Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topography Maps and Digimap
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topography Maps and Digimap
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topography Maps and Digimap. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topography Maps and Digimap
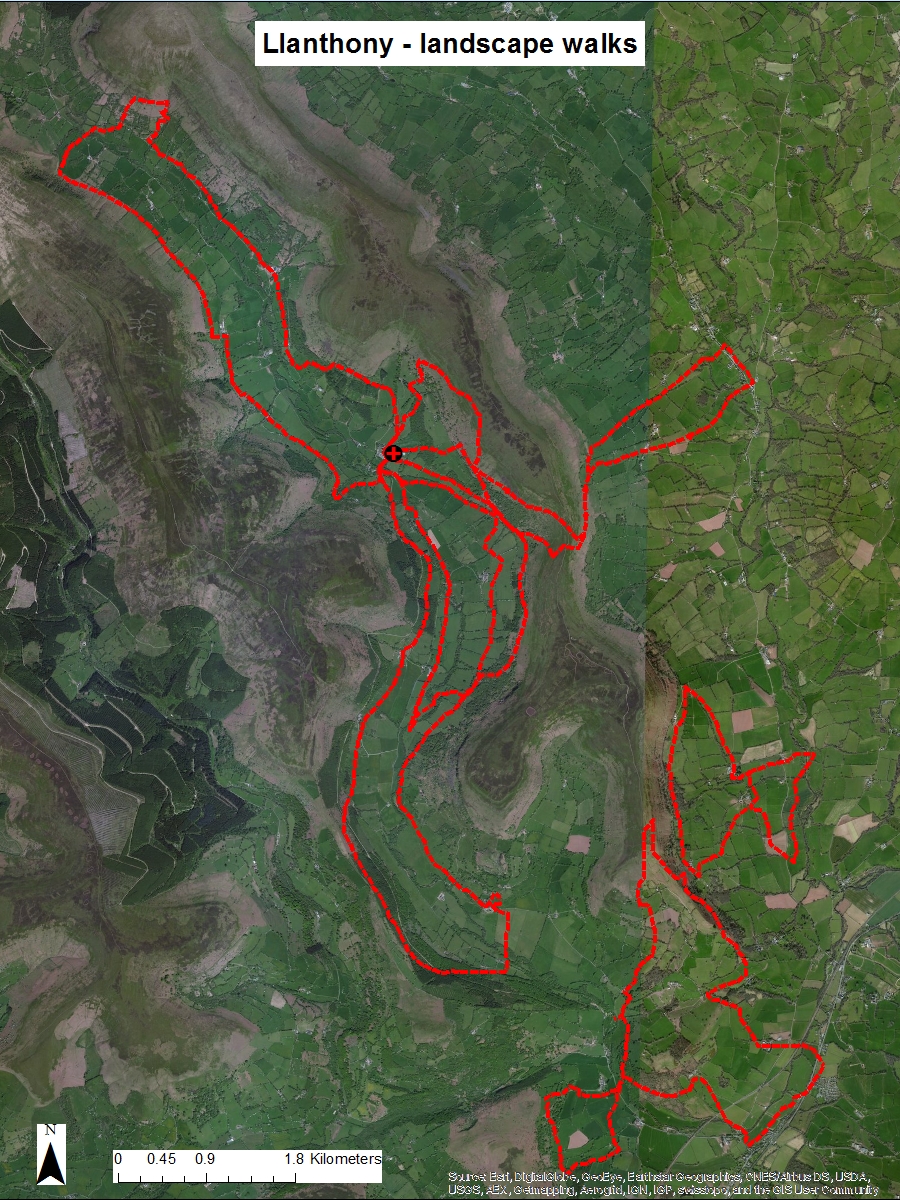
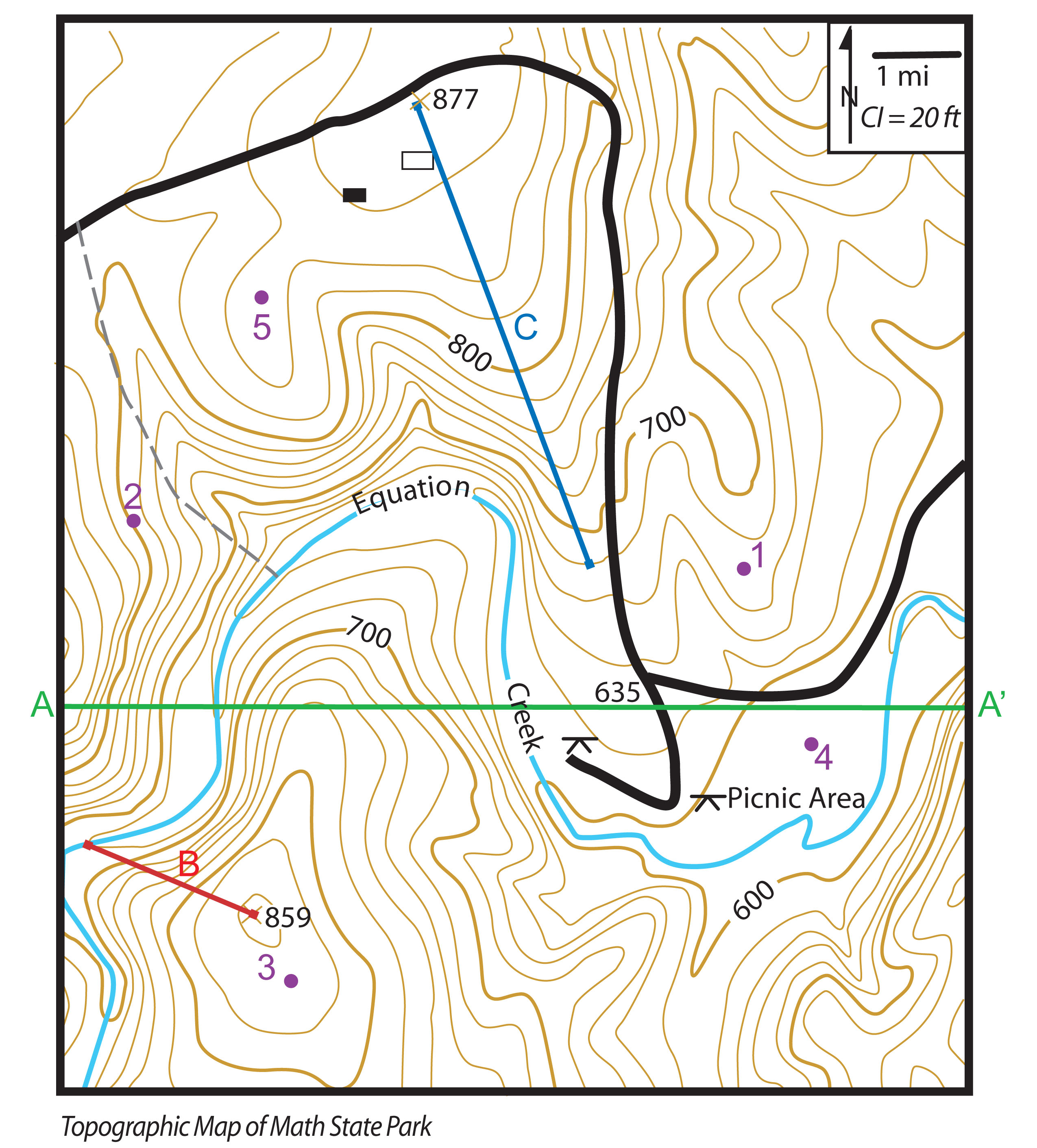
Topography maps, often referred to as topographic maps, are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, meticulously depicting its physical features and their elevations. These maps are essential tools for a wide range of disciplines, from urban planning and engineering to environmental