Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Reading and Topography
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Reading and Topography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Reading and Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Reading and Topography

The ability to read and interpret maps is a fundamental skill with applications across various disciplines, from navigation and exploration to environmental science and urban planning. A map serves as a visual representation of a particular area, conveying information about its physical features, geographical locations, and spatial relationships. This information is further enhanced by the study of topography, which delves into the shape and form of the Earth’s surface, encompassing its elevation, relief, and landforms.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to map reading and topography, exploring its significance, key elements, and practical applications. By understanding the intricate relationship between maps and topography, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of the natural world and develop valuable skills for navigating, analyzing, and interpreting geographical data.
The Fundamentals of Map Reading
Maps are essential tools for understanding and navigating the world around us. They provide a condensed and simplified representation of reality, allowing users to visualize vast areas and identify key features with ease. To effectively read and interpret a map, it is crucial to understand its fundamental components:
- Scale: This ratio indicates the relationship between the map’s distance and the corresponding distance on the ground. A large-scale map represents a smaller area with greater detail, while a small-scale map depicts a larger area with less detail.
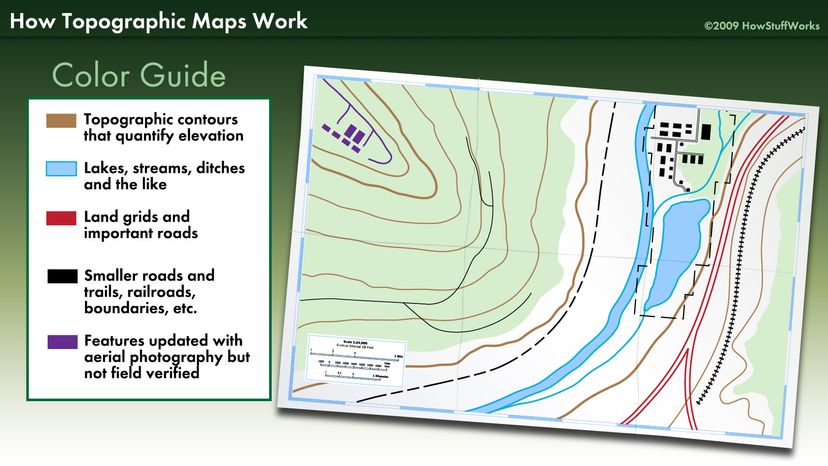
- Legend: This key provides definitions and explanations for symbols, colors, and other visual elements used on the map. Understanding the legend is crucial for interpreting the map’s information accurately.
- Orientation: Maps typically use North as the standard orientation, with compass directions (North, South, East, West) clearly marked. Understanding the map’s orientation is essential for navigating and determining relative positions.
- Grid System: Many maps employ a grid system, often based on latitude and longitude, to provide precise location coordinates. This system facilitates accurate location identification and measurement.
Deciphering Topography: A Visual Language of the Earth
Topography, the study of the Earth’s surface features, adds another layer of complexity and depth to map reading. It allows us to visualize the three-dimensional landscape, encompassing elevation changes, landforms, and natural features.
