Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
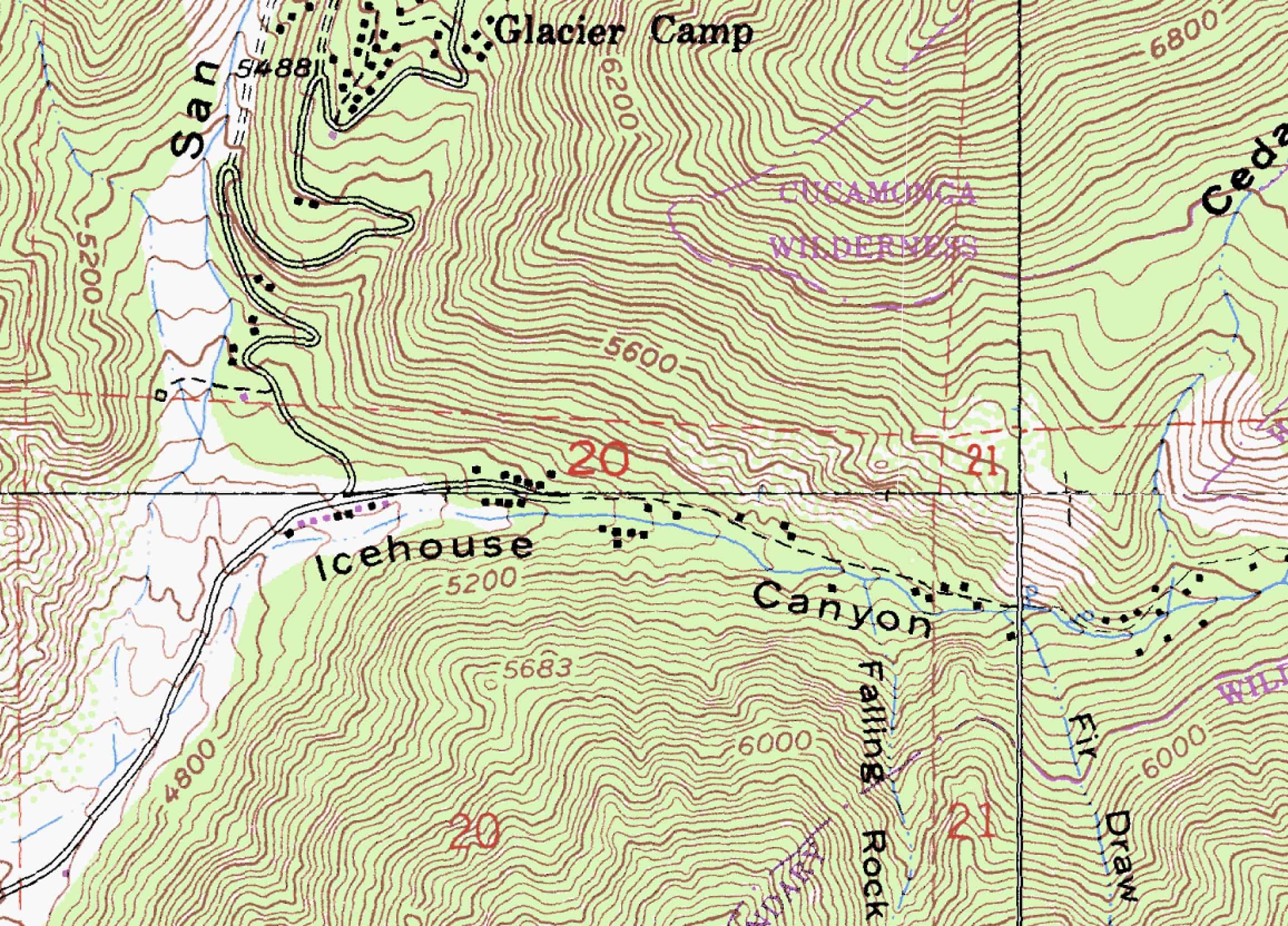
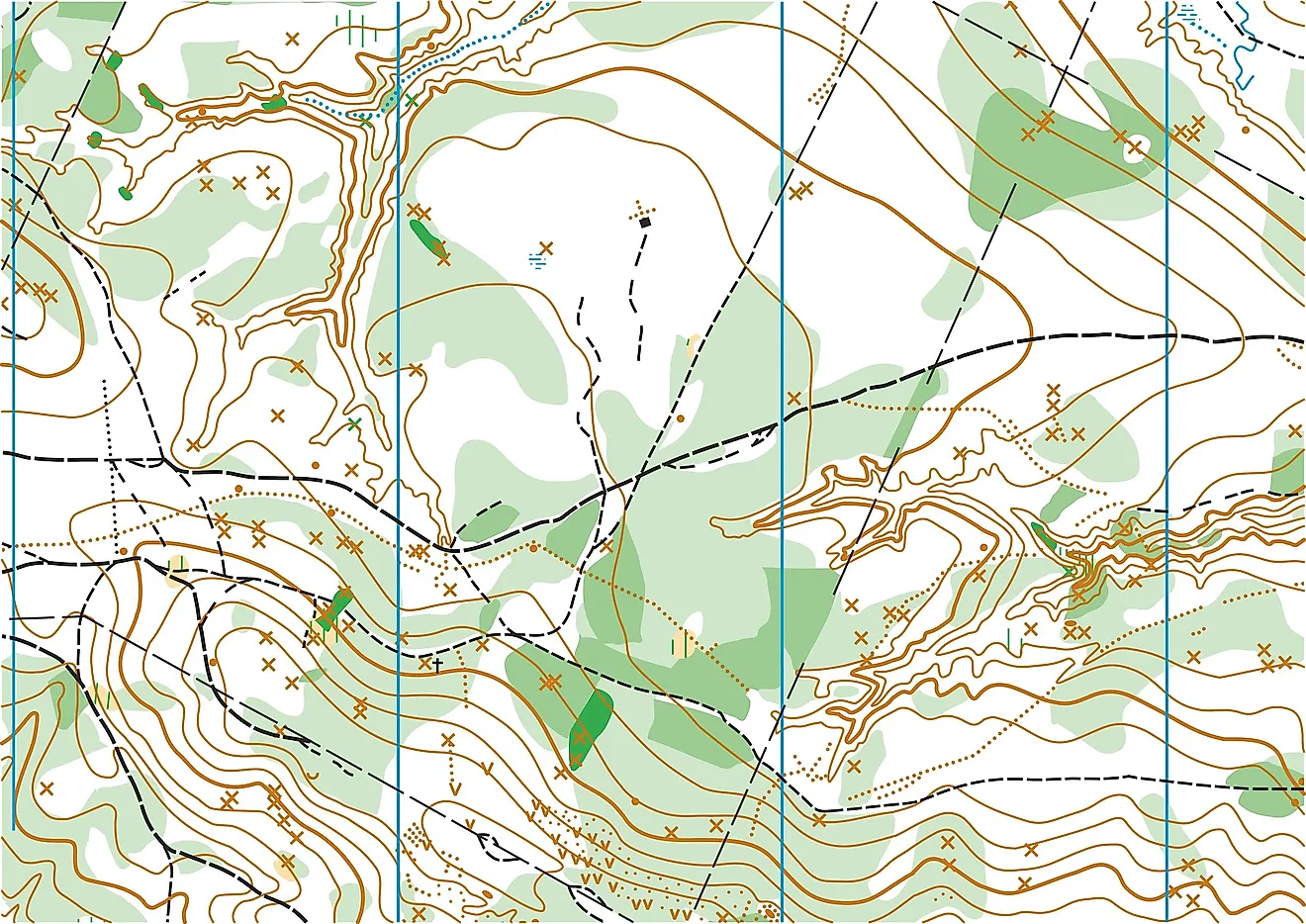
Topographic maps, often referred to as "topo maps," are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, meticulously crafted to depict not only the location of features but also their elevation and three-dimensional form. These maps are indispensable tools for a wide range of disciplines, from surveying and engineering to planning and recreation, offering insights into the terrain that are crucial for informed decision-making.
