The Topography of the Philippines: A Landscape Shaped by Tectonics and Time
Related Articles: The Topography of the Philippines: A Landscape Shaped by Tectonics and Time
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Topography of the Philippines: A Landscape Shaped by Tectonics and Time. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Topography of the Philippines: A Landscape Shaped by Tectonics and Time

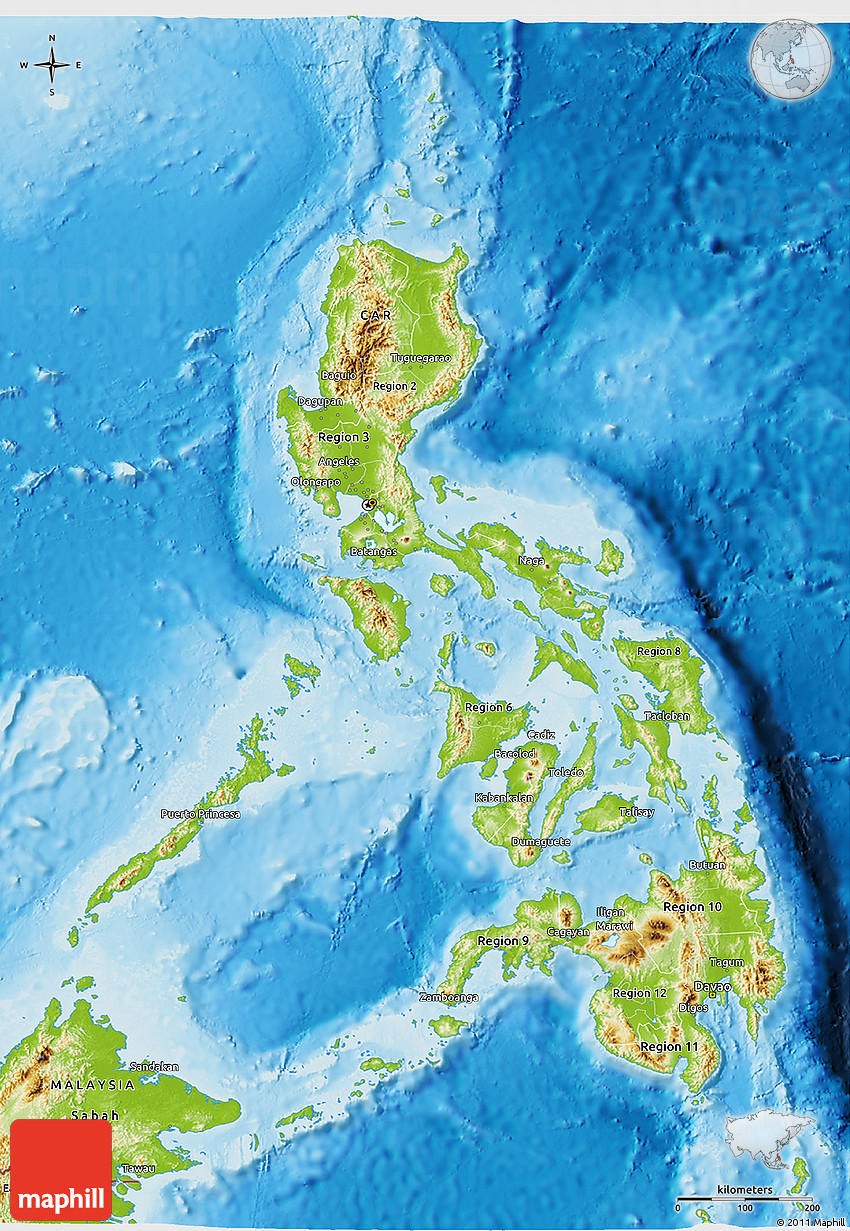
The Philippines, an archipelago nation in Southeast Asia, boasts a diverse and captivating topography, a product of complex geological forces and centuries of natural processes. Its landscape, a tapestry of mountains, valleys, plains, and coastlines, presents a unique and intricate geographical story. This article delves into the intricate details of the Philippine topography, exploring its origins, characteristics, and the profound impact it has on the country’s environment, culture, and development.
A Tapestry of Mountains and Valleys:
The Philippines is renowned for its mountainous terrain, with over 70% of its landmass covered by hills and mountains. The Cordillera Central, a formidable mountain range traversing Luzon, the largest island, is a testament to the country’s volcanic past. The range, home to the iconic Mount Pulag, the country’s third-highest peak, showcases a dramatic landscape of jagged peaks, deep valleys, and cascading waterfalls.
Beyond the Cordillera, other mountain ranges like the Zambales Mountains, Sierra Madre, and the Bicol Mountain Range contribute to the Philippines’ mountainous character. These ranges are punctuated by numerous volcanoes, some dormant, others active, adding to the dynamic nature of the landscape. The presence of these volcanoes, a consequence of the country’s location along the Pacific Ring of Fire, has significantly shaped the topography and the fertile soils of the Philippines.
