Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
Topography maps are invaluable tools for understanding and representing the Earth’s surface, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s elevation, features, and spatial relationships. These maps are essential for a multitude of applications, ranging from navigation and urban planning to environmental studies and disaster preparedness. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of topography maps, exploring their creation, interpretation, and diverse applications.
The Essence of Topography Maps:
Topography maps, also known as topographic maps, are graphical representations of the Earth’s surface, meticulously depicting the elevation and shape of the land. Unlike traditional maps that prioritize political boundaries and geographical features, topography maps prioritize the physical characteristics of the terrain. This is achieved through the use of contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation, effectively illustrating the terrain’s undulations and slopes.
Key Elements of a Topography Map:
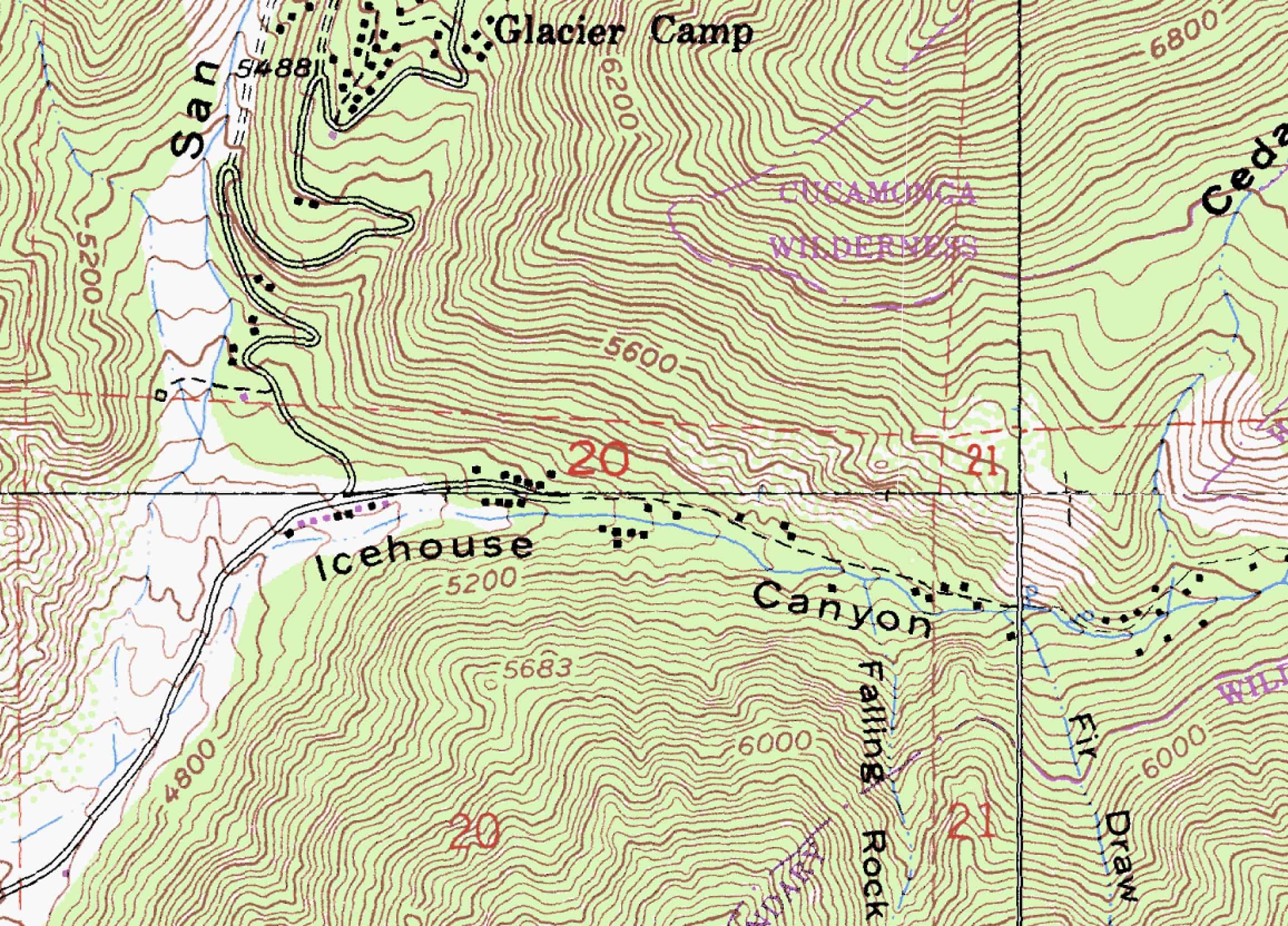
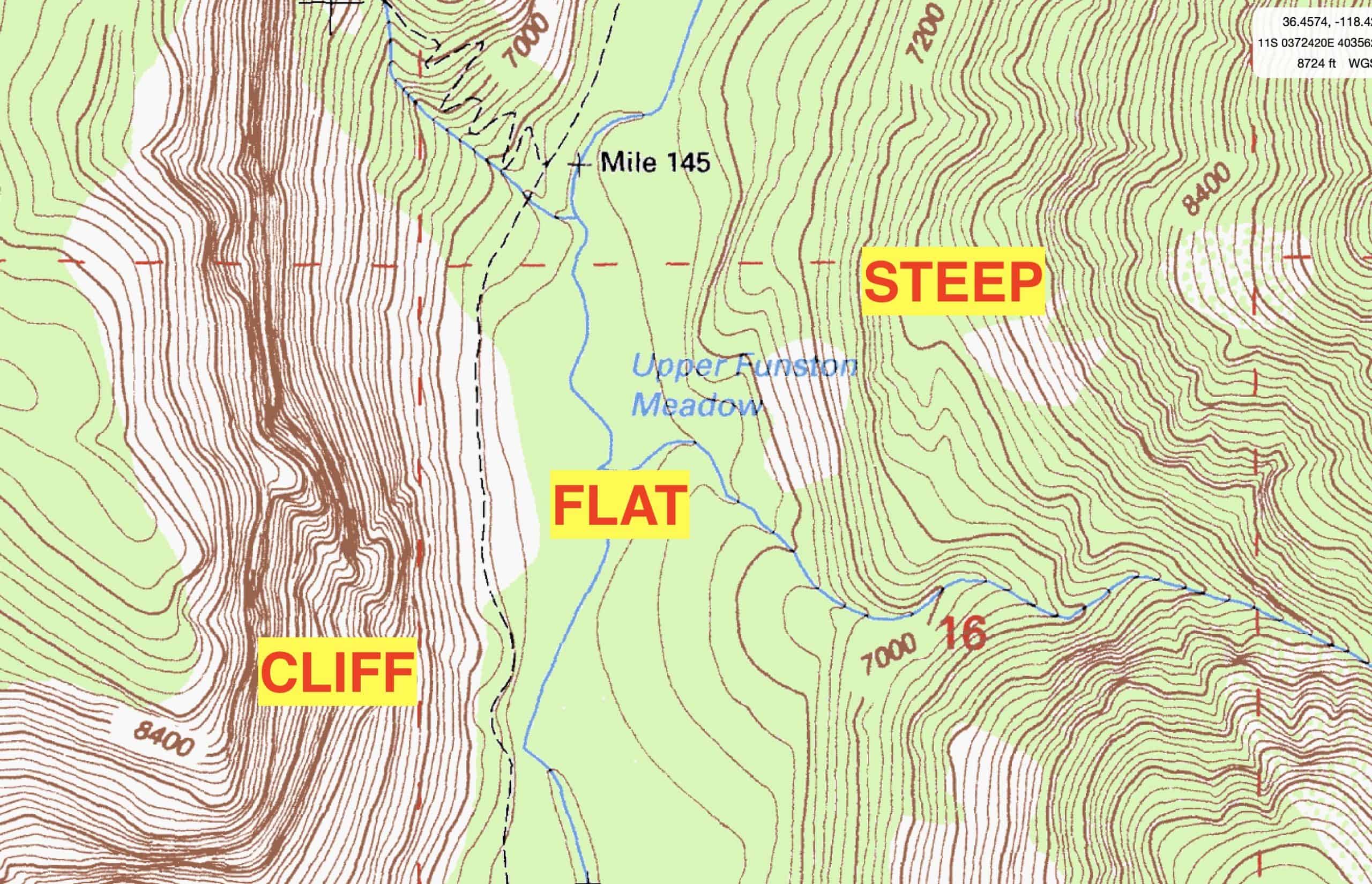
- Contour Lines: These lines are the foundation of topography maps, forming a network of interconnected curves that represent points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the terrain, while wider spacing indicates a gentler slope.
