Unraveling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps
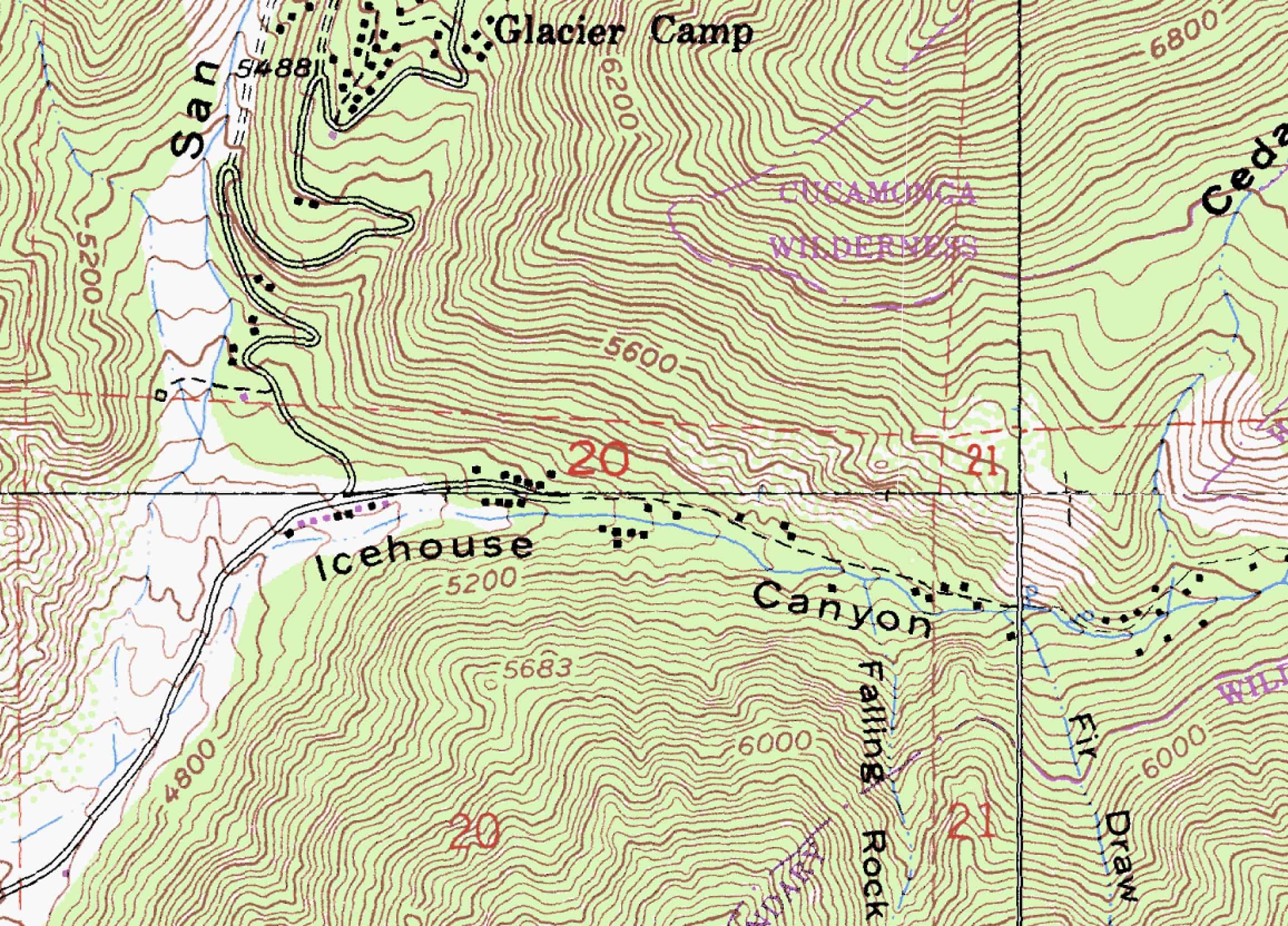
Topographic maps are more than just colorful representations of the Earth’s surface. They are intricate visual narratives, revealing the subtle and dramatic variations in elevation, landforms, and natural features that shape our world. These maps serve as essential tools for a wide range of disciplines, from engineering and surveying to environmental science and recreation, providing invaluable insights into the physical landscape and its complexities.