The Significance of Plains and Coastlines:
While mountains dominate the landscape, the Philippines also possesses fertile plains and extensive coastlines. The Central Plain of Luzon, known as the "Rice Granary of the Philippines," is a testament to the country’s agricultural prowess. This vast expanse of land, formed by alluvial deposits from surrounding rivers, provides fertile ground for rice cultivation, a staple food for the nation.
The Philippines’ extensive coastline, stretching over 36,000 kilometers, is another defining feature. Its numerous islands are fringed by beaches, lagoons, and coral reefs, attracting tourists and offering rich fishing grounds. These coastal areas play a vital role in the country’s economy, providing livelihood for millions and serving as gateways to the vast expanse of the Pacific Ocean.
The Impact of Topography on the Philippines:
The country’s topography has a profound impact on its environment, culture, and development.
Environmental Impact:
- Biodiversity: The varied topography creates a diverse range of habitats, supporting a rich biodiversity. From rainforests to mangrove swamps, from coral reefs to grasslands, the Philippines boasts an astonishing array of flora and fauna, making it a global biodiversity hotspot.
- Natural Disasters: The mountainous terrain and active volcanoes make the Philippines prone to natural disasters, including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, landslides, and typhoons. These events pose significant challenges to the country’s infrastructure and communities, demanding robust disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Water Resources: Mountains act as natural reservoirs, capturing rainfall and feeding rivers and streams. These water sources are crucial for agriculture, industry, and human consumption, highlighting the importance of sustainable water management.
Cultural Impact:
- Isolation and Diversity: The mountainous terrain has historically isolated communities, fostering unique cultural practices and traditions. This geographical isolation has led to the development of distinct languages, customs, and beliefs across different regions.
- Traditional Practices: The topography has influenced traditional practices like farming, fishing, and transportation. For instance, the use of rice terraces in mountainous areas showcases the ingenuity of Filipinos in adapting to the challenging terrain.
Development Impact:
- Infrastructure Challenges: The mountainous terrain poses significant challenges to infrastructure development, particularly in terms of road construction and transportation. This can hinder economic growth and access to essential services in remote areas.
- Resource Management: The topography influences resource management, particularly in terms of land use and water resources. The need for sustainable practices is paramount to ensure the long-term viability of these resources.
- Tourism Potential: The diverse topography, including stunning beaches, mountains, and waterfalls, offers immense potential for tourism. However, sustainable tourism practices are crucial to minimize the environmental impact and preserve the country’s natural beauty.
Understanding the Topography: Maps and Tools
Topography maps, essential tools for understanding and visualizing the landscape, provide valuable insights into the Philippines’ terrain. These maps depict elevation changes, landforms, and geographical features, enabling informed decision-making in various fields.
- Topographic Maps: These maps use contour lines to represent elevation, providing a detailed representation of the land’s shape. They are crucial for planning infrastructure projects, identifying potential risks, and understanding the flow of water.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellite imagery provides a comprehensive overview of the landscape, revealing details about land cover, vegetation, and urban development. These images are invaluable for monitoring deforestation, assessing natural disasters, and planning land use.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software integrates various data sources, including topographic maps, satellite imagery, and demographic data, to create interactive maps and analyze spatial relationships. This technology is increasingly utilized for disaster management, environmental monitoring, and urban planning.
FAQs on the Topography of the Philippines:
1. What is the highest point in the Philippines?
Mount Apo, located in Davao, is the highest peak in the Philippines, reaching a height of 2,954 meters.
2. How do the Philippines’ mountains influence its climate?
Mountains act as barriers to air movement, causing rain shadows and creating distinct microclimates. This can lead to variations in rainfall, temperature, and humidity across different regions.
3. What are the major rivers in the Philippines?
The Philippines has numerous rivers, including the Cagayan River, the longest in the country, the Pasig River, flowing through Manila, and the Agusan River, known for its biodiversity.
4. How does the topography affect the distribution of population in the Philippines?
The mountainous terrain restricts population density in many areas, with higher concentrations in plains and coastal areas.
5. What are the challenges posed by the Philippines’ topography to development?
The mountainous terrain presents challenges to infrastructure development, transportation, and access to services in remote areas.
Tips for Understanding and Using Topography Maps:
- Learn to read contour lines: Understanding contour lines is essential for interpreting elevation changes and identifying landforms.
- Utilize the map’s scale and legend: Pay attention to the map’s scale to determine distances and the legend to understand the symbols used.
- Consider the map’s purpose: Different maps are designed for specific purposes, so choose the appropriate map for your needs.
- Integrate multiple data sources: Combine topographic maps with satellite imagery and other data sources for a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
Conclusion:
The Philippines’ topography, a product of tectonic forces and time, is a defining feature of the country. Its mountains, valleys, plains, and coastlines create a unique and intricate landscape that shapes the environment, culture, and development of the nation. Understanding the topography is crucial for informed decision-making in various fields, from disaster management to sustainable development. As the Philippines continues to navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by its diverse landscape, a deep understanding of its topography will be paramount in ensuring a sustainable and prosperous future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Topography of the Philippines: A Landscape Shaped by Tectonics and Time. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!