Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topography Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topography Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topography Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topography Maps

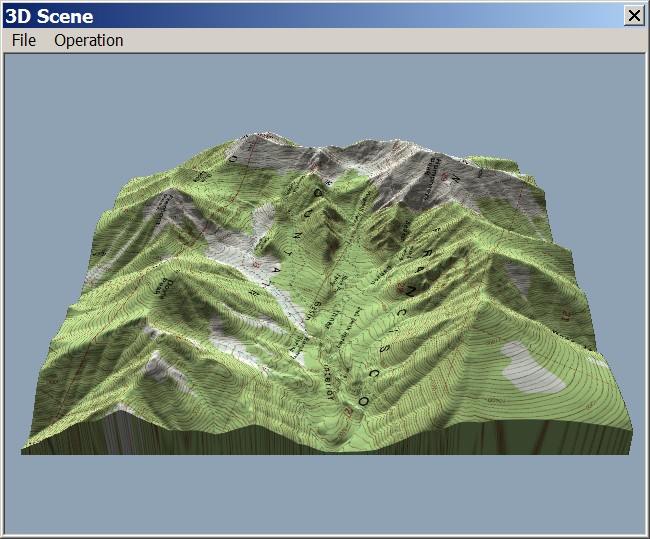
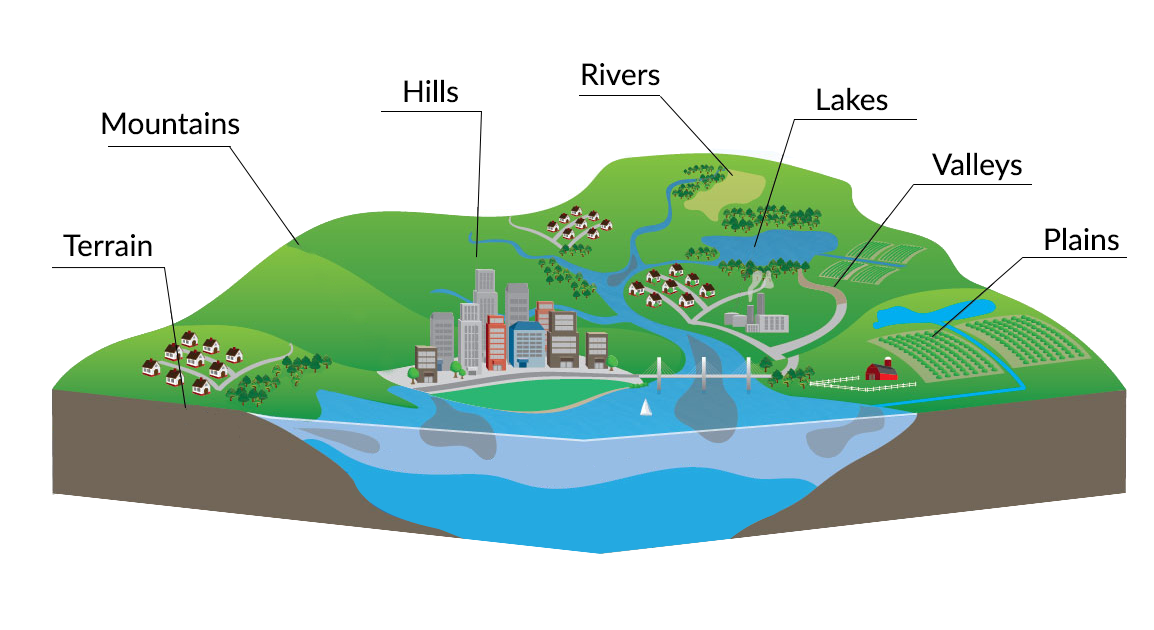
The Earth’s surface is a complex tapestry of mountains, valleys, plains, and coastlines. Understanding this intricate topography is crucial for a wide range of applications, from urban planning and infrastructure development to environmental monitoring and disaster preparedness. Traditional two-dimensional maps, while informative, often fall short in conveying the true three-dimensional nature of the terrain. This is where 3D topography maps come into play, offering a powerful and immersive visualization tool that revolutionizes our perception and understanding of the landscape.
Understanding the Fundamentals
A 3D topography map, also known as a digital terrain model (DTM) or digital elevation model (DEM), is a digital representation of the Earth’s surface. It utilizes a grid of data points, each representing a specific elevation value, to create a three-dimensional representation of the terrain. This data can be acquired through various methods, including:
- Aerial Photography: Using specialized cameras mounted on aircraft or drones, aerial photographs capture images of the landscape from above. These images are then processed to extract elevation data and create a 3D model.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR employs lasers to measure distances to the ground, generating highly accurate and detailed elevation data. This technology is particularly effective for capturing dense vegetation and complex terrain.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with sensors capture images of the Earth’s surface, providing vast coverage and data for creating 3D models.
