Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Turkey: A Deep Dive into the Earthquake Fault Line Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Turkey: A Deep Dive into the Earthquake Fault Line Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Turkey: A Deep Dive into the Earthquake Fault Line Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Turkey: A Deep Dive into the Earthquake Fault Line Map

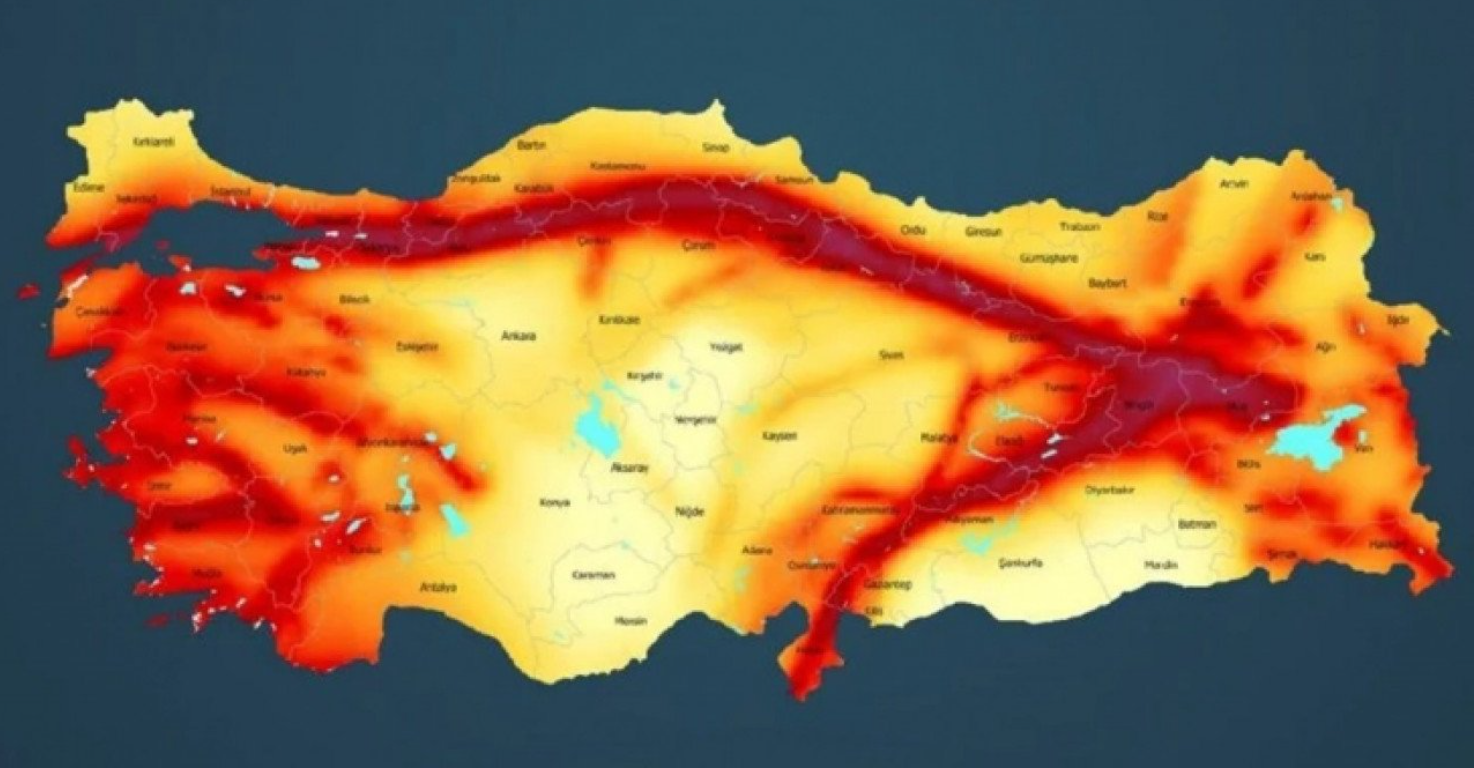
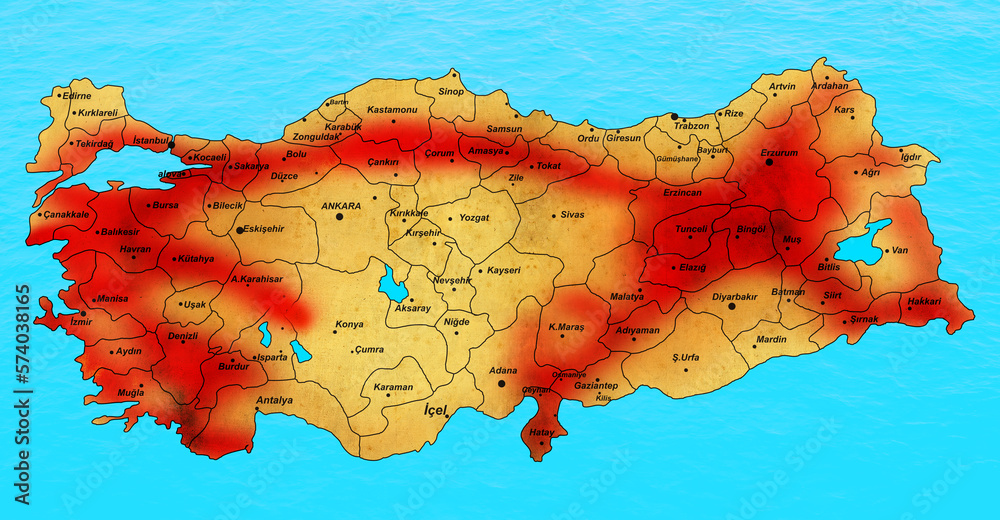
Turkey, a land of vibrant history and diverse landscapes, sits at a geographically precarious intersection, straddling the volatile Anatolian Plate. This tectonic setting, characterized by the relentless collision of the African, Arabian, and Eurasian plates, has rendered Turkey one of the most seismically active regions in the world. Understanding the intricate network of fault lines