Unraveling Turkey’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Locations
Related Articles: Unraveling Turkey’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Locations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling Turkey’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Locations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling Turkey’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Locations
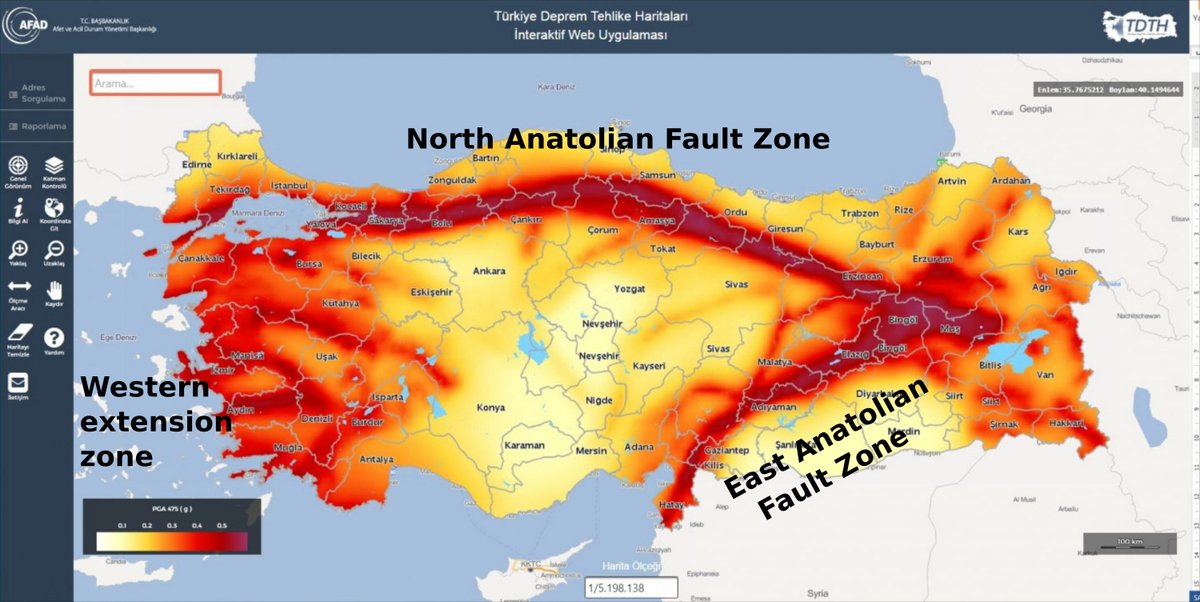
Turkey, a country nestled between the Eurasian and Arabian tectonic plates, experiences frequent seismic activity due to its location within the seismically active Mediterranean region. Understanding the distribution of earthquakes across Turkey is crucial for mitigating risks, planning for future events, and ensuring the safety of its population. This article delves into the intricate geography of earthquakes in Turkey, providing a comprehensive overview of their locations and the factors influencing their occurrence.
The Tectonic Dance: A Foundation for Understanding Turkey’s Earthquakes
The collision between the Eurasian and Arabian plates, coupled with the westward movement of the Anatolian plate, creates a complex geological environment in Turkey. This dynamic interaction manifests itself through various tectonic phenomena, including:
- The North Anatolian Fault Zone (NAFZ): This major fault system stretches for over 1,500 kilometers across northern Turkey, extending from the eastern Black Sea to the Aegean Sea. It is responsible for numerous destructive earthquakes, including the devastating 1999 İzmit earthquake that claimed over 17,000 lives.
- The East Anatolian Fault Zone (EAFZ): This fault system runs along the eastern border of Turkey, extending from the northern part of the country to the southeast, bordering Syria and Iraq. It has triggered significant earthquakes, such as the 2023 Kahramanmaras earthquakes, which caused widespread devastation and loss of life.
- The Aegean Sea Plate: The Aegean Sea Plate, a microplate within the Eurasian Plate, interacts with the Anatolian Plate, contributing to significant seismic activity in western Turkey, particularly in the Aegean region.
Mapping the Tremors: Visualizing Turkey’s Earthquake Zones
Visualizing the locations of earthquakes in Turkey provides valuable insights into the distribution of seismic activity. The Turkish Earthquake Research Foundation (DER) and the Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute (KOERI) maintain comprehensive earthquake catalogs, offering detailed information on the location, magnitude, and depth of past earthquakes. These data are often presented in the form of earthquake location maps, which can be used to:
- Identify High-Risk Zones: Areas with frequent and intense earthquakes are highlighted, allowing for targeted risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
- Understand Seismic Patterns: The distribution of earthquakes across Turkey reveals distinct zones of activity, reflecting the influence of major fault systems and tectonic movements.