- Elevation: Each contour line is associated with a specific elevation value, typically expressed in feet or meters. This allows for accurate determination of the height of any point on the map.
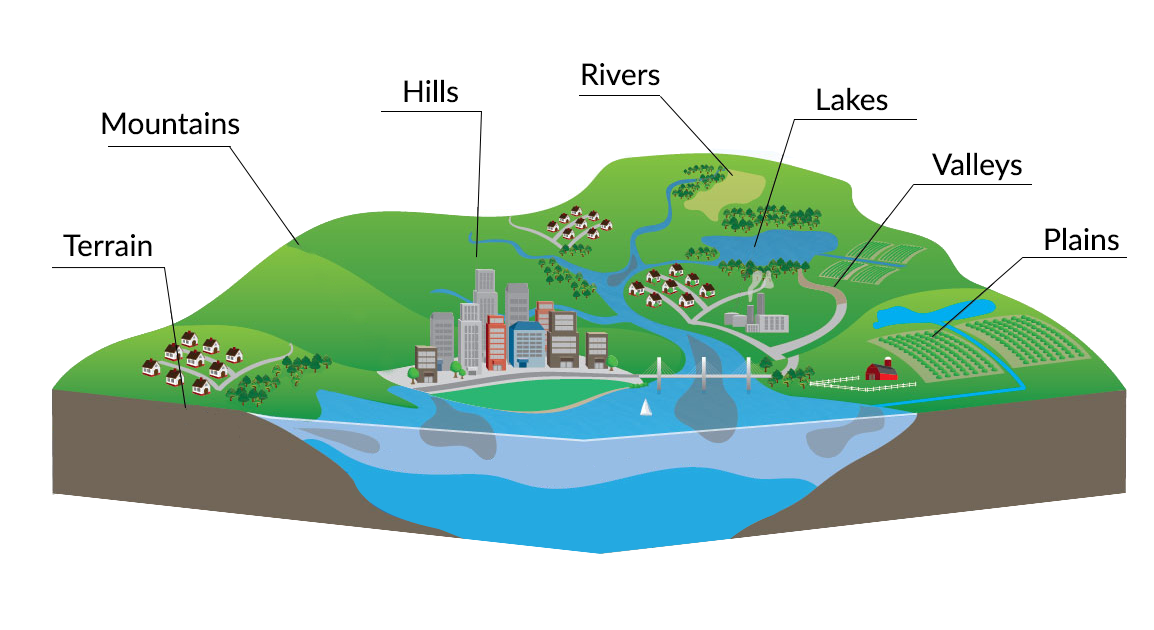
- Relief: The overall shape and form of the terrain, as represented by the arrangement and density of contour lines, is known as relief. It provides a visual understanding of the landscape’s features, including hills, valleys, plateaus, and depressions.
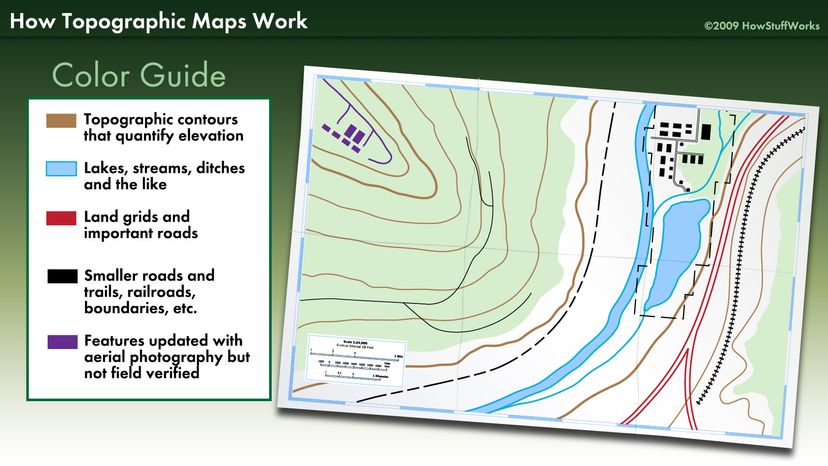
- Symbols and Legends: Topography maps employ a variety of symbols and legends to depict various features, such as roads, rivers, buildings, and vegetation. This information enhances the map’s utility by providing context and aiding in understanding the surrounding environment.