that crisscross the country is paramount for mitigating earthquake risks, informing infrastructure development, and safeguarding lives.
A Complex Geological Tapestry
The earthquake fault line map of Turkey paints a vivid picture of this complex geological dance. The map showcases a network of major and minor faults, each representing a potential rupture zone where earthquakes can originate. These faults are categorized by their geological characteristics, such as their orientation, length, and activity level.
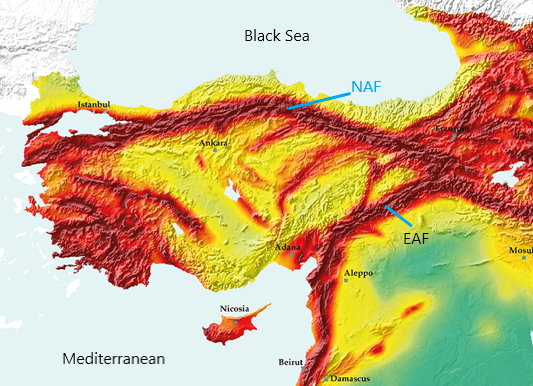
The North Anatolian Fault (NAF): A Tectonic Powerhouse
Dominating the northern landscape, the North Anatolian Fault (NAF) is the most prominent and active fault system in Turkey. Stretching for over 1,500 kilometers from the easternmost point of the country to the Sea of Marmara, the NAF is a left-lateral strike-slip fault. This