Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography 3D Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography 3D Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography 3D Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography 3D Maps

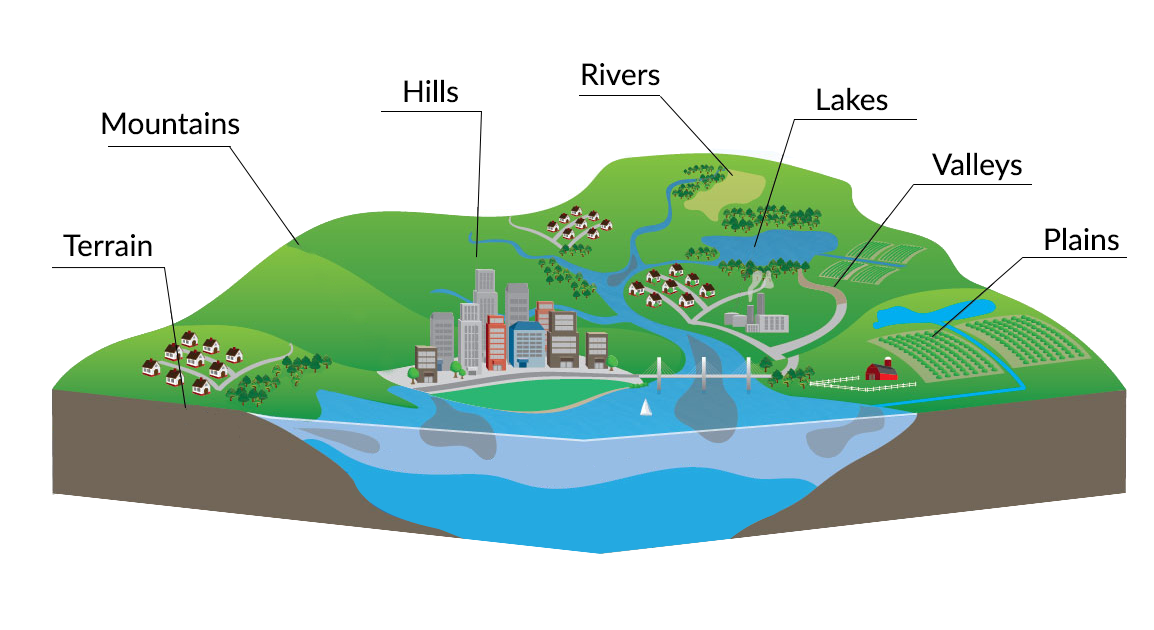
The Earth’s surface is a tapestry of intricate details, from towering mountains to sprawling valleys, winding rivers to vast plains. Understanding this intricate landscape is crucial for a myriad of applications, ranging from urban planning and infrastructure development to disaster preparedness and scientific research. Traditional two-dimensional maps have long served as the primary tools for representing this information, but the advent of three-dimensional (3D) mapping technology has revolutionized our ability to visualize and interact with the Earth’s topography.
Delving into the Realm of 3D Topography
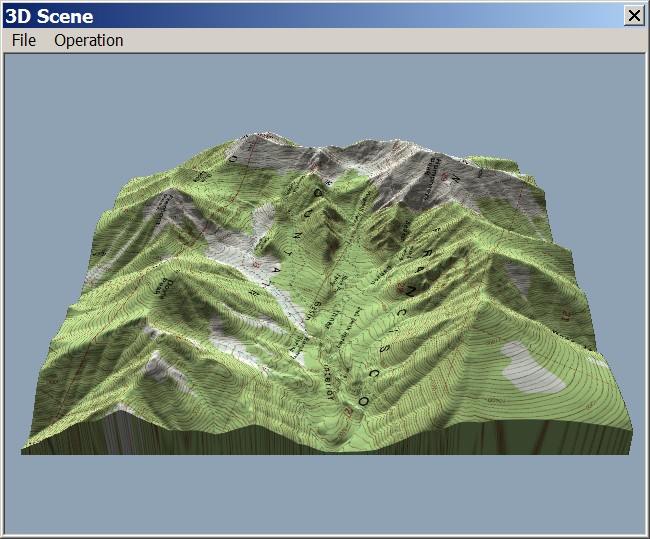
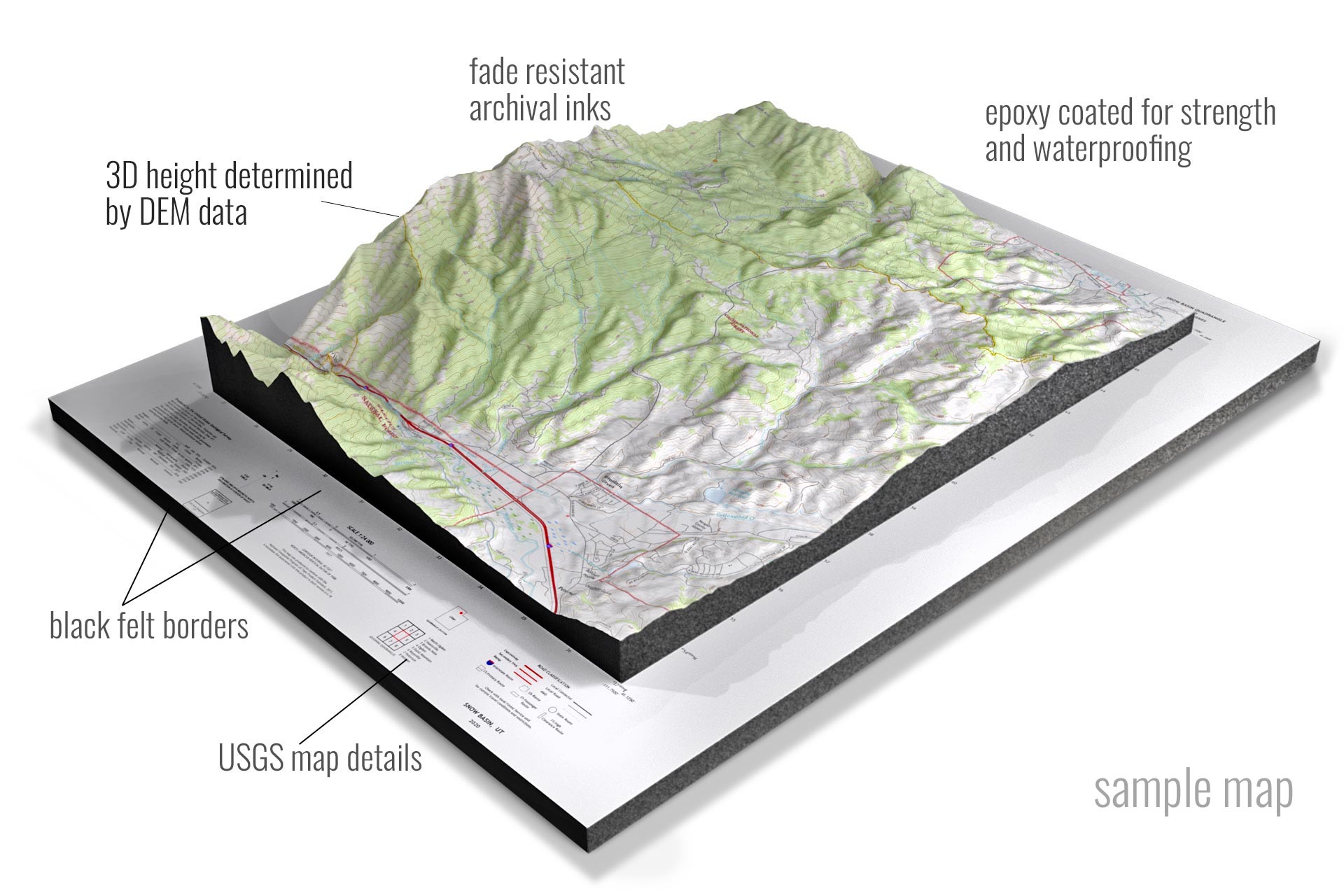
A topography 3D map, also known as a digital terrain model (DTM), is a digital representation of the Earth’s surface, capturing its elevation and other spatial characteristics. Unlike traditional maps that offer a flat, two-dimensional perspective, 3D maps provide a realistic and immersive representation of the landscape, allowing users to explore and analyze terrain features with unparalleled depth and detail.
The Building Blocks of 3D Topography
Creating a 3D topography map involves a multi-step process that leverages various data sources and technologies:
-
Data Acquisition: The foundation of any 3D map lies in acquiring accurate and comprehensive data about the Earth’s surface. This data can be gathered through various methods, including:
- Aerial Photography: High-resolution aerial images captured from aircraft or drones provide a detailed overview of the terrain.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with advanced sensors capture vast swaths of the Earth’s surface, offering global coverage and valuable data for 3D mapping.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR technology uses laser pulses to measure distances, generating highly precise elevation data, even in dense vegetation areas.
- Ground Surveys: Traditional ground surveys using GPS (Global Positioning System) and other surveying instruments provide accurate measurements of specific locations.
