Unveiling the Bedrock Foundation of Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to the Michigan Bedrock Topography Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Bedrock Foundation of Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to the Michigan Bedrock Topography Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Bedrock Foundation of Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to the Michigan Bedrock Topography Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Bedrock Foundation of Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to the Michigan Bedrock Topography Map

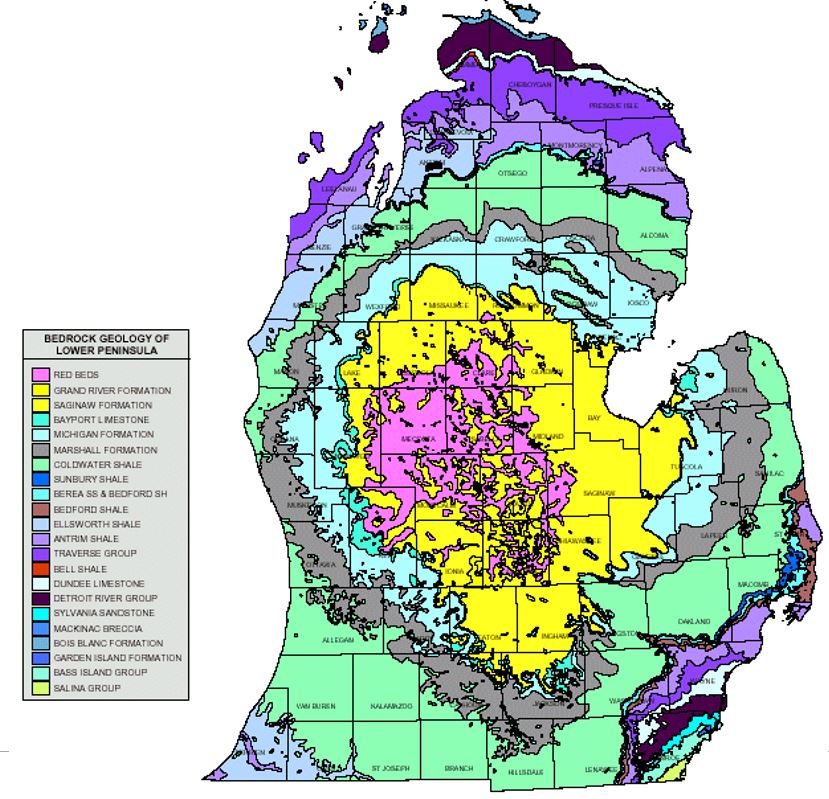
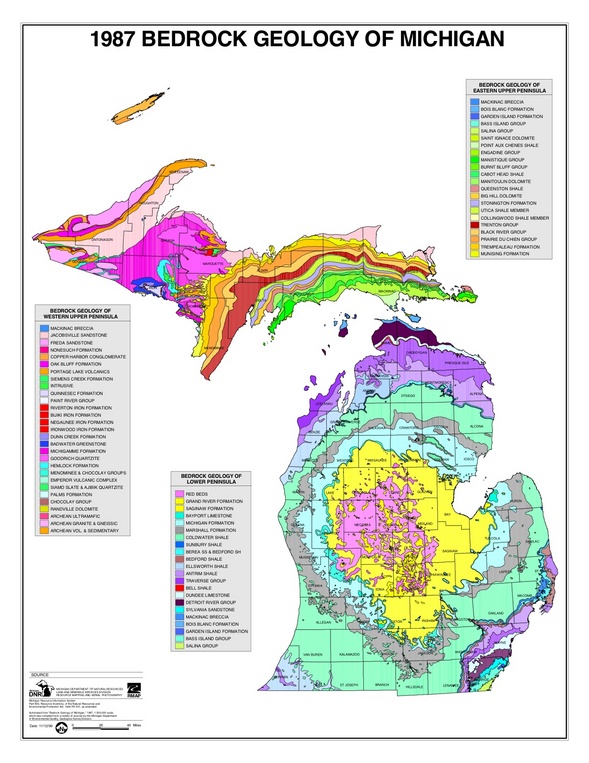
The Michigan bedrock topography map serves as a foundational document for understanding the geological history and structure of the state. This map, meticulously crafted through years of scientific research and data collection, reveals the hidden layers of rock beneath the surface, providing crucial insights into the formation of Michigan’s landscape, its natural resources, and the potential challenges it faces.
Delving into the Depths: Understanding Bedrock Topography
Bedrock, the solid rock that underlies the soil and loose sediments, forms the bedrock topography. It is a complex tapestry woven by geological forces over millions of years, shaped by tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, and the relentless erosion of wind, water, and ice. The Michigan bedrock topography map is a visual representation of this intricate geological history, showcasing the distribution of various rock types and their underlying structures.