studies and outdoor recreation. This comprehensive exploration delves into the intricacies of topography maps, highlighting the evolution of traditional maps into the digital realm with the advent of Digimap.
Understanding the Topography Map: A Window into the Earth’s Form
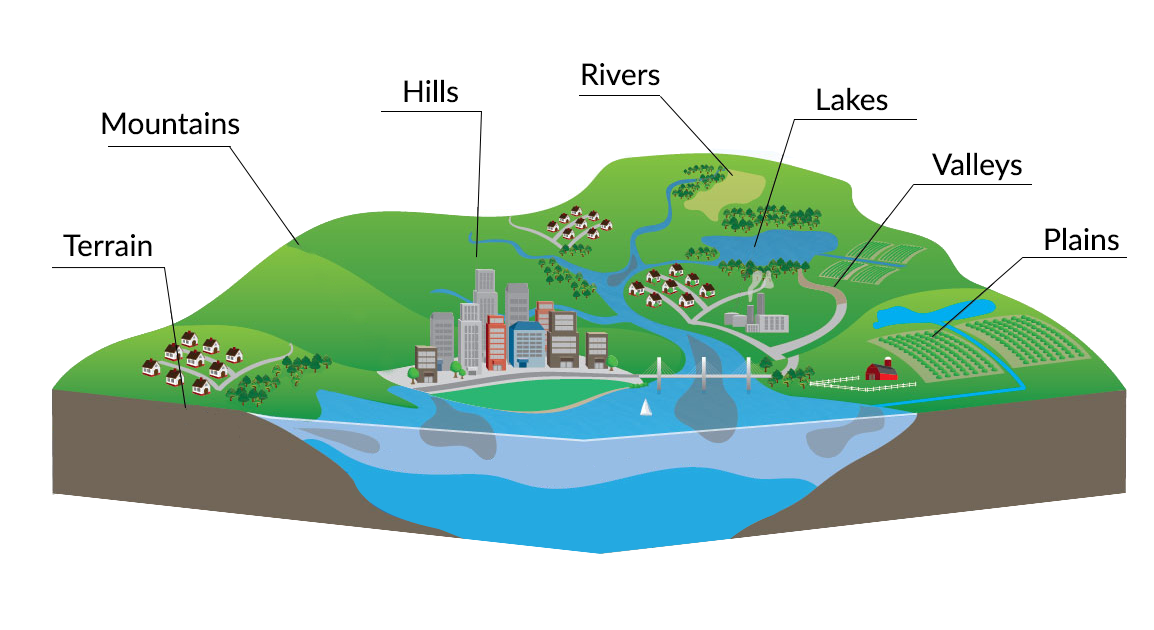
Topography maps are distinguished by their unique ability to capture the three-dimensional nature of the Earth’s surface in a two-dimensional format. This is achieved through a system of contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. These lines, akin to the level curves on a topographical map, provide a visual representation of the terrain’s undulations, slopes, and valleys.
