The Topography of Rome: A City Shaped by Time and Terrain
Related Articles: The Topography of Rome: A City Shaped by Time and Terrain
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Topography of Rome: A City Shaped by Time and Terrain. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Topography of Rome: A City Shaped by Time and Terrain
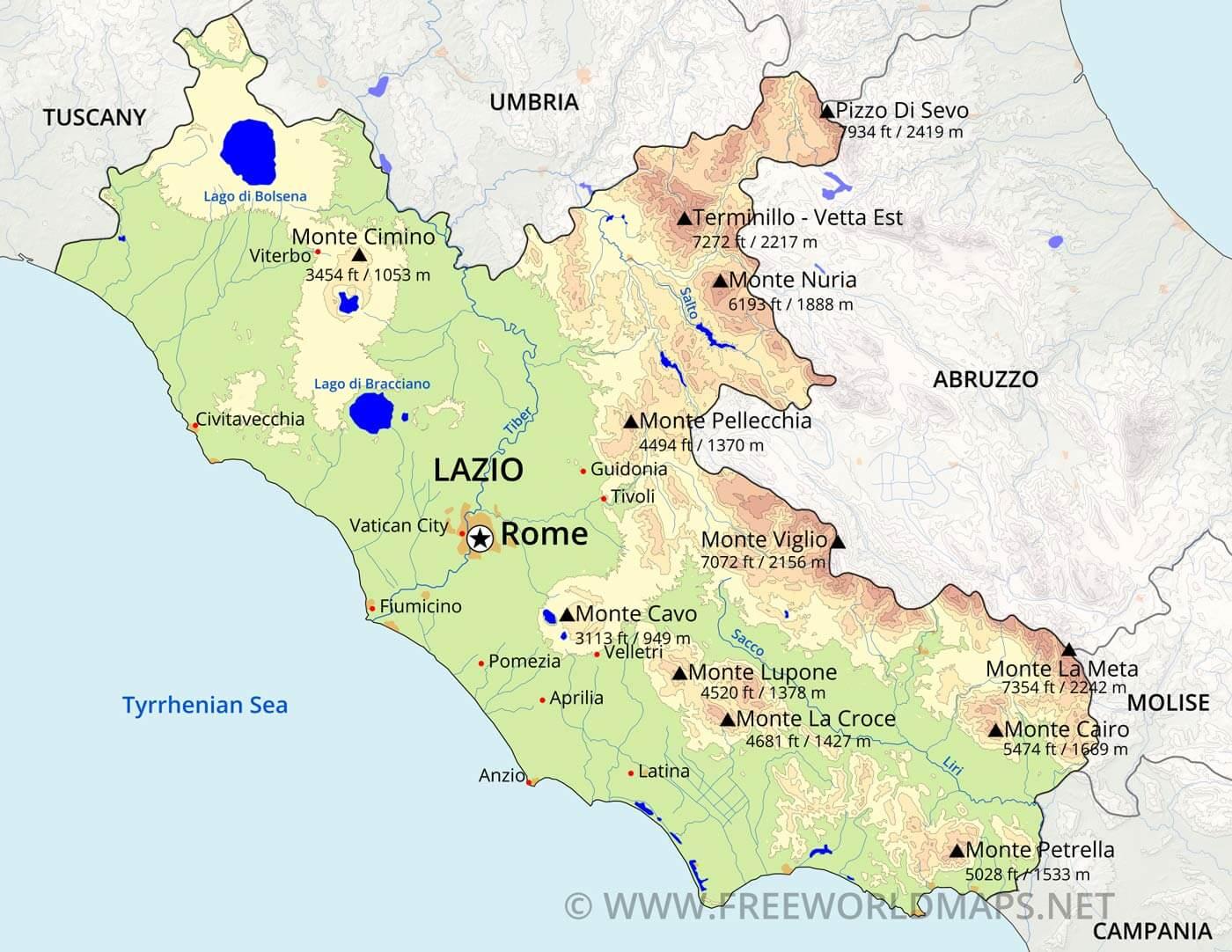
Rome, the Eternal City, boasts a captivating history etched not only in its monuments and ruins but also in its very terrain. The topography of Rome, a complex interplay of hills, valleys, and the Tiber River, has profoundly shaped its development, architecture, and even its identity.
