The Topography of Mexico: A Landscape of Diversity and Complexity
Related Articles: The Topography of Mexico: A Landscape of Diversity and Complexity
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Topography of Mexico: A Landscape of Diversity and Complexity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Topography of Mexico: A Landscape of Diversity and Complexity

Mexico, a land of vibrant culture and rich history, is also a nation of diverse and captivating topography. Its geographical features, ranging from towering mountains to expansive deserts, from lush rainforests to fertile valleys, have shaped its cultural identity, its economic development, and its environmental challenges. Understanding the topography of Mexico is crucial for appreciating its intricate tapestry of landscapes, its unique ecosystems, and its complex relationship with the natural world.
A Tapestry of Mountains and Plateaus
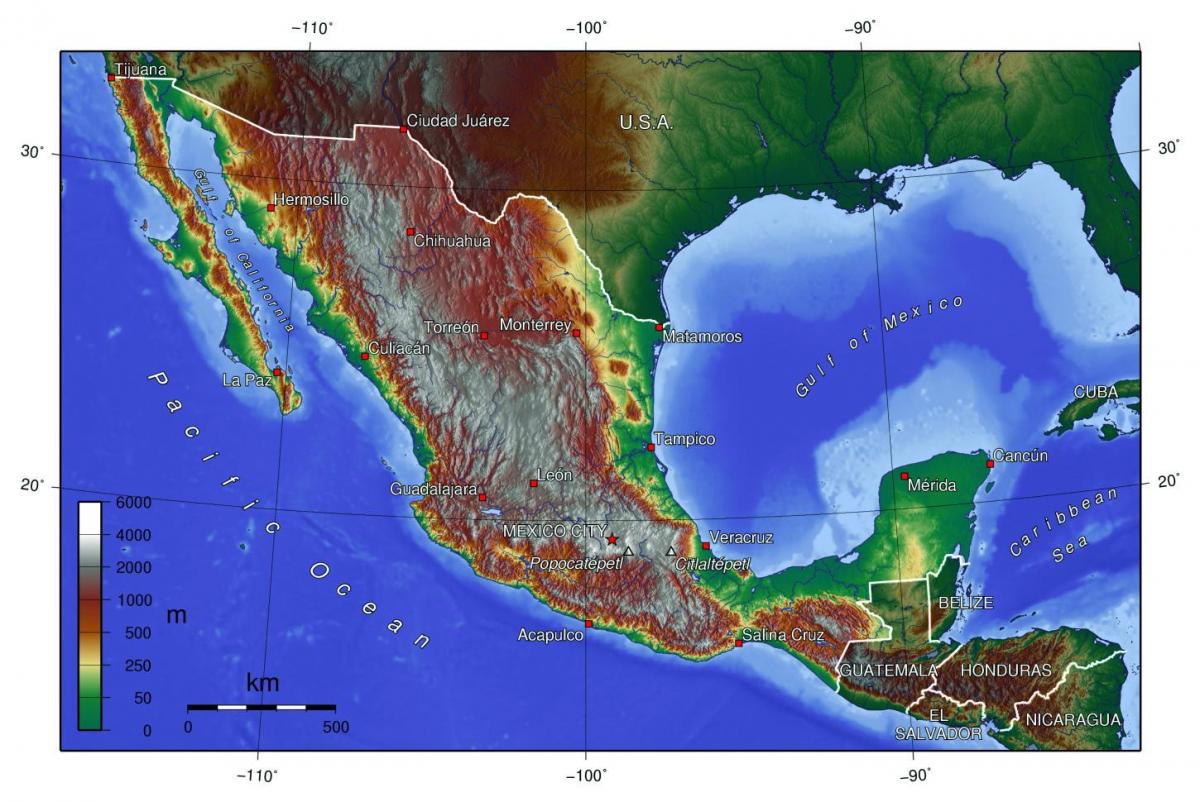
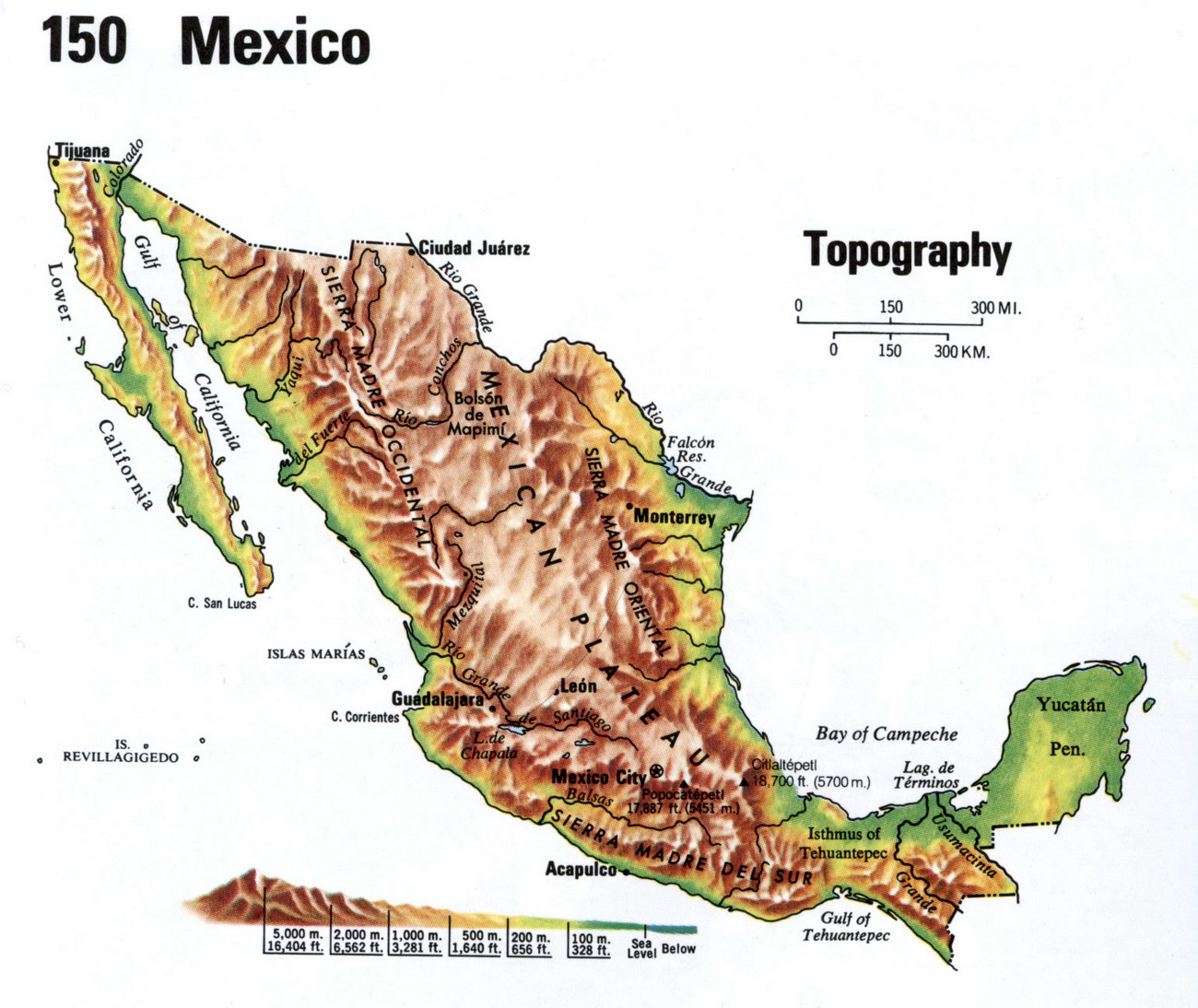
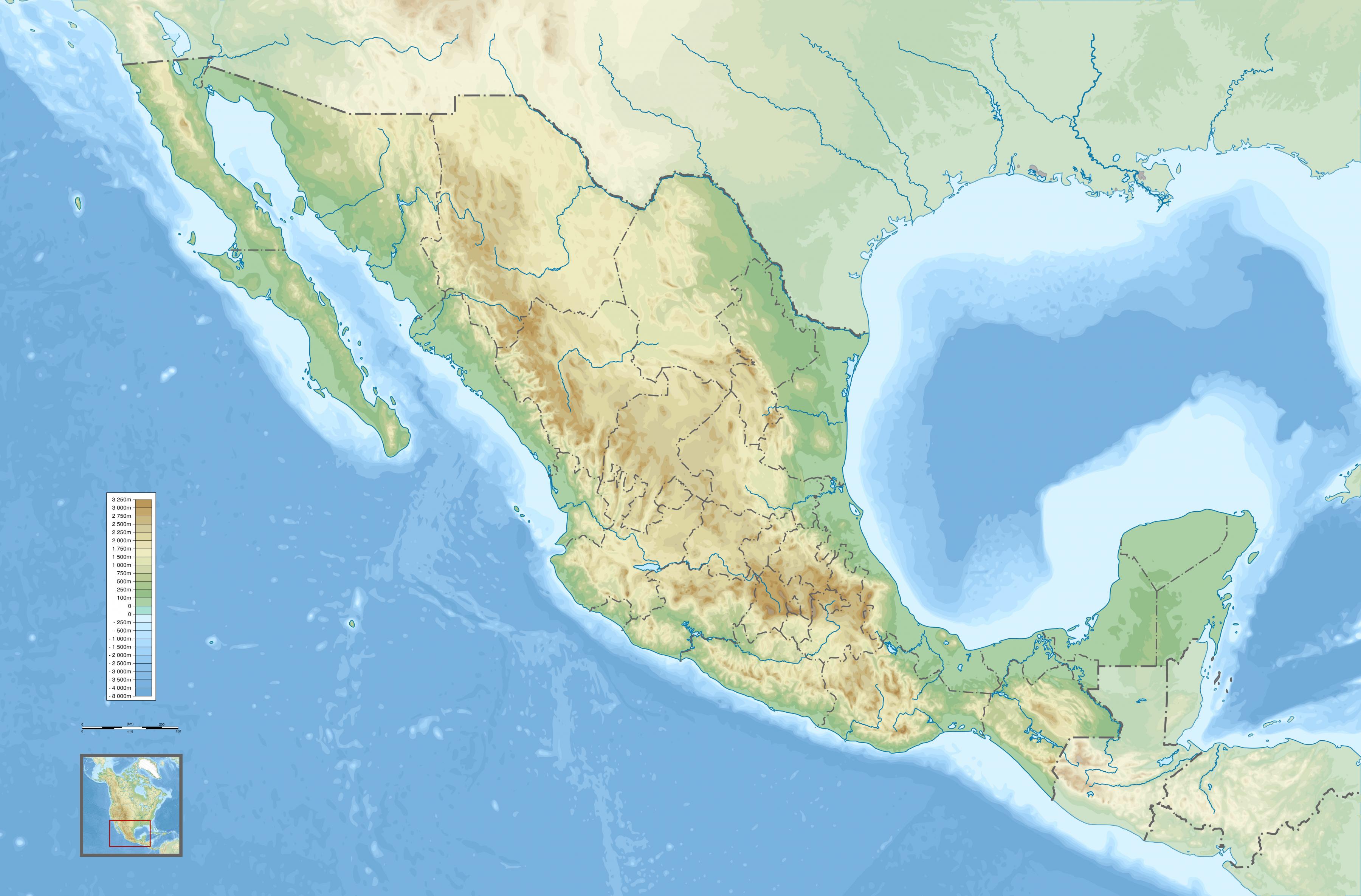
The dominant feature of Mexico’s topography is its mountainous terrain. The Sierra Madre Occidental, Sierra Madre Oriental, and Sierra Madre del Sur form a vast, interconnected mountain system that stretches across the country, creating a dramatic and rugged landscape. The Sierra Madre Occidental, rising along the western edge of the country, is characterized by its steep slopes, deep canyons, and volcanic peaks, including the iconic Cerro Mohinora. The Sierra Madre Oriental, running parallel to the eastern coast, is known for its limestone formations, deep valleys, and the dramatic Barranca del Cobre, a system of canyons even deeper than the Grand Canyon. The Sierra Madre del Sur, traversing the southern portion of Mexico, is a more diverse range with volcanic peaks, coastal lowlands, and fertile valleys.
These mountain ranges are interspersed with high plateaus, such as the Mexican Plateau, which forms the heart of the country. This plateau, extending from the northern border to the central highlands, is characterized by its high elevation, arid climate, and volcanic landscapes. The plateau is home to major cities like Mexico City and Guadalajara, and its fertile soils have supported agriculture for centuries.
Coastal Plains and Coastal Regions
Mexico’s coastline, extending over 9,000 kilometers, is a dynamic and diverse landscape. The Pacific coast, characterized by its rugged cliffs, sandy beaches, and rocky inlets, is home to a rich marine ecosystem and numerous coastal cities. The Gulf of Mexico coast, on the other hand, is characterized by its flat plains, mangrove swamps, and extensive lagoons. It is a major hub for the oil and gas industry and supports a thriving fishing industry.