Beyond elevation, topography maps incorporate a multitude of other features, including:
- Hydrography: Rivers, lakes, streams, and other water bodies are depicted, showcasing their courses and relationships to the surrounding landscape.
- Vegetation: Forests, grasslands, and other vegetation types are indicated, offering insights into the ecological diversity of the area.
- Cultural Features: Roads, railways, buildings, and other man-made structures are included, highlighting the human imprint on the landscape.
- Geographic Coordinates: Latitude and longitude lines are often incorporated, enabling precise location identification.
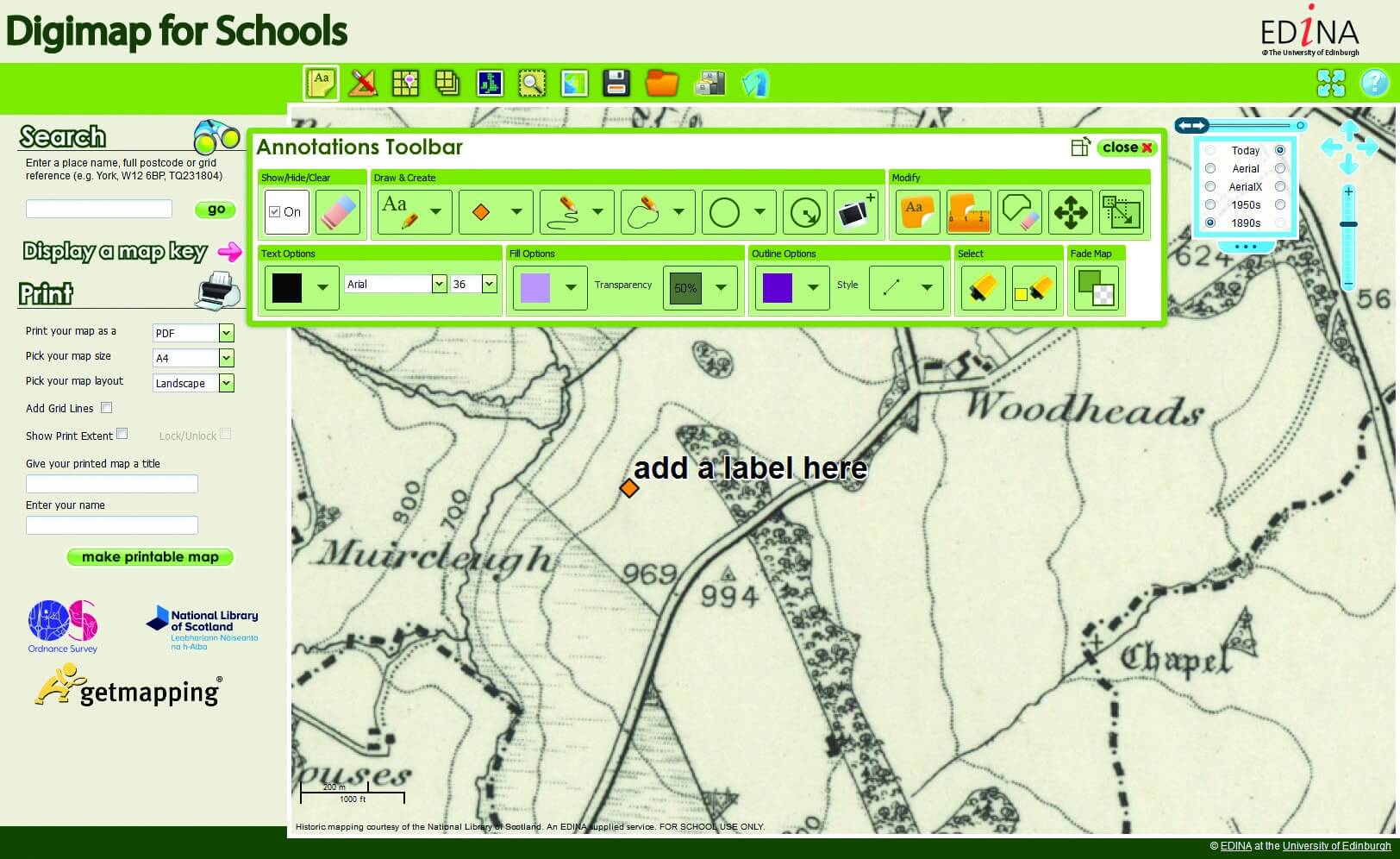
Digimap: Bridging the Gap Between Traditional Maps and Digital Technology
The advent of digital technology has revolutionized mapmaking, giving rise to Digimap, a digital platform that seamlessly integrates traditional topography maps with the power of computer technology. This integration offers numerous advantages over traditional paper maps:
- Interactive Exploration: Digimap allows users to zoom in and out, pan across the map, and access detailed information about specific features with a click of a mouse or touch of a screen.