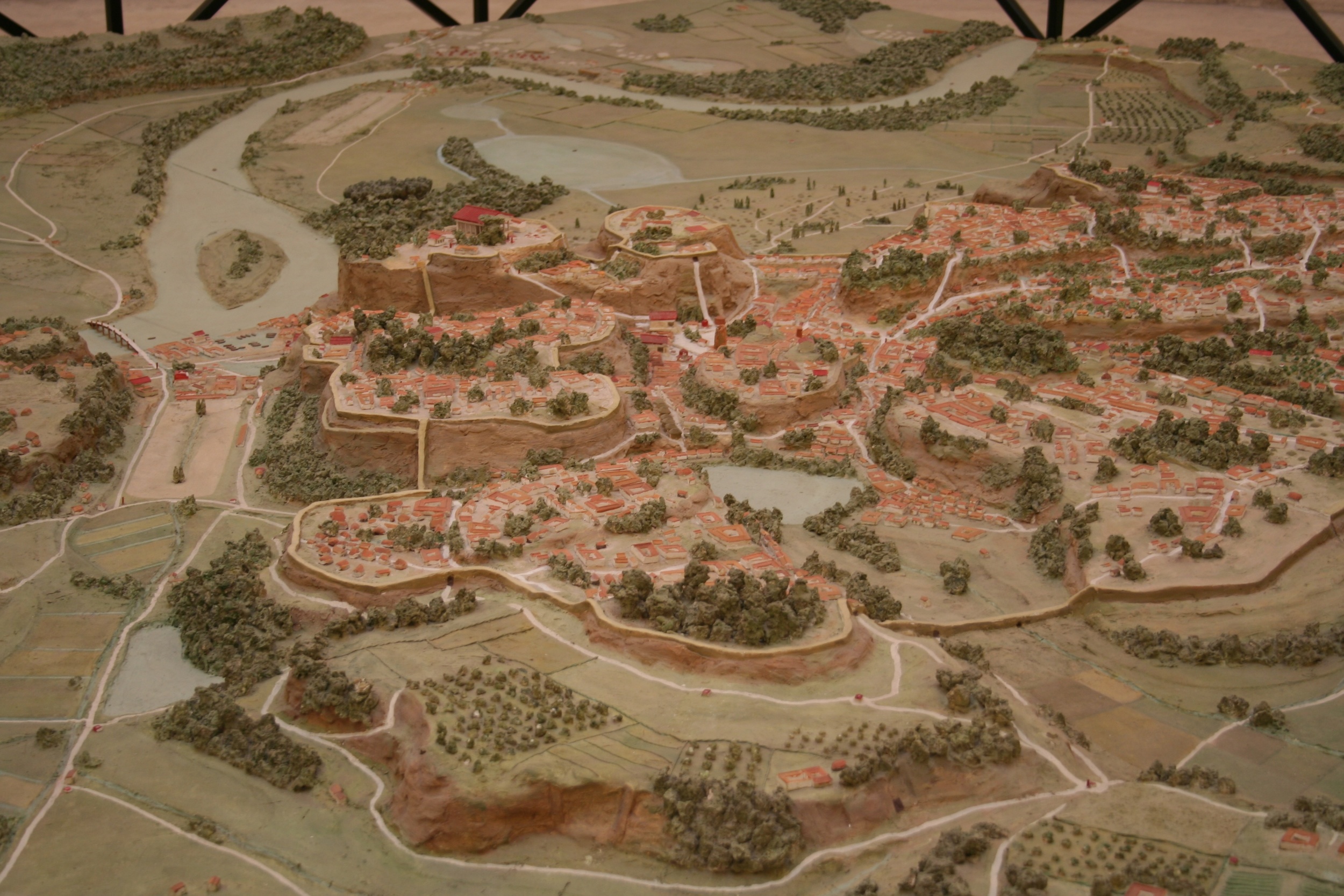
A City Built on Seven Hills:
Rome’s iconic silhouette is defined by its seven hills: Palatine, Aventine, Capitoline, Caelian, Esquiline, Quirinal, and Viminal. These hills, rising from the flat Tiber Valley, provided natural defenses and strategic vantage points. The Palatine Hill, the earliest settlement, offered a commanding position overlooking the river, making it an ideal location for the city’s founding.
The Tiber River: A Lifeline and a Barrier:
The Tiber River, snaking through the heart of Rome, has been a constant presence throughout the city’s history. It served as a vital transportation route, connecting Rome to the sea and facilitating trade. The river’s fertile banks provided sustenance, while its waters offered a source of drinking water and a means of defense. The river also acted as a natural barrier, protecting the city from invaders.
The Impact of Topography on Architecture:
The topography of Rome heavily influenced its architectural development. The city’s hills dictated the layout of its streets, which often climbed steeply, creating a network of winding roads and narrow alleys. The Romans adapted their building techniques to the terrain, constructing aqueducts to transport water across valleys and creating terraced gardens to maximize space on the hillsides.
The Role of Topography in Urban Planning:
Rome’s topography played a crucial role in its urban planning throughout history. The strategic location of the Palatine Hill, overlooking the river, established the city’s initial core. As the city expanded, the hills served as natural divisions, fostering the development of distinct neighborhoods and administrative districts.
