Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
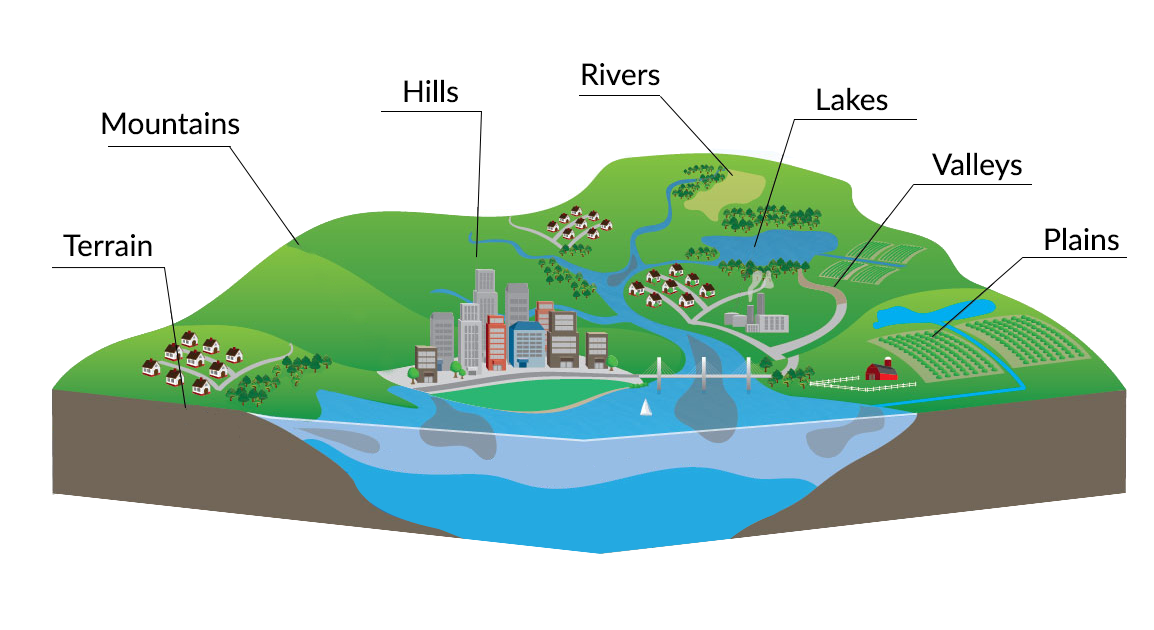
Topography, the study of the Earth’s surface features, plays a crucial role in understanding our planet’s physical characteristics. This field encompasses the analysis of elevation, relief, and the arrangement of natural and man-made elements that shape the landscape. Topography maps, specialized cartographic representations, serve as invaluable tools for visualizing and interpreting these complex features. They provide a visual language for understanding the Earth’s surface, offering insights into terrain, elevation changes, and the intricate relationship between landforms and human activities.
The Essence of Topography Maps: A Visual Language of the Earth’s Surface
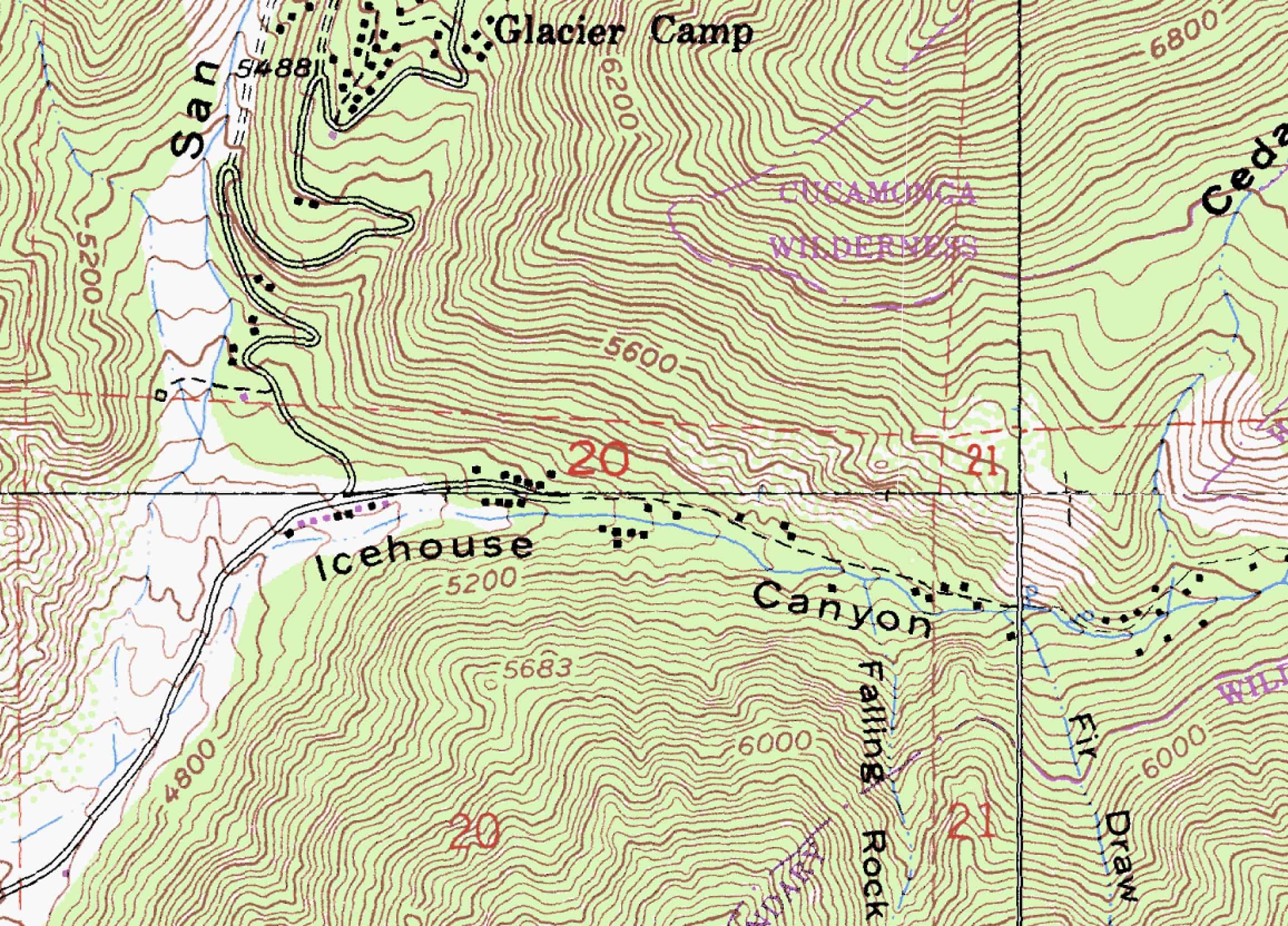