The Creation of Topography Maps:
The creation of topography maps involves a meticulous process that combines advanced surveying techniques and data processing. The primary method for acquiring elevation data is through surveying, which utilizes instruments like GPS receivers and total stations to determine precise coordinates and elevations.
In recent years, remote sensing techniques, such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and aerial photography, have revolutionized topography mapping. These technologies allow for rapid and efficient data acquisition, resulting in highly detailed and accurate maps.
Interpreting Topography Maps:
Understanding topography maps requires familiarity with the conventions and symbols employed. By analyzing the contour lines, one can discern the elevation changes, identify peaks and valleys, and visualize the overall terrain profile.
- Contour Intervals: The difference in elevation between adjacent contour lines is known as the contour interval. Understanding this interval is crucial for accurately interpreting the map’s scale and elevation changes.
- Slope: The steepness of a slope can be inferred by the spacing of contour lines. Closer lines indicate a steeper slope, while wider spacing suggests a gentler incline.
- Landforms: The arrangement of contour lines provides valuable insights into the presence of various landforms, such as hills, valleys, plateaus, and depressions.
Applications of Topography Maps:
Topography maps play a crucial role in a wide range of disciplines and applications, including:
- Navigation: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on topography maps to navigate challenging terrains, identify trails, and plan routes.
- Urban Planning: City planners utilize topography maps to analyze the feasibility of development projects, assess potential hazards, and optimize infrastructure placement.
- Engineering: Civil engineers rely on topography maps for designing roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects, ensuring proper alignment and stability.
- Environmental Studies: Ecologists and environmental scientists use topography maps to understand the distribution of plant and animal life, analyze watersheds, and assess the impact of environmental changes.
- Disaster Preparedness: Emergency responders utilize topography maps to assess the potential impact of natural disasters, plan evacuation routes, and coordinate relief efforts.
- Military Operations: The military relies on topography maps for strategic planning, navigation, and target identification in diverse terrains.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A: A topographic map focuses on the physical characteristics of the terrain, using contour lines to depict elevation changes. Regular maps prioritize political boundaries, geographical features, and human-made structures.
Q: How are contour lines used to represent elevation?
A: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, creating a network of curves that illustrate the terrain’s undulations. The closer the lines, the steeper the slope; wider spacing indicates a gentler incline.
Q: What are some common symbols used on topography maps?
A: Topography maps employ a variety of symbols to represent features like roads, rivers, buildings, and vegetation. These symbols are typically explained in a legend accompanying the map.
Q: How can I find a topography map for a specific area?
A: Topography maps are available from various sources, including government agencies like the USGS (United States Geological Survey), online mapping platforms, and specialized map stores.
Tips for Using Topography Maps:
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s scale and contour interval.
- Pay attention to the legend and symbols used.
- Use a compass and ruler for accurate navigation.
- Consider the terrain’s features and potential hazards.
- Practice interpreting contour lines and identifying landforms.
Conclusion:
Topography maps serve as indispensable tools for understanding and representing the Earth’s surface. They provide a visual representation of the terrain’s elevation, features, and spatial relationships, facilitating navigation, urban planning, environmental studies, and disaster preparedness. By understanding the principles of contour lines, symbols, and legends, individuals can effectively interpret and utilize topography maps for a wide range of applications. The comprehensive nature of topography maps makes them essential for informed decision-making in various fields, ensuring a deeper understanding of the physical landscape and its complexities.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!