- Inform Infrastructure Development: Knowledge of earthquake locations helps in designing and constructing earthquake-resistant buildings and infrastructure, minimizing potential damage and ensuring safety.
Beyond the Maps: Factors Influencing Earthquake Locations
While earthquake location maps provide a visual representation of seismic activity, understanding the underlying factors driving their occurrence is crucial. Key factors influencing earthquake locations in Turkey include:
- Fault Systems: The presence of major fault systems, like the NAFZ and EAFZ, directly influences earthquake locations. These faults act as zones of weakness, where tectonic stresses are released through earthquakes.
- Tectonic Plate Movement: The continuous movement of tectonic plates, particularly the collision between the Eurasian and Arabian plates, generates significant stress along fault lines, leading to earthquakes.
- Geological Structure: The underlying geological structure of Turkey, including the presence of sedimentary layers, volcanic rocks, and metamorphic formations, can influence the magnitude and location of earthquakes.
- Stress Accumulation: The accumulation of tectonic stress along fault lines over time eventually triggers earthquakes when the stress exceeds the strength of the rocks.
Understanding the Past, Preparing for the Future: The Importance of Earthquake Location Maps
Earthquake location maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding the seismic history of Turkey and predicting future events. By analyzing historical earthquake data and understanding the underlying geological processes, scientists can:
- Identify High-Risk Areas: Mapping past earthquakes helps in identifying areas prone to future seismic activity, allowing for targeted preparedness measures and risk mitigation strategies.
- Develop Earthquake Forecasting Models: Understanding earthquake patterns and the influence of tectonic forces allows for the development of more accurate earthquake forecasting models, providing crucial information for disaster preparedness.
- Design Earthquake-Resistant Structures: Knowledge of earthquake locations and their associated magnitudes informs the design of earthquake-resistant buildings and infrastructure, minimizing potential damage and ensuring public safety.
FAQs: Navigating the World of Turkey’s Earthquake Locations
1. Why is Turkey so prone to earthquakes?
Turkey’s location at the intersection of three tectonic plates, the Eurasian, Arabian, and Anatolian plates, creates a highly active seismic zone. The constant movement and interaction of these plates generate significant stress along fault lines, leading to frequent earthquakes.
2. What are the most earthquake-prone regions in Turkey?
The most earthquake-prone regions in Turkey are those located along the major fault systems, including the North Anatolian Fault Zone (NAFZ) and the East Anatolian Fault Zone (EAFZ). These regions include the Marmara Region, Istanbul, the Eastern Black Sea Region, and the Eastern Anatolia Region.
3. How can I find information about past earthquakes in Turkey?
The Turkish Earthquake Research Foundation (DER) and the Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute (KOERI) maintain comprehensive earthquake catalogs, providing detailed information on past earthquakes, including their location, magnitude, and depth. These data are often presented in the form of earthquake location maps, available online and through various publications.
4. How do earthquake location maps contribute to disaster preparedness?
Earthquake location maps help identify high-risk areas, allowing for targeted preparedness measures, such as building codes and emergency response plans. They also inform the design of earthquake-resistant structures, minimizing potential damage and ensuring public safety.
5. What are some tips for staying safe during an earthquake?
- Drop, cover, and hold on: During an earthquake, drop to the ground, cover your head and neck with your arms, and hold on to a sturdy object.
- Stay away from windows and heavy furniture: Windows and heavy furniture can shatter or fall during an earthquake, causing injuries.
- If you are indoors, stay inside: Do not attempt to exit a building during an earthquake, as falling debris poses a significant risk.
- If you are outdoors, move away from buildings and power lines: Seek open space away from potential hazards.
Conclusion: A Constant Vigilance for a Safer Future
Turkey’s seismic landscape is a testament to the dynamic nature of our planet. Understanding the distribution of earthquakes across the country is not only crucial for mitigating risks and planning for future events but also for ensuring the safety and well-being of its citizens. By utilizing earthquake location maps and continually enhancing our understanding of seismic activity, Turkey can move towards a future where the impacts of earthquakes are minimized, and resilience prevails.

