Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topography on Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topography on Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topography on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topography on Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topography on Maps
- 3.1 The Language of Contour Lines
- 3.2 Beyond Contour Lines: Additional Tools for Topography
- 3.3 The Importance of Topography on Maps
- 3.4 FAQs on Topography on Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding Topography on Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topography on Maps
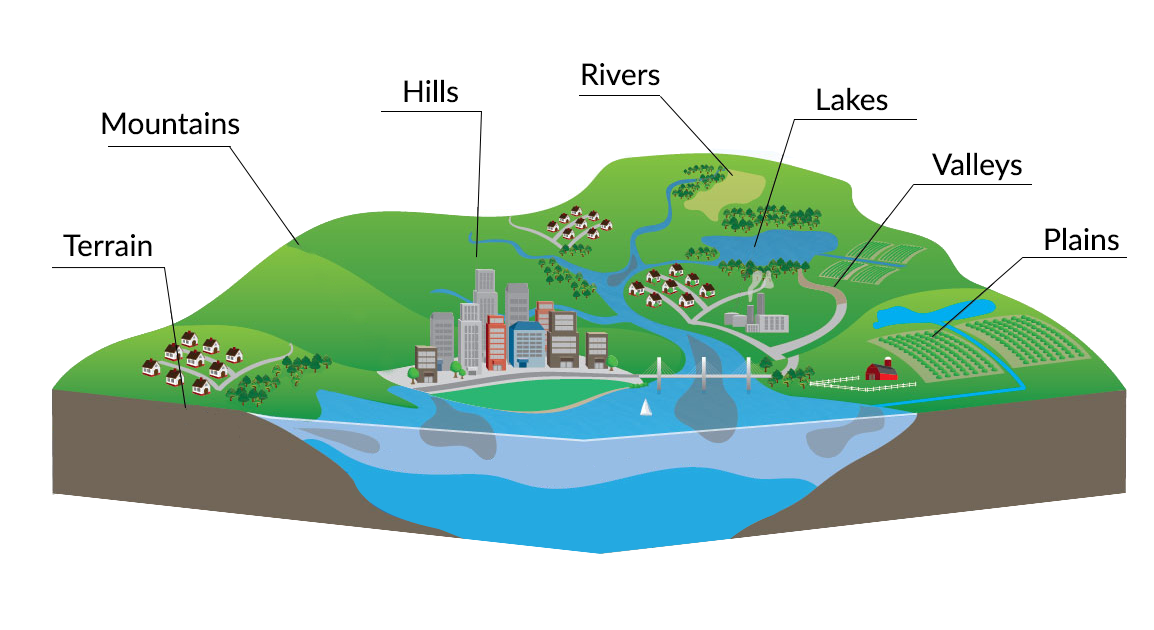
Topography, in the context of maps, is the science and art of representing the Earth’s surface features, particularly its relief, or the variation in elevation. It’s a visual language that translates the three-dimensional world onto a two-dimensional surface, enabling us to comprehend the shape, form, and distribution of landforms.
Imagine a map as a window into the landscape. Topography is the intricate framework that defines the window’s view, revealing the hills, valleys, mountains, plains, and everything in between. It provides a visual representation of the terrain, allowing us to understand the natural world in a way that transcends mere flatness.
