Expanse and Fertile Valleys:
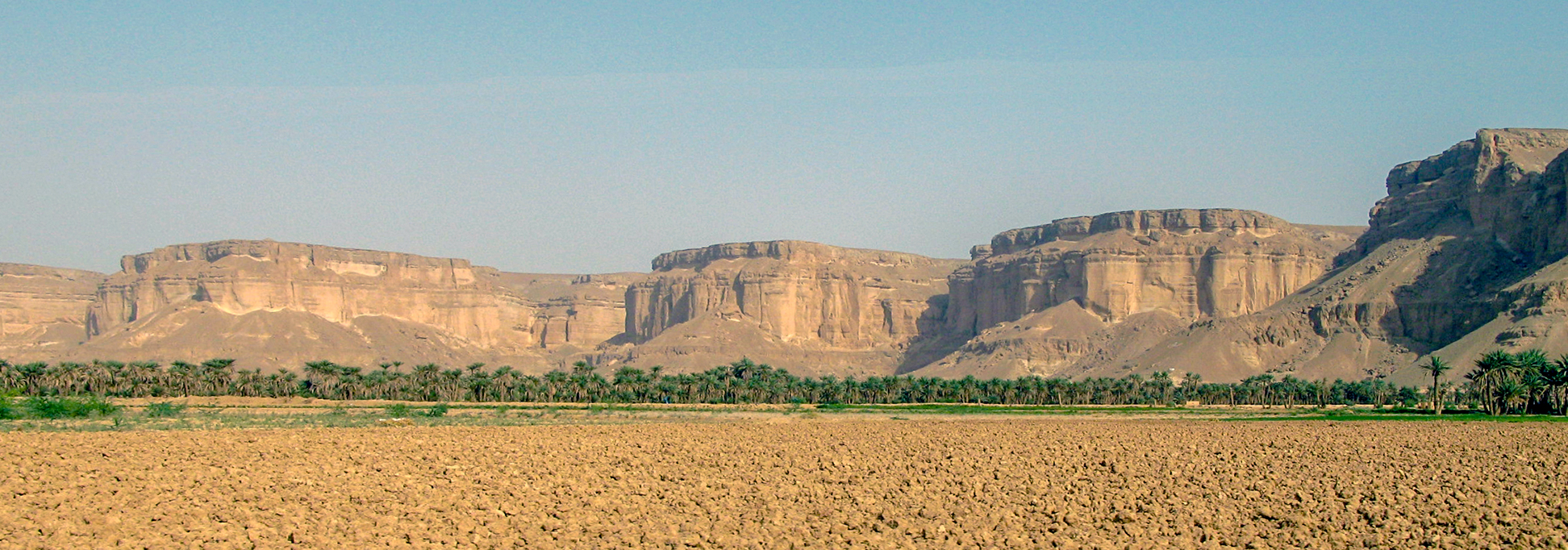
The vast expanse of the Empty Quarter (Rub’ al Khali) desert, the world’s largest contiguous sand desert, dominates the eastern region of Yemen. Its unforgiving terrain poses significant challenges for human habitation and economic activity. In stark contrast, the western flanks of the Sarawat Mountains are home to fertile valleys, known as Wadis. These valleys, fed by seasonal rainfall and the occasional flash floods, provide pockets of arable land, supporting agriculture and fostering settlements.
Coastal Plains and Islands:
Yemen’s coastline stretches over 2,000 kilometers, encompassing a variety of landscapes. The Red Sea coast is characterized by narrow coastal plains, often interrupted by rocky cliffs and inlets. The Gulf of Aden coastline, in contrast, is broader and more gently sloping, with sandy beaches and mangrove swamps. Scattered along the coastline are a series of islands, including Socotra, known for its unique flora and fauna.
The Impact of Topography on Yemen:
Yemen’s topography has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and societal dynamics. The mountainous terrain has historically provided refuge for diverse communities, fostering distinct cultures and languages. The isolation caused by the mountains has also contributed to the fragmentation of the country, making it vulnerable to internal conflicts and external influences.
The desert landscape has posed significant challenges for agriculture and economic development, forcing communities to adapt to harsh conditions and rely on traditional forms of subsistence. The fertile valleys, however, have acted as oases of life, attracting settlements and supporting agriculture, contributing to the country’s agricultural output.
The coastline has played a crucial role in Yemen’s history, serving as a conduit for trade and cultural exchange. However, the lack of extensive port infrastructure and the challenges posed by piracy have hampered its potential for economic growth.
The Importance of Understanding Yemen’s Topography:
Understanding Yemen’s topography is essential for addressing the country’s multifaceted challenges. It provides insights into:
- Resource Management: The distribution of water resources, particularly in the arid and semi-arid regions, is heavily influenced by topography. Understanding the flow of water and the location of aquifers is crucial for sustainable water management.