- Data Integration: Digimap platforms often incorporate data from multiple sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and geographic information systems (GIS), creating a comprehensive and layered view of the landscape.
- Dynamic Updates: Digimap platforms are continuously updated with new data, ensuring that users have access to the most accurate and current information.
- Accessibility and Sharing: Digimap enables users to easily share maps and data with colleagues, collaborators, and the public, facilitating collaboration and knowledge dissemination.
The Significance of Topography Maps and Digimap: A Multifaceted Impact
The significance of topography maps and Digimap extends far beyond their role as mere visual representations of the Earth’s surface. They serve as vital tools for a wide range of applications, including:
- Urban Planning and Development: Topography maps provide crucial information for urban planners, enabling them to assess site suitability, plan infrastructure development, and manage environmental impacts.
- Civil Engineering and Construction: Engineers rely on topography maps to design roads, bridges, buildings, and other infrastructure projects, ensuring that these structures are appropriately aligned with the terrain.
- Environmental Studies and Conservation: Topography maps are essential for understanding the distribution of natural resources, assessing environmental hazards, and planning conservation efforts.
- Outdoor Recreation and Adventure: Hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on topography maps to navigate trails, identify points of interest, and plan their adventures safely.
- Military and Defense: Topography maps are crucial for military operations, providing essential information about terrain, obstacles, and potential enemy positions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Topography Maps and Digimap
1. How are topography maps created?
Topography maps are typically created through a process called surveying, which involves measuring the elevation of points on the Earth’s surface. This data is then used to generate contour lines, which depict the terrain’s shape.
2. What are the different types of topography maps?
There are various types of topography maps, each designed for specific purposes. Some common types include:
- Topographic Maps: General-purpose maps depicting a wide range of features.
- Geological Maps: Maps highlighting geological formations and features.
- Soil Maps: Maps illustrating soil types and characteristics.
- Hydrographic Maps: Maps focusing on water bodies and their features.
3. How can I access Digimap?
Access to Digimap platforms often requires a subscription or license. Many organizations, including universities, government agencies, and private companies, offer access to Digimap services.
4. What are the limitations of topography maps and Digimap?
While topography maps and Digimap are powerful tools, they have certain limitations:
- Accuracy: The accuracy of topography maps depends on the quality of the survey data and the scale of the map.
- Data Availability: Data availability for specific areas may be limited, particularly for remote or sparsely populated regions.
- Interpretation: Understanding and interpreting topography maps requires a degree of technical knowledge and spatial reasoning.
Tips for Effective Utilization of Topography Maps and Digimap:
- Choose the Right Map: Select a map that is appropriate for your specific needs, considering the scale, detail, and intended use.
- Understand the Map Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on topography maps to accurately interpret the features depicted.
- Utilize the Tools: Take advantage of the interactive tools available on Digimap platforms to explore, analyze, and share map data.
- Collaborate and Share: Engage with others who use topography maps and Digimap to learn from their experiences and share your own insights.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Topography Maps and Digimap
Topography maps and Digimap have become indispensable tools for a diverse range of disciplines, enabling a deeper understanding of the Earth’s surface and facilitating informed decision-making. Their ability to capture the intricacies of terrain, integrate data from multiple sources, and provide interactive exploration capabilities makes them invaluable assets for urban planning, engineering, environmental studies, outdoor recreation, and numerous other fields. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of topography maps and Digimap will undoubtedly continue to evolve, further enhancing our ability to analyze, understand, and manage the world around us.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Deep Dive into Topography Maps and Digimap. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!