The coastal plains of Mexico are often fertile and support a variety of agricultural activities. However, they are also vulnerable to natural disasters such as hurricanes and flooding. The coastal regions of Mexico are also important for tourism, with their beautiful beaches and diverse ecosystems attracting visitors from around the world.
Volcanic Landscapes and Geothermal Activity
Mexico is located in the Ring of Fire, a region of intense seismic and volcanic activity. This geological activity has resulted in numerous volcanic peaks, including Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl, which dominate the landscape of central Mexico. These volcanoes, though potentially dangerous, have also enriched the soil, providing fertile grounds for agriculture.
Mexico’s volcanic activity also manifests in the form of geothermal energy. Numerous hot springs and geysers can be found throughout the country, providing a source of renewable energy and attracting tourists. The geothermal energy potential of Mexico is significant and offers a promising avenue for sustainable development.
The Importance of Topography in Shaping Mexico
The topography of Mexico has played a significant role in shaping its history, culture, and economy. The rugged mountain terrain, for example, has historically served as a barrier to communication and transportation, leading to the development of distinct regional cultures and languages. The fertile valleys and plateaus have supported agriculture, providing the foundation for the development of major cities and urban centers.
The topography of Mexico has also influenced its economic development. The coastal plains, for instance, have supported a thriving agricultural industry, while the coastal regions have become centers for tourism and fishing. The mountainous terrain has fostered the development of mining and forestry industries.
Furthermore, the topography of Mexico has shaped its environmental challenges. The country’s diverse ecosystems, ranging from arid deserts to lush rainforests, are home to a rich biodiversity. However, these ecosystems are vulnerable to deforestation, pollution, and climate change. The mountainous terrain, for example, is prone to landslides and erosion, while the coastal regions are vulnerable to rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
Understanding the Topography: Tools and Resources
Topography maps are essential tools for understanding the diverse and complex landscape of Mexico. These maps provide detailed information on elevation, terrain, and features such as rivers, lakes, and mountains. They are used by a wide range of professionals, including geographers, geologists, engineers, and planners, to study the land, manage resources, and plan infrastructure projects.
Several resources are available for accessing topography maps of Mexico. The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI) provides detailed topographic maps, as well as other geographical data, on its website. Online mapping platforms, such as Google Maps and OpenStreetMap, also offer topographic maps of Mexico, allowing users to explore the country’s landscape in detail.
FAQs about Topography Maps of Mexico
Q: What information can I find on a topography map of Mexico?
A: Topography maps of Mexico provide information on elevation, terrain, and features such as rivers, lakes, mountains, and settlements. They can also show the distribution of natural resources, such as forests and minerals.
Q: How can I use a topography map to plan a trip to Mexico?
A: Topography maps can help you identify areas of interest, such as mountains, canyons, or coastal regions. They can also help you plan your route and identify potential challenges, such as steep slopes or difficult terrain.
Q: What are some of the benefits of using topography maps?
A: Topography maps provide a visual representation of the land, allowing users to understand its physical characteristics and features. They can be used for a variety of purposes, including planning infrastructure projects, managing natural resources, and studying the environment.
Q: How can I access topography maps of Mexico?
A: Several resources are available for accessing topography maps of Mexico, including the National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI) website, online mapping platforms such as Google Maps and OpenStreetMap, and specialized mapping services.
Tips for Using Topography Maps of Mexico
- Choose the right scale: The scale of the map should be appropriate for your needs. For example, a large-scale map is best for detailed planning, while a small-scale map is suitable for general overview.
- Understand the symbols: Topography maps use specific symbols to represent features such as elevation, terrain, and water bodies. Familiarize yourself with these symbols before using the map.
- Use multiple sources: Combine topography maps with other resources, such as satellite imagery and aerial photographs, for a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
Conclusion
The topography of Mexico is a captivating tapestry of mountains, plateaus, coastal plains, and volcanic landscapes. This diverse and complex landscape has shaped the country’s history, culture, and economy, and continues to present both opportunities and challenges. Topography maps are essential tools for understanding and appreciating the intricate beauty and complexity of Mexico’s physical geography. By using these maps, we can gain a deeper understanding of the country’s natural resources, its environmental challenges, and its potential for sustainable development.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Topography of Mexico: A Landscape of Diversity and Complexity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!