- Infrastructure Development: The mountainous terrain and the vast deserts present significant challenges for infrastructure development, particularly in terms of transportation and communication networks. Understanding the topography is essential for designing and implementing infrastructure projects that are effective and cost-efficient.
- Conflict and Security: The rugged terrain has historically provided safe havens for armed groups and rebels, making it difficult to maintain security and stability. Understanding the topography can assist in developing strategies for conflict resolution and peacebuilding.
- Economic Development: The topography influences the potential for economic development in different regions. Understanding the distribution of resources, the challenges posed by the terrain, and the opportunities presented by the coastline is crucial for formulating effective economic development strategies.
FAQs Regarding Yemen’s Topography:
1. What are the main topographical features of Yemen?
Yemen’s main topographical features include its mountain ranges (Sarawat Mountains), vast deserts (Rub’ al Khali), fertile valleys (Wadi*s), and coastal plains.
2. What is the highest point in Yemen?
The highest point in Yemen is Jabal Nabi Shu’ayb, located in the Sarawat Mountains, with an elevation of 3,666 meters.
3. How does Yemen’s topography affect its climate?
Yemen’s topography has a significant influence on its climate. The mountains create a rain shadow effect, with the western slopes receiving more rainfall than the eastern slopes. The deserts are extremely arid, while the coastal plains experience a more moderate climate.
4. What are the challenges posed by Yemen’s topography?