means that the two sides of the fault move horizontally past each other in opposite directions, creating significant stress along the fault zone. The NAF is responsible for numerous devastating earthquakes throughout history, including the 1939 Erzincan earthquake (magnitude 7.9), which remains one of the deadliest earthquakes in Turkish history.
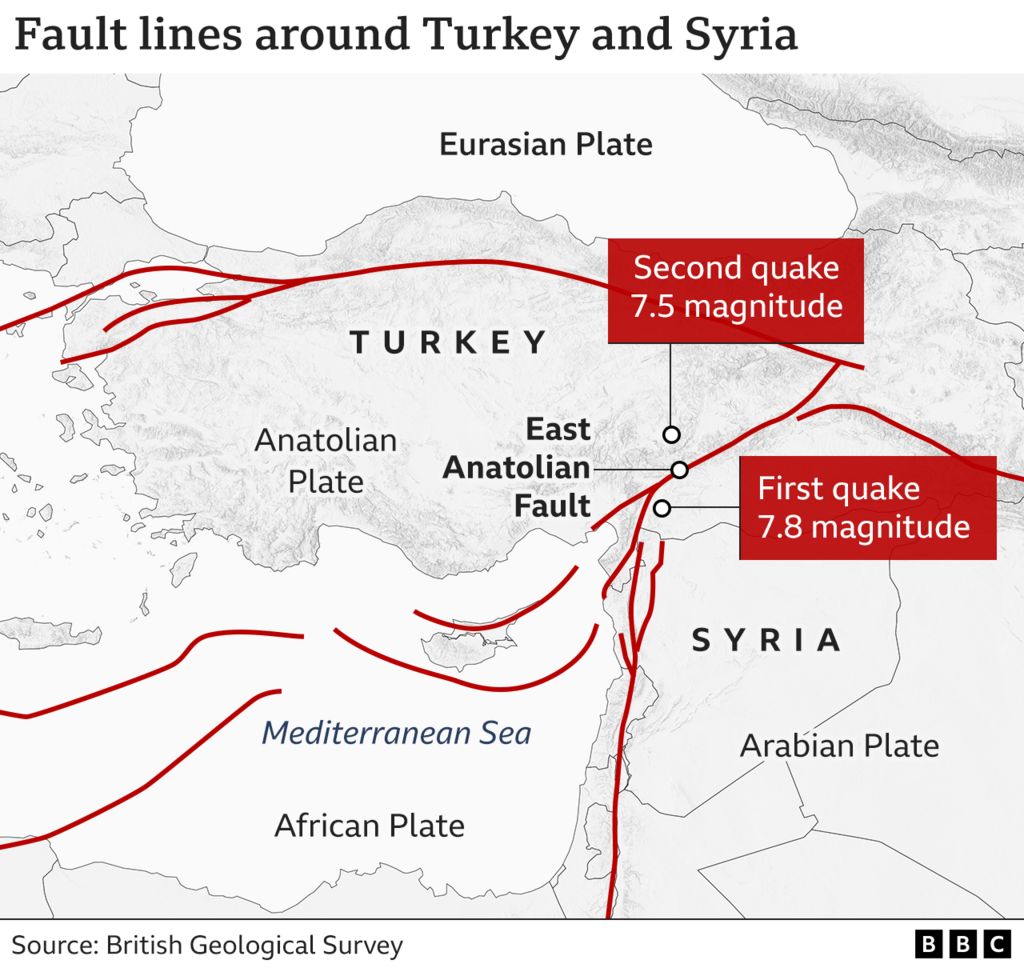
The East Anatolian Fault (EAF): A Seismic Partner
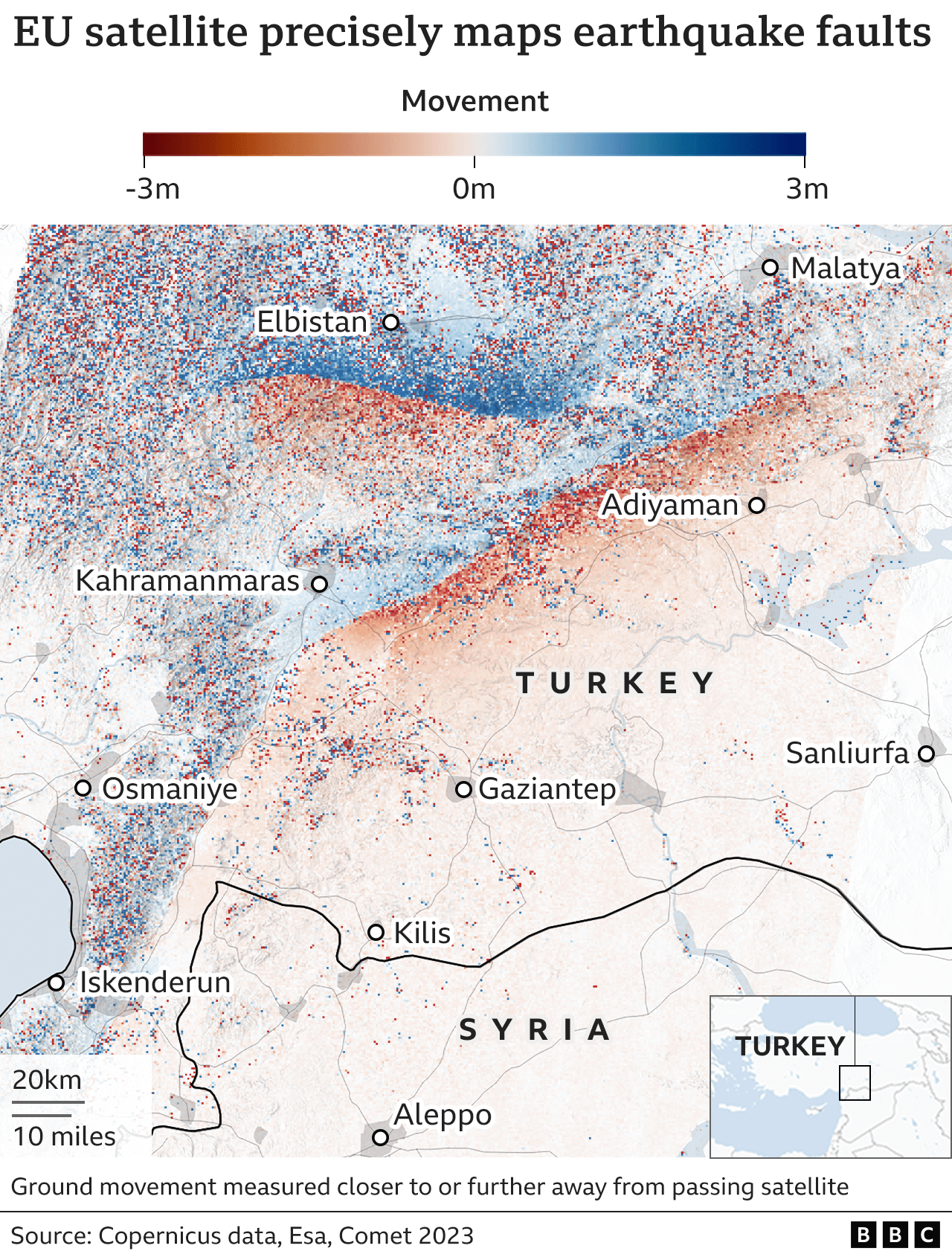
The East Anatolian Fault (EAF), running parallel to the NAF in the eastern part of Turkey, is another major fault system. It is a right-lateral strike-slip fault, characterized by horizontal movement in the same direction on both sides of the fault. The EAF has also generated numerous earthquakes, including the 2023 Kahramanmaras earthquakes (magnitude 7.8 and 7.5), which tragically devastated the region.
