Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps

Maps are fundamental tools for understanding and navigating our world. They provide a visual representation of geographical features, allowing us to comprehend spatial relationships and plan our journeys. However, a standard map often falls short in depicting the intricacies of the Earth’s surface, particularly its elevation and relief. This is where topographic maps step in, offering a detailed and nuanced portrait of the landscape.
Understanding Topographic Maps: A Visual Language of Elevation
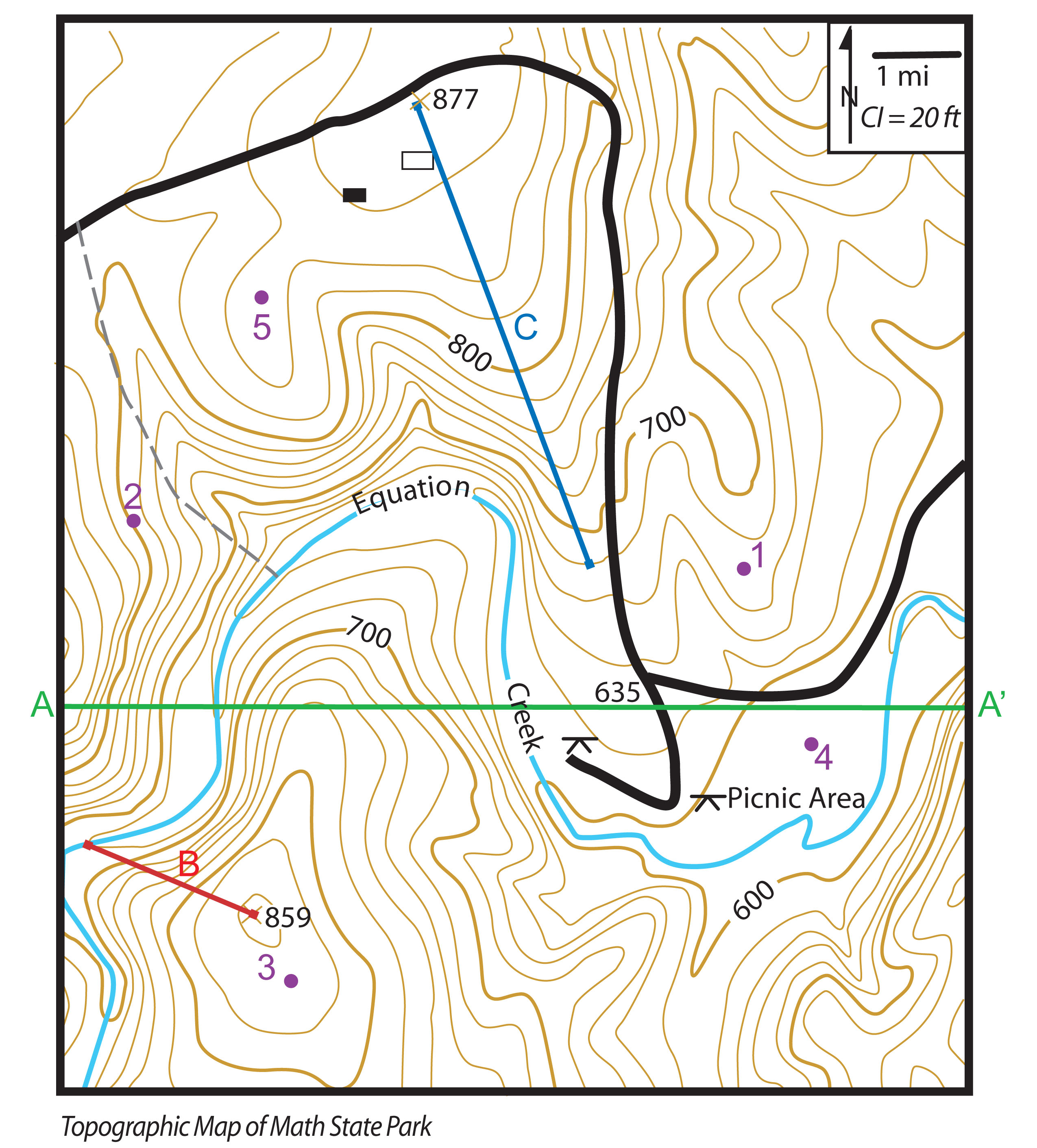
Topographic maps, often referred to as "topo maps," are specialized cartographic representations that portray the Earth’s surface in three dimensions. Unlike basic maps that primarily focus on location and boundaries, topographic maps incorporate elevation data, showcasing the undulations and variations in terrain. This information is presented through contour lines, a series of interconnected lines that represent points of equal elevation. Each contour line connects points on the map with the same height above sea level, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s shape and gradient.