Understanding the Language of Topography
At the heart of topographic maps lies the concept of elevation. This refers to the vertical distance of a point on the Earth’s surface above a reference level, typically sea level. Topographic maps employ a system of contour lines to depict these variations in elevation. Each contour line connects points of equal elevation, creating a visual representation of the landscape’s undulations. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the incline.
Beyond Contour Lines: A Multifaceted Representation
Topographic maps go beyond simply illustrating elevation. They incorporate a rich tapestry of information, including:
- Landform features: Mountains, valleys, hills, plateaus, and other prominent landforms are clearly depicted, providing a comprehensive understanding of the landscape’s structure.
- Water features: Rivers, lakes, streams, and other bodies of water are meticulously mapped, showcasing the flow of water across the terrain.
- Cultural features: Roads, buildings, bridges, and other human-made structures are included, offering a glimpse into the interplay between human activity and the natural environment.
- Vegetation: Forests, grasslands, and other vegetation types are often represented, providing insights into the distribution of plant life across the landscape.
The Significance of Topographic Maps
The value of topographic maps extends far beyond their aesthetic appeal. They are indispensable tools for a wide range of applications, including:
- Planning and Development: Engineers, architects, and urban planners rely on topographic maps to assess site suitability, plan infrastructure projects, and design sustainable development strategies.
- Environmental Management: Environmental scientists and resource managers utilize topographic maps to study land use patterns, assess environmental impacts, and develop conservation strategies.
- Recreation and Adventure: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts use topographic maps to navigate unfamiliar terrain, plan routes, and ensure safety during expeditions.
- Military Operations: Military strategists and commanders rely on topographic maps for planning troop movements, identifying strategic locations, and assessing battlefield conditions.
- Scientific Research: Geographers, geologists, and other scientists use topographic maps to conduct field studies, analyze landforms, and understand the Earth’s dynamic processes.
The Evolution of Topographic Maps
The history of topographic maps is intertwined with the evolution of cartography and surveying techniques. Early maps were often crude and inaccurate, relying on rudimentary methods for determining elevation. However, advancements in surveying technology, such as the invention of the theodolite and the development of precise leveling techniques, led to the creation of increasingly accurate and detailed topographic maps.
The advent of aerial photography and satellite imagery revolutionized mapmaking, providing new perspectives on the Earth’s surface. Digital mapping technologies, including Geographic Information Systems (GIS), have further transformed the field, allowing for the creation of interactive and dynamic maps that can be easily updated and shared.
FAQs about Topographic Maps
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a road map?
A: While both maps depict geographical information, topographic maps focus on elevation and landform features, while road maps prioritize road networks and points of interest.
Q: How are contour lines used to represent elevation?
A: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, creating a visual representation of the landscape’s undulations. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the incline.
Q: How can I read a topographic map?
A: Understanding the key symbols and conventions used on topographic maps is crucial for accurate interpretation. Look for the map legend, which provides a key to the symbols and explains the meaning of different colors and patterns.
Q: What are some common uses of topographic maps?
A: Topographic maps are used in a wide range of applications, including planning and development, environmental management, recreation, military operations, and scientific research.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps
- Study the map legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions used on the map.
- Pay attention to the contour lines: Understand how contour lines represent elevation and slope.
- Use a compass and altimeter: These tools are essential for accurate navigation and elevation determination.
- Consider the scale of the map: Choose a map with an appropriate scale for your intended use.
- Practice map reading: Familiarize yourself with the map by studying it before heading out into the field.
Conclusion
Topographic maps are essential tools for understanding and navigating the complexities of the Earth’s surface. They offer a wealth of information about elevation, landforms, water features, cultural features, and vegetation, providing valuable insights for a wide range of disciplines. As technology continues to advance, topographic maps will continue to evolve, offering even more comprehensive and accurate representations of our world. By mastering the language of topography, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the landscape and the crucial role it plays in our lives.


