Unveiling the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Topography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Topography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Topography
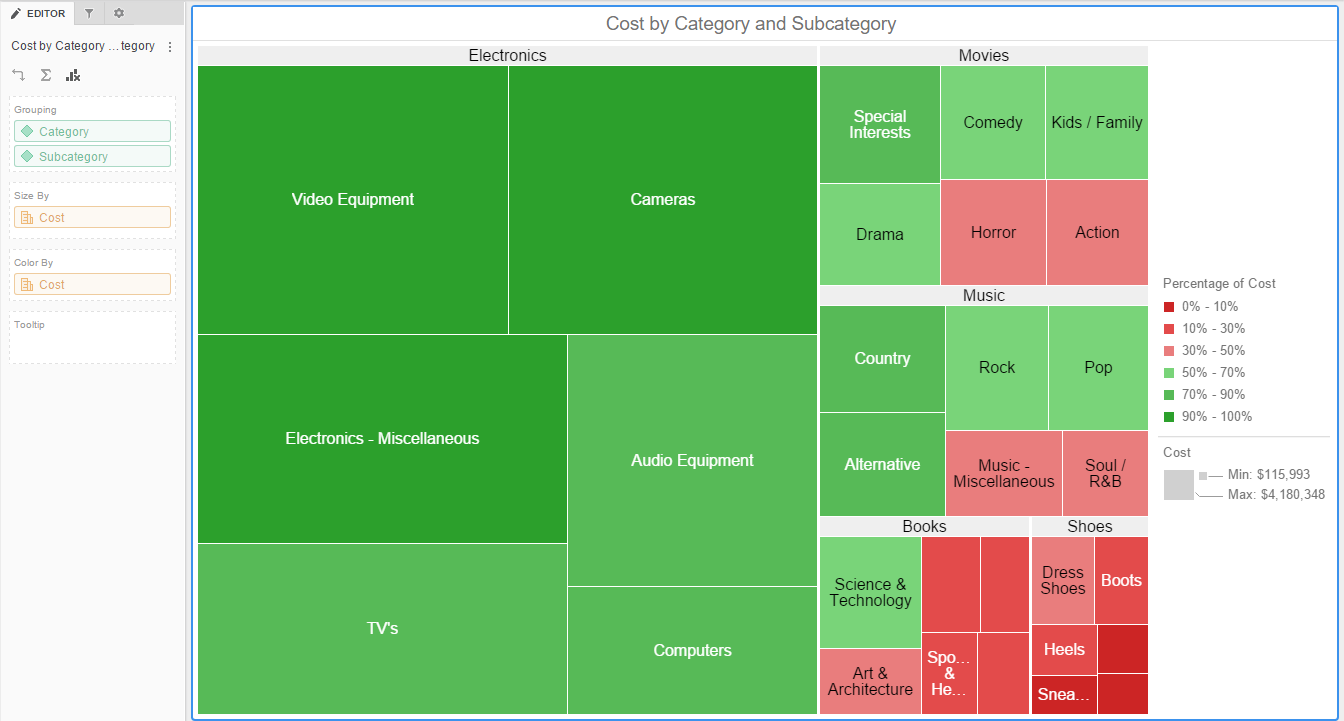
The world of data visualization is vast and ever-evolving. Among the many tools available to transform raw data into insightful narratives, heat maps stand out for their ability to reveal patterns and trends in a visually compelling manner. While often associated with geographical maps, heat maps transcend the realm of location to encompass diverse datasets, offering a powerful means to understand complex information. This article