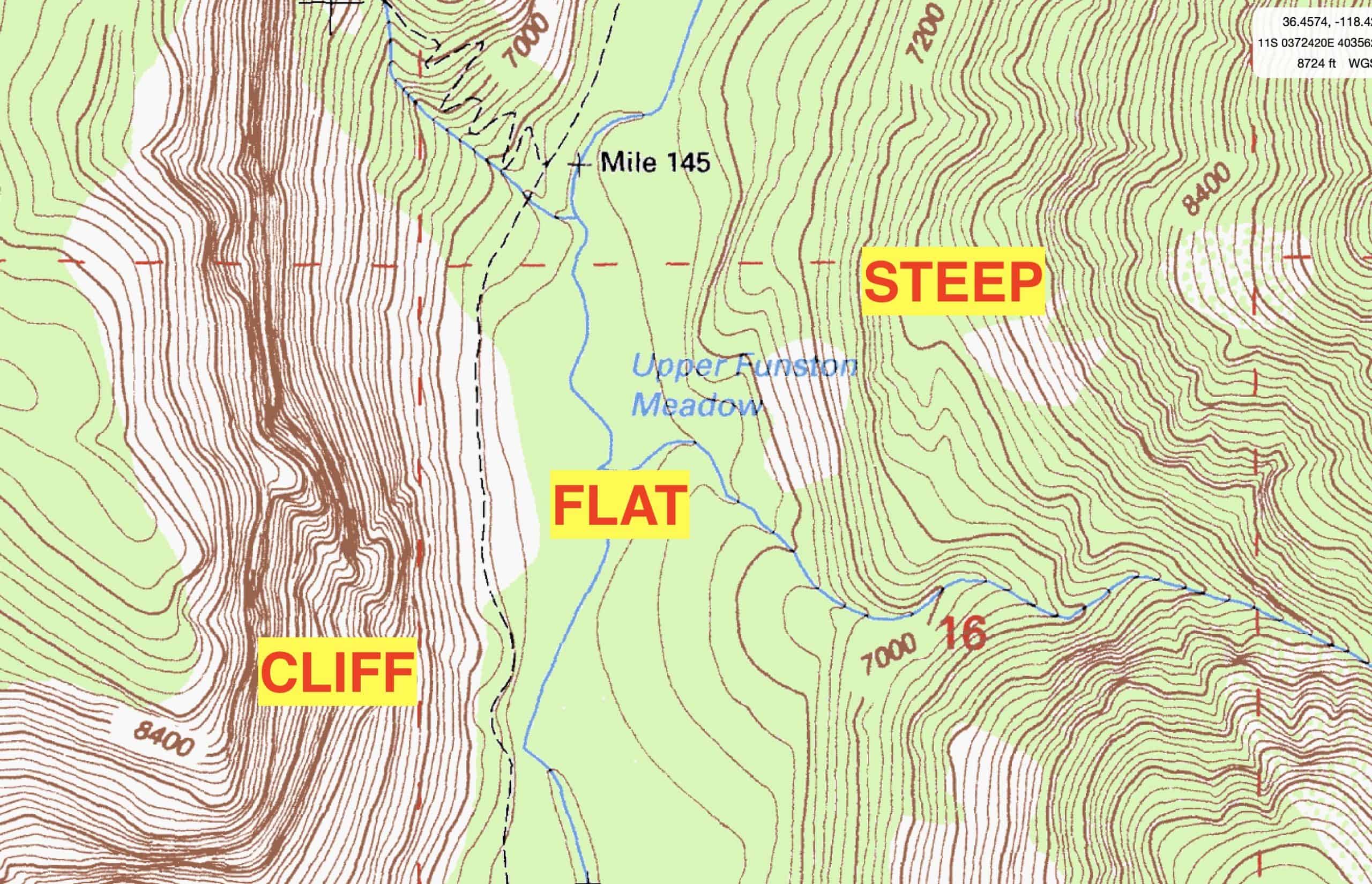
Topography maps, often referred to as topographic maps, are distinguished by their unique ability to translate three-dimensional terrain onto a two-dimensional plane. This transformation is achieved through a system of contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. By analyzing the spacing and direction of these lines, one can decipher the steepness of slopes, the location of valleys and ridges, and the overall configuration of the terrain.
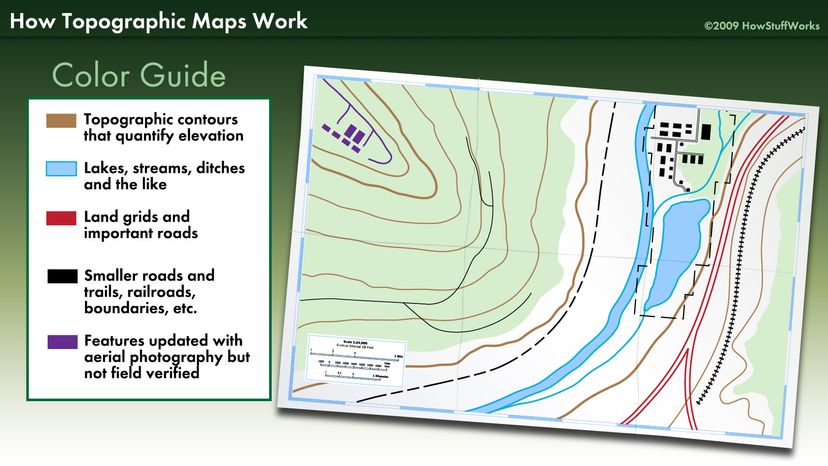
Key Elements of Topography Maps: Deciphering the Visual Language
Topography maps are a rich tapestry of information, incorporating various symbols and conventions to represent different features:
-
Contour Lines: These are the cornerstone of topography maps, depicting the shape of the land by connecting points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart, the gentler the incline.
-
Elevation: Numbers inscribed along contour lines or at specific points indicate the exact elevation above a designated datum, typically mean sea level.
-
Relief: The difference in elevation between the highest and lowest points within a given area, often depicted through shading or hachures, provides a visual representation of the terrain’s ruggedness or flatness.
-
Hydrography: Blue lines represent rivers, streams, and lakes, conveying information about drainage patterns and water bodies.
-
Cultural Features: Roads, buildings, bridges, and other man-made structures are depicted with specific symbols, highlighting the interaction between human activity and the natural landscape.