The Sea of Marmara Fault: A Ticking Time Bomb
The Sea of Marmara Fault, situated beneath the Sea of Marmara, is a particularly concerning fault zone. This active fault is responsible for several destructive earthquakes in Istanbul, including the 1999 İzmit earthquake (magnitude 7.6). The proximity of the Sea of Marmara Fault to Istanbul, a densely populated metropolis, raises significant concerns about the potential for future catastrophic earthquakes.
Beyond the Major Faults: A Network of Seismic Activity
Beyond the NAF, EAF, and the Sea of Marmara Fault, numerous other fault lines crisscross Turkey, contributing to the country’s seismic vulnerability. These faults are often less prominent but can still trigger significant earthquakes, particularly in regions with high population densities.
The Importance of the Earthquake Fault Line Map
The earthquake fault line map serves as a vital tool for understanding and mitigating seismic risks in Turkey. It provides valuable insights into:
- Earthquake Hazard Assessment: The map helps identify areas with high seismic hazard, enabling authorities to prioritize earthquake preparedness measures, including building codes, emergency response plans, and public awareness campaigns.
- Infrastructure Planning: Understanding the location and activity of fault lines is crucial for infrastructure planning, ensuring that critical structures, such as dams, bridges, and power plants, are located in areas with minimal seismic risk.
- Urban Development: The map informs urban development strategies, guiding the construction of new settlements away from high-risk areas.
- Earthquake Forecasting: While predicting the exact timing and magnitude of earthquakes remains a challenge, the map helps researchers and seismologists identify areas with increased seismic potential, facilitating early warning systems and preparedness efforts.
FAQs About the Turkey Earthquake Fault Line Map
Q: How is the earthquake fault line map created?
A: The earthquake fault line map is created through a combination of geological fieldwork, geophysical surveys, and analysis of historical earthquake data. Geologists conduct field studies to identify and map fault lines, while geophysical surveys, such as seismic reflection profiling, provide insights into the subsurface structure of the Earth. Historical earthquake records, including eyewitness accounts, damage reports, and seismological data, help researchers understand the past activity of faults.
Q: How often is the map updated?
A: The earthquake fault line map is constantly updated as new research and data become available. Advances in geophysical imaging techniques, the discovery of new fault lines, and the occurrence of earthquakes provide valuable information that necessitates map revisions.
Q: What are the limitations of the map?
A: While the earthquake fault line map provides valuable insights, it has limitations. It may not capture all fault lines, particularly those that are buried or inactive. Additionally, the map does not predict the exact timing or magnitude of future earthquakes.
Tips for Using the Earthquake Fault Line Map
- Consult with Experts: For detailed information and interpretation of the earthquake fault line map, consult with experts in geology, seismology, and earthquake engineering.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on the latest research and developments related to earthquake hazards in Turkey.
- Prepare for Earthquakes: Take steps to prepare for earthquakes, such as securing heavy objects, developing an emergency plan, and learning basic first aid.
Conclusion
The earthquake fault line map of Turkey is a powerful tool for understanding and mitigating seismic risks. It highlights the complex tectonic setting of the country, revealing the intricate network of fault lines that pose a constant threat. By utilizing the information provided by the map, authorities, researchers, and individuals can work together to build a more resilient and safer future for Turkey. Recognizing the inherent seismic vulnerability of the region, embracing preparedness measures, and continuously investing in research and infrastructure development are crucial steps towards mitigating the impact of earthquakes and safeguarding lives.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry of Turkey: A Deep Dive into the Earthquake Fault Line Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!