- Ground Surveys: Traditional surveying techniques using instruments like total stations and GPS receivers can also be used to collect elevation data for generating 3D models, albeit with a smaller coverage area compared to aerial or satellite methods.
Benefits of 3D Topography Maps
The adoption of 3D topography maps has significantly impacted various fields, offering numerous advantages over traditional 2D representations. These benefits include:
- Enhanced Visualization: 3D topography maps provide a more intuitive and realistic representation of the terrain, allowing users to visualize the landscape from different perspectives. This enhanced visualization is particularly helpful for tasks such as site planning, construction projects, and emergency response.
- Improved Analysis: By providing a three-dimensional perspective, 3D topography maps enable more accurate analysis of terrain characteristics, including slope, aspect, and elevation changes. This information is crucial for various applications, such as hydrological modeling, landslide susceptibility analysis, and wildlife habitat mapping.
- Precise Measurements: 3D topography maps facilitate precise measurement of distances, areas, and volumes, which is essential for tasks like land surveying, infrastructure design, and resource management.
- Interactive Exploration: Many 3D topography map software applications offer interactive features, allowing users to zoom, pan, and rotate the map to explore the terrain in detail. This interactivity enhances user engagement and facilitates a deeper understanding of the landscape.
- Integration with Other Data: 3D topography maps can be seamlessly integrated with other geospatial data, such as satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and demographic information, creating a comprehensive and multi-layered representation of the environment.
Applications of 3D Topography Maps
The versatility of 3D topography maps has led to their widespread adoption across numerous sectors, including:
- Urban Planning and Development: 3D topography maps play a crucial role in urban planning by providing a detailed understanding of the terrain, enabling efficient infrastructure development, transportation planning, and urban renewal projects.
- Civil Engineering and Construction: These maps are indispensable for civil engineers and construction professionals, facilitating site analysis, project planning, and construction management. They provide essential data for earthworks calculations, slope stability assessments, and road and bridge design.
- Environmental Management: 3D topography maps are invaluable for environmental monitoring and management. They enable the analysis of land cover changes, deforestation, and habitat fragmentation, supporting conservation efforts and sustainable resource management.
- Disaster Preparedness and Response: In disaster situations, 3D topography maps provide crucial information for emergency response teams. They help identify areas at risk, plan evacuation routes, and optimize resource allocation.
- Military and Defense: 3D topography maps are essential for military operations, providing a detailed understanding of the terrain, facilitating troop deployment, and supporting target acquisition.
- Tourism and Recreation: 3D topography maps enhance the tourist experience by providing immersive views of landscapes and attractions. They are also used in outdoor recreation activities like hiking, skiing, and mountain biking, offering detailed information about trails and terrain features.
FAQs about 3D Topography Maps
Q: What is the difference between a 3D topography map and a 2D map?
A: While both types of maps represent the Earth’s surface, a 3D topography map provides a three-dimensional representation of the terrain, showcasing elevation changes and creating a more realistic visual experience. 2D maps, on the other hand, are flat representations of the landscape, limited in their ability to convey the true nature of the terrain.
Q: How accurate are 3D topography maps?
A: The accuracy of 3D topography maps depends on the data acquisition method used. LiDAR data typically provides the highest level of accuracy, followed by aerial photography and satellite imagery. The accuracy is also influenced by factors like the resolution of the data and the presence of vegetation or other obstacles.
Q: What are the limitations of 3D topography maps?
A: While 3D topography maps offer significant advantages, they also have limitations. For example, they may not accurately represent dynamic features like water bodies or vegetation that change over time. Additionally, the accuracy of the data can be affected by factors like atmospheric conditions and the presence of dense vegetation.
Q: How can I access and use 3D topography maps?
A: Various online platforms and software applications provide access to 3D topography maps. Some popular options include Google Earth, ArcGIS Pro, and QGIS. These platforms offer tools for visualization, analysis, and integration with other geospatial data.
Tips for Using 3D Topography Maps Effectively
- Choose the Right Data Source: Select a data source that best suits the specific needs of your project, considering factors like accuracy, resolution, and coverage area.
- Understand the Data Resolution: Be aware of the data resolution, as it determines the level of detail in the 3D model. Higher resolution data provides a more accurate representation of the terrain.
- Use Appropriate Software: Choose a software application that provides the necessary tools for visualization, analysis, and integration with other data.
- Explore Interactive Features: Take advantage of interactive features like zooming, panning, and rotating the map to gain a comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
- Combine with Other Data: Integrate 3D topography maps with other geospatial data to create a richer and more informative representation of the environment.
Conclusion
3D topography maps have emerged as an indispensable tool for various disciplines, revolutionizing our understanding of the Earth’s surface. Their ability to provide a realistic and immersive representation of the terrain, coupled with their analytical capabilities, has enabled significant advancements in fields like urban planning, environmental management, and disaster preparedness. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and accurate 3D topography maps, further enhancing our ability to analyze, understand, and manage the complex landscape we inhabit.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Topography Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!