The Essence of Topographic Maps
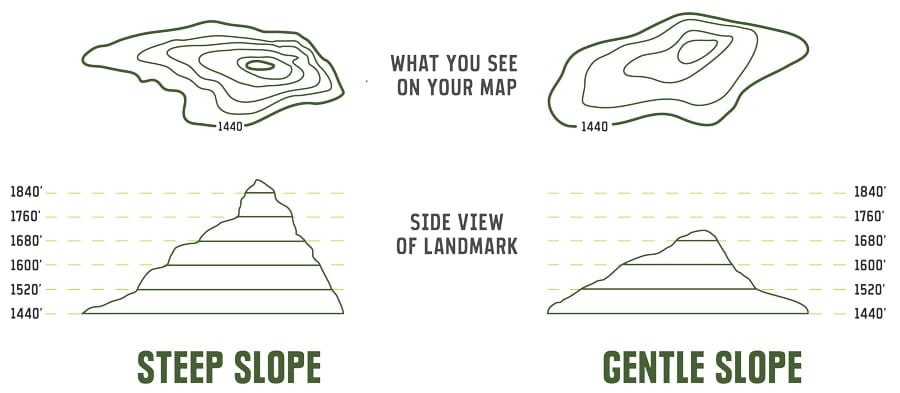
At the heart of topographic maps lies the principle of contour lines, which are lines connecting points of equal elevation. These lines dance across the map, revealing the undulating nature of the terrain. A close examination of these lines reveals a wealth of information:
- Elevation: The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope. Conversely, widely spaced lines indicate gentler gradients.
- Landform Recognition: Contour lines delineate specific landforms, such as hills, valleys, ridges, and depressions.
- Drainage Patterns: The flow of water is evident in the direction of contour lines, revealing rivers, streams, and other water bodies.
Beyond contour lines, topographic maps incorporate a diverse array of symbols and conventions to represent a wide range of features:
- Natural Features: Forests, lakes, swamps, and other natural elements are depicted with specific symbols, providing a clear understanding of the natural landscape.
- Cultural Features: Roads, buildings, bridges, and other man-made structures are included, offering a glimpse into the human imprint on the terrain.
- Elevation Data: Elevation data is typically presented in a variety of ways, including spot heights, contour intervals, and shaded relief, providing a comprehensive understanding of the vertical dimension of the landscape.
The Significance of Topographic Maps
The value of topographic maps extends far beyond mere visual representation. They serve as fundamental tools in a multitude of fields:
- Surveying and Engineering: Topographic maps are essential for land surveying, construction planning, and infrastructure development. They provide accurate data on terrain gradients, elevation changes, and landform characteristics, guiding engineering decisions and ensuring the stability and functionality of structures.
- Resource Management: Topographic maps play a crucial role in resource management, enabling the identification of potential water sources, mineral deposits, and other valuable resources. They inform decisions related to land use, conservation, and sustainable development.
- Urban Planning and Development: Topographic maps are invaluable for urban planning, guiding the development of infrastructure, transportation systems, and residential areas. They provide insights into the terrain’s suitability for various purposes, minimizing potential risks and ensuring efficient urban development.
- Recreation and Outdoor Activities: For hikers, campers, and outdoor enthusiasts, topographic maps are indispensable companions. They provide detailed information about trails, elevations, and potential hazards, enhancing safety and enriching the outdoor experience.
- Military Operations: Topographic maps have been essential for military operations throughout history. They provide crucial information about terrain, elevation changes, and potential obstacles, aiding in strategic planning and tactical decision-making.
Navigating the Landscape of Topographic Maps: Frequently Asked Questions
1. How are topographic maps created?
Topographic maps are created through a process known as surveying, which involves measuring the elevation and location of various points on the Earth’s surface. Traditionally, this was done using instruments like theodolites and levels. However, modern techniques rely heavily on aerial photography, satellite imagery, and advanced surveying technologies, providing faster and more accurate data collection.