The Language of Contour Lines
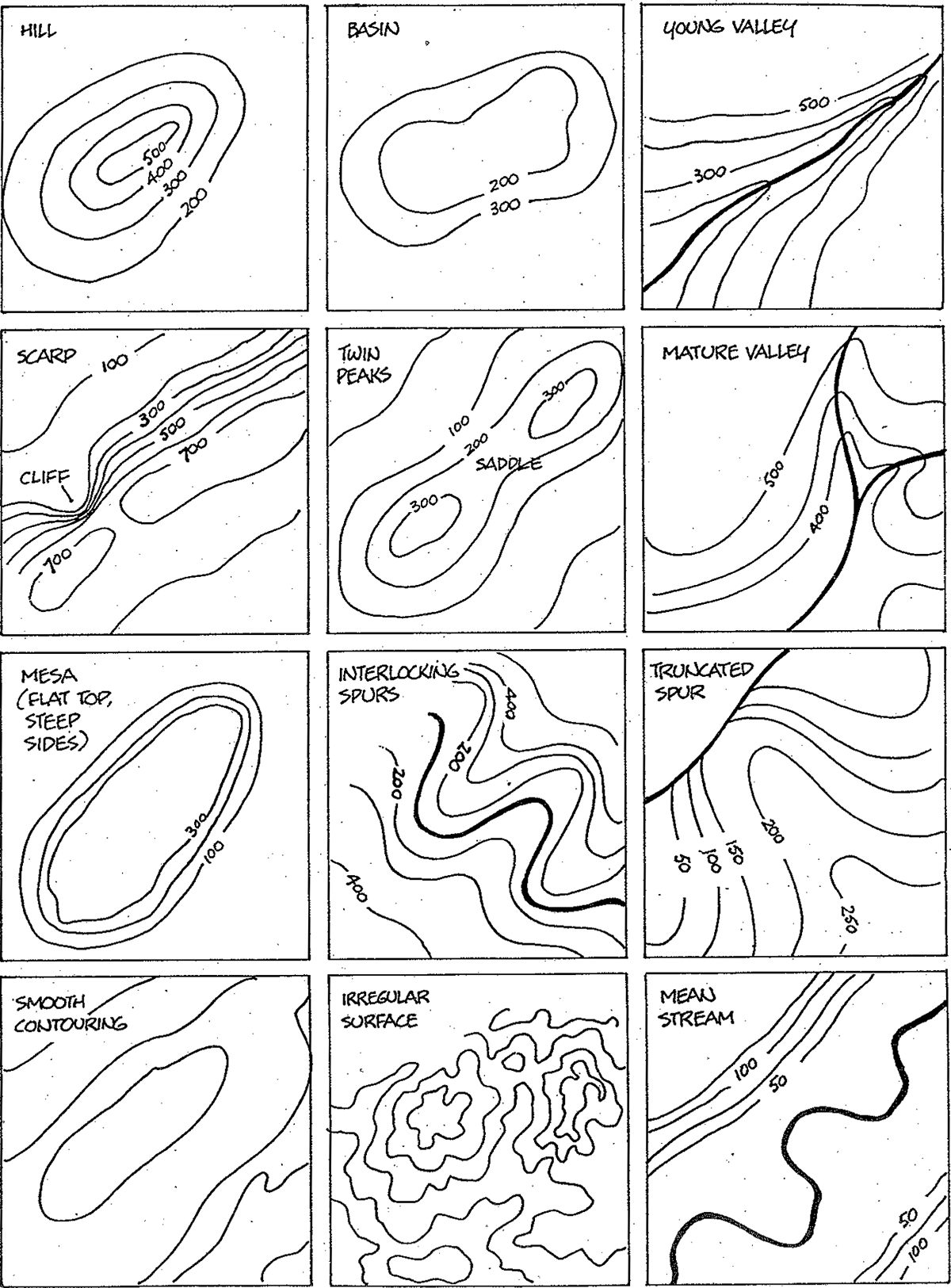
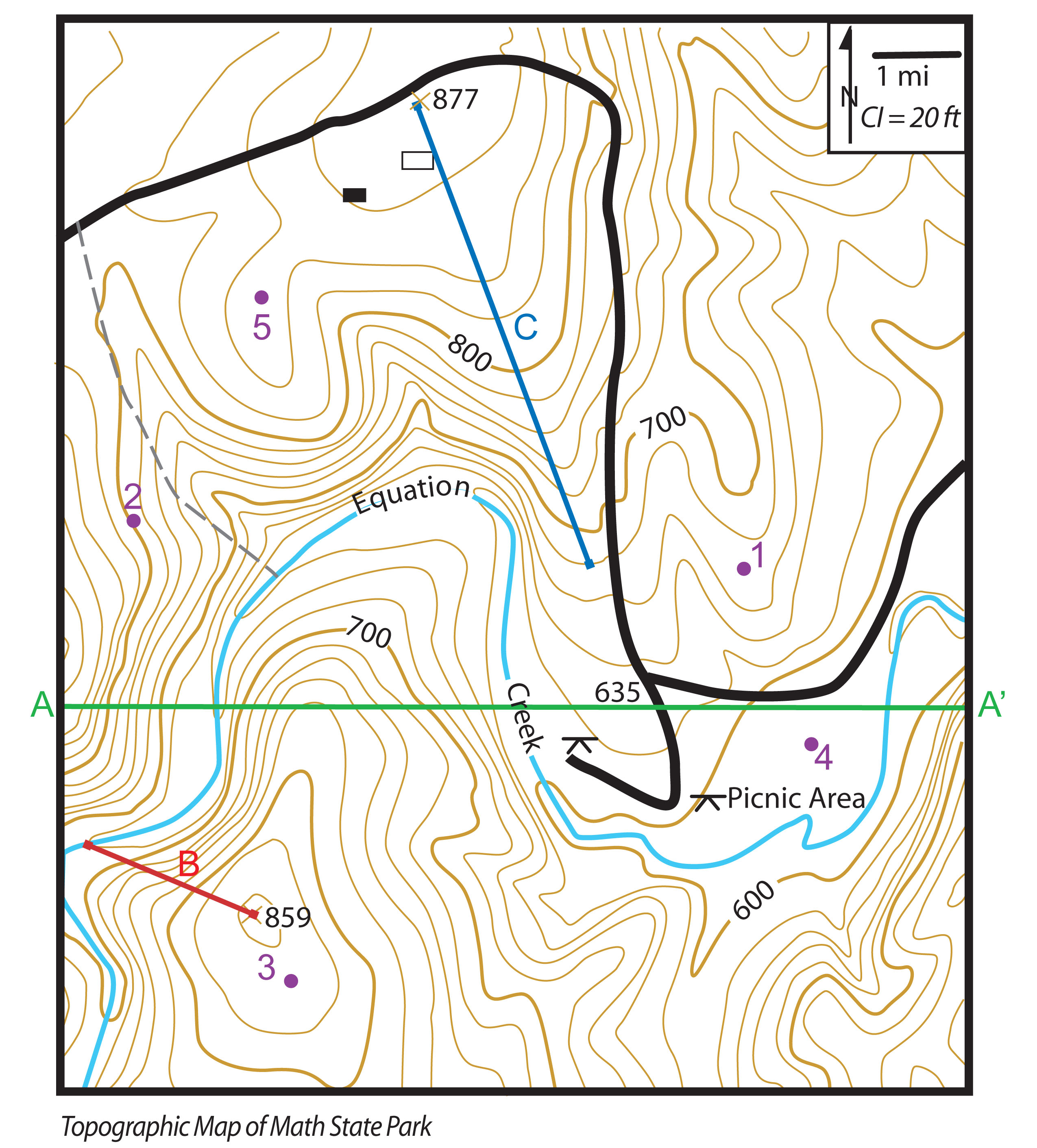
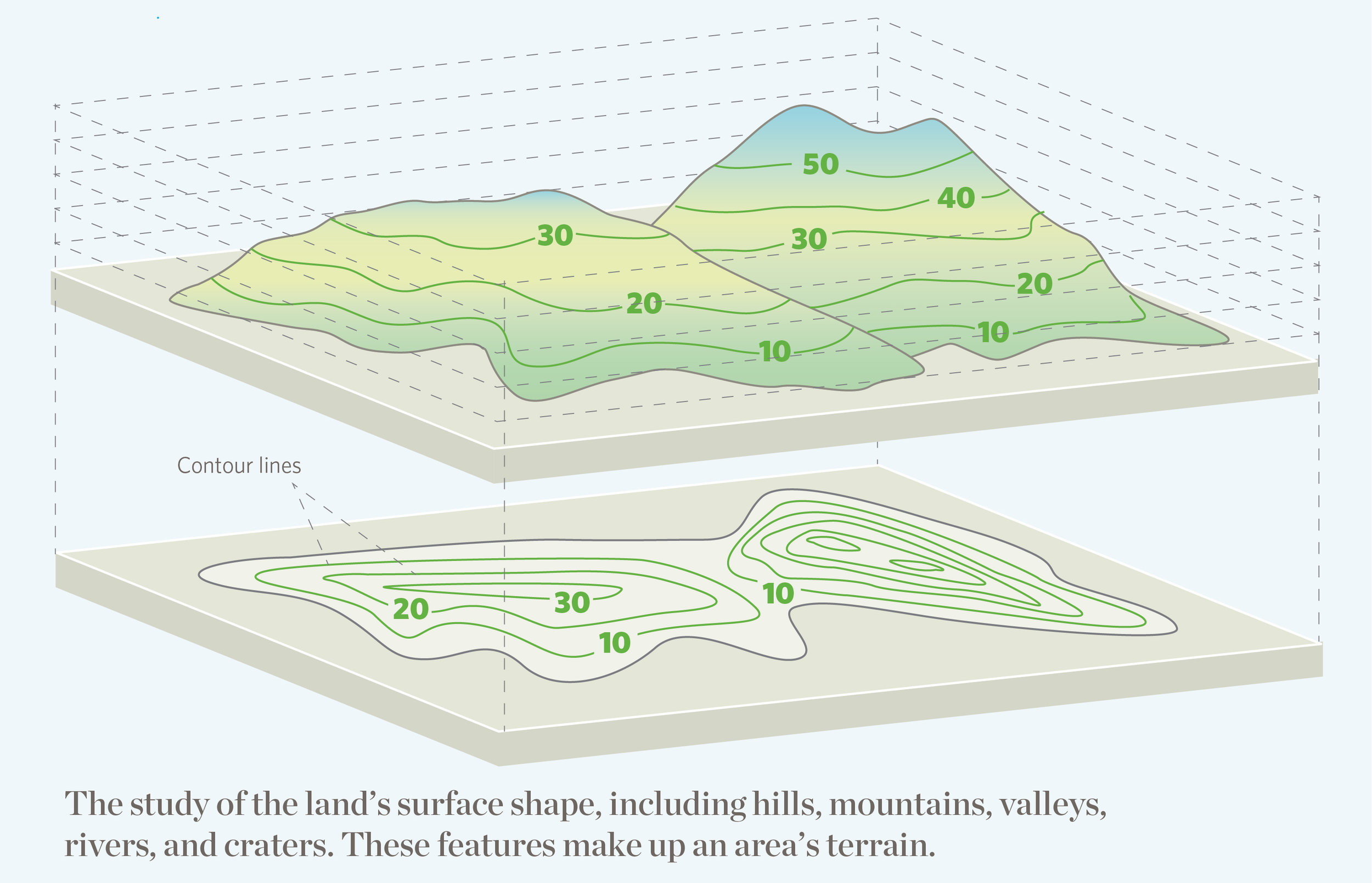
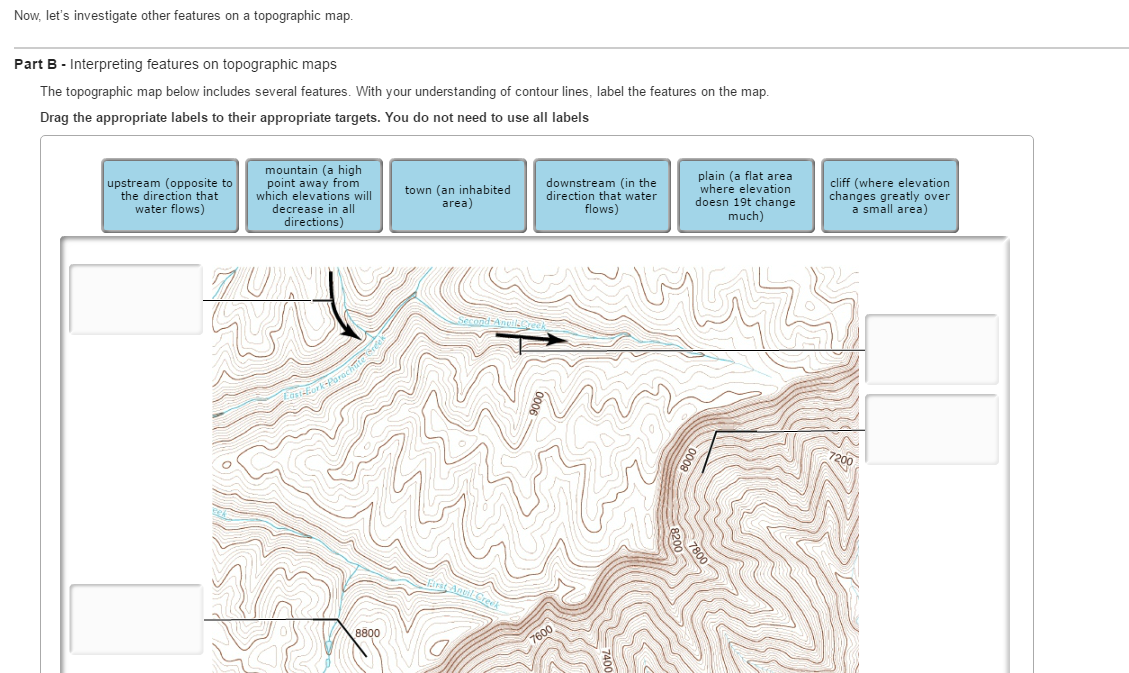
The most common method of depicting topography on maps is through contour lines. These are lines that connect points of equal elevation, forming a series of interconnected curves that trace the ups and downs of the terrain. Imagine a series of horizontal slices through a mountain, each slice representing a specific height. The contour lines on a map represent the outlines of these slices, providing a visual representation of the mountain’s shape and slope.
