Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Survey Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Survey Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Survey Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Survey Maps

The world around us, with its intricate variations in elevation, slopes, and landforms, holds a wealth of information crucial for numerous endeavors. Understanding this complex landscape is the domain of topography, and its visual representation, the topography survey map, serves as a vital tool for diverse disciplines. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of topography survey maps, exploring their creation, interpretation, applications, and significance in shaping our understanding and interaction with the environment.
Defining the Landscape: The Essence of Topography
Topography, derived from the Greek words "topos" (place) and "graphein" (to write), essentially translates to "describing a place." It encompasses the study and depiction of the Earth’s surface, focusing on its three-dimensional form, including elevation, slopes, natural features like hills, valleys, and water bodies, and man-made structures. This detailed understanding of the terrain is crucial for various fields, from civil engineering to urban planning, environmental management, and even military operations.
Mapping the Terrain: The Role of Topography Survey Maps
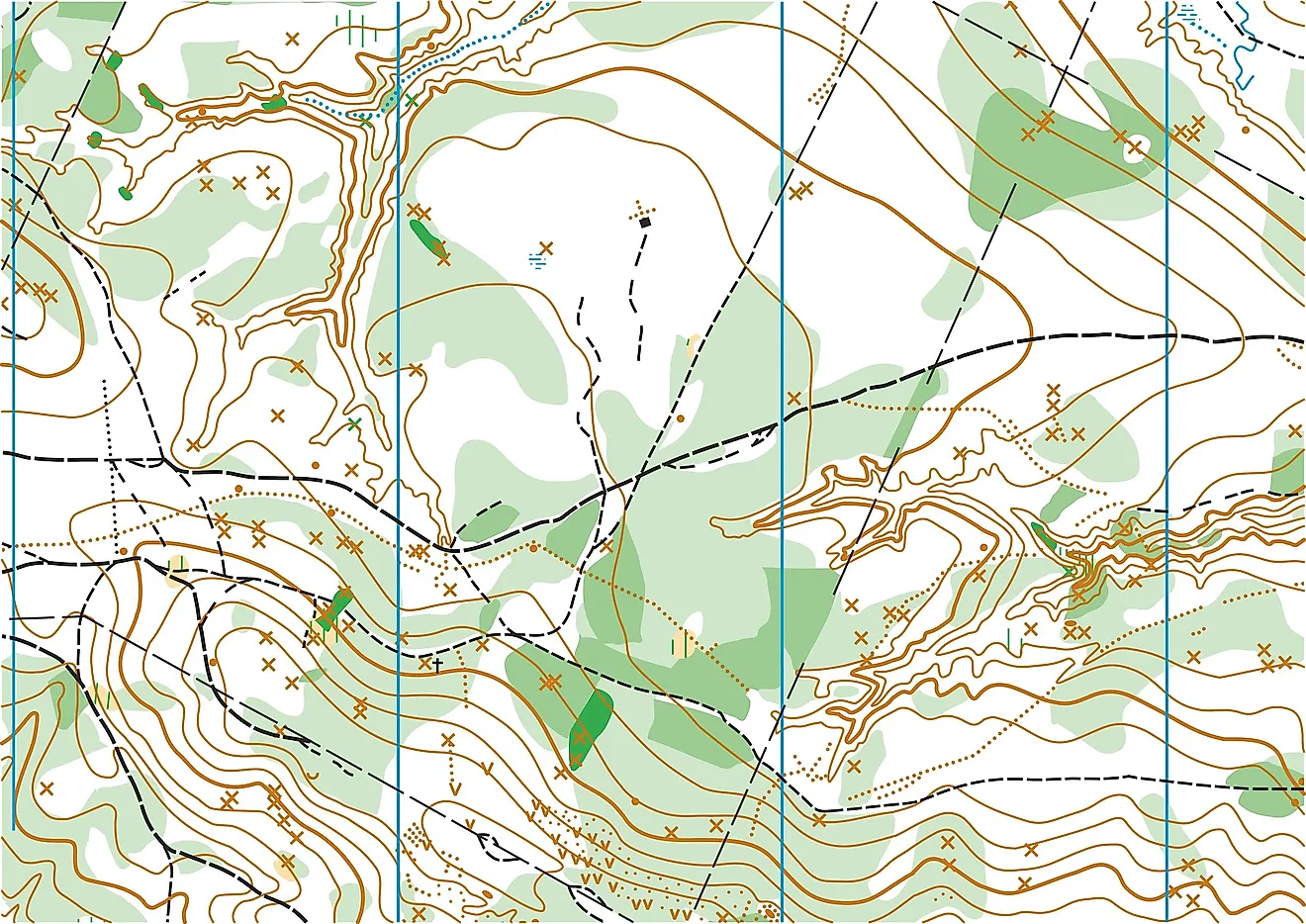
Topography survey maps, also known as topographic maps, serve as visual representations of the terrain, capturing the intricate details of the landscape. These maps are not mere depictions of land boundaries; they are meticulously crafted documents that provide a comprehensive overview of the Earth’s surface, incorporating a range of information vital for decision-making in various fields.