Deciphering the Language of Contours: Interpreting the Landscape
Contour lines are the key to understanding topographic maps. They offer a systematic and intuitive way to grasp the terrain’s topography. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the slope. Conversely, widely spaced contour lines indicate a gentle incline. By tracing the flow of contour lines, one can visualize valleys, ridges, hills, and depressions.
Beyond Elevation: Additional Information Encoded on Topographic Maps
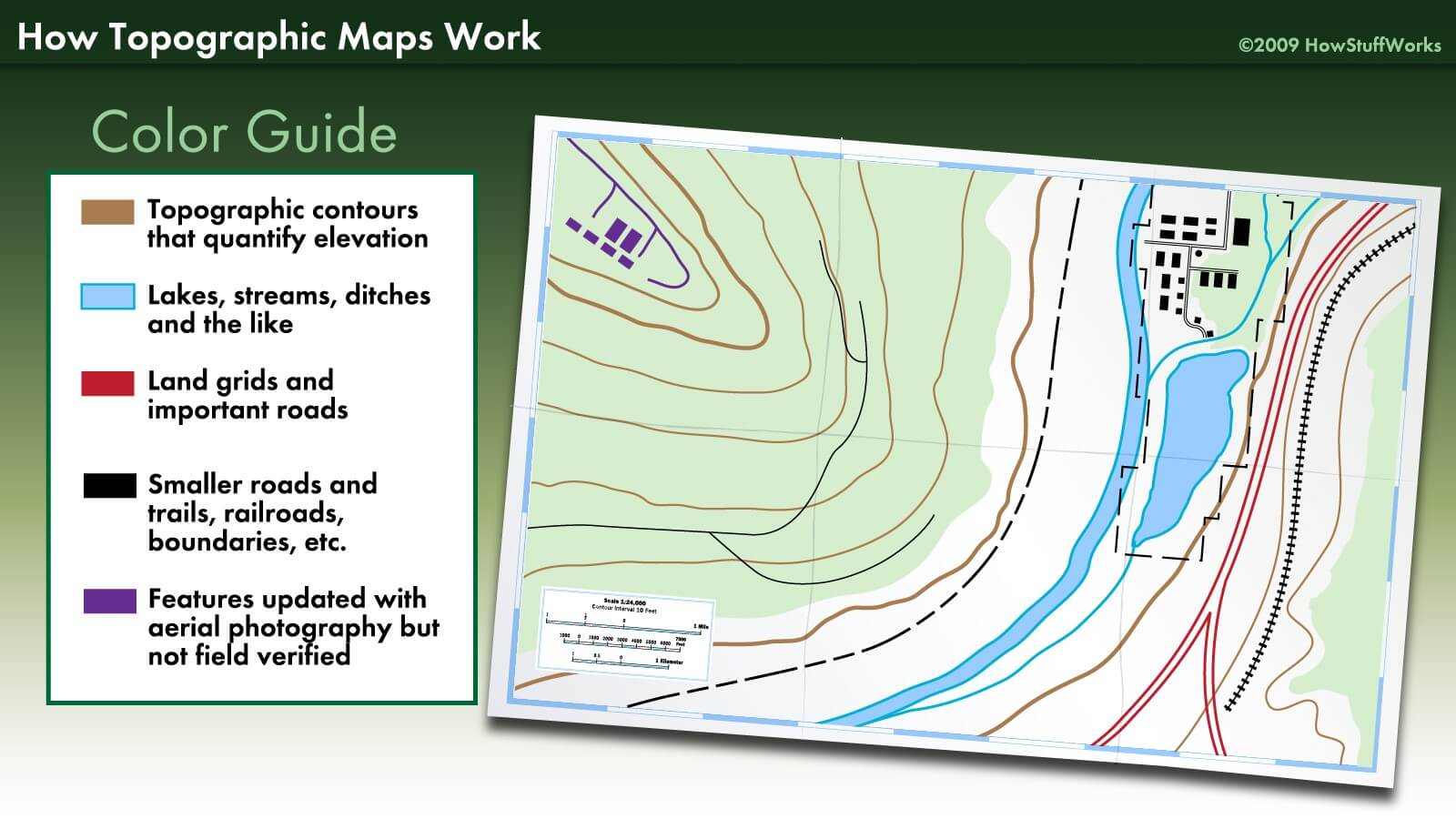
Topographic maps are not limited to depicting elevation. They often incorporate other essential geographical features, enhancing their utility for various applications. These may include:
- Hydrography: Rivers, lakes, streams, and other water bodies are depicted, providing valuable information about water resources and drainage patterns.