-
Data Processing: Once the data is acquired, it undergoes rigorous processing and analysis to create a 3D representation of the terrain. This involves:
- Georeferencing: Aligning the collected data with geographic coordinates to ensure accurate spatial positioning.
- Interpolation: Filling in gaps in the data using algorithms that estimate elevation values based on surrounding data points.
- Model Creation: Generating a 3D model of the terrain using specialized software that interprets the processed data.
Unveiling the Benefits of 3D Topography Maps
The ability to visualize and interact with the Earth’s topography in three dimensions offers a wealth of benefits across various fields:
-
Urban Planning and Development: 3D maps provide valuable insights into the terrain, helping urban planners assess site suitability for development, optimize infrastructure layouts, and minimize environmental impact.
-
Infrastructure Development: From road and railway construction to bridge design, 3D maps assist engineers in planning and implementing infrastructure projects efficiently, minimizing risks and optimizing resource allocation.
-
Disaster Management: 3D topography maps play a crucial role in disaster preparedness and response. They enable accurate flood modeling, landslide risk assessment, and evacuation route planning, saving lives and minimizing damage.
-
Environmental Monitoring: 3D maps are essential for monitoring environmental changes, such as deforestation, erosion, and pollution, aiding in conservation efforts and sustainable resource management.
-
Scientific Research: Geologists, geographers, and other researchers use 3D maps to analyze geological formations, study climate change impacts, and understand complex ecological processes.
-
Military and Defense: 3D maps provide critical information for military operations, supporting terrain analysis, target identification, and mission planning.
Navigating the Landscape of 3D Topography: FAQs
1. What are the different types of 3D topography maps?
- Digital Terrain Models (DTMs): Represent the bare Earth’s surface, excluding vegetation and structures.
- Digital Surface Models (DSMs): Include all features, such as buildings, trees, and other objects, providing a complete representation of the surface.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): Focus solely on elevation data, providing a simplified representation of the terrain.
2. What are the key software tools used for creating and visualizing 3D topography maps?
- ArcGIS Pro: A comprehensive Geographic Information System (GIS) software that offers powerful tools for creating and analyzing 3D maps.
- QGIS: An open-source GIS platform with extensive 3D mapping capabilities.
- Blender: A free and open-source 3D modeling software that can be used for creating and visualizing 3D maps.
- Google Earth: A popular online platform that provides access to global 3D terrain models and satellite imagery.
3. What are the limitations of 3D topography maps?
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of a 3D map depends on the quality and resolution of the source data. Inaccuracies in the data can lead to errors in the 3D model.
- Data Availability: Not all areas of the world have readily available high-resolution data for 3D mapping.
- Computational Requirements: Creating and processing large 3D models can require significant computational resources and specialized hardware.
4. How are 3D topography maps used in everyday life?
- Navigation Apps: Many navigation apps use 3D terrain data to provide more realistic and accurate route guidance.
- Virtual Reality Experiences: 3D topography maps are used to create immersive virtual reality environments for gaming, training, and exploration.
- Online Maps: Many online mapping platforms, such as Google Maps, offer 3D views of various locations, enhancing user experience.
5. What are the future trends in 3D topography mapping?
- Increased Data Resolution: Advancements in sensor technology and data processing techniques are leading to higher-resolution 3D maps, providing even greater detail and accuracy.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are being used to automate data processing, improve model accuracy, and extract valuable insights from 3D maps.
- Real-time Updates: Real-time data acquisition and processing technologies are enabling the creation of dynamic 3D maps that reflect changing terrain conditions.
Tips for Effective Use of 3D Topography Maps
- Choose the Right Software: Select software that meets your specific needs and offers the necessary tools for creating, visualizing, and analyzing 3D maps.
- Understand Data Sources: Be aware of the source and quality of the data used to create the 3D map, as this will affect the accuracy and reliability of the model.
- Explore Visualization Options: Experiment with different visualization techniques, such as color-coding, transparency, and lighting effects, to effectively communicate terrain features and patterns.
- Use 3D Maps in Conjunction with Other Data: Combine 3D maps with other data sources, such as aerial photographs, satellite imagery, and environmental data, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Stay Updated with New Technologies: Keep abreast of advancements in 3D mapping technologies, data acquisition methods, and software tools to enhance your capabilities.
Conclusion
3D topography maps have emerged as indispensable tools for visualizing and understanding the Earth’s surface. They provide a powerful means to analyze terrain features, plan infrastructure projects, assess environmental impacts, and support scientific research. As technology continues to evolve, 3D mapping will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world around us, driving innovation, and addressing the challenges of a changing planet.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography 3D Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!