-
Vegetation: Symbols represent forests, grasslands, and other types of vegetation, offering insights into the ecological diversity of the area.
Beyond the Basics: Unveiling the Applications of Topography Maps
Topography maps are far more than static representations of the Earth’s surface; they are dynamic tools with a wide array of applications across various fields:
-
Land Management and Planning: Topography maps are essential for land use planning, ensuring that development projects are located in suitable areas, minimizing environmental impact, and maximizing resource utilization.
-
Civil Engineering and Construction: These maps provide crucial data for infrastructure projects, enabling engineers to assess terrain conditions, determine optimal routes for roads and pipelines, and design structures that accommodate the topography.
-
Environmental Studies: Topography maps are indispensable for understanding natural processes, such as erosion, sedimentation, and water flow, allowing researchers to analyze environmental changes and predict future trends.
-
Military Operations: Topography maps play a critical role in military planning and execution, providing information on terrain features, potential obstacles, and optimal routes for troop movements and operations.
-
Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on topography maps for navigation, identifying trails, assessing terrain difficulty, and planning safe and enjoyable excursions.
-
Scientific Research: Topography maps are invaluable for studying geological formations, understanding tectonic activity, and analyzing the distribution of natural resources.
The Evolution of Topography Maps: From Paper to Digital
Traditionally, topography maps were printed on paper, requiring specialized skills to interpret and utilize. However, advancements in technology have ushered in a new era of digital topography maps, offering unparalleled flexibility and accessibility:
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software integrates topography data with other spatial information, enabling users to analyze complex relationships between different layers of data, such as elevation, land use, and population density.
-
Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These three-dimensional representations of the Earth’s surface, derived from satellite imagery and aerial surveys, provide highly detailed and accurate topographic information, accessible through various platforms.
-
Online Mapping Services: Websites and mobile applications offer interactive topography maps, allowing users to zoom in and out, explore specific areas, and access real-time data updates.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Topography Maps
Q: How are topography maps created?
A: Topography maps are created through a combination of field surveys, aerial photography, and satellite imagery. Surveyors use specialized instruments to measure elevation and distances, while aerial photographs and satellite images capture the landscape from above. These data are then processed and integrated to generate a detailed topographic map.
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a contour map?
A: The terms "topographic map" and "contour map" are often used interchangeably. However, technically, a contour map specifically refers to the representation of elevation using contour lines, while a topographic map encompasses a broader range of information, including cultural features, vegetation, and other details.
Q: What are the benefits of using digital topography maps over traditional paper maps?
A: Digital topography maps offer several advantages over their paper counterparts:
- Accessibility: Digital maps are readily available online and on mobile devices, eliminating the need for physical copies.
- Interactivity: Users can zoom in and out, rotate the map, and access additional layers of information, providing a more immersive and customizable experience.
- Real-time updates: Digital maps can be updated with real-time data, ensuring accuracy and relevance.
- Integration with other data: Digital maps can be integrated with other spatial information, such as weather data, population density, and land use, enabling comprehensive analysis and decision-making.
Q: How can I learn to read and interpret topography maps?
A: Learning to read and interpret topography maps requires practice and familiarity with the symbols and conventions used. There are numerous online resources, textbooks, and workshops available to guide individuals in developing their topographic map reading skills.
Tips for Effective Utilization of Topography Maps
- Understanding Scale: Pay attention to the map’s scale to accurately determine distances and elevation changes.
- Analyzing Contour Lines: Observe the spacing and direction of contour lines to interpret the steepness of slopes and the location of valleys and ridges.
- Interpreting Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used to represent different features, such as roads, buildings, and vegetation.
- Utilizing Multiple Sources: Combine topography maps with other sources of information, such as aerial photographs and satellite imagery, for a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Regularly practice reading and interpreting topography maps to enhance your skills and develop a deeper understanding of terrain features.
Conclusion: A Window into the Earth’s Surface
Topography maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding the Earth’s surface, revealing its intricate features and complex relationships between landforms and human activities. By providing a visual language for interpreting terrain, elevation changes, and other key characteristics, topography maps empower individuals and organizations across various fields to make informed decisions, plan effectively, and navigate the landscape with confidence. As technology continues to advance, the evolution of digital topography maps promises even greater accessibility, interactivity, and analytical capabilities, further enhancing our ability to explore and understand the Earth’s surface.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!