delves into the essence of heat map topography, exploring its applications, benefits, and the nuances that make it a valuable tool for data analysis and communication.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Heat Map Topography
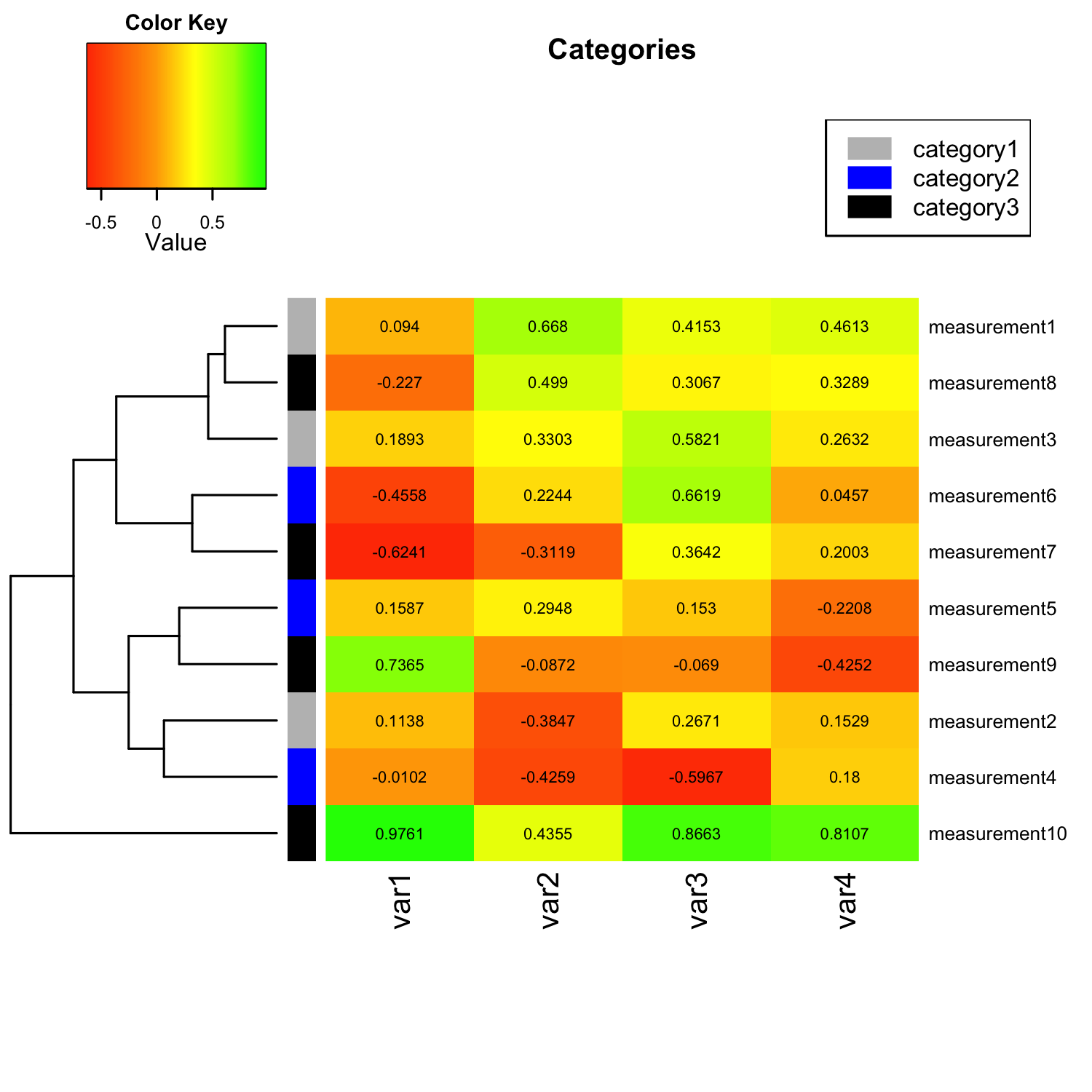
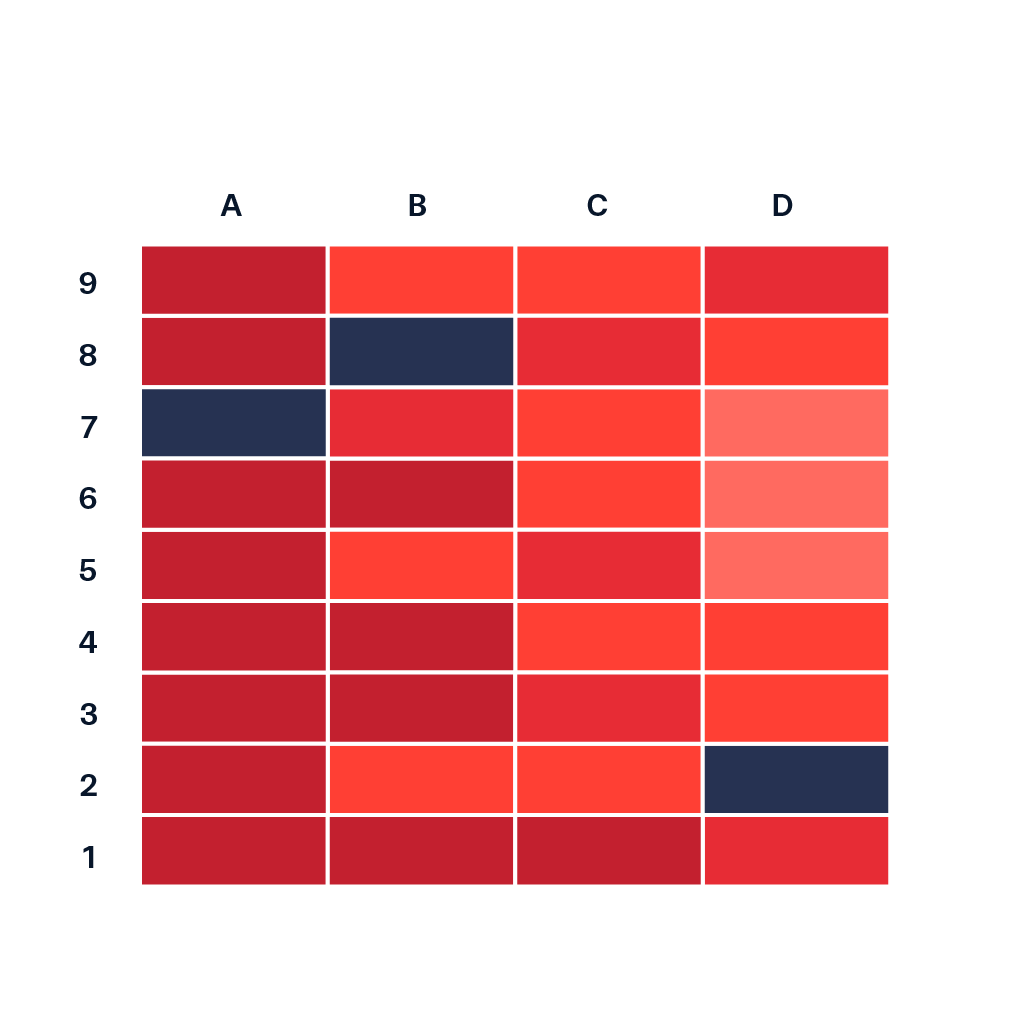
At its core, heat map topography leverages color gradients to depict the distribution and intensity of data points across a defined space. The color scheme, typically ranging from cool colors (representing low values) to warm colors (representing high values), allows for a quick and intuitive interpretation of data clusters and outliers. This visual representation provides a clear and concise overview of the data landscape, revealing areas of high concentration, low activity, or potential anomalies.
Beyond Geographic Maps: Expanding the Scope of Heat Map Topography
While the term "topography" often evokes images of geographical maps, the application of heat maps extends far beyond geographical data. Heat map topography finds its utility in diverse fields, including:
- Business Analytics: Identifying customer demographics, product popularity, website traffic hotspots, and marketing campaign effectiveness.
- Finance: Analyzing stock market trends, identifying investment opportunities, and understanding market sentiment.