The closer together the contour lines, the steeper the terrain. Conversely, widely spaced contour lines indicate a gentler slope. This relationship between contour line spacing and slope steepness is crucial for understanding the terrain’s characteristics. For instance, a map with tightly packed contour lines might depict a rugged mountain range, while a map with loosely spaced contour lines might represent a rolling plain.
Beyond Contour Lines: Additional Tools for Topography
While contour lines are the primary tool for depicting topography, other methods contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the landscape. These include:
-
Elevation Tints: Areas of similar elevation are shaded with different colors, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s overall shape and form.
-
Hill Shading: This technique uses shading to simulate the effect of sunlight on the terrain, creating a three-dimensional effect that enhances the visual perception of hills, valleys, and other features.
-
Spot Heights: These are numerical values that indicate the precise elevation of specific points on the map, providing detailed information about individual peaks, valleys, and other significant features.
-
Cross Sections: These are vertical slices through the terrain, revealing the elevation profile along a specific line. They offer a more detailed view of the terrain’s vertical structure.
The Importance of Topography on Maps
The significance of topography on maps cannot be overstated. It plays a vital role in:
-
Navigation: Topography provides crucial information for navigating through unfamiliar terrain, enabling travelers to understand the landscape, identify potential obstacles, and plan efficient routes.
-
Planning and Development: Understanding the topography of an area is essential for planning infrastructure projects, such as roads, dams, and buildings. It helps engineers and planners identify suitable locations, assess potential risks, and minimize environmental impact.
-
Environmental Studies: Topography plays a crucial role in understanding the distribution of natural resources, such as water, soil, and vegetation. It aids in assessing the impact of human activities on the environment and developing strategies for sustainable resource management.
-
Disaster Response: Understanding the topography of an area is essential for preparing for and responding to natural disasters, such as floods, earthquakes, and landslides. It allows for efficient evacuation planning, resource allocation, and damage assessment.
-
Scientific Research: Topographic maps provide valuable data for a wide range of scientific disciplines, including geology, hydrology, and ecology. They enable researchers to study landforms, analyze geological processes, and understand the interactions between the Earth’s surface and its atmosphere.
FAQs on Topography on Maps
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A: A topographic map emphasizes the representation of elevation and terrain features, using contour lines, elevation tints, and other techniques. Regular maps, such as road maps, focus on showing roads, cities, and other human-made features, with less emphasis on terrain.
Q: How accurate are topographic maps?
A: The accuracy of topographic maps depends on the scale and purpose of the map. Large-scale maps, which cover smaller areas in greater detail, are generally more accurate than small-scale maps that cover larger areas.
Q: What are some common uses of topographic maps?
A: Topographic maps are used by hikers, campers, explorers, engineers, planners, scientists, and others who need to understand the terrain and navigate through unfamiliar areas.
Q: How can I learn to read topographic maps?
A: There are numerous resources available online and in print that teach the fundamentals of reading topographic maps. These resources typically cover the basics of contour lines, elevation tints, and other topographic symbols.
Q: Can I create my own topographic map?
A: While creating a detailed topographic map requires specialized software and equipment, you can use readily available tools, such as online mapping platforms or smartphone apps, to generate basic topographic maps.
Tips for Understanding Topography on Maps
-
Start with the basics: Familiarize yourself with the fundamental concepts of contour lines, elevation tints, and other topographic symbols.
-
Practice reading maps: Use online resources, topographic maps of your local area, or even hiking maps to practice reading and interpreting topographic information.
-
Pay attention to the scale: The scale of a map determines the level of detail and accuracy of the topographic information.
-
Look for patterns: Observe the patterns formed by contour lines, elevation tints, and other symbols to understand the overall shape and form of the terrain.
-
Use multiple sources: Combine topographic maps with other sources of information, such as satellite imagery or aerial photographs, for a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
Conclusion
Topography on maps is a powerful tool that unlocks the secrets of the Earth’s surface. It allows us to visualize and comprehend the complexities of the landscape, enabling navigation, planning, scientific research, and environmental management. By understanding the language of contour lines, elevation tints, and other topographic symbols, we can gain valuable insights into the world around us. The ability to read and interpret topographic maps empowers us to navigate through unfamiliar terrain, make informed decisions about development, and protect our planet’s precious resources.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topography on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!