A Journey Through Time: Michigan’s Bedrock History
The bedrock of Michigan is primarily composed of sedimentary rocks, formed from the accumulation and solidification of sediments over eons. These sediments were deposited in ancient seas and lakes, revealing a story of changing environments and tectonic shifts. The map highlights the presence of various rock formations, including:
- Cambrian and Ordovician Sediments: Found in the northern and eastern regions, these rocks are predominantly composed of sandstone, shale, and limestone, reflecting the deposition in shallow marine environments.
- Silurian and Devonian Sediments: Located in the central and southern portions of the state, these formations exhibit a wider range of rock types, including dolomite, gypsum, and salt, reflecting a transition to deeper marine environments and the influence of evaporative conditions.
- Mississippian and Pennsylvanian Sediments: Concentrated in the western and southwestern areas, these rocks are primarily composed of sandstone, shale, and coal, indicating the presence of extensive swamps and forests during this period.
- Glacial Deposits: The most recent geological event to shape Michigan’s bedrock is the Pleistocene glaciation. The map reveals the distribution of glacial till, a mixture of clay, sand, gravel, and boulders deposited by retreating glaciers. These deposits significantly influence the state’s soil fertility, groundwater resources, and surface topography.
Beyond the Surface: The Significance of Bedrock Topography
The Michigan bedrock topography map is not merely a static representation of geological history; it serves as a vital tool for various disciplines and applications:
- Resource Exploration: The map helps locate and understand the distribution of valuable natural resources, including oil, natural gas, minerals, and groundwater. For instance, the presence of specific rock formations can indicate potential areas for hydrocarbon exploration or the presence of aquifers.
- Land-Use Planning: Understanding the bedrock topography is crucial for land-use planning and development. It provides insights into soil suitability for agriculture, the potential for construction, and the risks associated with geological hazards such as landslides and sinkholes.
- Environmental Management: The map aids in understanding the movement of groundwater, the potential for contamination, and the suitability of different areas for waste disposal. This knowledge is critical for ensuring the sustainability of water resources and protecting the environment.
- Geological Research: The bedrock topography map serves as a foundational resource for ongoing geological research, providing data for understanding tectonic activity, the evolution of landscapes, and the impact of climate change on geological processes.
Navigating the Map: A Guide to Understanding its Features
The Michigan bedrock topography map is a complex document that requires careful interpretation. Here are some key features to understand:
- Rock Formations: The map uses different colors and patterns to represent various rock formations, each with its unique geological characteristics and potential resource implications.
- Structural Features: The map depicts geological structures like faults, folds, and unconformities, which reveal the forces that have shaped the bedrock. These structures can influence the distribution of resources and the occurrence of geological hazards.
- Elevations and Depths: The map may include contour lines or other elevation data, providing information on the depth of bedrock and its influence on surface topography.
- Legend and Scale: A legend explains the symbols and colors used on the map, while the scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the most common rock types found in Michigan’s bedrock?
Michigan’s bedrock primarily consists of sedimentary rocks, including sandstone, shale, limestone, dolomite, gypsum, and salt. These rocks were formed over millions of years through the deposition and solidification of sediments in ancient seas and lakes.
2. How does the bedrock topography influence Michigan’s surface features?
The bedrock topography significantly influences the state’s surface features. For instance, areas with easily eroded bedrock, such as shale, tend to have rolling hills and valleys, while areas with more resistant bedrock, like sandstone, may exhibit steeper slopes and cliffs.
3. What are some of the geological hazards associated with Michigan’s bedrock?
Michigan’s bedrock topography presents certain geological hazards, including landslides, sinkholes, and groundwater contamination. Areas with weak or fractured bedrock are more susceptible to these hazards.
4. How can I access the Michigan bedrock topography map?
The Michigan bedrock topography map is available through various sources, including the Michigan Geological Survey, the United States Geological Survey, and online repositories.
5. What are the potential benefits of using the bedrock topography map?
The bedrock topography map offers numerous benefits, including understanding resource distribution, informing land-use planning, supporting environmental management, and facilitating geological research.
Tips for Utilizing the Michigan Bedrock Topography Map
- Consult the Legend: Carefully review the legend to understand the symbols, colors, and patterns used on the map.
- Consider the Scale: Pay attention to the scale to accurately interpret distances and features on the map.
- Use Additional Resources: Combine the bedrock topography map with other geological and environmental data for a more comprehensive understanding of the area.
- Seek Expert Guidance: Consult with geologists or other experts for assistance in interpreting complex geological features or addressing specific questions.
Conclusion
The Michigan bedrock topography map serves as a crucial resource for understanding the state’s geological history, identifying potential resources, and informing responsible land-use practices. This map, a testament to decades of scientific research and data collection, provides a window into the hidden depths of Michigan, revealing the complex tapestry of rock formations and geological structures that have shaped the state we know today. By utilizing this map and understanding its implications, we can make informed decisions about resource management, environmental protection, and sustainable development, ensuring a brighter future for Michigan’s natural heritage.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Bedrock Foundation of Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide to the Michigan Bedrock Topography Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!