Here are some key elements of topography that are often represented on maps:
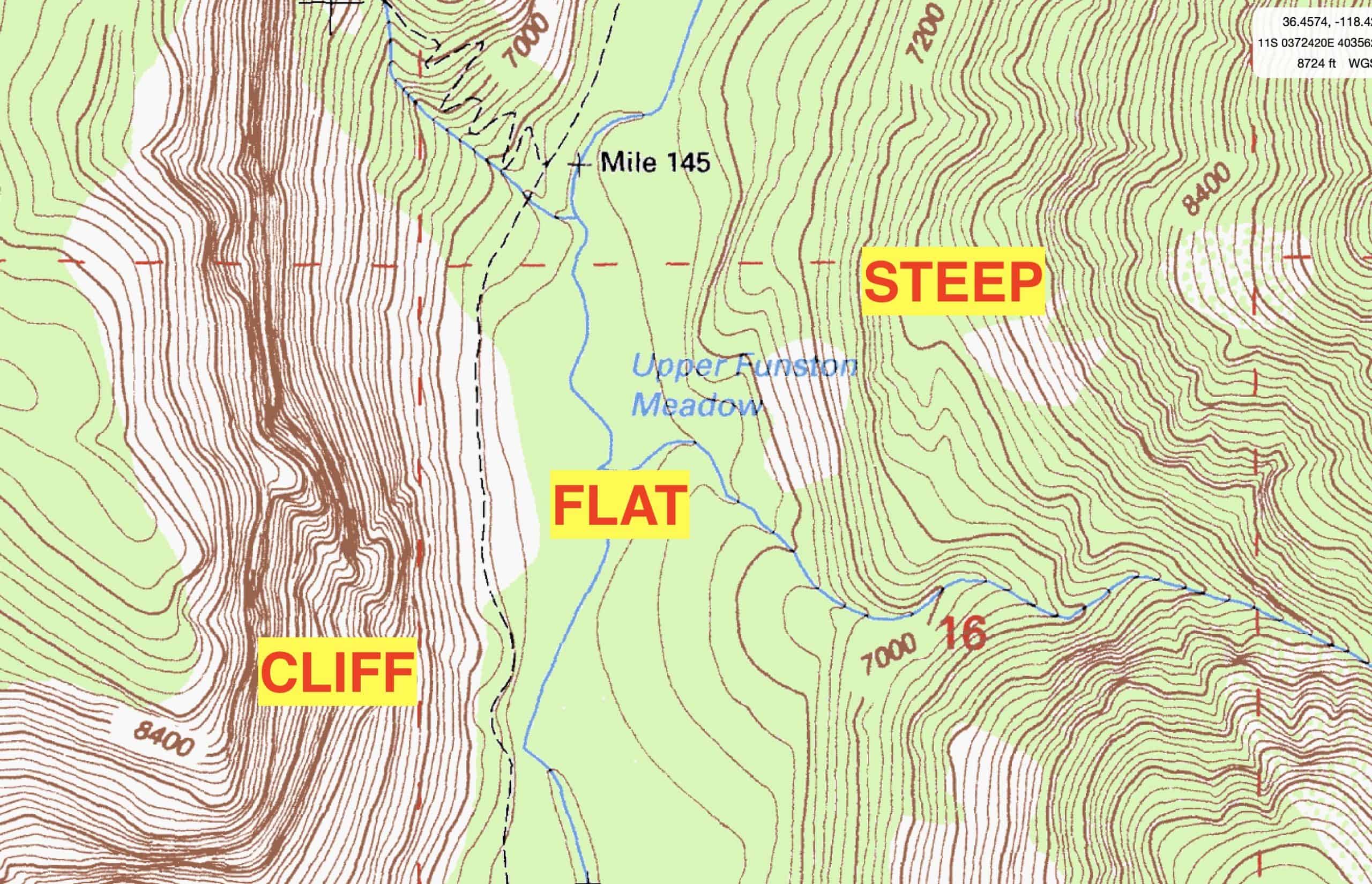
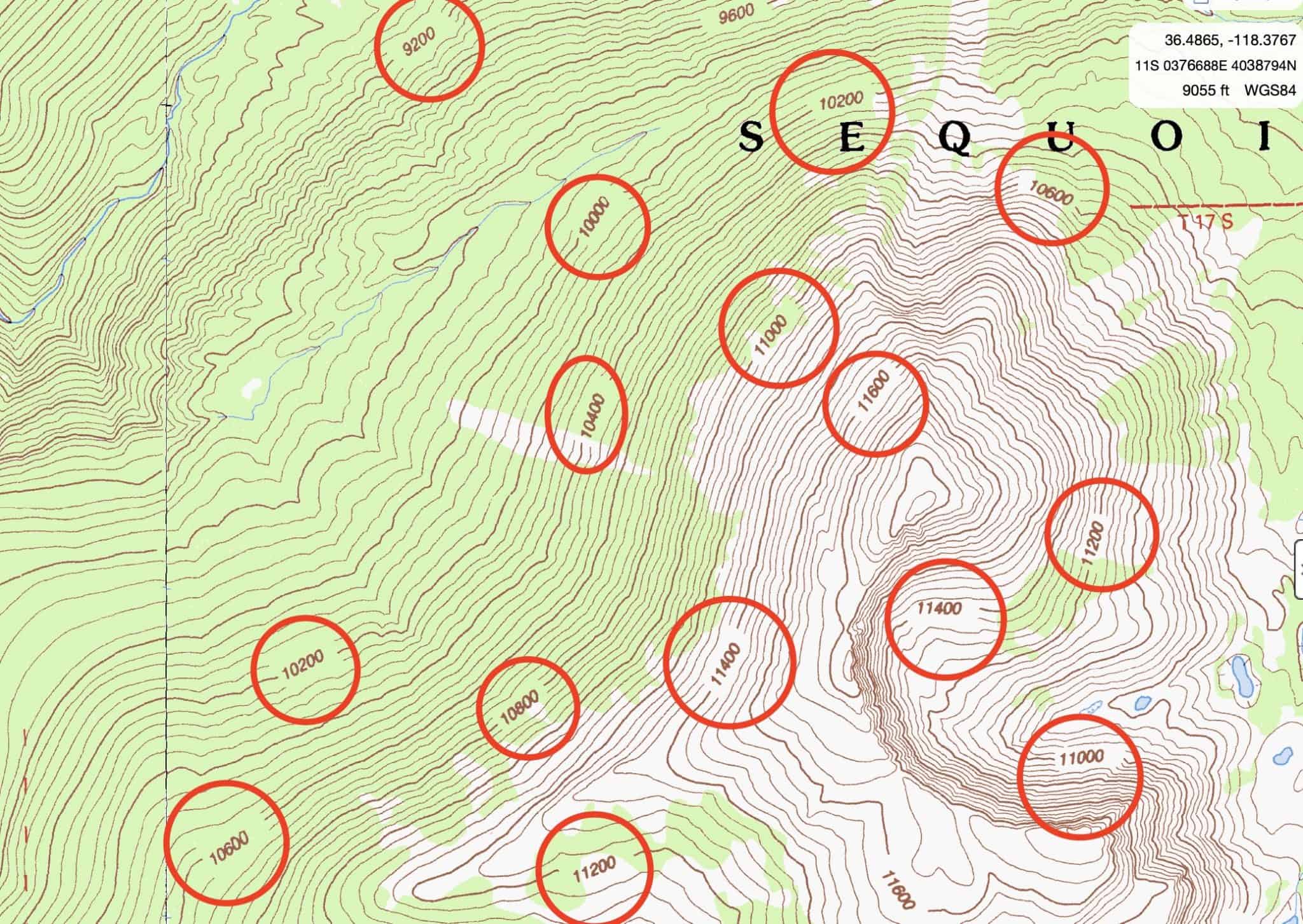
- Elevation: This refers to the height of a point on the Earth’s surface relative to sea level. It is typically indicated using contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the terrain.
- Relief: This describes the overall shape and form of the land, including its highs and lows. Maps often use shading, colors, or other visual techniques to represent relief.
- Landforms: These are distinctive natural features of the Earth’s surface, such as mountains, valleys, hills, and plateaus. Maps often depict landforms using symbols, labels, and contour lines.
- Water Features: Rivers, lakes, oceans, and other bodies of water are essential components of topography. Maps often represent them using blue lines or symbols, indicating their location and direction of flow.
Map Reading Activities: Engaging with Topography
Engaging in map reading activities can significantly enhance understanding of topography and spatial relationships. These activities can range from simple exercises to more complex projects, depending on the learning objectives and available resources.
Here are some examples of map reading activities that can be used to explore topography:
- Contour Line Interpretation: Students can analyze contour lines on a map to determine elevation changes, identify landforms, and understand the steepness of slopes.