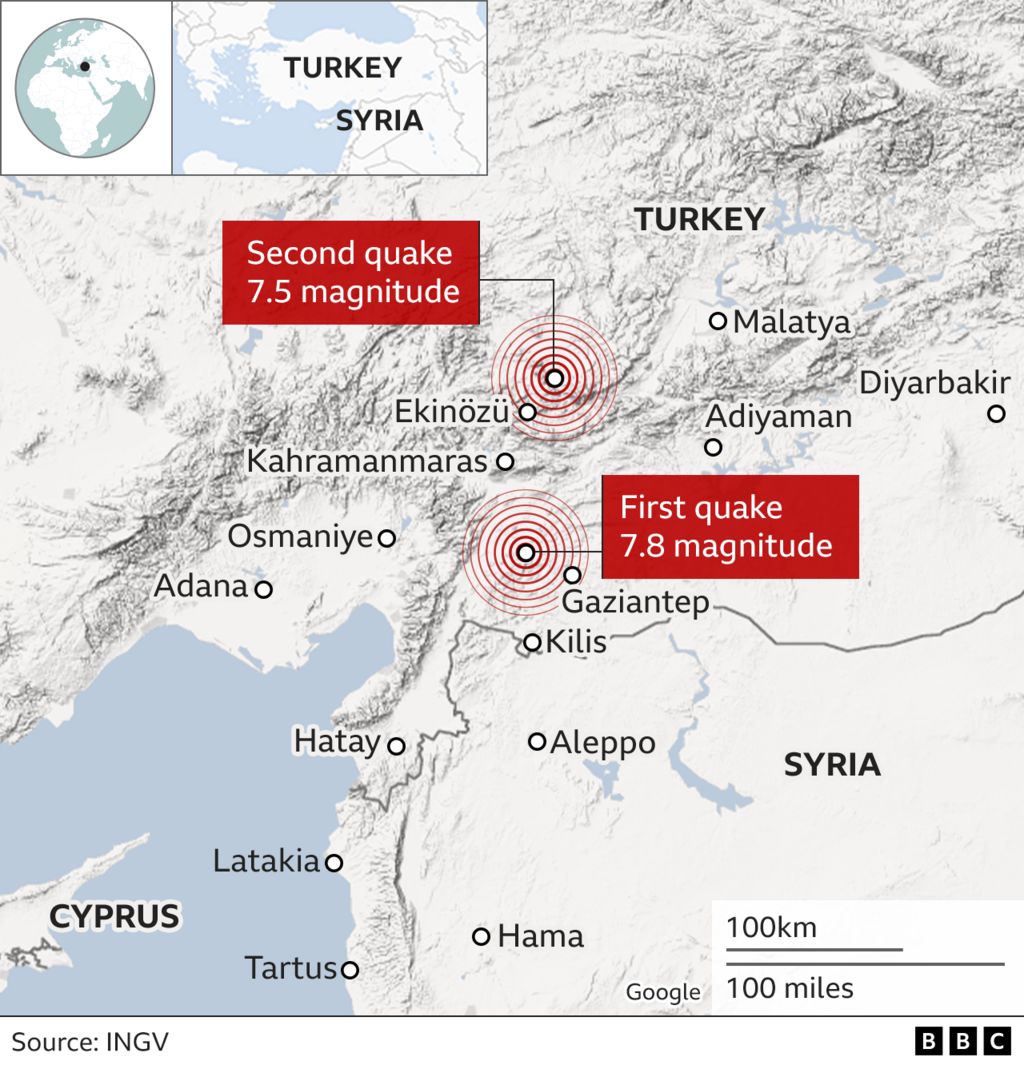

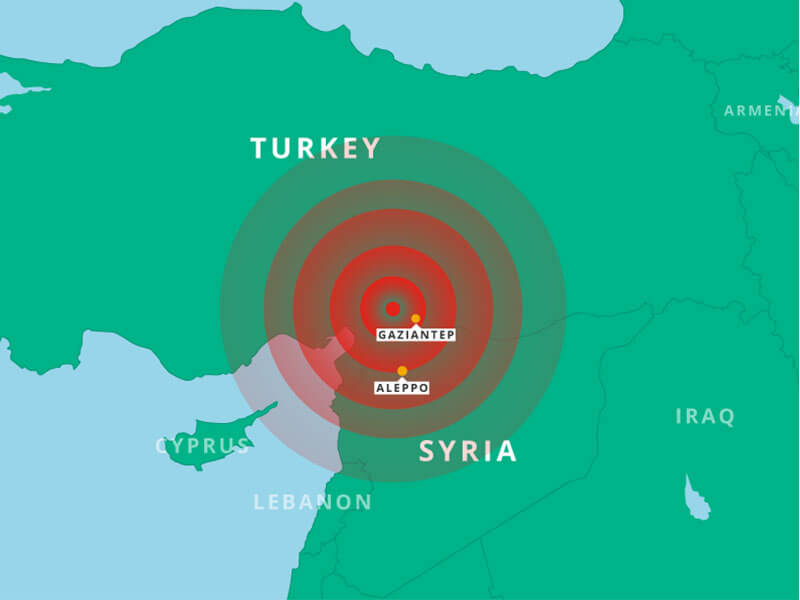




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling Turkey’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Locations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!