The Foundation of Accuracy: Surveying Techniques
The creation of topography survey maps relies on precise surveying techniques, employing advanced instruments and methodologies to collect data about the terrain. Traditional methods like leveling and triangulation, involving the use of theodolites, levels, and other surveying equipment, are still widely employed, particularly for large-scale projects. However, modern techniques like GPS (Global Positioning System) and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) have revolutionized the process, offering faster, more efficient, and highly accurate data acquisition.
Decoding the Map: Understanding the Elements
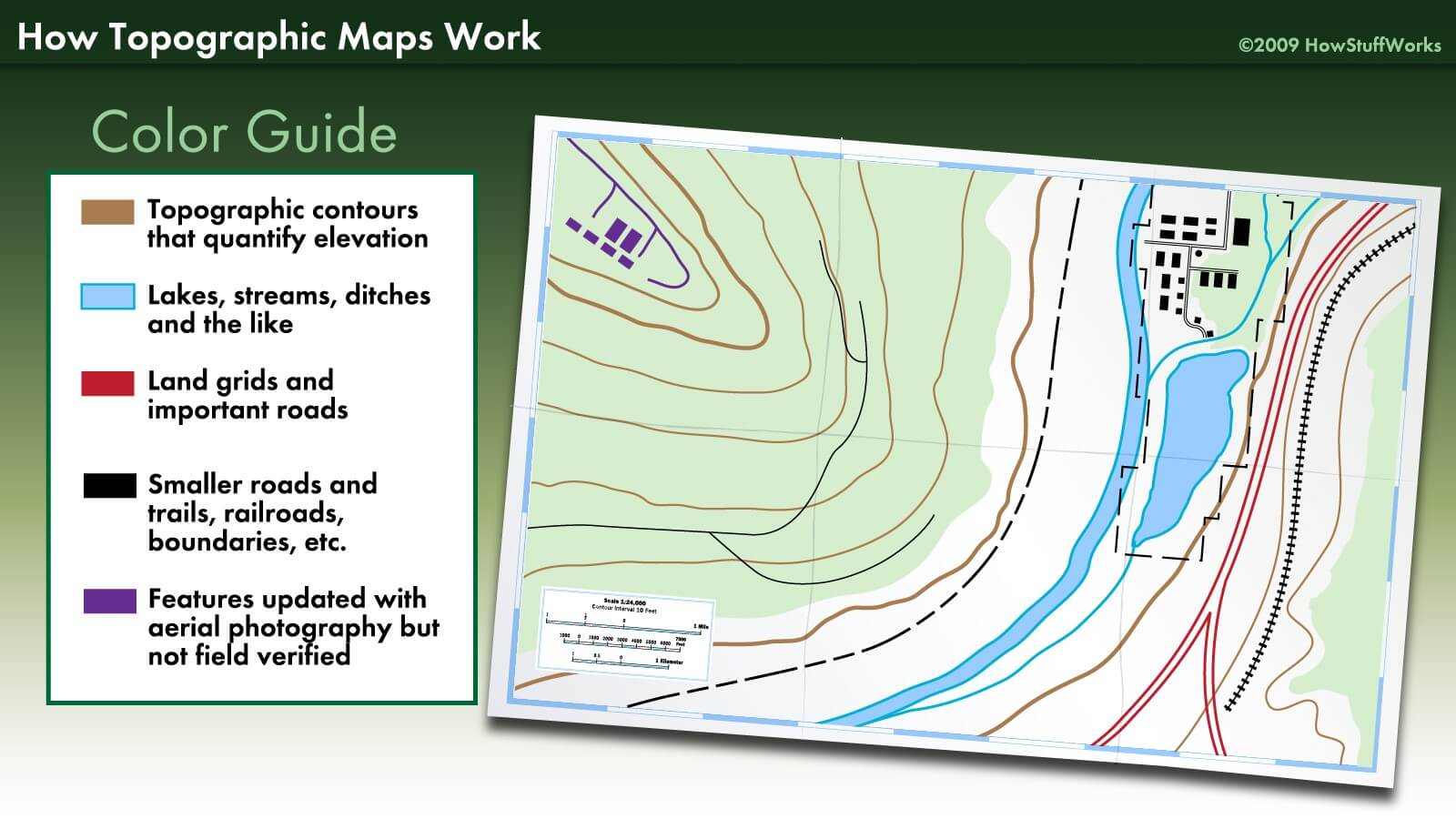
Topography survey maps are characterized by their intricate symbology, designed to convey a wealth of information in a concise and visually appealing manner. Key elements include:
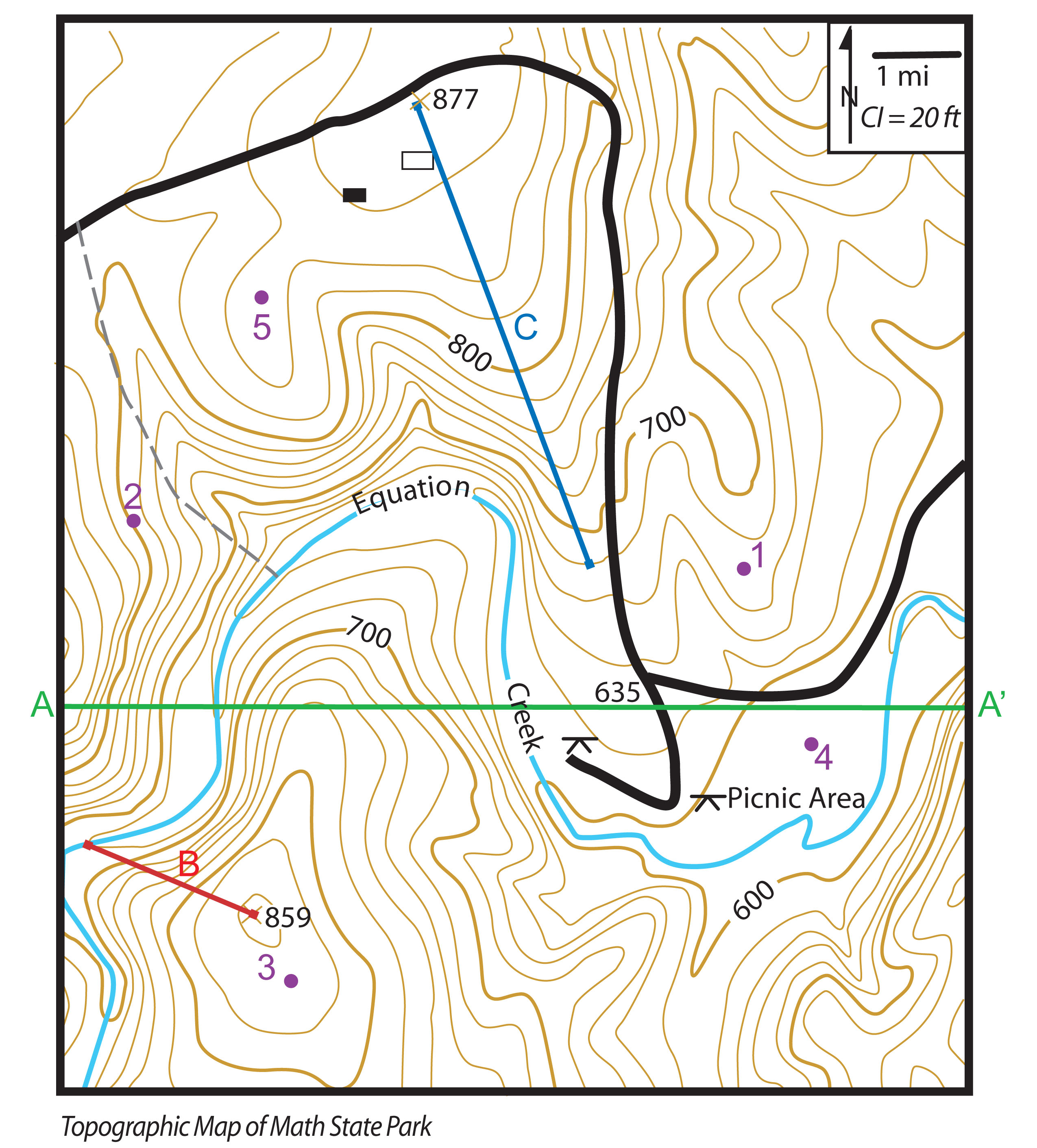
- Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s slope and shape. Contour lines closer together indicate steeper slopes, while lines spaced further apart represent gentler slopes.