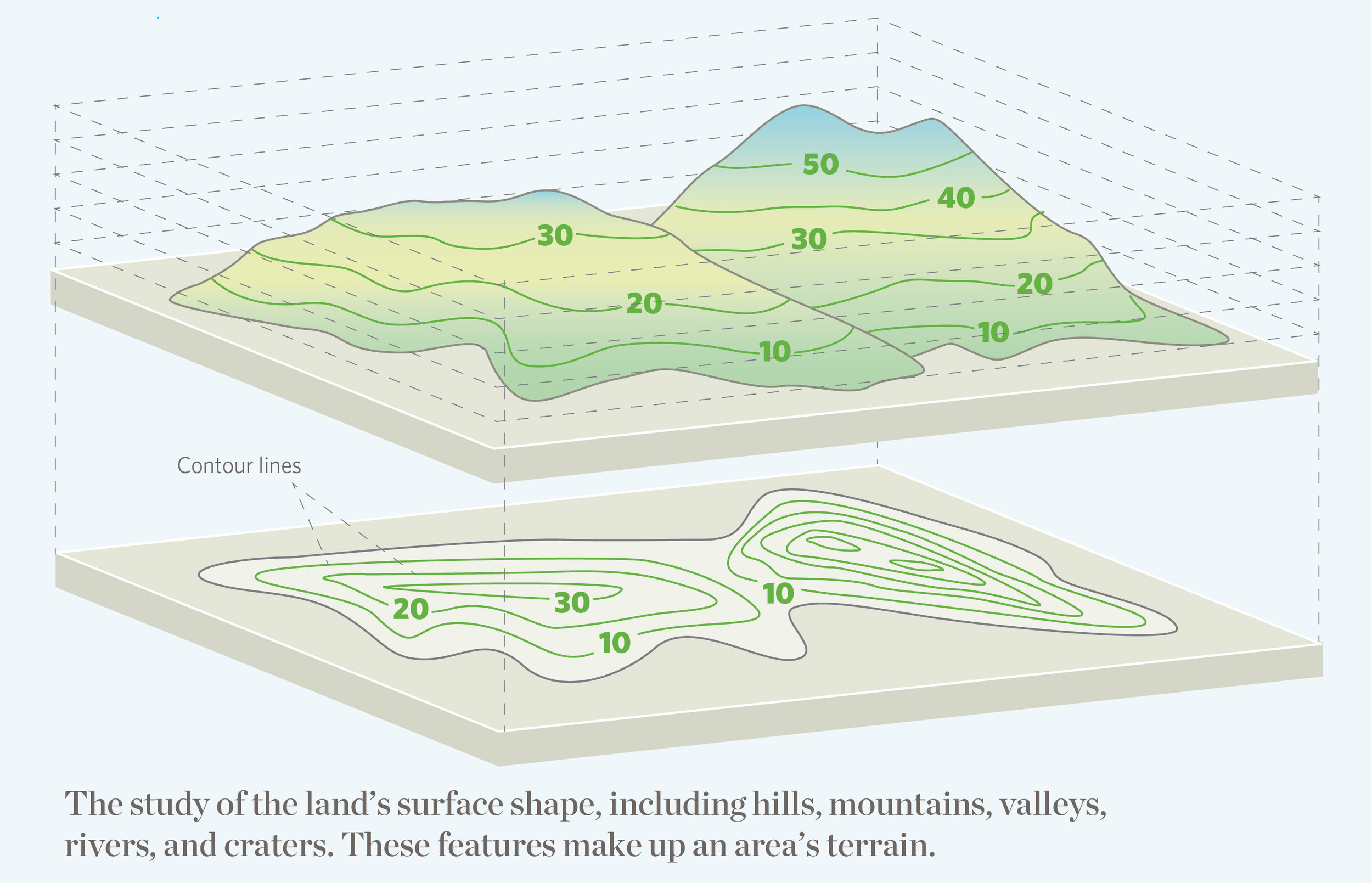


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topographic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!