- Cultural Features: Roads, trails, buildings, and other man-made structures are marked, offering insights into human activity and infrastructure.
- Vegetation: Forests, grasslands, and other types of vegetation are often represented, providing information about the ecological makeup of the area.
- Land Use: Agricultural areas, urban zones, and other land use categories may be indicated, offering insights into human impact on the landscape.
The Importance of Topographic Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Topographic maps are indispensable tools across a wide range of disciplines and applications, demonstrating their significance in various aspects of human endeavor.
- Navigation and Exploration: For hikers, climbers, and adventurers, topographic maps are essential for navigating challenging terrain, identifying potential hazards, and planning safe routes.
- Environmental Management: Environmental scientists and resource managers rely on topographic maps to understand landforms, assess ecological conditions, and plan conservation strategies.
- Urban Planning and Development: City planners and developers utilize topographic maps to analyze terrain, identify suitable locations for infrastructure, and minimize environmental impact.
- Military Operations: The military extensively uses topographic maps for strategic planning, troop movements, and terrain analysis, particularly in mountainous or complex environments.
- Geological Studies: Geologists use topographic maps to interpret geological formations, identify potential mineral deposits, and assess the risk of landslides or earthquakes.
- Hydrological Studies: Hydrologists rely on topographic maps to analyze watershed boundaries, understand water flow patterns, and assess flood risks.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Topographic Maps
1. What are the different types of topographic maps?
Topographic maps are available in various scales, each serving specific purposes. Large-scale maps provide detailed information over smaller areas, suitable for local planning and navigation. Small-scale maps cover larger regions but offer less detail, suitable for regional planning and understanding broader geographical patterns.
2. How can I access topographic maps?
Topographic maps are readily available through various sources:
- Government Agencies: The United States Geological Survey (USGS) and similar agencies in other countries offer free access to topographic maps online and in print.
- Mapping Software: Numerous mapping software programs, such as ArcGIS and QGIS, allow users to access and analyze topographic data.
- Commercial Vendors: Companies specializing in mapping and surveying provide topographic maps in various formats, including digital and printed versions.
3. What are the advantages of using topographic maps over other types of maps?
Topographic maps offer a distinct advantage over standard maps by providing detailed elevation information, enabling users to understand the terrain’s three-dimensional structure. This facilitates accurate navigation, environmental analysis, and informed decision-making in various applications.
4. How can I learn to read and interpret topographic maps?
Learning to read topographic maps requires understanding the language of contour lines and their significance. Numerous resources are available to aid in this process, including online tutorials, educational videos, and introductory books on cartography and map reading.
5. How are topographic maps created?
Topographic maps are created through a combination of surveying techniques and digital data processing. Traditionally, surveyors used instruments like theodolites and levels to measure elevation and create contour lines manually. Today, advanced technologies like LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and aerial photography provide high-resolution elevation data, which is then processed and incorporated into topographic maps.
Tips for Effective Use of Topographic Maps
- Understand the Scale: Pay close attention to the map’s scale, as it determines the level of detail and the distance represented by each unit on the map.
- Interpret Contour Lines: Practice recognizing the relationship between contour lines and terrain features, understanding the significance of close spacing and wide spacing.
- Utilize the Legend: Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend, which explains the symbols and markings used to represent various features.
- Consider the Purpose: Determine the specific application for which you are using the map, as this will guide your interpretation and focus.
- Combine with Other Data: Integrate topographic maps with other data sources, such as satellite imagery and aerial photographs, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps are powerful tools that transcend mere location indicators. They provide a detailed and nuanced representation of the Earth’s surface, enabling us to understand the landscape’s complexities and make informed decisions. By embracing the language of contour lines and understanding their significance, we unlock the potential of topographic maps to navigate, explore, manage, and understand our world in a richer and more comprehensive manner. From navigating treacherous trails to planning sustainable urban development, topographic maps serve as indispensable guides, illuminating the intricate tapestry of our planet’s surface.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/topomap2-56a364da5f9b58b7d0d1b406.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!