- Elevation Profile Creation: By plotting elevation data from contour lines, students can create elevation profiles, which visually represent the terrain along a specific route or path.
- Landform Identification and Classification: Students can use maps to identify and classify various landforms, such as mountains, valleys, hills, and plateaus. This exercise helps them develop their ability to recognize and interpret different topographic features.
- Navigation and Route Planning: Students can practice navigating using maps, planning routes, and determining the best paths to reach specific destinations. This activity emphasizes the practical applications of map reading and topography.
- Geographic Data Analysis: Students can use maps and topographic data to analyze environmental issues, such as deforestation, erosion, or flooding. This activity helps them understand the relationship between topography and environmental processes.
Benefits of Map Reading and Topography
The ability to read and interpret maps, combined with an understanding of topography, offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Spatial Awareness: Map reading develops spatial awareness, enabling individuals to visualize and understand relationships between objects and locations. This skill is crucial for navigation, planning, and environmental analysis.
- Improved Problem-Solving Skills: Interpreting maps and topographic data requires critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By analyzing information and drawing conclusions, individuals can develop their analytical abilities.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Understanding topography and its influence on the environment can inform decision-making in various fields, including urban planning, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
- Increased Appreciation for the Natural World: Studying topography fosters an appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the natural world. It allows individuals to understand the processes that shape the Earth’s surface and the interconnectedness of various ecosystems.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Maps and topographic data serve as common ground for communication and collaboration across disciplines. They facilitate the sharing of information and the development of shared understanding.
FAQs about Map Reading and Topography
Q: What are the different types of maps?
A: Maps come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose. Some common types include:
- Topographic maps: These maps focus on the elevation and relief of the land, using contour lines to represent terrain.
- Road maps: These maps primarily show roads, highways, and other transportation routes.
- Political maps: These maps depict political boundaries, countries, and states.
- Thematic maps: These maps focus on specific themes, such as population density, climate, or resource distribution.
Q: How can I improve my map reading skills?
A: There are several ways to improve map reading skills:
- Practice regularly: The more you practice reading and interpreting maps, the better you will become at understanding their information.
- Use different types of maps: Familiarize yourself with different map types and their specific features.
- Attend workshops or courses: Many organizations offer workshops and courses on map reading and navigation.
- Explore the outdoors: Using maps to navigate and explore the natural world provides practical experience and enhances understanding.
Q: What are some practical applications of map reading and topography?
A: Map reading and topography have numerous practical applications, including:
- Navigation and Exploration: Maps are essential tools for navigating unfamiliar terrain and exploring new areas.
- Land Use Planning: Topographic data helps planners understand the suitability of land for different uses, such as agriculture, urban development, or conservation.
- Disaster Response: Maps and topographic information are crucial for disaster response efforts, providing information on affected areas, evacuation routes, and potential hazards.
- Environmental Monitoring: Topographic data can be used to monitor changes in the environment, such as deforestation, erosion, or flooding.
- Resource Management: Maps and topographic data help manage natural resources, such as water, forests, and minerals.
Tips for Effective Map Reading and Topography Interpretation
- Start with the Legend: Always begin by carefully reviewing the map’s legend to understand the symbols, colors, and other visual elements used.
- Consider the Scale: Pay attention to the map’s scale to determine the level of detail and the area represented.
- Identify Key Features: Focus on identifying key features, such as roads, rivers, mountains, and cities, to orient yourself on the map.
- Use Contour Lines Effectively: Practice interpreting contour lines to understand elevation changes and identify landforms.
- Relate Map Information to Real-World Observations: Whenever possible, try to relate the map information to your observations in the real world to enhance your understanding.
Conclusion
Map reading and topography are essential skills that empower individuals to understand and interpret the world around them. By engaging with maps and topographic data, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the natural world, develop critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, and enhance our decision-making capabilities. Whether navigating unfamiliar terrain, planning a journey, or analyzing environmental issues, the ability to read and interpret maps and topographic information remains a valuable asset in a world increasingly reliant on spatial data.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Reading and Topography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!