Unraveling the Landscape of Beijing: A Topographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape of Beijing: A Topographical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape of Beijing: A Topographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape of Beijing: A Topographical Exploration
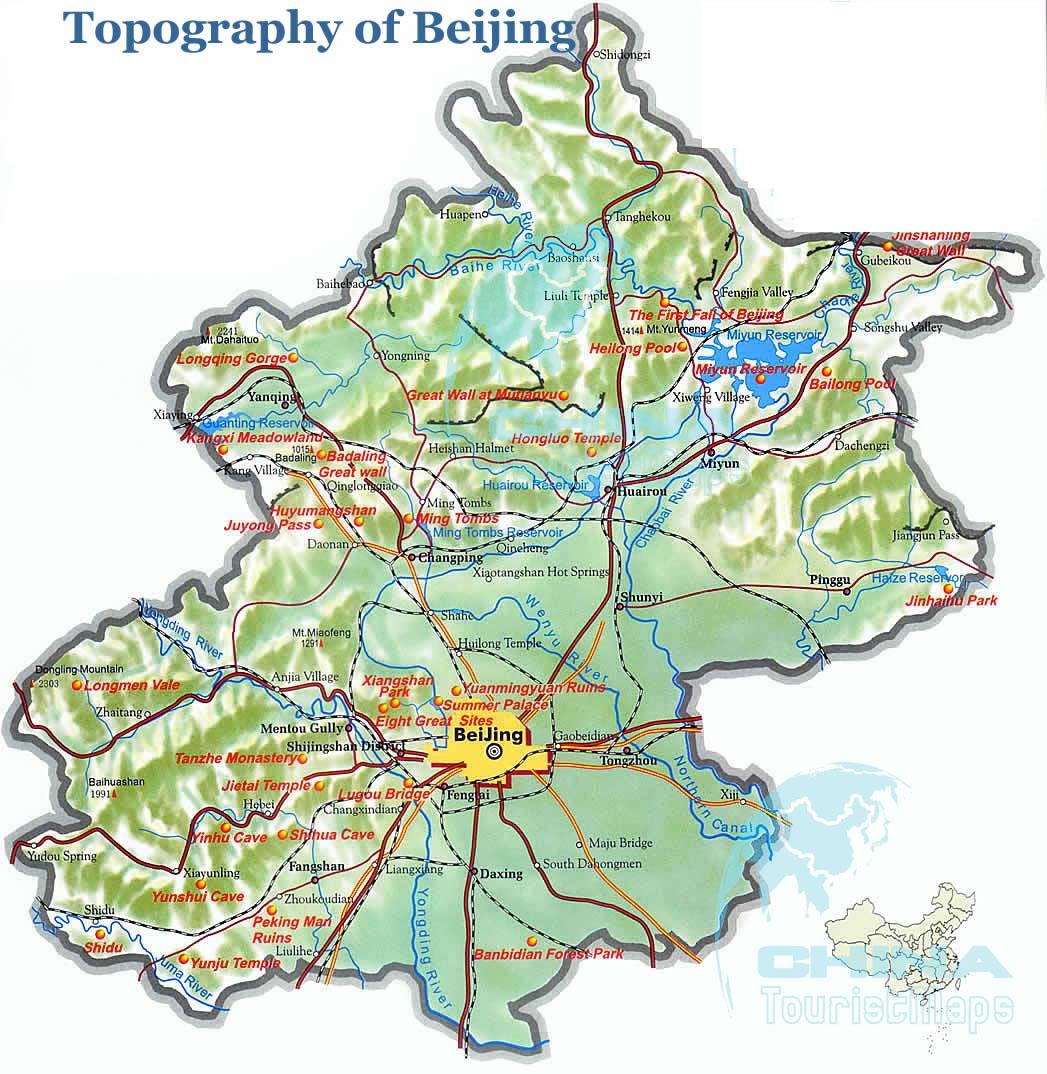
Beijing, the bustling capital of China, boasts a rich history and vibrant culture, but its story is also deeply intertwined with its unique topography. Understanding the city’s landscape, its mountains, plains, and waterways, is crucial for comprehending its development, challenges, and future potential. This exploration delves into the intricacies of Beijing’s topographical map, highlighting its significance in shaping the city’s past, present, and future.
A Tapestry of Terrain:
The Beijing topography map reveals a diverse landscape, characterized by a central plain surrounded by hills and mountains. This arrangement has profoundly influenced the city’s layout, its historical development, and its current urban planning.
- The North China Plain: The heart of Beijing rests on the vast North China Plain, a fertile expanse that has historically supported agriculture and provided a foundation for urban growth. This flat terrain facilitated the construction of roads, canals, and infrastructure, contributing to the city’s expansion.
- The Yanshan Mountains: To the north and west, the Yanshan Mountains rise, forming a natural barrier that has historically protected Beijing from northern invaders. These mountains also offer scenic beauty and recreational opportunities, attracting tourists and residents alike.