Yemen’s topography poses significant challenges for transportation, communication, and economic development. The mountainous terrain makes it difficult to build roads and infrastructure, while the deserts are difficult to traverse and unsuitable for agriculture.
5. How has Yemen’s topography shaped its culture?
Yemen’s topography has played a significant role in shaping its diverse cultures. The isolation created by the mountains has led to the development of distinct communities with unique traditions and languages.
Tips for Understanding Yemen’s Topography:
- Use a detailed topographical map of Yemen: This will help you visualize the country’s terrain and understand the location of its major features.
- Read about the different regions of Yemen: Each region has its own unique topographical characteristics and cultural traditions.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and articles provide information on Yemen’s topography, climate, and history.
- Watch documentaries and films: Visual media can provide a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities presented by Yemen’s terrain.
Conclusion:
Yemen’s topography is a defining characteristic of the country, shaping its history, culture, and societal dynamics. Understanding the intricate interplay of its mountains, deserts, valleys, and coastlines is crucial for comprehending the country’s challenges and opportunities. By recognizing the influence of topography on resource management, infrastructure development, conflict, and economic development, we can better understand Yemen’s complex reality and contribute to its sustainable future.





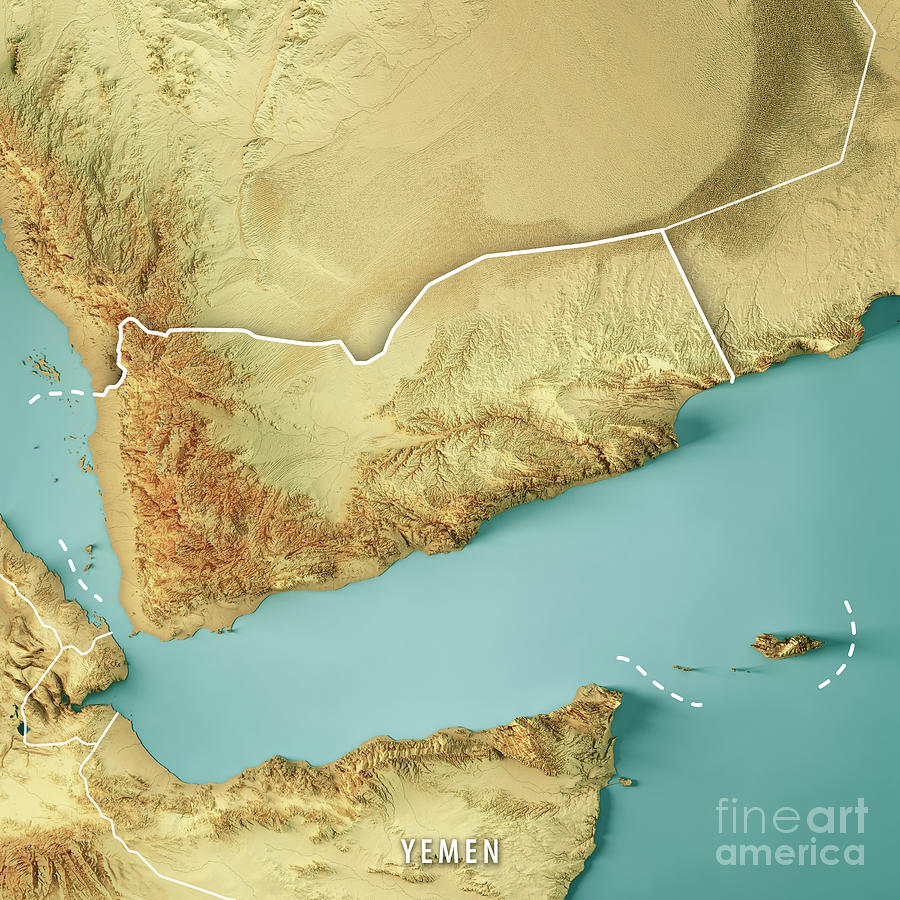

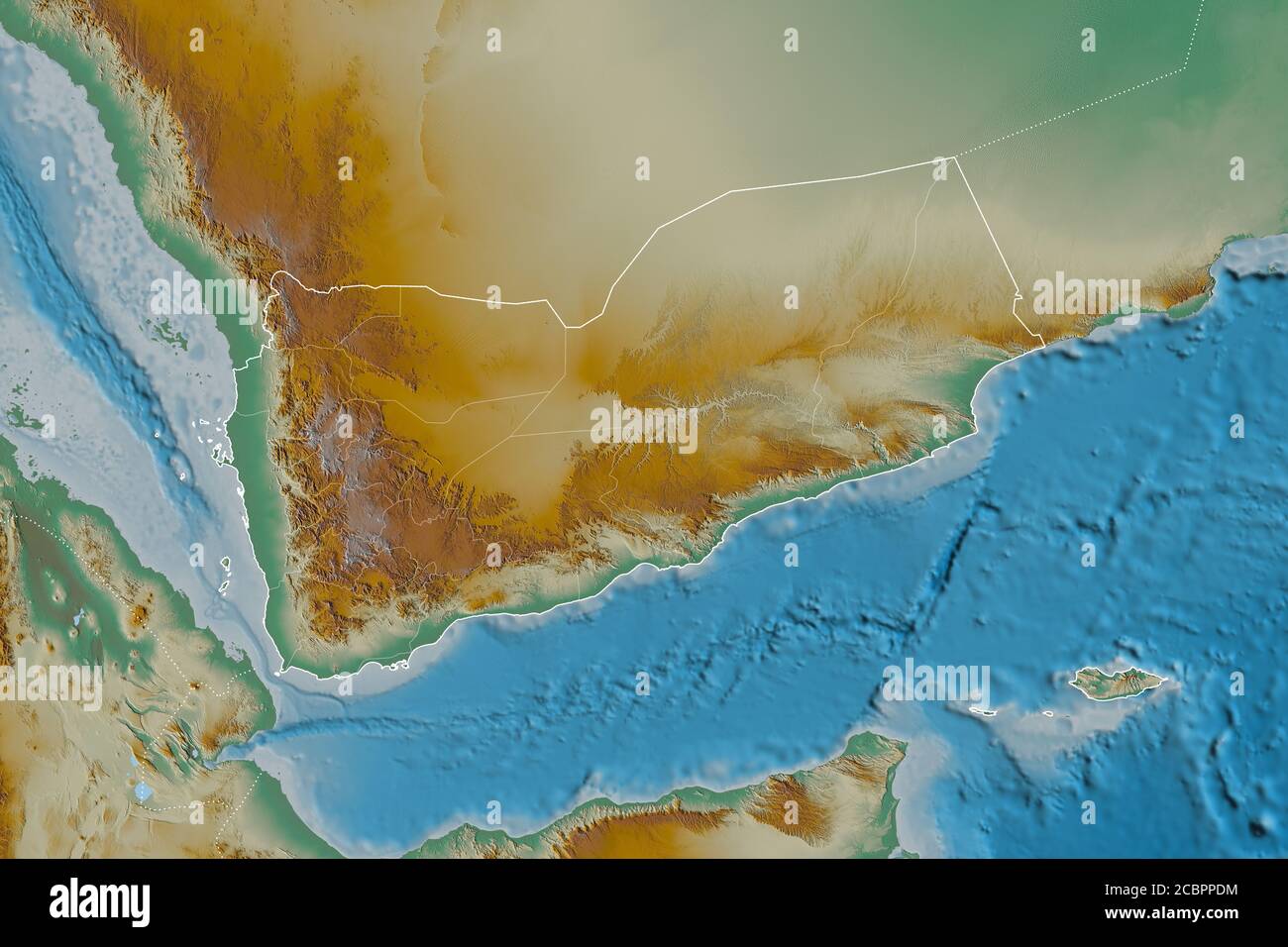
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Topographical Landscape of Yemen: A Journey Through Diverse Terrain. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!