- Healthcare: Visualizing disease prevalence, patient demographics, and resource allocation in hospitals.
- Research and Development: Analyzing experimental data, identifying areas of interest in scientific research, and visualizing complex relationships between variables.
- Social Sciences: Mapping crime rates, population density, and social media trends.
The Advantages of Employing Heat Map Topography
The widespread adoption of heat map topography across various disciplines stems from its numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Data Visualization: Heat maps offer a visually compelling way to represent data, making complex information easily accessible and understandable.
- Pattern Recognition: By highlighting areas of high and low concentration, heat maps facilitate the identification of trends, clusters, and outliers that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Data Comparison: Heat maps allow for the comparison of different datasets, revealing similarities, differences, and potential correlations.
- Intuitive Communication: The use of color gradients and visual cues makes heat maps an effective tool for communicating complex data to diverse audiences, regardless of their technical expertise.
- Data Exploration and Discovery: Heat maps can serve as a starting point for further analysis, prompting researchers to delve deeper into specific areas of interest.
Navigating the Nuances: Considerations for Effective Heat Map Topography
While heat maps offer a powerful tool for data visualization, effective implementation requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Data Selection and Preparation: The quality and relevance of the data are paramount. Data cleaning, transformation, and appropriate scaling are essential for accurate and meaningful visualization.
- Color Scheme Selection: The choice of color palette plays a crucial role in conveying information effectively. Choosing a visually appealing and informative color scheme is vital for clear communication and data interpretation.
- Scale and Resolution: Determining the appropriate scale and resolution for the heat map is essential. Too much detail can overwhelm the viewer, while insufficient detail may obscure important patterns.
- Data Aggregation and Clustering: Aggregating data into meaningful clusters can enhance the clarity and interpretability of the heat map.
- Interactive Features: Incorporating interactive elements, such as zoom, pan, and data filtering, can enhance user engagement and provide deeper insights.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries on Heat Map Topography
Q1: What types of data are suitable for heat map representation?
A: Heat maps are effective for visualizing data that can be represented as a continuous variable across a defined space. This includes data such as geographical location, time series data, population density, sales figures, website traffic, and more.
Q2: How do I choose the right color scheme for my heat map?
A: Consider the nature of the data, the intended audience, and the message you want to convey. Typically, warmer colors represent higher values, while cooler colors represent lower values. Ensure the chosen color scheme is visually appealing, contrasting, and easy to interpret.
Q3: What are the limitations of heat map topography?
A: While powerful, heat maps have limitations. They may not be suitable for representing discrete data or data with multiple dimensions. Additionally, they can be prone to misinterpretation if not carefully designed and presented.
Q4: How can I make my heat maps more interactive and engaging?
A: Incorporating interactive features, such as zoom, pan, data filtering, and tooltips, can enhance user engagement and provide deeper insights. Consider using interactive visualization tools or libraries that support these features.
Tips for Effective Heat Map Topography
- Start with a clear objective: Define the specific insights you aim to gain from the heat map.
- Choose the right tool: Select a data visualization tool or software that offers robust heat map capabilities.
- Keep it simple and focused: Avoid overwhelming the viewer with too much information.
- Use clear labels and legends: Ensure the heat map is self-explanatory with clear labels and a legend to explain the color scheme.
- Test and iterate: Refine the heat map based on user feedback and data analysis.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Heat Map Topography
Heat map topography is a versatile and powerful tool for data visualization, offering a clear and intuitive way to understand complex information. By leveraging color gradients to represent data intensity across a defined space, heat maps reveal patterns, trends, and outliers, facilitating data exploration, analysis, and communication. From business analytics to scientific research, heat maps find applications across diverse fields, empowering users to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. As technology advances and data becomes increasingly complex, heat map topography will continue to play a crucial role in unlocking the hidden stories within data, transforming raw information into actionable knowledge.



![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Topography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!