2. What is the difference between a topographic map and a geographical map?
While both types of maps depict the Earth’s surface, they differ in their focus. Geographical maps prioritize the location and distribution of geographical features, while topographic maps emphasize the terrain’s elevation and three-dimensional form. Topographic maps are characterized by contour lines, which are absent in geographical maps.
3. What is a contour interval, and why is it important?
A contour interval represents the vertical difference in elevation between two adjacent contour lines. This interval is crucial for interpreting the map’s data. A smaller contour interval indicates a more detailed representation of the terrain, while a larger interval provides a broader overview.
4. How can I read a topographic map?
Reading a topographic map involves understanding the symbols, conventions, and data presented. It requires recognizing contour lines, interpreting elevation changes, and identifying different landforms. Numerous resources, including online tutorials and guidebooks, provide detailed explanations and practice exercises to enhance map reading skills.
5. What are the advantages of using digital topographic maps?
Digital topographic maps offer several advantages over traditional paper maps:
- Interactivity: Digital maps allow users to zoom, pan, and rotate the map, providing a dynamic and interactive experience.
- Data Integration: Digital maps can integrate various data layers, such as satellite imagery, aerial photography, and GPS data, creating a more comprehensive and informative representation.
- Portability: Digital maps can be accessed on smartphones, tablets, and computers, making them readily available and portable.
Navigating the Landscape: Tips for Effective Use
- Understand the Map Scale: The map scale indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. Familiarize yourself with the scale to accurately assess distances and elevations.
- Interpret Contour Lines: Pay close attention to the contour lines, recognizing their spacing, direction, and shape to understand the terrain’s slope, landforms, and drainage patterns.
- Utilize Map Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on the map, including those representing natural features, cultural features, and elevation data.