- The Taihang Mountains: To the southwest, the Taihang Mountains stand tall, offering a dramatic backdrop to the city. These mountains provide valuable resources, including timber and minerals, and play a crucial role in regulating Beijing’s climate.
- The Yongding River: Flowing through the city from west to east, the Yongding River has played a vital role in Beijing’s history. It served as a transportation route, a source of water, and a natural defense mechanism. However, the river has also been prone to flooding, posing challenges to urban development.
Historical Significance:
Beijing’s topography has deeply impacted its historical development. The central plain provided a strategic location for establishing a capital city, facilitating trade and communication with other parts of the country. The surrounding mountains offered natural protection, making the city a desirable location for political and military power.
The historical layout of Beijing reflects its topographical features. The Forbidden City, the heart of imperial power, was strategically placed on the northern edge of the central plain, with the mountains serving as a natural defense against potential threats. The city walls, constructed over centuries, were designed to enclose and protect the city from invaders.
Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities:
While Beijing’s topography has shaped its history, it also presents contemporary challenges and opportunities. The flat terrain of the central plain makes the city susceptible to air pollution, as pollutants tend to accumulate in low-lying areas. The mountains, while offering scenic beauty, also create barriers to air circulation, exacerbating pollution problems.
However, the topography also presents opportunities for sustainable urban development. The mountains offer potential for renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power. The Yongding River, while posing flood risks, can be harnessed for water management and recreational activities.
Urban Planning and Development:
Understanding Beijing’s topography is crucial for effective urban planning and development. The city’s layout, transportation infrastructure, and environmental management strategies must be carefully considered in relation to the unique features of its landscape.
- Transportation Infrastructure: The central plain provides a suitable location for road and rail networks, facilitating the movement of people and goods. However, the mountains pose challenges for transportation, requiring careful planning and construction of tunnels and bridges.
- Environmental Management: The city’s topography plays a crucial role in air quality and water management. Urban planning strategies must address the challenges of air pollution and flood mitigation, taking into account the terrain’s influence on these factors.
- Urban Sprawl and Green Spaces: The central plain’s flatness has contributed to urban sprawl, but it also offers opportunities for developing green spaces and parks. These green spaces can improve air quality, provide recreational opportunities, and enhance the city’s overall aesthetic appeal.
FAQs about Beijing Topography:
1. What are the key topographical features of Beijing?
Beijing’s topography is characterized by a central plain surrounded by hills and mountains. The main features include the North China Plain, the Yanshan Mountains, the Taihang Mountains, and the Yongding River.
2. How has Beijing’s topography influenced its history?
The central plain provided a strategic location for establishing a capital city, while the surrounding mountains offered natural protection. The city’s historical layout reflects these topographical features.
3. What are the contemporary challenges posed by Beijing’s topography?
The flat terrain contributes to air pollution, while the mountains create barriers to air circulation. The Yongding River poses flood risks.
4. How can Beijing’s topography be leveraged for sustainable urban development?
The mountains offer potential for renewable energy sources, while the Yongding River can be harnessed for water management and recreation.
5. What are the key considerations for urban planning in Beijing?
Urban planning must address transportation infrastructure, environmental management, urban sprawl, and the development of green spaces, all taking into account the city’s unique topographical features.
Tips for Understanding Beijing Topography:
- Consult topographical maps: Use online resources and printed maps to visualize the city’s terrain and understand its key features.
- Explore different perspectives: Visit different parts of the city, from the central plain to the surrounding mountains, to experience the diverse landscape firsthand.
- Learn about historical development: Explore historical sites and museums to understand how the city’s topography has shaped its past.
- Engage with local communities: Talk to residents and experts to gain insights into the challenges and opportunities presented by Beijing’s unique landscape.
Conclusion:
The topography of Beijing is not merely a geographical feature but a defining element of the city’s identity. Its mountains, plains, and waterways have shaped its history, influenced its development, and continue to present both challenges and opportunities. Understanding the city’s landscape is essential for appreciating its past, navigating its present, and envisioning its future. As Beijing continues to evolve, its topography will remain a crucial factor in shaping its urban landscape and defining its place in the world.
![the topographic map of Beijing [7]. Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353747298/figure/fig1/AS:1053981463830528@1628300171555/the-topographic-map-of-Beijing-7.png)
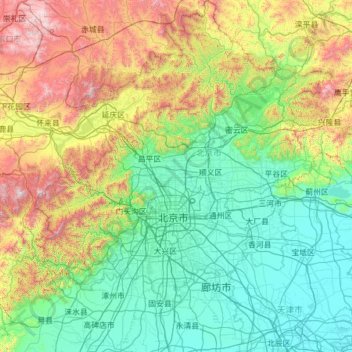





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape of Beijing: A Topographical Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!