A Topography that Evolved:
Rome’s topography is not static. Over centuries, the city has been shaped by both natural forces and human intervention. The Tiber River has shifted its course, altering the landscape. The hills have been leveled and reshaped to accommodate new constructions, creating a dynamic interplay between the natural and the man-made.
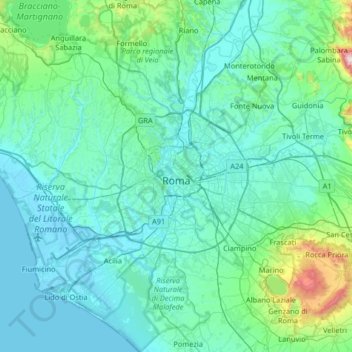
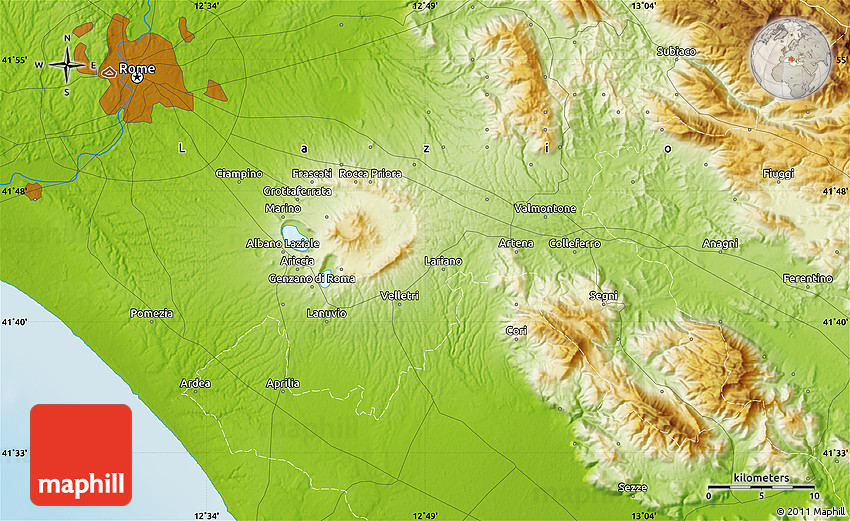
Mapping the Terrain: Topography Maps and Their Significance:
Topography maps are invaluable tools for understanding and navigating the complex terrain of Rome. These maps, using contour lines to depict elevation changes, reveal the city’s three-dimensional form, providing insights into its historical development, urban planning, and architectural features.
Benefits of Studying Rome’s Topography:
- Historical Context: Topography maps offer a visual representation of the city’s historical evolution, revealing how its growth was influenced by the terrain.
- Urban Planning: Understanding the topography helps to inform modern urban planning initiatives, ensuring that new developments are integrated with the city’s natural landscape.
- Architectural Appreciation: Topography maps provide context for architectural marvels, showcasing how structures were adapted to the terrain and the challenges faced by ancient builders.
- Tourism and Exploration: Topography maps are indispensable for tourists, providing a deeper understanding of the city’s layout and facilitating exploration of its hidden gems.
FAQs on Topography Maps of Rome:
Q: What are the main features depicted on a topography map of Rome?
A: Topography maps of Rome typically depict the city’s seven hills, the Tiber River, major roads and streets, significant historical sites, and elevation changes using contour lines.
Q: How do contour lines on a topography map help understand Rome’s terrain?
A: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the city’s hills, valleys, and slopes. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the terrain.
Q: Are there specific types of topography maps available for Rome?
A: Yes, there are various types of topography maps available, including detailed maps focusing on specific areas, historical maps showing the city’s evolution, and interactive digital maps offering three-dimensional perspectives.
Q: How can I access topography maps of Rome?
A: Topography maps of Rome can be found online, in travel guides, and at tourist information centers. Many online mapping platforms offer interactive topography maps with various layers and features.
Tips for Using Topography Maps of Rome:
- Study the Key: Familiarize yourself with the map’s key, understanding the symbols and colors used to represent different features.
- Focus on Elevation: Pay attention to the contour lines, as they reveal the city’s steepness and the challenges faced by ancient builders.
- Consider Historical Context: Use the map to visualize the city’s historical development, imagining how the terrain influenced the city’s growth.
- Plan Your Route: Use the map to plan your itinerary, considering the topography and its impact on walking distances and accessibility.
Conclusion:
The topography of Rome is not merely a physical landscape but a fundamental element of its identity. It is a testament to the city’s resilience, its adaptability, and its enduring connection to the past. Understanding Rome’s topography through maps provides a deeper appreciation for its history, architecture, and urban fabric, revealing a city intricately woven into the very terrain on which it stands.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Topography of Rome: A City Shaped by Time and Terrain. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!