- Elevation Points: These points, often marked with a numerical value, represent specific elevations on the map, providing precise height references.
- Relief Shading: This technique utilizes shading to visually enhance the terrain’s three-dimensional form, highlighting hills, valleys, and other landforms.
- Symbols: A diverse range of symbols represent various features, including roads, buildings, vegetation, water bodies, and other man-made or natural elements.
- Scale: The scale of the map indicates the relationship between distances on the map and corresponding distances on the ground. This crucial element ensures accurate representation and interpretation of the terrain.
Applications: A Spectrum of Possibilities
Topography survey maps are indispensable tools across diverse fields, playing a crucial role in:
- Civil Engineering: Planning and designing roads, bridges, dams, and other infrastructure projects require accurate topographic data to ensure stability, functionality, and environmental compatibility.
- Urban Planning: Understanding the topography is essential for urban development, enabling efficient land use, minimizing environmental impact, and optimizing infrastructure placement.
- Environmental Management: Topography maps are vital for studying and managing natural resources, identifying potential hazards like landslides and floods, and planning conservation efforts.
- Military Operations: Military strategists rely heavily on topography maps for planning troop movements, identifying strategic locations, and understanding the terrain’s influence on operations.
- Geological Studies: Geologists utilize topography maps to analyze geological formations, identify fault lines, and study the distribution of mineral resources.
- Agriculture: Understanding the topography is crucial for efficient irrigation, soil management, and optimizing crop production in various terrains.
- Recreation and Tourism: Topography maps are essential for hikers, campers, and outdoor enthusiasts, providing valuable information about trails, elevation changes, and potential hazards.
Unveiling the Benefits: A Closer Look at the Value
The importance of topography survey maps stems from their ability to provide a comprehensive and accurate representation of the terrain, enabling informed decision-making across various fields. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Planning and Design: Topography maps provide a detailed understanding of the terrain, allowing for accurate planning and design of infrastructure projects, urban development schemes, and other endeavors.
- Improved Safety and Risk Mitigation: By identifying potential hazards like steep slopes, flood-prone areas, and landslide-susceptible zones, topography maps contribute to safer infrastructure development and minimize environmental risks.
- Efficient Resource Management: Understanding the topography enables optimal utilization of land and water resources, promoting sustainable development and minimizing environmental impact.
- Informed Decision-Making: Topography maps provide a wealth of information, empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding land use, infrastructure development, environmental management, and other critical areas.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: Topography maps serve as a common language for professionals across diverse disciplines, facilitating effective communication and collaboration during planning, development, and implementation.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a contour map?
A: A topographic map is a comprehensive representation of the terrain, incorporating contour lines, elevation points, and other symbols to depict the landscape. A contour map specifically focuses on depicting elevation changes using contour lines, representing points of equal elevation.
Q: How often are topography survey maps updated?
A: The frequency of updates depends on factors like the purpose of the map, the rate of change in the terrain, and the level of detail required. For dynamic environments with significant changes, frequent updates are necessary, while maps for static areas might require less frequent updates.
Q: What are the limitations of topography survey maps?
A: Topography maps, while valuable tools, have limitations. They represent a snapshot in time, and changes in the terrain can occur after the map is created. Additionally, the level of detail and accuracy can vary depending on the scale and surveying techniques employed.
Q: How can I access topography survey maps?
A: Topography survey maps are available from various sources, including government agencies like the United States Geological Survey (USGS), private surveying companies, and online mapping platforms.
Tips for Utilizing Topography Survey Maps Effectively
- Understand the Map’s Scale: Always check the map’s scale to accurately interpret distances and elevations.
- Study the Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on the map to understand the features represented.
- Interpret Contour Lines: Understand how contour lines depict elevation changes and slopes.
- Consider the Map’s Age: Be aware of the map’s creation date and potential changes in the terrain since then.
- Use Additional Resources: Supplement topography maps with other sources of information like aerial photographs and satellite imagery.
Conclusion: Embracing the Landscape’s Story
Topography survey maps are not merely static representations of the land; they are powerful tools that unlock a deeper understanding of the landscape, enabling informed decision-making and responsible stewardship of our environment. By embracing their intricate details, we can navigate the complexities of the terrain, plan for a sustainable future, and appreciate the intricate beauty of the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Survey Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!