- Consider Map Purpose: Always consider the purpose of the map and the specific information you need to extract. Choose a map with an appropriate scale and level of detail for your intended use.
- Practice Map Reading: Regular practice is key to developing proficiency in map reading. Utilize online resources, guidebooks, and real-world experiences to enhance your skills.
Conclusion: A Window into the Earth’s Surface
Topographic maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding and interpreting the Earth’s surface. They provide a comprehensive representation of terrain, elevation, and landforms, enabling informed decision-making across a wide range of disciplines. From surveying and engineering to resource management and recreation, topographic maps remain indispensable resources for navigating and understanding the complexities of our planet’s landscape. As technology advances, digital topographic maps offer enhanced interactivity, data integration, and accessibility, further solidifying their importance in the modern world.
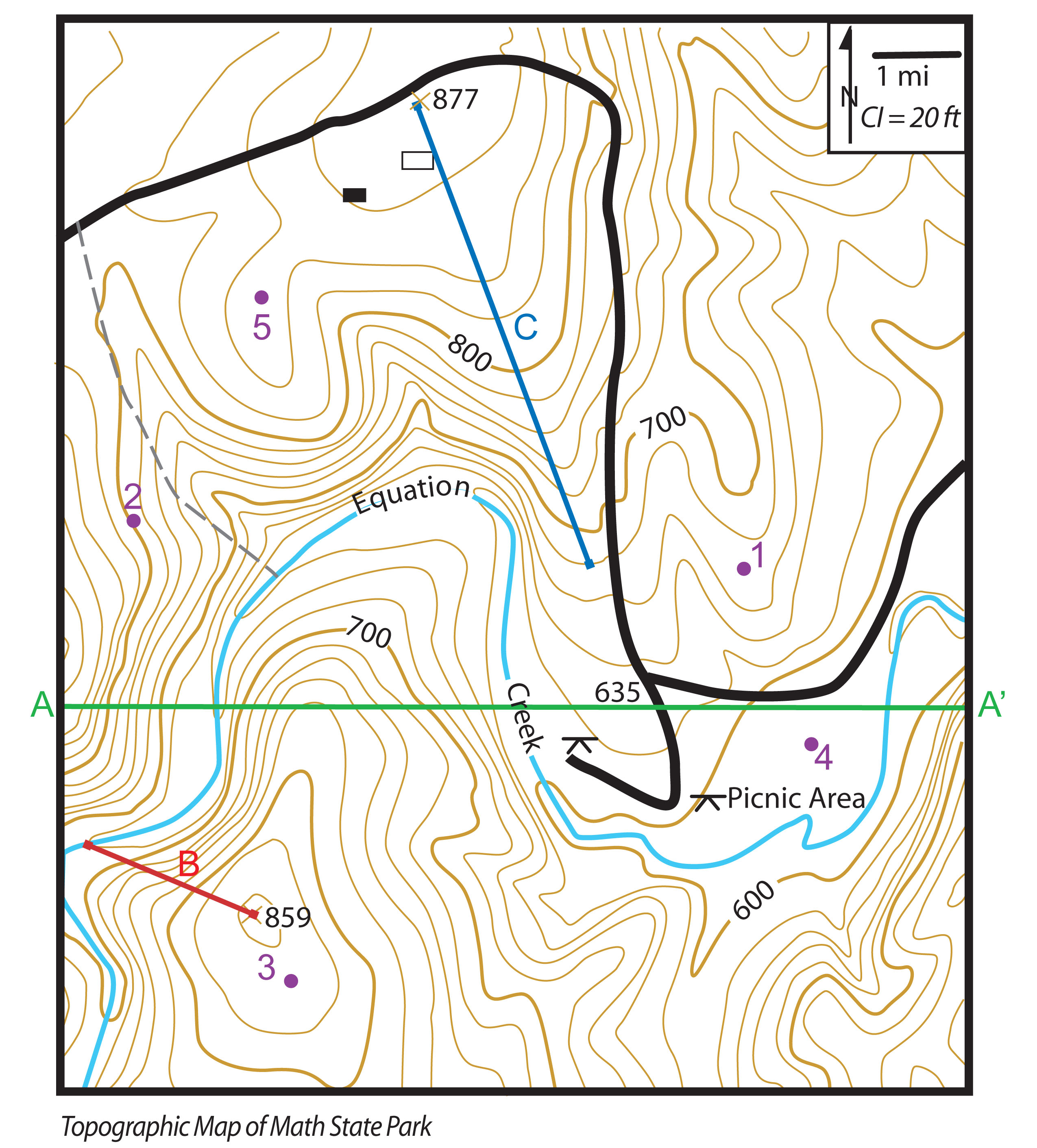
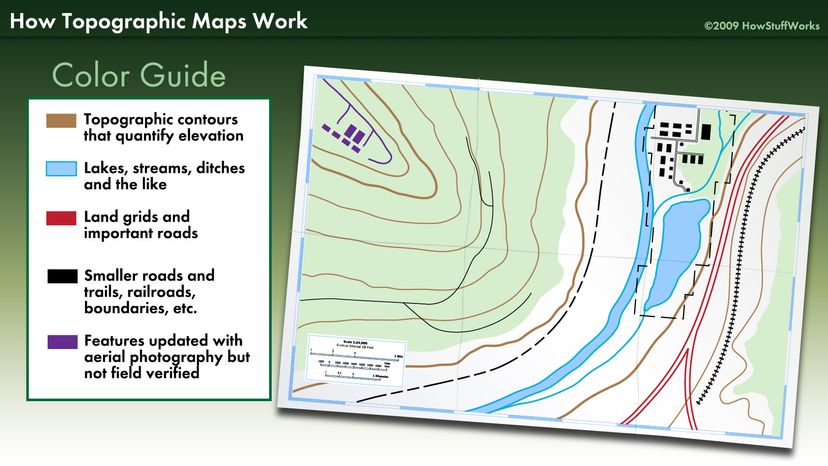



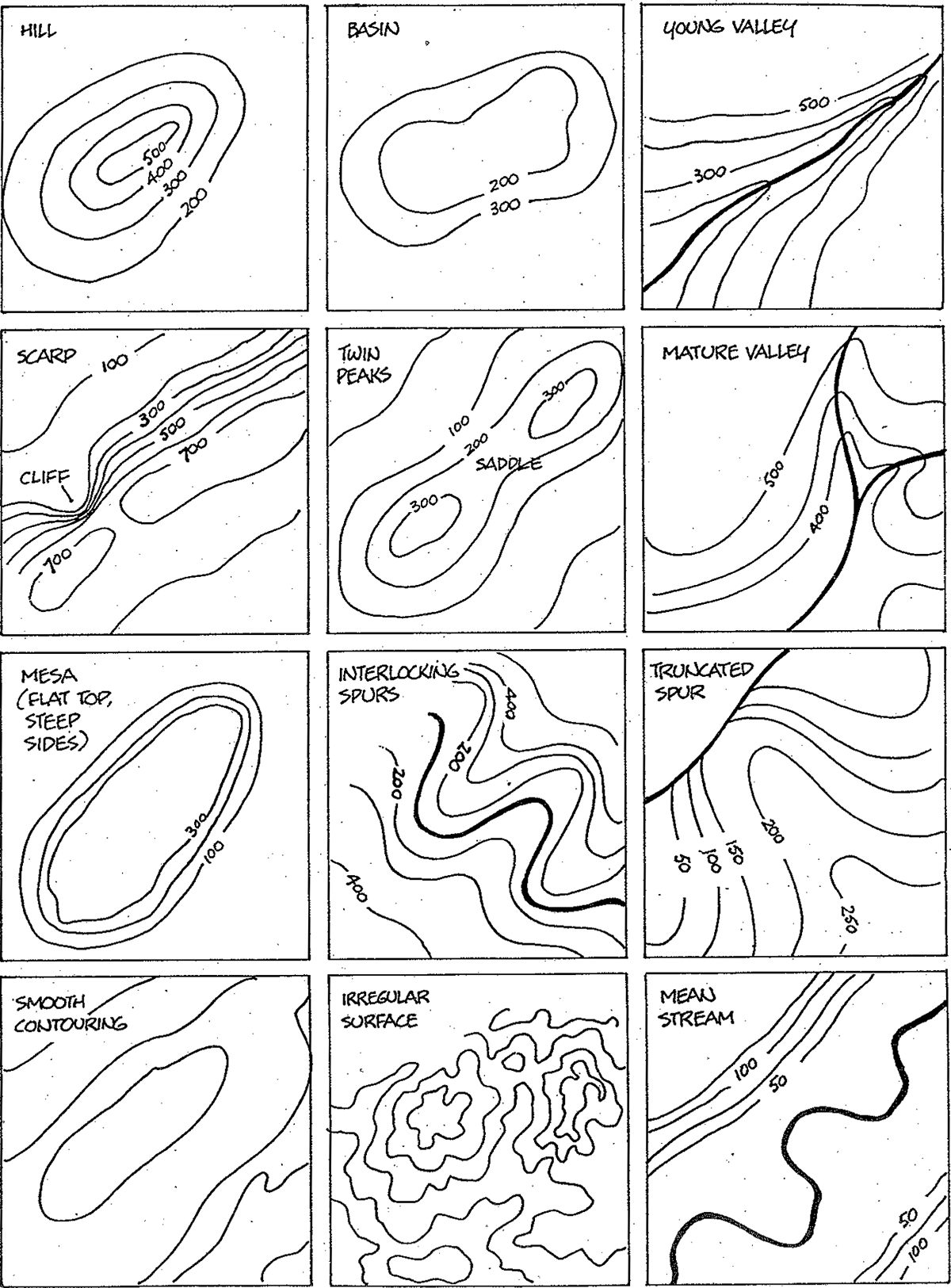
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!